методичка по английскому языку. Московский государственный медикостоматологический университет
 Скачать 1.11 Mb. Скачать 1.11 Mb.
|
|
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Wordbuilding -er, -or - суффикс, образующий существительные to read - читать a reader - читатель to teach - учить a teacher - учитель 1. Guess the meanings and translate: to retain - удерживать a retainer - to regulate - регулировать a regulator - to examine - экзаменовать an examiner - to think - думать a thinker - to dress -перевязывать рану a dresser – 2. Learn the names of the inner organs of the human body 1 the neck - шея 2 the laryngx - гортань 3 the trachea - трахея 4 the shoulder - плечо 5 the aorta - аорта 6 the heart - сердце 7 the diaphragm - диафрагма 8 the stomach - желудок 9 the spleen -селезенка 10. the bowels - кишечник 11. the appendix - слепая кишка 12 the colon - толстая кишка 13 the liver - печень 14 the ribs - ребра 15 the lungs - легкие 16 the upper - верхняя полая вена vena cava 3. Translate the words of Latin and Greek origin: the alimentary canal, reservoir, to mix, secretion, to concentrate, process, to contain, accessory organs, the pancreas, the peritoneum, the duodenum, the parotid glands, submaxillary, sublingual, the gallbladder. 4. Read the text and be able to answer some questions: The digestive system consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs. The alimentary canal is formed by the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, small intestine, stomach, large intestine and rectum. The accessory structures are the teeth, tongue, salivary glands, hard and soft palates, liver, gallbladder and pancreas. The layers of the alimentary tract (from within outward) are mucous, submucous, muscular and serous. The organs of the digestive system contained in the abdomen are covered with the serous coat - the peritoneum. The mouth is the first division of the alimentary tract. Important structures of the mouth are the tongue, which contains the end organ for taste, and the teeth which divide and mix the food. There are two sets of teeth: first - the deciduous or milk teeth, and later - the permanent teeth. The esophagus conveys food from the pharynx to the stomach. The stomach is a dilated portion of the alimentary canal lying in the upper abdomen just under the diaphragm. The 5 million or more glands in its walls secrete about 3 quarts of gastric juice a day. The stomach is a retaining and mixing reservoir jn which the process of digestion continues. The small intestine is a thin-walled muscular tube about 7 metres long. The large intestine is about 1.5 metres long. The glands that pour secretions into the alimentary canal are the salivary glands in the mouth, and the liver and gallbladder and pancreas in the abdominal cavity. The large salivary glands consist of the parotid, submaxillary and sublingual ones. They supply water, ferments and mucus to the food which is ground up by the teeth. The liver is the largest gland in the body. It secretes bile and has many other important functions. The gallbladder is attached to the under surface of the liver. It concentrates the bile. The pancreas is a long slender organ. The bile and pancreatic ducts empty into the duodenum.
EXERCISES Ex. 1. Listen to the tape-recording of the text and be ready to read the text aloud. Ex. 2. Give English equivalents: вспомогательные органы, дробить и перемешивать пищу, пищевод, расширенная часть, секретировать, молочные зубы, околоушные железы, постоянные зубы, слюнные железы, снабжать водой и ферментами, концентрировать желчь, брюшная полость. Ex. 3. Choose the correct form of the verb. Translate:
Ex. 4. Translate:
Ex. 5. Answer the following questions and check your answers:
Ex. 6. Listen to the text and answer the question: "How does the food get to the cella?" FROM MOUTH TO CELLS What happens to the food we eat? How does it get to the cells? First, the food goes into the digestive tract The food enters your body by the mouth. Then it goes down the esophagus, a tube between your mouth and your stomach. Then, it goes into your stomach, a big pouch at the top of your abdomen. Then, more tubes, over twenty feet of them -your small intestine and your large intestine. But your food doesn't go along unchanged. When it comes into your body, the food is made up of millions and millions of big molecules held together in chunks. While the chunks are broken up physically by the teeth and the contraction of the stomach and intestines, the big molecules are broken up chemically by the digestive juices. From big protein molecules come somewhat smaller molecules of aminoacids; from fats come fatty acids and glycerine and from carbohydrates like the starches come the simple sugars. The whole process of physical and chemical break-down is called digestion. Ex. 7. Answer these questions and check your answers:
