Арсланова_Г_А_и_др_Essential_English_for_Biology_Students (1). Kazan federal university
 Скачать 7.01 Mb. Скачать 7.01 Mb.
|
|
VI. Give Russian equivalents to the following English terms:
VII. Find synonyms among the pool of words:
VIII. Answer the following questions. Use all information given before: 1. What is plant material rich in? 2. Do plants make their food for themselves? 3. What is chlorophyll? 4. What is the role of chlorophyll? 5. What process is called photosynthesis? 6. What are two main stages in photosynthesis? 7. What is the difference between light-dependent and light-independent stage? 8. What is the main site of photosynthesis in most plants? IX. Match the sentence halves. Make complete sentences:
X. Read and translate the short text without any dictionary: Fact of life: It has been estimated that if all the land surface of the Earth could support plants, enough food could be produced to feed 1000 billion people. Of course, this is unrealistic because not all land is suitable for growing plants, and some land is needed for urban and recreational uses. However, even if only 7 per cent of the land surface were made agriculturally productive, plants could produce enough food to support 79 billion people. According to United Nations estimates, in 1994 the world population was 5.6 billion and is likely to be about 8.2 billion by 2025. XI. Food for thought: Less than one per cent of the solar energy that falls on the Earth is used by plants for photosynthesis. Suggest what happens to the other 99 per cent of solar energy. Text 7.2 Factors Affecting The Rate Of Photosynthesis ■ Essential targets: By the end of this text you should be able to: ● describe the main factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis; ● explain the meaning of the compensation point; ● define the law of limited factors. Pre-reading ■ Talk about the following two questions with your partner. 1. Is photosynthesis affected by many factors? 2. How does photosynthesis depend on light intensity, temperature, wind velocity, carbon dioxide level? Then scan the text to compare your ideas with the author`s. ■ Read the given text and make your essential assignments: The rate of photosynthesis can be measured as the volume of carbon dioxide taken in by a part per init time, or as the amount of carbohydrate produced per unit time. In laboratory investigations, the rate is commonly estimated as the volume of oxygen released per unit time, which is more easily measured. However, this method does not give an accurate measure of photosynthesis. Some of the oxygen generated by photosynthesis is used by the plant for respiration. Respiration goes on all the time, even when photosynthesis is at its height. So using oxygen liberation as a measure of photosynthesis gives an underestimate of the true rate. We are actually measuring the rate of photosynthesis above a point called the compensation point, defined as: the point at which the rate of photosynthesis in a plant is in exact balance with the rate of respiration, so there is no net exchange of carbon dioxide or oxygen. The compensation point is usually related to a particular light intensity or carbon dioxide level. Factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis Photosynthesis is affected by many factors, both external (in the environmental) and internal (inside the plant). External factors include light intensity, the wavelength of light, carbon dioxide levels, temperature, wind velocity, and water and mineral supplies. Internal factors include type and concentration of photosynthetic pigments, enzyme and water content, and leaf structure, and position. The effect of many of these factors is difficult to determine quantitatively because they interact, they also affect other processes in the plant. For example, the importance of water to photosynthesis cannot be demonstrated easily. Simply depriving a plant of water kills it, but the cause of death may not be connected with photosynthesis. The importance of water can be demonstrated using water labeled with a heavy isotope of oxygen, 18O, and tracing the isotope using an instrument called a mass spectrometer which can measure the masses of atoms. One batch of Chlorella (green algae) is placed in water in which the oxygen atoms have been replaced by the heavy isotope. Then a second batch of Chlorella in unlabelled water is given a supply of carbon dioxide labeled with 18O. Only the first batch of Chlorella gives off oxygen labeled with 18O, confirming that the oxygen formed in photosynthesis comes only from water, not from carbon dioxide. Light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature are three external factors that are relatively easy to manipulate. Consequently they have been the focus of many investigations on photosynthesis. Light intensity T 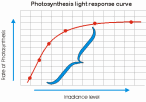 he rate of photosynthesis is directly proportional to light intensity. A typical plant responds to changes in light intensity. Very high light intensities may actually damage some plants, reducing their ability to photosynthesise. The light compensation point (the light intensity at which the rate of photosynthesis is exactly balanced by the rate of respiration) varies for different plants. Two major groups have been identified: sun plants and shade plants. Sun plants include most temperate trees, such as oak. They photosynthesise best at high light intensities. Shade plants include those of the shrub layer, such as ferns. Their light compensation point is relatively low, but they cannot photosynthesise very efficiently at high light intensities. Consequently sun plants outcompete shade plants at high light intensities. Carbon dioxide levels The average carbon dioxide content of the atmosphere is about 0.04 per cent. As long as there is no other factor limiting photosynthesis, an increase in carbon dioxide concentration up to 0.5 per cent usually results in an increase in the rate of photosynthesis. However, concentrations above 0.1 per cent can damage leaves. Therefore the optimum concentration of carbon dioxide is probably just under 0.1 per cent. In dense, warm, and well-lit vegetation, low levels of carbon dioxide often limit the rate of photosynthesis. Growers of greenhouse tomatoes recognise this and provide a carbon dioxide enriched atmosphere for their plants. Temperature Changes in temperature have little effect on the reactions of the light-dependent stage because these are driven by light, not heat. However, the reactions of the Calvin cycle are catalysed by enzymes which, like all enzymes, are sensitive to temperature. The effect of temperature on these reactions is similar to its effects on other enzymes. The optimum temperature varies foe each species, but many temperate plants have an optimum temperature between 25° C and 30° C. Law of limiting factors So far we have looked at the effects of isolated factors. However, under natural conditions plants are subjected to many factors simultaneously. The law of limiting factors state that: when a physiological process depends on more than one essential factor being favourable, its rate at any given moment is limited by the factor at its least favourable value and by that factor alone. When other factors are kept constant, an improvement in the value of the limiting factor leads to an increase in the rate of the process. Conversely, when the rate of the process does not increase in response to an improvement in an important factor, some other factor is limiting to process. For a process to go at its maximum rate, all factors must be at their optimum level. ■ Glossary of essential terms for you to know
■ Your Essential Assignments I. Quick check: 1. Why is difficult to demonstrate the importance of water to photosynthesis? 2. How does the light compensation point of a shade plant differ from that of a sun plant? II. Fill in the missing words:
III. Use monolingual English dictionary and write down what could the words given below mean: concentration, factor, intensity, light, wavelength, vegetation. IV. Match these words with their definitions:
V. Find English equivalents to the following word combinations:
VI. Give Russian equivalents to the following English terms:
VII. Find synonyms among the pool of words:
VIII. Answer the following questions. Use all information given before: 1. How can the rate of photosynthesis be measured? 2. What is the compensation point? 3. What is the compensation point related to? 4. Is photosynthesis affected by external and internal factors? 5. What do external factors include? 6. What do internal factors include? 7. What is the effect of light intensity, carbon dioxide level, temperature on the rate of photosynthesis? 8. What does the law of limiting factors state? IX. Match the sentence halves. Make complete sentences:
X. Read and translate the short text without any dictionary: Fact of life: The atmosphere contains less than 0.04 per cent carbon dioxide, yet each year plants make more than 200 billon tones of carbon compounds from this meagre supply of carbon dioxide. XI. Food for thought: Seaweeds grow on rocky shores, in zones with different species growing at different heights above the low-tide mark. Suggest how the light compensation point of seaweeds at the low-tide mark differs from that of seaweeds close to the high-water mark. |
