Учебное пособие Астрономия. Космическая техника и технологии Алматы, 2012 удк 802. 0 52 629. 7 (0758) ббк 81. Англ. 923
 Скачать 1.02 Mb. Скачать 1.02 Mb.
|
|
Choose the correct answer: 1) According to the passage, which of the following statements is/are true of the Hubble Telescope? I) It is unable to observe light on the infrared part of the spectrum. II) It will be replaced by the James Webb Space Telescope in 2014. III) It was initially constructed in 1946, but not launched until 1990. a) I only b) II only c) III only d) I and II only e) II and III only 2) According to the passage, who had the idea for the Hubble Telescope? a) H.G. Wells b) Albert Einstein c) Lyman Spitzer, Jr. d) Edwin P. Hubble e) James Webb 3) In line 33, vicissitudes most closely means a) long delays which may compromise the shuttle launch b) toxic emissions which may cause corrosion around the mirror c) sound waves which may penetrate the mirror d) atmospheric conditions which may compromise the mirror e) shaking and quivering which may cause changes in the mirror 4) In the context of the passage, which of the following best articulates the author’s opinion of the inception of the Hubble? a) It was a pipedream with little imminent chance of success. b) It was a literary vehicle with little basis in reality. c) It was an emergency response to the quickening Space Race. d) It was based on a scientific proposition which was not proven. e) It was a waste of time and money which were needed elsewhere. 5)The primary purpose of the passage is to a) draw a comparison between H.G. Wells’ notion of time travel with Albert Einstein’s Special Theory of Relativity. b) discuss the construction of the Hubble Space Telescope as a tool for exploring deep space. c) examine difficulties which precipitated construction of corrective lenses for the Hubble’s primary mirror. d) describe the circumstances which underlay the mid–century national drive toward a large space–based observatory. e) dispute the argument that the Hubble Telescope functions as a modern–day time machine. 6) It can be inferred that the author regards time travel as a) an effective hook for a work of fiction, but an improbability in the reality of astronomy. b) an interesting literary notion, but proven to be impossible by Einstein’s Special Theory. c) a persuasive topic in fiction, as well as a hypothetical possibility in light of Einstein’s Special Theory. d) a ridiculous idea whose time has come and gone, as well as an astronomical improbability. e) the incoherent literary construction of a fictional author, with little relevance to today’s scientific community. 7) It can be inferred from the passage that scientists believe that time is a) a constant. b) unidirectional. c) a spatial dimension. d) an impenetrable mystery. e) an imaginary construction. Text 8C Hubble Space Telescope Configuration 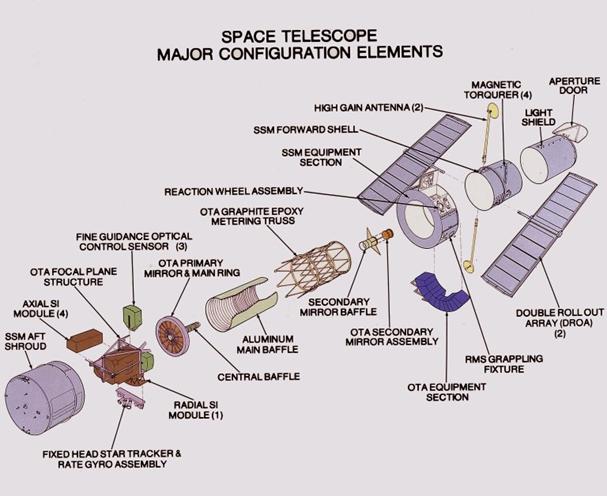 This illustration shows the Hubble Space Telescope’s (HST’s) major configuration elements. The spacecraft has three interacting systems: The Support System Module (SSM), an outer structure that houses the other systems and provides services such as power, communication, and control; The Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), which collects and concentrates the incoming light in the focal plane for use by the Scientific Instruments (SI); and five SIs. The SI Control and Data Handling (CDH) unit controls the five SI’s, four that are housed in an aft section focal plane structure and one that is placed along the circumference of the spacecraft. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth’s atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope. Choose the correct answer: 1) The spacecraft has ___ interacting systems a) one b) two c) three 2) The Support System Module (SSM) is a) an outer structure that houses the other systems and provides services such as power, communication, and control b) system which collects and concentrates the incoming light in the focal plane for use by the Scientific Instruments c) unit controls the five SI’s, four that are housed in an aft section focal plane structure and one that is placed along the circumference of the spacecraft 3) The Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA) is a) an outer structure that houses the other systems and provides services such as power, communication, and control b) system which collects and concentrates the incoming light in the focal plane for use by