Lesson 5 DEFINITION OF SOME SCIENCES AND SPECIALITIES Wordbuilding -ic - суффикс, образующий прилагательные от существительных science - наука scientific - научный 1. Guess the meaning and translate: anatomy- - anatomic a microscope - microscopic therapy - therapeutic physiology - physiologic orthopaedy - orthopaedic 2. Translate the international words and the words of Latin origin: oral, dental arch, periodontal, to practice medicine, orthopaedy, membrane, microscopic structure, cure 3. You'll come across these words and word combinations in the text: dental surgery - зубоврачебная хирургия at the same time - одновременно to describe - описывать to deal with - обращаться, иметь дело с к/л, ч/л a living being - живое существо a gum - десна 4. Read the text and be able to answer some questions: Medicine is a science and an art at the same time. Its aim is to treat (cure) and recognize different diseases. To get the necessary knowledge, the medical students have to study various branches of medical science. They attend lectures on Anatomy, Histology, Biology, Physiology, Microbiology, Biochemistry, Pharmacology, and other subjects. At the Stomatology institutes the students of the senior years attend lectures on special subjects, for example: on dental surgery (stomatological surgery), dental therapy (stomatological therapy), orthopaedy, general surgery, pathological physiology and anatomy. Anatomy is the science or branch of knowledge that deals with the parts and structure of human or animal bodies. Anatomy of man describes the structure of the human body. Physiology is the science of the functions or actions of living organisms in their gross or minute structures. Physiology seeks out and tells what each part of the body does. In other words: Anatomy discloses what is present,. Physiology tells how it works (functions). Pathology explains why it doesn't work (diseases), Histology or Microscopic Anatomy is the science which deals with microscopic structure of animal tissues. Biology is the science of life, the study of living beings. Stomatology is the science which deals with human teeth, gums, dental arches, mucous, fibrous and periodontal membranes of the oral cavity. The knowledge of the structure and functions of the human organism is necessary to those who practice medicine. In order to get knowledge in various fields of medicine, medical students attend lectures of their professors, they dissect corpses, animals, examine organic tissues under the microscope, and make experiments on aminals. One who devotes himself to science and pursues studies in some branches of knowledge is a scientist. A professor is one who publicly teaches and delivers lectures on any branch of science. Those who attend lectures at a university or an institute are students. A physician is a medical man who treats and cures diseases.
EXERCISES Ex. I. Listen to the tape-recording of the text and prepare the fast reading of it. Ex. 2. Give English equivalents: лечение и распознавание болезней, приобретать знания, отрасли медицинской науки, посещать лекции, биохимия, фармакология, стоматологическая хирургия, ортопедия, иметь дело с чем-либо, ставить опыты на животных. Ex. 3. Choose the correct form of the verb and translate:
Ex. 4. Translate from Russian:
Ex. 5. Answer the following questions and check your answers:
Lesson 6 THE TEETH 1. Guess the meanings of the words of Latin and Greek origin: the incisors, the canines, the molars, the premolars, a tubercle , lateral, medial, substance, a foramen, to be composed of, anterior, posterior. 2. Study the pictures and name the dental structures of the tooth and its parts: 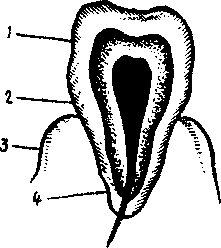 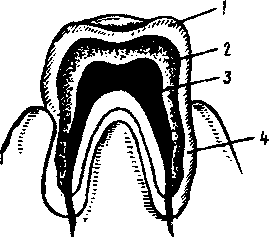 Parts of the Tooth: DentalTissues: 1. a crown 1.the enamel 2. a neck 2. the dentine 3. a gum 3. the cement 3. a root 4. the pulp 3. While reading the text pay your attention to the use of the Infinitive as attribute: give the correct translation of them.
