|
|
Отчет Численные методы вариант 10. численные методы. 1 Метод итерации
Численные методы
Вариант 10
№1

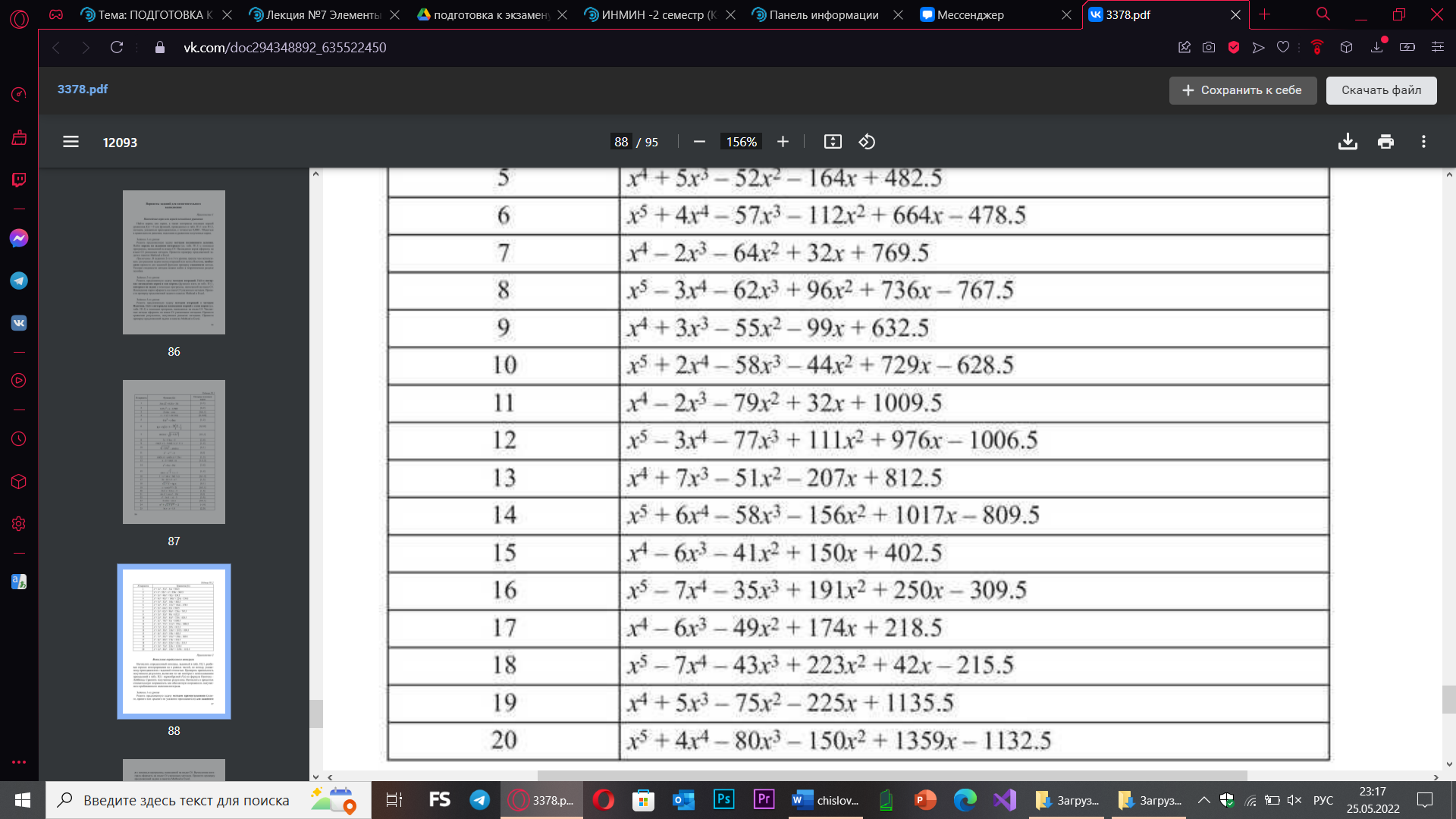
Метод итерации
Метод итераций основан на последовательном приближении к корню однородного уравнения. Исходную функцию нужно привести к виду 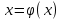 , где , где 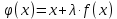 , , 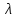 является произвольно подобранной константой. Значения на интервале близ корня подставляются в преобразованное уравнение и сравниваются между собой, пока их разность не станет меньше заданной точности. является произвольно подобранной константой. Значения на интервале близ корня подставляются в преобразованное уравнение и сравниваются между собой, пока их разность не станет меньше заданной точности.
