Which switch characteristic helps keep traffic local and alleviates network congestion?
high port density
fast port speed
large frame buffers
fast internal switching
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Switches that have a lot of ports (high port density) reduce the number of switches required and keep some of the traffic locally on the switch, thus removing the need to send it between switches.
|
Which switch component reduces the amount of packet handling time inside the switch?
ASIC
dual processors
large buffer size
store-and-forward RAM
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) are used in Cisco switches to speed up switch operations so that the switch can have an increased number of ports without degrading switch performance.
|
Refer to the exhibit. A switch receives a Layer 2 frame that contains a source MAC address of 000b.a023.c501 and a destination MAC address of 0050.0fae.75aa. Place the switch steps in the order they occur. (Not all options are used.)
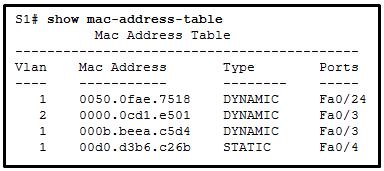 CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 17CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 001 CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 17CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 001
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The first step a switch does when processing a frame is to see if the source MAC address is in the MAC address table. If the address is not there, the switch adds it. The switch then examines the destination MAC address and compares it to the MAC address table. If the address is in the table, the switch forwards the frame out the corresponding port. If the address is missing from the table, the switch will forward the frame to all ports except the port through which the frame arrived.
|
What information is added to the switch table from incoming frames?
source MAC address and incoming port number
destination MAC address and incoming port number
source IP address and incoming port number
destination IP address and incoming port number
Answers Explanation & Hints:
A switch “learns” or builds the MAC address table based on the source MAC address as a frame comes into the switch. A switch forwards the frame onward based on the destination MAC address.
|
Which switching method ensures that the incoming frame is error-free before forwarding?
cut-through
FCS
fragment free
store-and-forward
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Two methods used by switches to transmit frames are store-and-forward and cut-through switching. The store-and-forward method performs error checking on the frame using the frame check sequence (FCS) value before sending the frame. In contrast, cut-through switching sends the frame as soon as the destination MAC address part of the header has been read and processed.
|
Refer to the exhibit. How many broadcast domains are displayed?
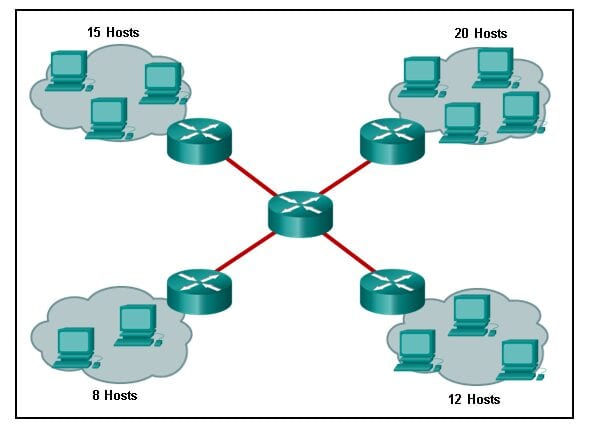 CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 09 CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 09
1
4
8
16
55
Answers Explanation & Hints:
A router defines a broadcast boundary, so every link between two routers is a broadcast domain. In the exhibit, 4 links between routers make 4 broadcast domains. Also, each LAN that is connected to a router is a broadcast domain. The 4 LANs in the exhibit result in 4 more broadcast domains, so there are 8 broadcast domains in all.
|
Under which two occasions should an administrator disable DTP while managing a local area network? (Choose two.)
when connecting a Cisco switch to a non-Cisco switch
when a neighbor switch uses a DTP mode of dynamic auto
when a neighbor switch uses a DTP mode of dynamic desirable
on links that should not be trunking
on links that should dynamically attempt trunking
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Cisco best practice recommends disabling DTP on links where trunking is not intended and when a Cisco switch is connected to a non-Cisco switch. DTP is required for dynamic trunk negotiation.
|
Which two characteristics describe the native VLAN? (Choose two.)
Designed to carry traffic that is generated by users, this type of VLAN is also known as the default VLAN.
The native VLAN traffic will be untagged across the trunk link.
This VLAN is necessary for remote management of a switch.
High priority traffic, such as voice traffic, uses the native VLAN.