4. Listen to the tape-recording of the text and be ready to read the text aloud. There are two sets of teeth: the deciduous or milk teeth and permanent ones. The deciduous teeth are 20 in number 5 on each side of the upper and the lower jaw, namely: 2 incisors, 1 canine, and 2 molars. There are 32 adult or permanent teeth: 8 on each side above and below namely: 2 incisors, 1 canine, 2 premolars, and 3 molars. Each tooth is divided into a crown above the level of the gum, a neck surrounded by the gum, and a root or roots embedded in the jaw. The crowns are chisel-shaped in incisor teeth, peg-shaped in canine teeth, have two tubercles in premolar teeth; have several tubercles in molar teeth. The upper teeth usually form a wider arch than the lower teeth and therefore overlap them. Each root tapers to a point. The roots of the incisors, canine, premolar teeth are single. Each upper molar has three roots - two lateral and one medial, each lower molar has two roots: anterior and posterior. The bulk of each tooth is composed of an exceedingly hard substance called dentine. The crown is covered with a thin layer of a still harder substance called enamel. The root is covered with a modified bone called cement In the interior of each tooth there is a cavity called the pulp cavity, which contains vessels and nerves. The vessels and nerves enter the tooth through a foramen at the tip of each root. The first deciduous tooth to erupt is one of the incisors and it should appear about six months after birth; all milk teeth should have appeared by the end of the second year. The first permanent tooth to erupt is one of the first molars and it should appear during the sixth year. By the twelfth year all the permanent teeth should have erupted except the third molar, which appears at the time between 17 and 30. EXERCISES Ex. 1. Give English equivalents: временные зубы, постоянные зубы, появляться, прорезываться, резцы, клыки, коронка, шейка, десна, корень, бугорок, отверстие, вещество дентин, цемент, эмаль, перекрывать. Ex. 2. Choose the correct form of the verb:
Ex. 3. Give the correct form of the Predicate:
Ex. 4. Listen to the tape-recording of the text "Teeth" and be ready to answer some questions. TEETH The teeth are implanted on the borders of the upper and lower jaw bones. The jaw bones are covered with a tissue known as the gum, which encircles the lower portion of each tooth. Two sets of teeth are developed during life. The first set is the milk or baby teeth. These develop shortly after the seventh month usually and are lost during childhood, when the second set of teeth or the permanent ones appear. The teeth differ from each other in form and hence in their usage. The front teeth, orthe incisors, are sharp and serve for cutting and tearing. The back teeth have large bases or crowns utilized in grinding and crushing the food. A tooth consists of three parts - the crown, the neck and the root. The tooth itself is composed of a hard outer covering surrounding the central pulp cavity which contains a blood vessel and a nerve. The outer covering consists of a very firm hard substance, the enamel. This is the protective covering of the teeth. Beneath this is dentine, a softer and less resistant material than the enamel. When the enamel is broken the dentine soon suffers. Ex. 6. Answer the following questions and check your answers:
Lesson 7 THE MOUTH CAVITY Wordbuilding -sub - префикс, указывающий на положение ниже чего-либо lingual - язычный sublingual - подъязычный 1.Guess the meanings and translate: group - группа subgroup - division - деление subdivision - maxillary - челюстной submaxillary - mandibular - нижнечелюстной submandibular - cutaneous - кожный subcutaneous - conscious - сознание subconscious - normal -нормальный subnormal - structure - структура substructure - title - заголовок subtitle - 2. Try to remember these word combinations before reading the text: to be subjected to - подвергаться the prime organs - главные органы alveolar ridges - альвеолярные отростки insalivation - смачивание слюной deglutition - глотание to be invested - быть погруженным to pour saliva - изливать слюну to extend - простираться dentition - ряд зубов 3. Look at the picture and show the accessory organs of the digestive system: 1 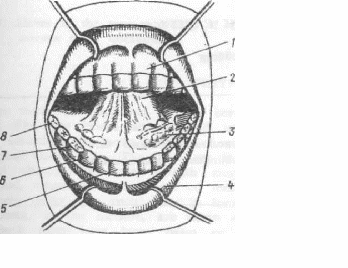 the gum the gum2 the tongue 3 the sublingual glands 4 the lips 5 the incisors 6 the canines 7 the premolars 8 the molars 9 the wisdom tooth 4. Read the text and be ready to answer some questions: The mouth is an oval-shaped cavity situated at the beginning of the alimentary canal. In the mouth there are the teeth, tongue, and alveolar ridges, invested by the gum. The secretions of the parotid, submaxillary and sublingual glands are poured into the mouth cavity and in it the food is subjected to the processes of mastication and insalivation previous to deglutition. The teeth are the prime organs of mastication, and are implanted in the alveolar cavities. A tooth is composed of four distinct structures:
The teeth of the first dentition are termed deciduous or temporary teeth. The temporary teeth are replaced by the permanent teeth. The anatomical divisions of a tooth are:
The temporary teeth are twenty in number, ten in each jaw, namely: four incisors, two canines and four molars. The permanent teeth are thirty two in number, sixteen to each jaw, namely: incisors - four, canines - two, premolars - four, molars - six. The third or last molar is called the wisdom tooth. The incisors occupy the anterior central part of each maxillary arch. The function of this class of teeth is to cut the food. The canine teeth are situated next to the incisors, two to each jaw. These teeth are for tearing the food. The premolars, four to each jaw, are next to the canine teeth. They have two distinct cusps on their surfaces. The molars occupy the posterior part of the alveolar arch and are six on each jaw. The function of the premolars and molars is to grind the food during mastication.