Условия работы этого метода:
непрерывность исходной функции и ее первой производной на заданном отрезке;
Функция 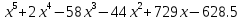 непрерывна на отрезке [-10;10], ее производная 5x4 + 8x3 – 174x2 – 88x + 729 – тоже. непрерывна на отрезке [-10;10], ее производная 5x4 + 8x3 – 174x2 – 88x + 729 – тоже.
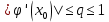 ; ;
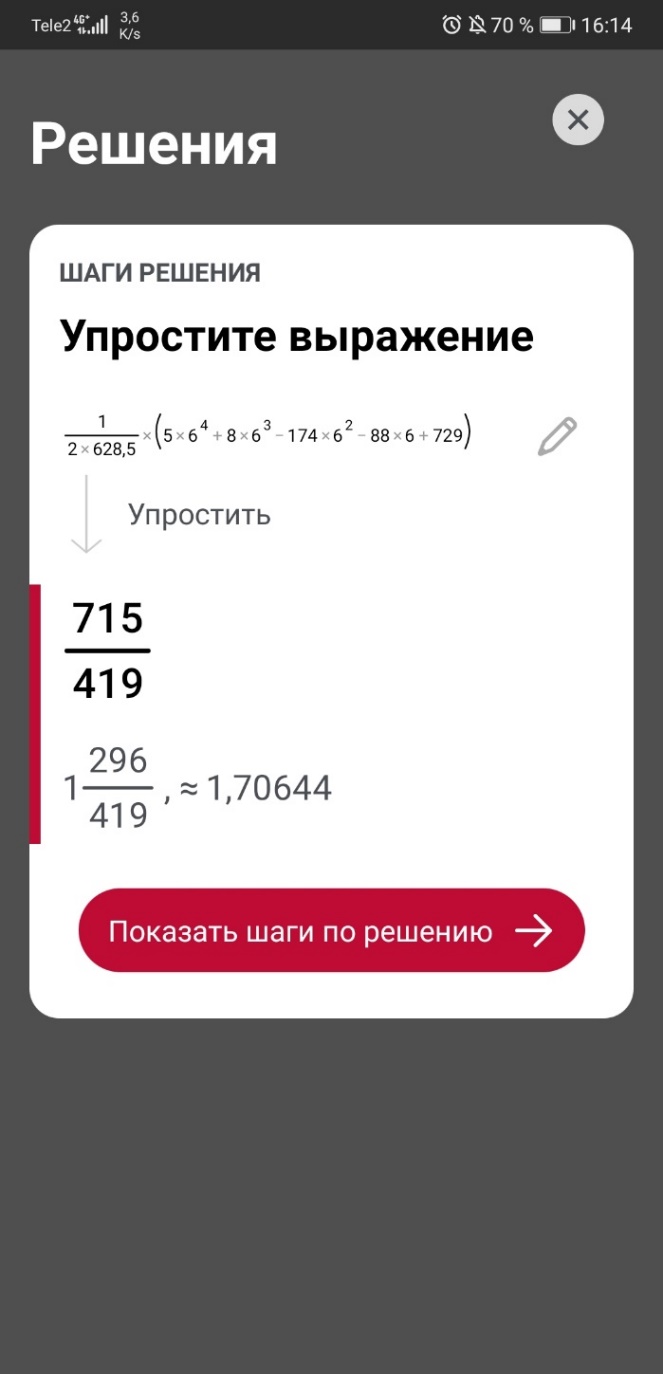
Путем преобразований привела к виду: 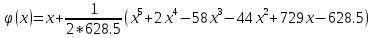 . .