The native VLAN provides a common identifier to both ends of a trunk.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The native VLAN is assigned to 802.1Q trunks to provide a common identifier to both ends of the trunk link. Whatever VLAN native number is assigned to a port, or if the port is the default VLAN of 1, the port does not tag any frame in that VLAN as the traffic travels across the trunk. At the other end of the link, the receiving device that sees no tag knows the specific VLAN number because the receiving device must have the exact native VLAN number. The native VLAN should be an unused VLAN that is distinct from VLAN1, the default VLAN, as well as other VLANs. Data VLANs, also known as user VLANs, are configured to carry user-generated traffic, with the exception of high priority traffic, such as VoIP. Voice VLANs are configured for VoIP traffic. The management VLAN is configured to provide access to the management capabilities of a switch.
|
On a switch that is configured with multiple VLANs, which command will remove only VLAN 100 from the switch?
Switch# delete flash:vlan.dat
Switch(config-if)# no switchport access vlan 100
Switch(config-if)# no switchport trunk allowed vlan 100
Switch(config)# no vlan 100
Answers Explanation & Hints:
To remove all VLANs from a switch, the delete flash:vlan.dat command would be used. To change the assigned VLAN for an interface, the no switchport access vlan 100 interface configuration command would be used. To remove VLAN 100 as an allowed VLAN on a trunk, the no switchport trunk allowed vlan 100 would be used, but this would not remove the VLAN from the switch. To delete a single VLAN, such as VLAN 100, the no vlan 100 global configuration command would be used.
|
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is reviewing port and VLAN assignments on switch S2 and notices that interfaces Gi0/1 and Gi0/2 are not included in the output. Why would the interfaces be missing from the output?
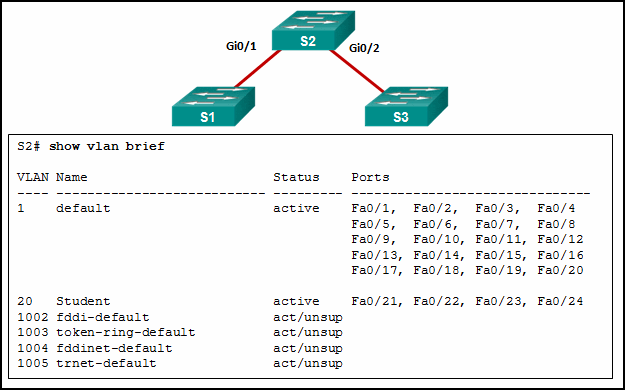 CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 08 CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 08
There is a native VLAN mismatch between the switches.
There is no media connected to the interfaces.
They are administratively shut down.
They are configured as trunk interfaces.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Interfaces that are configured as trunks do not belong to a VLAN and therefore will not show in the output of the show vlan brief commands.
|
A network contains multiple VLANs spanning multiple switches. What happens when a device in VLAN 20 sends a broadcast Ethernet frame?
All devices in all VLANs see the frame.
Devices in VLAN 20 and the management VLAN see the frame.
Only devices in VLAN 20 see the frame.
Only devices that are connected to the local switch see the frame.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
VLANs create logical broadcast domains that can span multiple VLAN segments. Ethernet frames that are sent by a device on a specific VLAN can only be seen by other devices in the same VLAN.
|
Refer to the exhibit. All workstations are configured correctly in VLAN 20. Workstations that are connected to switch SW1 are not able to send traffic to workstations on SW2. What could be done to remedy the problem?
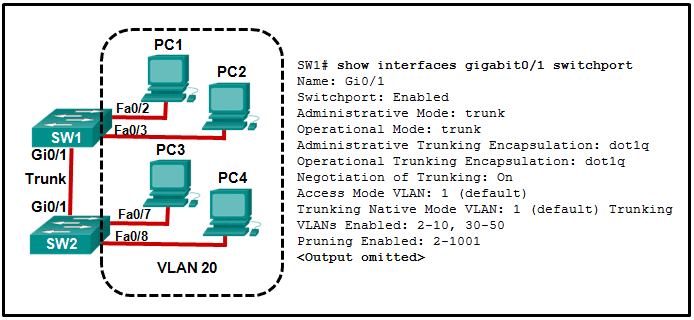 CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 07 CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 07
Allow VLAN 20 on the trunk link.
Enable DTP on both ends of the trunk.
Configure all workstations on SW1 to be part of the default VLAN.