EXERCISES Ex. 1. Listen to the tape-recording of the text and prepare the fast reading of it. Ex. 2. Give English equivalents: овально-очерченная полость, секреция, жевание, ячейка, челюстная дуга, бугорок, разрезать пищу, первый ряд зубов, глотание, подвергаться, размалывать пищу.
Ex. 3 Give the correct forms of the verbs.
Ex. .4 Translate the text without a dictionary: The mouth is a part of the digestive system. There are the teeth, tongue, and salivary glands in the mouth. The cavity of the mouth is divided into two portions: the vestibule and the cavity proper. The vestibule of the mouth is a space bounded by the lips and cheeks. The lips and cheeks contain the mimic muscles. The oral cavity proper is bounded by the hard and soft palates. The hard palate separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. The mucous membrane covers the lips, and cheeks to the alveolar processes of the jaws. In the mouth the food is ground by the teeth and mixed with water, mucous and other secretions of the salivary glands. Saliva has the direct influence on the teeth and provides an optimal level of metabolic activity in the body. There are many salivary glands in the mouth; three principal pairs are recognized: the sublingual glands, submaxillary glands and parotids. The salivary glands regulate the water supply of the body. Ex. 5. Answer the questions and check your answers:
Lesson 8 DENTAL TISSUES Wordbuilding -ive - суффикс, образующий прилагательные со значением "способный на ч/л" to form - образовывать formative - образовательный to talk - разговаривать talkative - разговорчивый 1. Choose the right Russian equivalent: EXPRESSIVE 1. Выраженный 2. выражаемый 3. выразительный DECISIVE 1. решенный 2. решительный 3. решающий CONNECTIVE 1. соединительный 2. соединенный 3. соединяемый DIRECTIVE 1. направляющий 2. направляемый 3. направленный 2. Translate the international words and the words of Latin and Greek origin: a function, to protect, substance, the gingiva, a process, compact, the characteristic form, implanted, friction, tactile. 3. You'll come across these word combinations in the text: dental tissues - зубные ткани supporting tissues - поддерживающие ткани exposed tissues - незащищенные ткани to wear - носить, изнашивать(ся) to resemble - напоминать beyond the border - выше границы (над границей) amount - количество to overlap - перекрывать to fasten - прикреплять suspensory mechanism - поддерживающий механизм to give rise to smth. - дать начало ч.-л. 4. Read the text and be able to answer some questions. The human teeth are made up of four tissues: the enamel, the dentine, the cementum and the pulp. The enamel is the white, compact and very hard substance. The enamel covers the exposed parts of the softer underlying dentine. Its function is to protect the tooth against the wear and friction. The dentine is the chief substance or tissue of the teeth composing the bulk of the tooth and the characteristic form of the tooth. It surrounds the tooth pulp, and is covered by the enamel on the exposed part of the tooth and by the cementum on the part implanted in the jaw. The dentine resembles a bone, but is harder and denser. The cementum closely resembles in structure an ordinary bone. It covers the dentine beyond the border of the enamel, overlapping it slightly at the gingival line and forming the surface of the root. Its function is to furnish the attachment of the fibres of the periodontal membrane which fastens the tooth to the bone. The cementum is relatively small in amount in the child but it increases during life. The pulp is the soft vascular tissue occupying the pulp chamber and the root canals of a tooth, composed of nerves, blood vessels and connective tissue. It is the remain of the formative organ which has given rise to the dentine. The pulp of the tooth is one of the most sensitive structures of the body. THE SUPPORTING TISSUES The human teeth are supported on the alveolar and supporting bones, the periodontal membrane and the gingivae. The alveolar processes of the maxillary bones grow up around the roots of the teeth, so that the roots fit into the holes of the bone. The periodontal membrane performs three functions: (a) it maintains the teeth in their functional positions through its suspensory mechanisms; (b) it takes part in the formation of the bone of its own alveolar walls and of the cementum; (c) it provides through its tactile sensory mechanisms, for protection against the swallowing of hard, sharp and potentially dangerous materials.