Производная от этого: 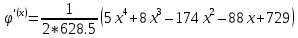 . .
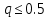 – для того, чтобы пользоваться соотношением – для того, чтобы пользоваться соотношением 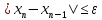 , где , где 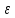 – точность расчетов (это соотношение используется в коде). – точность расчетов (это соотношение используется в коде).
Подставляя начальные значения (-7, -4, 1, 4, 6):
 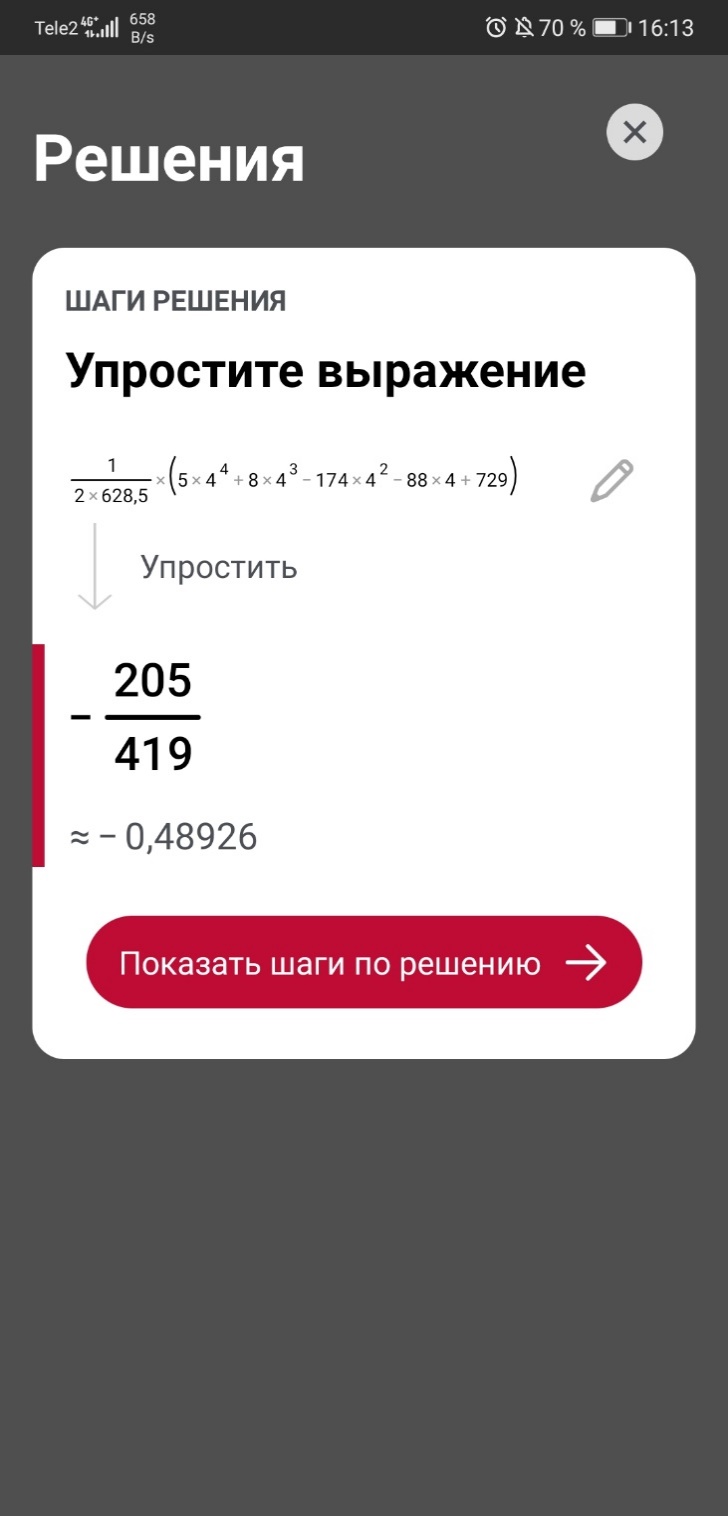 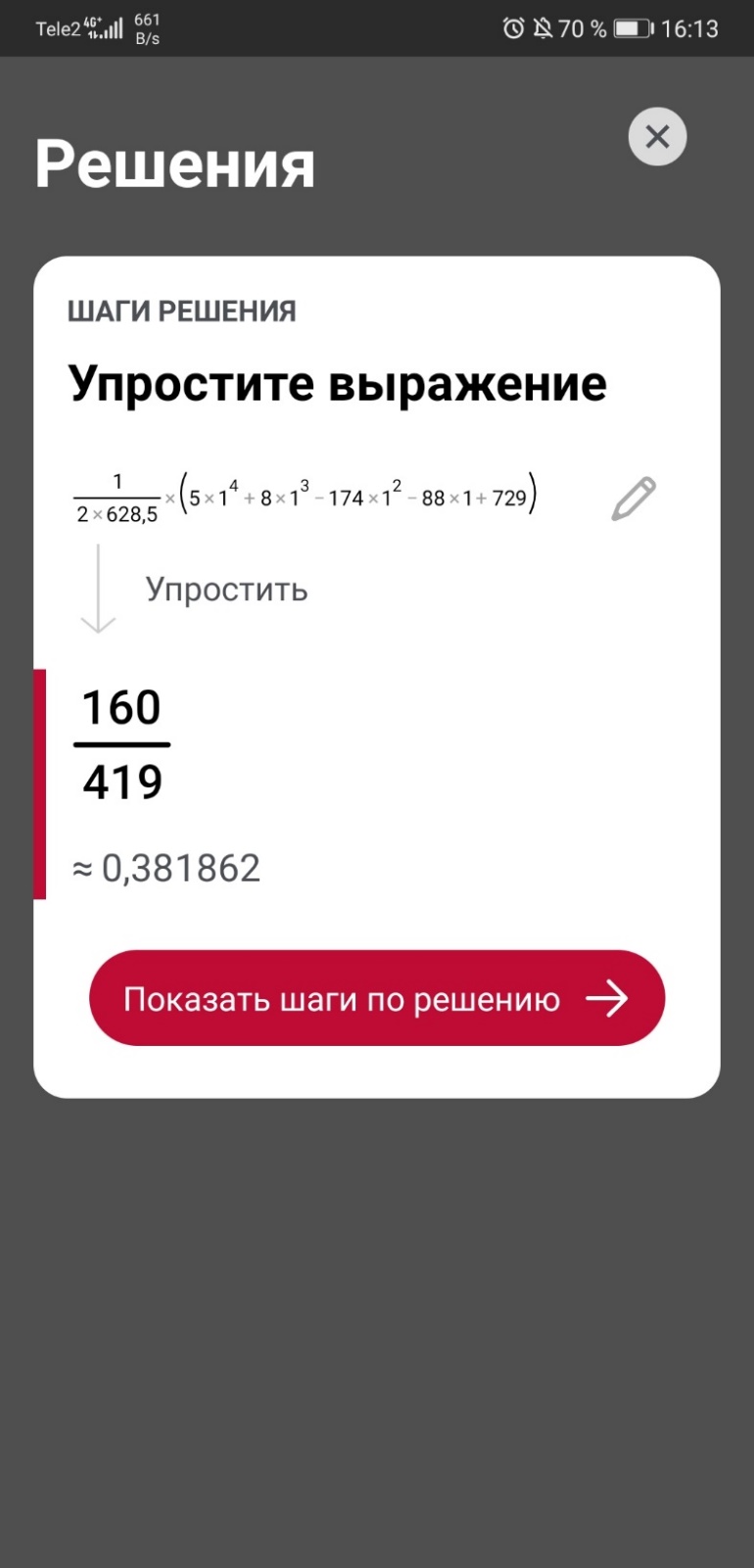
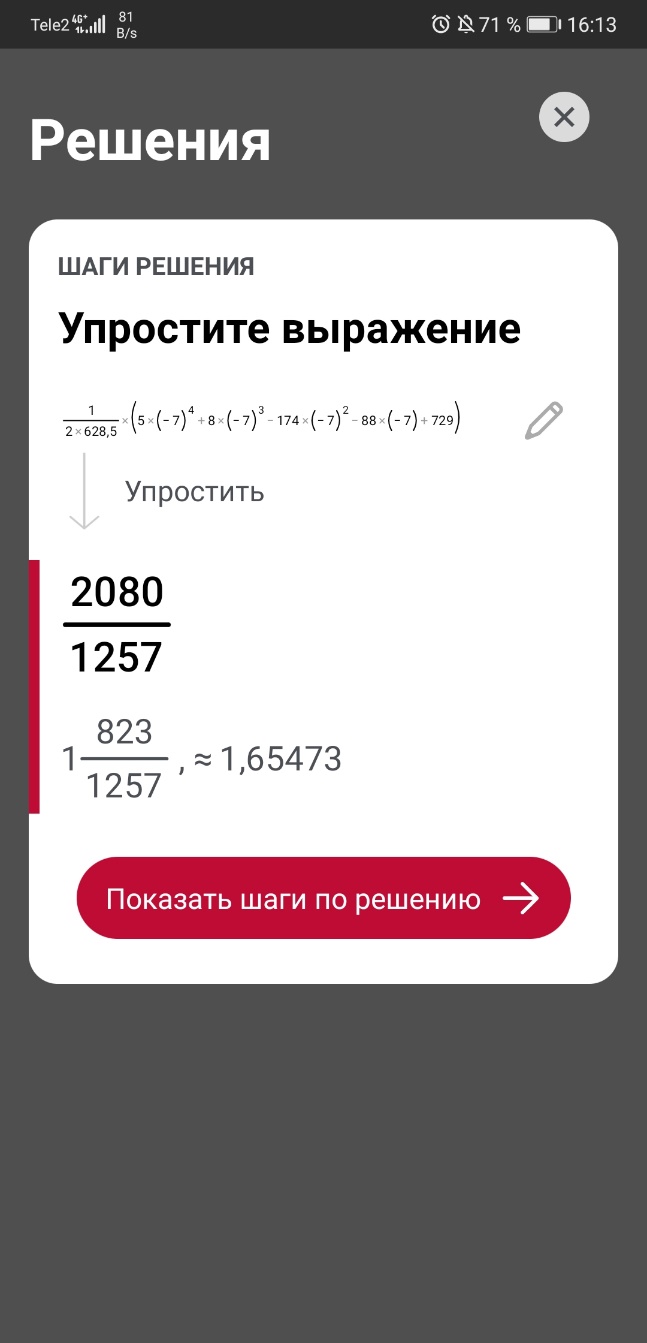 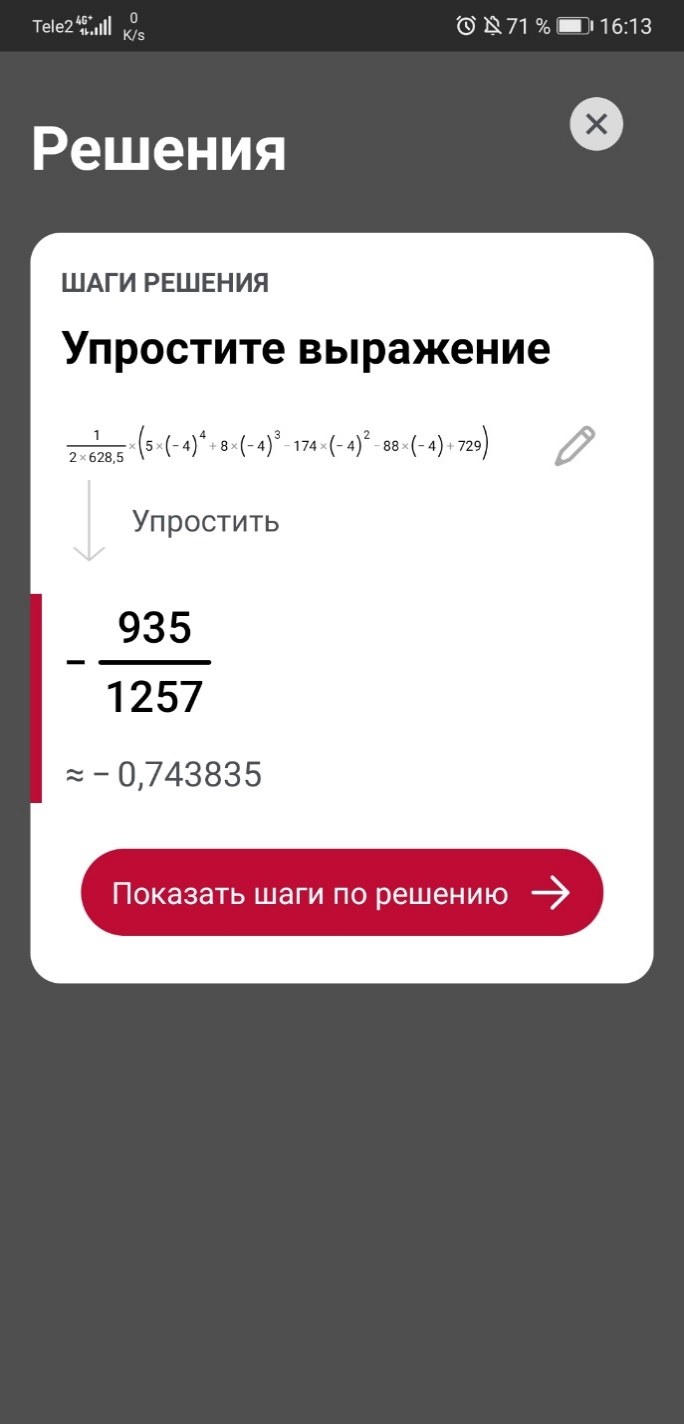
C#
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp19
{
class Program
{
delegate double fx(double i);
// производная для определения возрастания/убывания
static double f3(double x)
{
return 5 * Math.Pow(x, 4) + 8 * Math.Pow(x, 3) - 174 * Math.Pow(x, 2) - 88 * x + 729;