the Scientific Instruments c) unit controls the five SI’s, four that are housed in an aft section focal plane structure and one that is placed along the circumference of the spacecraft 4) The SI Control and Data Handling (CDH) a) an outer structure that houses the other systems and provides services such as power, communication, and control b) system which collects and concentrates the incoming light in the focal plane for use by the Scientific Instruments c) unit controls the five SI’s, four that are housed in an aft section focal plane structure and one that is placed along the circumference of the spacecraft 5) The purpose of the HST is a) is to study the Earth from a low-Earth orbit b) is to study the Moon from a low-Earth orbit c) is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit 6) The ___ had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST a) NASA b) Marshall Space Flight Center c) European Space Agency Quiz: The Hubble Space Telescope 1) NASA calls the Hubble Space Telescope an "orbiting observatory". What is the main advantage that an orbiting, or space-bound telescope, has over an earth-bound telescope? a) It is not affected by earth's atmosphere or weather b) It does not require a focusing system c) It is less expensive to build d) It does not need a power supply 2) One of the original goals of the Hubble Space Telescope was to find an accurate value for the Hubble's Law. What is Hubble's Law? a) the intensity of light emitted from a star b) the speed that a galaxy moves away from us (on earth) is proportional to its distance from us c) the rotational speed of a galaxy is related to it diameter d) the relative age of the universe compared to the Milky Way galaxy 3) The Hubble Space Telescope has sent back amazing images of nebulae, including the Horsehead Nebula and the Ring Nebula. What is a nebula? a) an ice field around outer planets b) a meteor shower c) an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas, helium gas and other ionised gases d) a distant galaxy 4) What instrument on the Hubble Space Telescope allows scientists to get the most information on the chemical composition of celestial bodies? a) the Wide Field and Planetary Camera b) the Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph c) the Fine Guidance Sensors d) the Faint Object Camera 5) The Wide Field Camera 3 was installed in the Hubble Space Telescope in 2008. What light spectrum does this instrument use? a) the visible light spectrum b) the ultraviolet spectrum c) the infrared spectrum d) all of these 6) To test the instruments on the Hubble Space Telescope, NASA technicians wear "bunny suits", which are protective suits that cover their heads, torso, legs and feet. The main reason they wear these suits is: a) to protect against scratching the instruments b) to keep a neutral electrical charge on the technicians c) to protect against personal injury from the instruments d) to protect the instruments from lint and other contaminants 7) How are major repairs or upgrades to the Hubble Space Telescope made? a) Astronauts perform the repairs or upgrades b) Repairs or upgrades are not made- the instruments have a limited life c) The repairs or upgrades are made by on-board computers d) Repairs or upgrades are made by robots 8) The Wide Field Camera aboard the Hubble Space Telescope does not have real lenses. a) True b) False 9) Like land-based telescopes, the Hubble Space Telescope has a primary mirror. What is special about this mirror? a) It has a magnesium fluoride overcoat b) It has a honeycomb shape to save weight c) It can withstand changes in temperatures d) All of these 10) The NASA facility most involved in the mission of the Hubble Space Telescope is: a) Goddard Space Flight Center b) Jet Propulsion Laboratory c) Marshall Space Flight Center d) Kennedy Space Center Listening 1 Edwin Hubble You are going to listen to American Radio Program. Today, Richard Rael and Tony Riggs tell the story of American astronomer Edwin Hubble. He changed our ideas about the universe and how it developed. For questions 1-10 complete the sentence: 1) Edwin Hubble made his most important discoveries in the ___. 2) Edwin Powell Hubble was born in ___ in Marshfield, Missouri. 3) Edwin Hubble went to Queen’s College at Oxford, England where he studied ___. 4) At the University of Chicago he studied ___. 5) Hubble watched the night sky with instruments at the university’s Yerkes Observatory. His research involved a major question astronomers could not answer: What are ___? 