EXERCISES Ex. 1. Listen to the tape-recording of the text and prepare the reading of it. Ex. 2. Give English equivalents: зубные ткани, поддерживающие ткани, защищать, изнашивать, трение, незащищенные ткани, по десневой линии, над границей, перекрывать, поддерживающий механизм, защита, альвеолярные отростки, осязательный, образовательный. \ Ex. 3. Supply the correct form of the Participle:
Ex. 4. Translate, using the necessary form of the Participle:
Ex. 5. Answer the following questions and check your answers:
Ex. 6. Translate the text without a dictionary. The cement is the layer of a modified bone which encases the whole of the tooth except its crown. It begins at the neck as a very thin layer which slightly overlaps the enamel. From there it is continued increasing in amount towards the apex, which is formed entirely of this substance. It is relatively, small in amount in children, but it increases during life. The pulp of the tooth is composed of a number of branched fibrous tissue ceils. Their processes form a fine network, which contains numerous blood-vessels, nerves, and lymph vessels. The most superficial of these cells are arranged in the young tooth, lying on the surface of the tooth against the destine; they are known as odontoblasts for they are active in the formation of the dentine. The vessels of the tooth-pulp are numerous. Fine nerve bundles run through the pulp, the root canals towards the crown of the tooth and some of their fibres enter the odontoblasts Sayer. The alveolar periosteum is a layer of fibrous tissue free from elastic fibre but well supplied both with blood vessels and nerves. Ex. 7. Answer these questions and check your answers:
Ex. 8. Speak on the dental tissues and their functions using the picture below. Lesson 9 THE SUPERIOR MAXILLARY BONES Wordbuilding -ly - суффикс, образующий наречие deep - глубокий deeply – глубоко 1. Guess the meaning of the adverbs and translate them: anterior - anteriorly loud - loudly posterior - posteriorly quick - quickly name - namely bad - badly vertical - vertically happy - happily wide - widely careful .- carefully 2. Translate the words of Latin origin: the canine fossa, the orbit, a depression, internal, external, the first bicuspid teeth, tuberosity, to perforate, to occupy, a pyramid. 3. Make the Grammar analysis of the following sentences. Translate them:
4. Pay your attention to these word combinations: the floor of the orbit - основание глазницы the nares - носовая полость to enter into the formation - принимать участие в формирования something like - подобно to bound, boundary - ограничивать, граница 5. Study the picture. 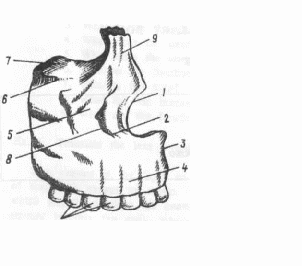 1the nasal notch 2 the infra-orbital foramen 3 the median line 4 the facial surface 5 the zygomalic process 6 the infra-orbital surface 7 the orbital surface 8 the canine fossa 9 the frontal process 10 the alviolar arches 6. Read the text and be ready to answer some questions: The bones of the face consisting of the mandible and the superior maxillary bones form much of the anterior portion of the face. The superior maxillary bones are closely knit together except the mandible which is movable. The superior maxillary bones, being knit together on the median line of the face, are two in number, and of very irregular form. They occupy the anterior upper part of the face and consist of a body and processes. Being the largest bones of the face except the mandible, they enter into the formation of three cavities, namely: the orbit, the mouth and the nares. The body is the central part of the bone. The body is shaped something like a pyramid and exhibits four surfaces, namely: the external or facial, the posterior or zygomatic, the superior or orbital and the internal or palatine. The facial surface is directed forwards and vertically, the lower border being more protruded than the upper one. This surface presents a depression just above the canine and the first bicuspid teeth. It is called the canine fossa. Above the canine fossa, there is the infra-orbital foramen for the nerve of the same name. The zygomatic surface is situated posteriorly forming the anterior boundary of the zygomatic fossa. Between it and the facial surface there is a well-developed ridge extending from the molar region to the base of the zygomatic process. The posterior surface has a bulging called tuberosity. It is connected with the palate bones and bounds the antrum behind. Being perforated by three or four small holes the posterior surface transmits nerves and blood vessels to the molar teeth. The orbital surface of the superior maxillae forms the greater part of the floor of the orbit.
