реферат. Реферат Выпускная квалификационная работа содержит 5 глав, написанных в 106
 Скачать 2.82 Mb. Скачать 2.82 Mb.
|
Breаkdоwn of composite insulationAgeing is the process by which the electrical and mechanical properties of insulation normally becomes worse in condition (deteriorate) with time. Ageing occurs mainly due to oxidation, chemical degradation, irradiation, and electron and ion bombardment on the insulation. Tracking is another process by which ageing of the insulation occurs. Usually partial discharge tests are used in ageing studies to estimate the discharge magnitudes, discharge inception, and extinction voltages. Change of loss angle (tanδ) during electrical stressing provides information of the deterioration occurring in insulation systems. The knowledge of the mechanical stresses in the insulation, controlling of the ambient conditions such as temperature and humidity, and a study of the gaseous products evolved during ageing processes will also help to control the breakdown process in composite insulation. Finally, stress control in insulation systems to avoid high electric stress regions is an important factor in controlling the failure of insulation systems. The basic empirical equation to describe the breakdownIn practice, to describe the aging processes of insulators and finding time to breakdown are often used empirical equation: exponentialequationoftheform: 𝑟 p = 𝐵 · 𝑒−𝑏𝐸, (1) where B,bare the coefficients that reflect the conditions of the experiment. theequationsedateof thekind: 𝑟 p = · 𝐸−𝑛, (2) where A,nis constant depending on the material of the dielectric. thecombined equationofthekind: ∆W 𝑟 p = 𝐶𝑈−𝑛 · 𝑒 T , (3) Here C, n – constants, ∆W – the height of the potential barrier, T – temperature, K, k is the Boltzmann's constant. 3The experimental partDefinition of short-term breakdown voltage Before the start of testing for long-term strength, we need to determine the momentary breakdown voltage at which the samples will be tested in the future. To assess short-term breakdown voltage, the samples are tested for breakdown voltage in alternating current frequency of 50 Hz in water, on a high- voltage installation is shown in Fig.7 in accordance with GOST 2990-78. Test 10 groups of samples of wires for 5 samples in each group. To create the most rigid test conditions that mimic operating conditions, samples of pre- wound wire placed in a heat chamber and kept at a temperature of 250 . Removing any groups of samples was every two days, and then were tested to determine the short-term breakdown voltage (Fig.2.). 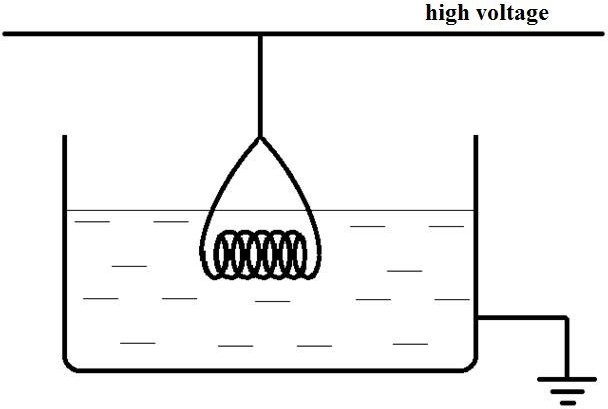 Fig.2. The definition of short-time breakdown voltage insulation wire specimens after exposure to elevated temperatures The results of tests on the breakdown voltage of samples of wires with a solid polyimide insulation are given in table 1. Table 1 – test Results for breakdown voltage in the initial state and after exposure to a temperature of 250
The results obtained by changing the breakdown voltage wiring patterns with a solid polyimide insulation can determine the average short-term breakdown voltage of 12.3 kV. Description of the experimental results on time before breakdown On the basis of the previous section 3.1., we chose the level of the test voltage - 9, 7 kW. The temperature selected for conducting tests: 80, 100, 120,140,150. Then the samples of the first batch are placed in a heat chamber, we set the desired temperature aging (Fig.2.)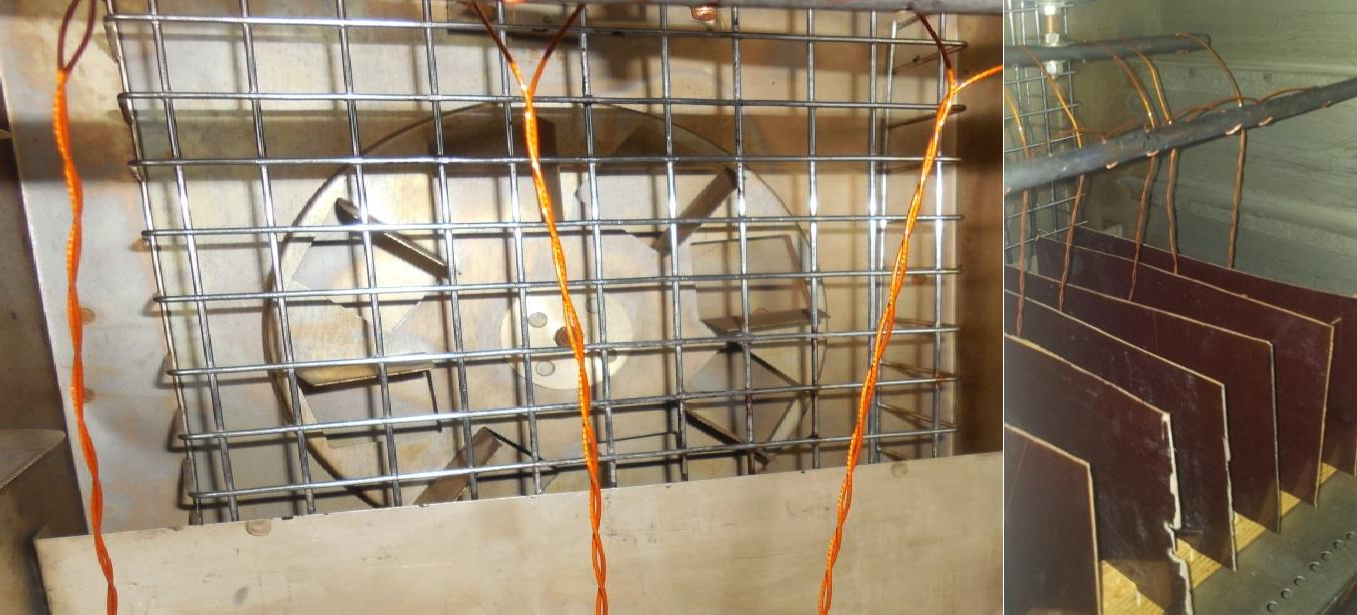  Fig.2. General view of the samples placed in a heat chamber It should be noted that each successive batch of samples is laid at another temperature to eventually evaluate the effect of temperature on the time to breakdown. Once a breakdown occurs, the time is recorded. The test results are shown in Table 1. Table 1 – The test results for up to breakdown
ConclusionFrom the outcome of our investigation it is possible to conclude that the results will be used in design, production and operation of polyimide insulated wires and cables. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