}
// исходная функция
static double f2(double x)
{
return Math.Pow(x, 5) + 2 * Math.Pow(x, 4) - 58 * Math.Pow(x, 3) - 44 * Math.Pow(x, 2) + 729 * x - 628.5;
}
// функция, приведенная к рекомендованному виду, коэффициент (1 / (2*506.5)) работает при убывании
static double f1(double x)
{
return (x + (1 / (2*628.5)) * (Math.Pow(x, 5) + 2 * Math.Pow(x, 4) - 58 * Math.Pow(x, 3) - 44 * Math.Pow(x, 2) + 729 * x - 628.5));
}
// коэффициент (1 / (-2*506.5)) работает при возрастании
static double f0(double x)
{
return (x + (1 / (2*(-628.5))) * (Math.Pow(x, 5) + 2 * Math.Pow(x, 4) - 58 * Math.Pow(x, 3) - 44 * Math.Pow(x, 2) + 729 * x - 628.5));
}
// метод итераций
static double iter(fx f, double x0, double eps)
{
double x1, dx;
do
{
x1 = f(x0);
dx = Math.Abs(x0 - x1);
x0 = x1;
}
while (dx >= eps);
return x0;
}
//метод, определяющий начальное значение
static int kl(int a, int b, double[] pred)
{
int k = 0;
for (double i = a; i < b; i++)
{
if (f2(i) * f2(i + 1) < 0)
{
pred[k] = i+1;
k++;
}
}
return k;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = -1000, b = 1000;
double eps = 0.00001;
double[] pred = new double[5];
double x0, x2 = 0;
kl(a, b, pred);
for (int i = 0; i <= 4; i++)
{
x0 = pred[i];
//при возрастании функции производная положительна