6) In his first observations from Mount Wilson, Hubble used a telescope with a mirror one hundred fifty-two centimeters across. He studied objects within our own ___. And he made an important discovery about nebulae. 7) An astronomer at Harvard College, Henrietta Leavitt, had discovered that these periods of brightness could be used to measure the star’s distance from Earth. Hubble made the measurements. They showed that the Andromeda nebula laid far ___ our Milky Way Galaxy. 8) Hubble proposed a system to describe galaxies by their ___. His system still is used today. He also showed that galaxies are similar in the kinds of bright objects they contain. All galaxies, he said, are related to each other, much as members of a family are related to each other. 9) The Doppler Effect explains changes in the length of light waves or sound waves as they move toward you or away from you. Light waves from an object speeding away from you will stretch into longer wavelengths. They appear red. Light waves from an object speeding toward you will have shorter wavelengths. They appear ___. 10) Observations of forty-six galaxies showed Hubble that the galaxies were traveling away from Earth. The observations also showed that the speed was linked directly to the galaxies’ distance from Earth. Hubble discovered that the farther away a galaxy is, the greater its speed. This scientific rule is called “___.” 11) Hubble left the Mount Wilson Observatory during World War Two. He did research for the United States War Department. He returned after the war. Then, he spent much of his time planning a new, much larger telescope in southern California. The telescope was completed in nineteen forty-nine. It had a mirror ___ centimeters across. It was named after astronomer George Ellery Hale. 2 Kepler Telescope 1 Listen to the news and complete the gaps in the text: 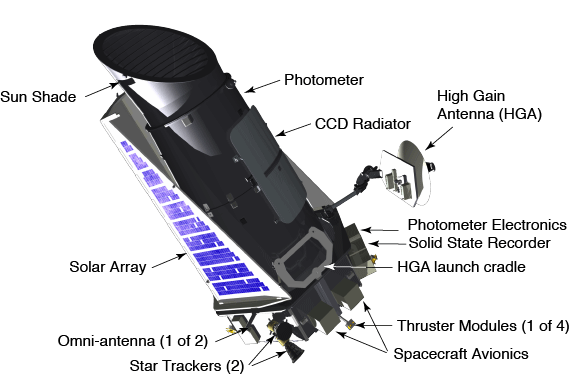 NASA has successfully launched a ___ (1) carrying a planet-hunting telescope. The powerful Kepler telescope will search for planets similar to the Earth. Scientists believe there are good chances of finding a planet like ours somewhere out there in the ___ (2). There are billions and billions of stars in the heavens. If one planet is the right distance from one of these stars, then conditions might be right to support life. The planet’s atmosphere should neither be too hot nor too cold. The planet would also need ___(3). The telescope is named after the German 17th-Century astronomer Johannes Kepler. It will spend more than three years looking for dark specks against the brightness of a hundred-thousand stars. These specks could be Earth-like planets. The manager of the $600-million project Jim Fanson said: "We have a feeling like we're about to set sail across an ___ (4) to discover a new world." NASA’s space science boss Ed Weiler agreed that the mission was a “historical” landmark in space exploration. However, he couldn’t say whether or not the telescope would find another ___ (5). “It very possibly could tell us that Earths are very, very common...or that Earths are really, really, really rare - perhaps we're the only Earth,” he said. He told reporters how important Kepler’s journey was, saying: "It really attacks some basic human questions that have been asked since that first man or woman looked up at the sky and asked, “___ (6).” 1 TRUE / FALSE: Look at the article and say whether these sentences are true (T) or false (F). If it false, correct the sentence: a) NASA will soon launch a telescope that will look for planets like ours. b) Scientists believe the chances of finding an Earth-like planet are good. c) A German astronomer called Kepler invented the telescope. d) The telescope will look at stars for a hundred thousand years. e) The project manager likened the mission to voyaging to new worlds. f) A NASA boss said he would build a landmark on any new planets. g) The boss said it’s possible we may be the only Earth in the galaxy. h) The boss said a basic question for the human race is ‘Are we lonely?’ 2 Synonym match: Match the following synonyms from the article: 1 search a) require 2 finding b) voyage 3 support c) scarce 4 need d) sustain 5 specks e) look for 6 set sail f) fundamental 7 landmark g) embark 8 rare h) locating 9 journey i) milestone 10 basic j) spots
3 Phrase match: Match the following phrases from the article (sometimes more than one. combination is possible):
|