Configure all workstations on SW2 to be part of the native VLAN.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Enabling DTP on both switches simply allows negotiation of trunking. The “Negotiation of Trunking” line in the graphic shows that DTP is already enabled. The graphic also shows how the native VLAN is 1, and the default VLAN for any Cisco switch is 1. The graphic shows the PCs are to be in VLAN 20.
|
What happens to switch ports after the VLAN to which they are assigned is deleted?
The ports are disabled.
The ports are placed in trunk mode.
The ports are assigned to VLAN1, the default VLAN.
The ports stop communicating with the attached devices.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The affected ports must be reconfigured for an active VLAN.
|
Match the IEEE 802.1Q standard VLAN tag field with the description. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 002
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The IEEE 802.1Q standard header includes a 4-byte VLAN tag:
Type – A 2-byte value called the tag protocol ID (TPID) value.
User priority – A 3-bit value that supports level or service implementation.
Canonical Format Identifier (CFI) – A 1-bit identifier that enables Token Ring frames to be carried across Ethernet links.
VLAN ID (VID) – A 12-bit VLAN identification number that supports up to 4096 VLAN IDs.
|
Refer to the exhibit. In what switch mode should port G0/1 be assigned if Cisco best practices are being used?
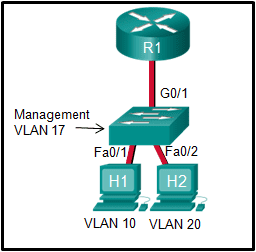 CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 04 CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 04
access
trunk
native
auto
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The router is used to route between the two VLANs, thus switch port G0/1 needs to be configured in trunk mode.
|
Match the DTP mode with its function. (Not all options are used.)
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 003
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The dynamic auto mode makes the interface become a trunk interface if the neighboring interface is set to trunk or desirable mode. The dynamic desirable mode makes the interface actively attempt to convert the link to a trunk link. The trunk mode puts the interface into permanent trunking mode and negotiates to convert the neighboring link into a trunk link. The nonegotiate mode prevents the interface from generating DTP frames.
|
Port Fa0/11 on a switch is assigned to VLAN 30. If the command no switchport access vlan 30 is entered on the Fa0/11 interface, what will happen?
Port Fa0/11 will be shutdown.
An error message would be displayed.
Port Fa0/11 will be returned to VLAN 1.
VLAN 30 will be deleted.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
When the no switchport access vlan command is entered, the port is returned to the default VLAN 1. The port will remain active as a member of VLAN 1, and VLAN 30 will still be intact, even if no other ports are associated with it.
|
Which command displays the encapsulation type, the voice VLAN ID, and the access mode VLAN for the Fa0/1 interface?
show vlan brief
show interfaces Fa0/1 switchport
show mac address-table interface Fa0/1
show interfaces trunk
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The show interfaces switchport command displays the following information for a given port:
Switchport
Administrative Mode
Operational Mode
Administrative Trunking Encapsulation
Operational Trunking Encapsulation
Negotiation of Trunking
Access Mode VLAN
Trunking Native Mode VLAN
Administrative Native VLAN tagging
Voice VLAN
|
Refer to the exhibit. A technician is programming switch SW3 to manage voice and data traffic through port Fa0/20. What, if anything, is wrong with the configuration?
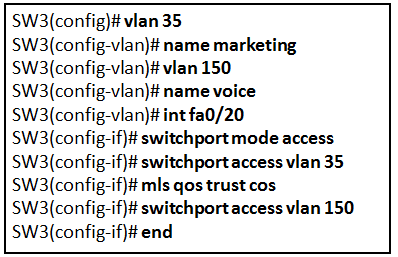 CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 02 CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 02
There is nothing wrong with the configuration.
Interface Fa0/20 can only have one VLAN assigned.
The mls qos trust cos command should reference VLAN 35.
The command used to assign the voice VLAN to the switch port is incorrect.
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The voice VLAN should be configured with the switchport voice vlan 150 command. A switch interface can be configured to support one data VLAN and one voice VLAN. The mls qos trust cos associates with the interface. Voice traffic must be trusted so that fields within the voice packet can be used to classify it for QoS.
| |
 Скачать 0.55 Mb.
Скачать 0.55 Mb. CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 17CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 001
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 17CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4 Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 001 CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 09
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 09 CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 08
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 08 CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 07
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 07 CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 04
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 04 CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 02
CCNA2 v7 SRWE – Modules 1 – 4: Switching Concepts, VLANs, and InterVLAN Routing Exam Answers 02