EXERCISES Ex. 1. Listen to the tape-recording of the text and prepare the fast reading of it. Ex. 2. Give English equivalents: углубление, быть просверленным, хорошо развитый гребень, лицевая поверхность кости, инфра-орбитальное отверстие, основание глазницы, небная поверхность, зубной канал, отросток, нижняя челюсть. Ex. 3. Translate, paying attention to the Participles and their functions:
Ex. 4. Insert the necessary word:
Ex. 5. Answer the questions and check your answers:
Ex. 6. Read the text "The Maxillary Bones" and answer the question: "What surface has the infra-orbital groove?" The superior maxillary bones by their union form the arch of the upper jaw and each bone presents for examination a body and four processes, e.g. zygomatic, frontal, alveolar and palatal. The superior maxillary bones are the largest of the face except the mandible. The body is the central part of the bone and has four surfaces. The external surface is irregularly convex and has the so called "canine fossa". The nasal surface forms the lateral boundary of the nasal cavity. At the lower aspect of the zygomatic surface there is the "maxillary tuberosity" and the posterior dental vessels and nerves enter the bone. The superior face of the bone has the infra-orbital groove, which, passing forwards, becomes canalised and divided into two branches, one terminating in the infra-orbital foramen; whilst the smaller branch transmits the anterior dental nerves and vessels to the front teeth of the upper jaw. Lesson 10 ТНE MANDIBLE 1. Listen to the following words and word combinations and learn their meanings before reading the text: a pair of rami, a coronoid process, a condyloid process, to surmount, a consti icted part, a symphysis menti, an outer surface, convex, concave. 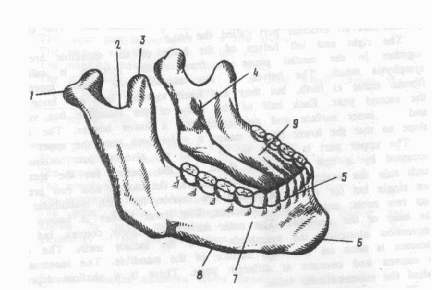 2. Study the picture and remember the following expressions: 1.the condyloid process -мыщелковый отросток; 2. the mandibular notch - нижне-челюстная вырезка; 3. the coronoid process -венечный отросток; 4. the mandibular foramen -нижне-челюстное отверстие; 5. the upper border of the mandible -верхняя граница нижней челюсти; 6. the lower border of the mandible -нижняя граница нижней челюсти; 7. the mental foramen -подбородочное отверстие; 8. the outer surface of the mandible -внешняя поверхность нижней челюсти; 9. the inner surface of the mandible -внутренняя поверхность нижней челюсти. 3. Pay your attention to the use of the Complex Subject in these sentences. Translate them:
4. Read the text and be ready to answer some questions: The mandible lies below the anterior part of the cranium and is the skeleton of the lower part of the face. It has the body and a pair of flat, broad rami, which stand up from the posterior part of the body. Each ramus is surmounted by two processes: the anterior is named the coronoid process, and the posterior is the condyloid one. The condyloid process has an articular part called the head. The right and left halves of the body of the mandible are united together in the medial plane in front. Their junction is called the symphysis menti. The halves of the mandible are joined together by fibrous tissue at birth, but they are fused together into one bone during the second year. Each half of the body of the mandible has an outer and inner surface and an upper and a lower border. The surfaces slope so that the lower border makes a wider arch than the upper border. The upper pan is known to be called the alveolar part because it is occupied by a rowof alveoli, those are the sockets for the teeth. On each side the sockets for the two incisors, the canine and two premolars are single but for the three molars are double, for each mandibular molar has two roots: anterior and posterior. The lower border is known to be the base of the mandible. The outer surface is slightly convex, but has a depression alongside the symphysis below the incisor teeth. The mental foramen is seen on the outer surface of the mandible. The inner surface is convex and concave at different parts. There is a shallow depression called the submandibular fossa. The mandibular foramen leads into a canal which runs in the substance of the bone and carries the vessels and nerves for the teeth. The mandible is the only bone of the face which has movement. The temporamandibular joint is known to make a wide range of mandibular motion. This joint consists of two joints on either side of the mandible, which articulates with temporal bones on either side of the head. The mandible serves as the attachment of the elevator muscles which consist of the masseter, temporal and internal pterygoid muscles.
EXERCISES Ex. I. Listen to the text and prepare the fast reading of it. Ex. 2. Give English equivalents; передний, задний, верхний, нижний, ветвь, отростки, венечный отросток, суставный отросток, наружная поверхность, внутренняя поверхность, соединение, подбородочный шов, отверстие, объединять, подъязычная ямка, Ex. 3. Choose the necessary preposition.
by, at, on, in, with, from, for, of, into Ex, 4. Translate paying attention to the Complex Subject.
Ex. 5. Translate.
|
