Арсланова_Г_А_и_др_Essential_English_for_Biology_Students (1). Kazan federal university
 Скачать 7.01 Mb. Скачать 7.01 Mb.
|
UNIT VII. PHOTOSYNTHESISText 7.1. Photosynthesis: An Overview■ 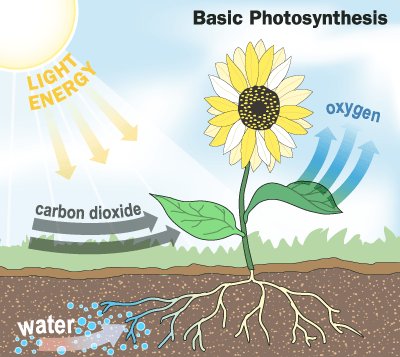 Essential targets: Essential targets:By the end of this text you should be able to: describe the overall process of photosynthesis and its importance to life on Earth; describe the structure and function of a chloroplast. Pre-reading ■ Discuss these questions with your partner. Then quickly scan the text to see if you were right. 1. What is photosynthesis? 2. Why is photosynthesis considered as the basis of life? ■ Read the given text and make your essential assignments: Most plants have no structures for ingesting and digesting food. They have no mouth and no alimentary canal, yet plant material is rich in carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Instead of obtaining their food from other organisms, plants make it for themselves using simple ingredients. They are autotrophs (self-feeders). What is photosynthesis? A typical plant takes in carbon dioxide (from the air) and water (from the soil) and builds these up into sugars and other complex substances. Oxygen is released as a waste product. The energy in the chemical bonds of the raw materials carbon dioxide and water is less than the energy in the chemical bonds of the products. Therefore the reaction is endergonic and requires an external source of free energy. This energy is supplied by sunlight that falls on the plant. A green substance, chlorophyll, enables the plant to trap light energy and use it to make sugars. The process of using sunlight to build up complex substances from simpler ones is called photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is a complex process which takes place in a series of small steps. There are two main stages in photosynthesis: a light-dependent stage in which water is broken down into hydrogen and oxygen using light energy; and light-independent stage in which the hydrogen reacts with carbon dioxide to form a carbohydrate. Water is re-formed in this reaction. The light-dependent stage happens only in the light; the light-independent stage happens both when it is light and when it is dark. Covering glucose to other substances The glucose formed by photosynthesis is used as the raw material for other chemical reactions. It is the main substrate used in respiration. Some of the glucose is covered to other carbohydrates: cellulose to form cell walls; sucrose to be transported to other parts of the plant; and starch for storage. Some of the glucose is combined with minerals from the soil to make proteins and other complex organic substances. Although light is needed for making glucose, it is not needed for turning the glucose into these other substances. Photosynthesis: the basis of life Green life has been steadily pumping out oxygen as a waste product of photosynthesis for millions of years. Some of the oxygen is used as a raw material for respiration, but most of it has accumulated in the atmosphere. So the very existence of our oxygen-rich atmosphere depends on the photosynthesising activities of green life. Animals cannot make their own food. The only way they can obtain complex organic substances is by eating other organisms. These organisms ultimately depend on the ability of plants to harvest energy from sunlight to make food from carbon dioxide and water. Life on Earth is almost entirely solar powered. The site of photosynthesis A 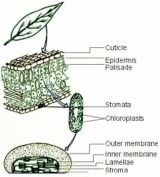 lthough, leaves are the main sites of photosynthesis in most plants, it can take place in any part that is green. These green parts have chloroplasts, which contain all the biochemical machinery necessary for the light-dependent and light-independent stages of photosynthesis. Chloroplasts act as compartments, isolating the photosynthetic reactions from other cellular activities. Each chloroplast consists of two membranes enclosing a gelatinous matrix called the stroma. The stroma contains ribosomes, circular DNA, and enzymes used in photosynthesis. Suspended in the stroma are thylakoids. These are disk-like membrane sacs, several of which are stacked in a group to form a granum (plural grana). The space inside each thylakoid in a stack is connected with the other thylakoids in the stack, forming a continuous fluid-filled compartment called the thylakoid space. The thylakoid membranes contain photosynthetic pigments, including chlorophyll. ■ Glossary of essential terms for you to know
■ Your Essential Assignments I. Quick check: 1. During photosynthesis, what gas is: a. raw material b. product? 2. Give the precise location in a typical terrestrial plant of: a. the light-dependent stage b. the light-independent stage of photosynthesis. II. Fill in the missing words:
III. Use monolingual English dictionary and write down what could the words given below mean: plant, leave, ingredient, substance, raw, energy. IV. Match these words with their definitions:
V. Find English equivalents to the following word combinations:
|