if (f3(x0) > 0)
{
x2 = iter(f0, x0, eps);
}
//при убывании - отрицательна
if (f3(x0) < 0)
{
x2 = iter(f1, x0, eps);
}
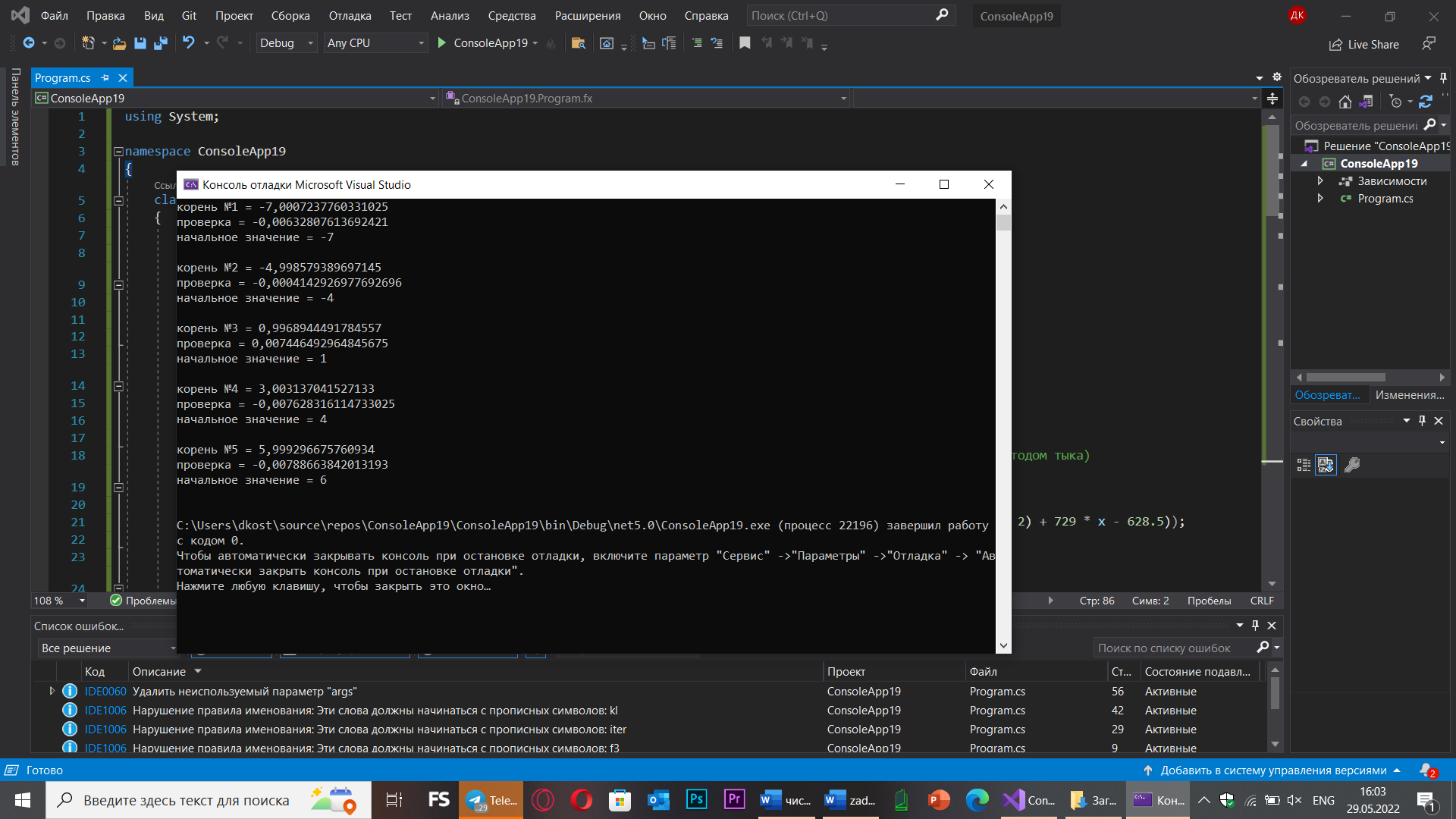
Console.WriteLine("корень №{0} = {1}", i + 1, x2);
Console.WriteLine("проверка = {0}", f2(x2));
Console.WriteLine("начальное значение = {0}", pred[i]);
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}
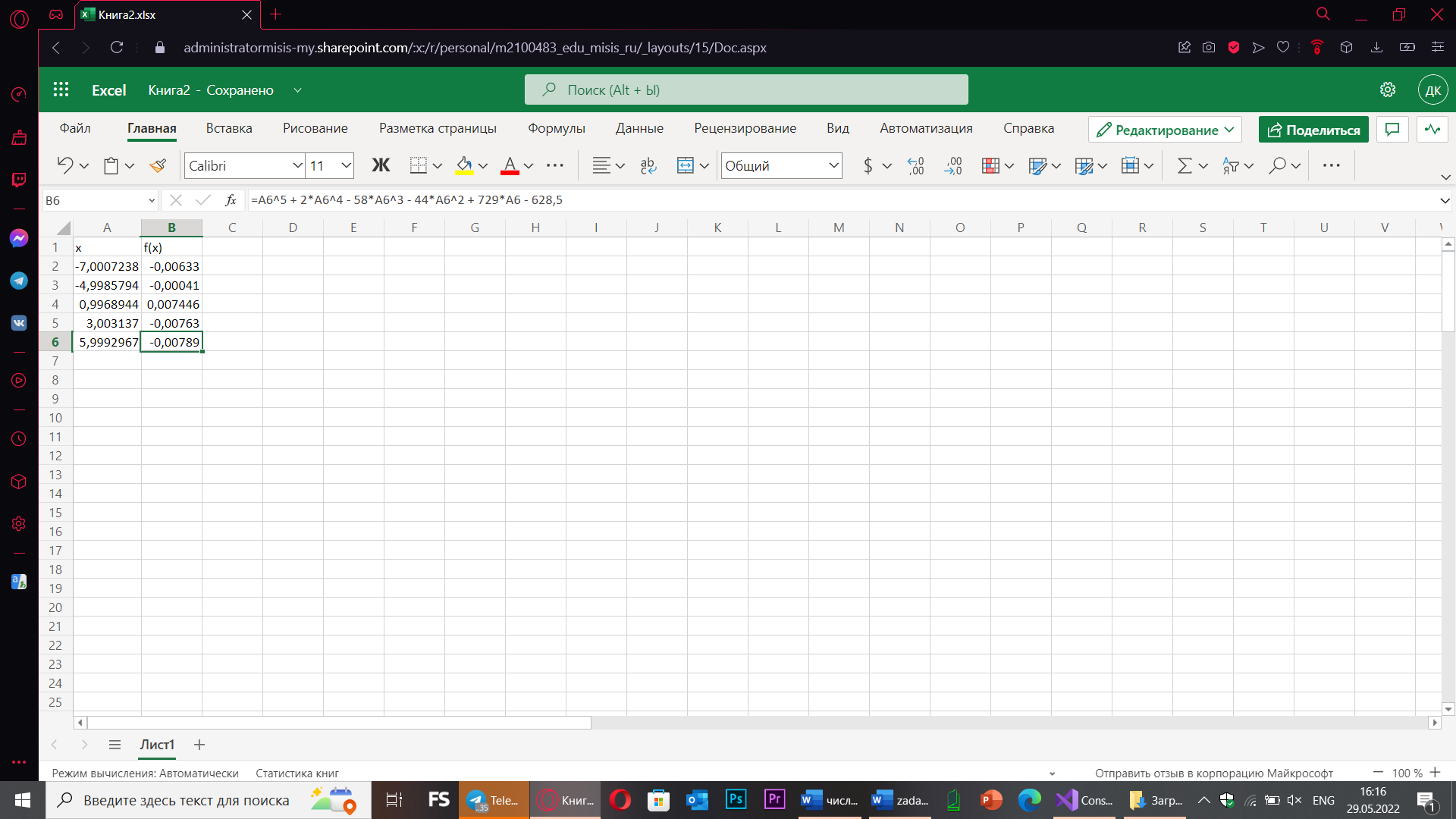
Excel:
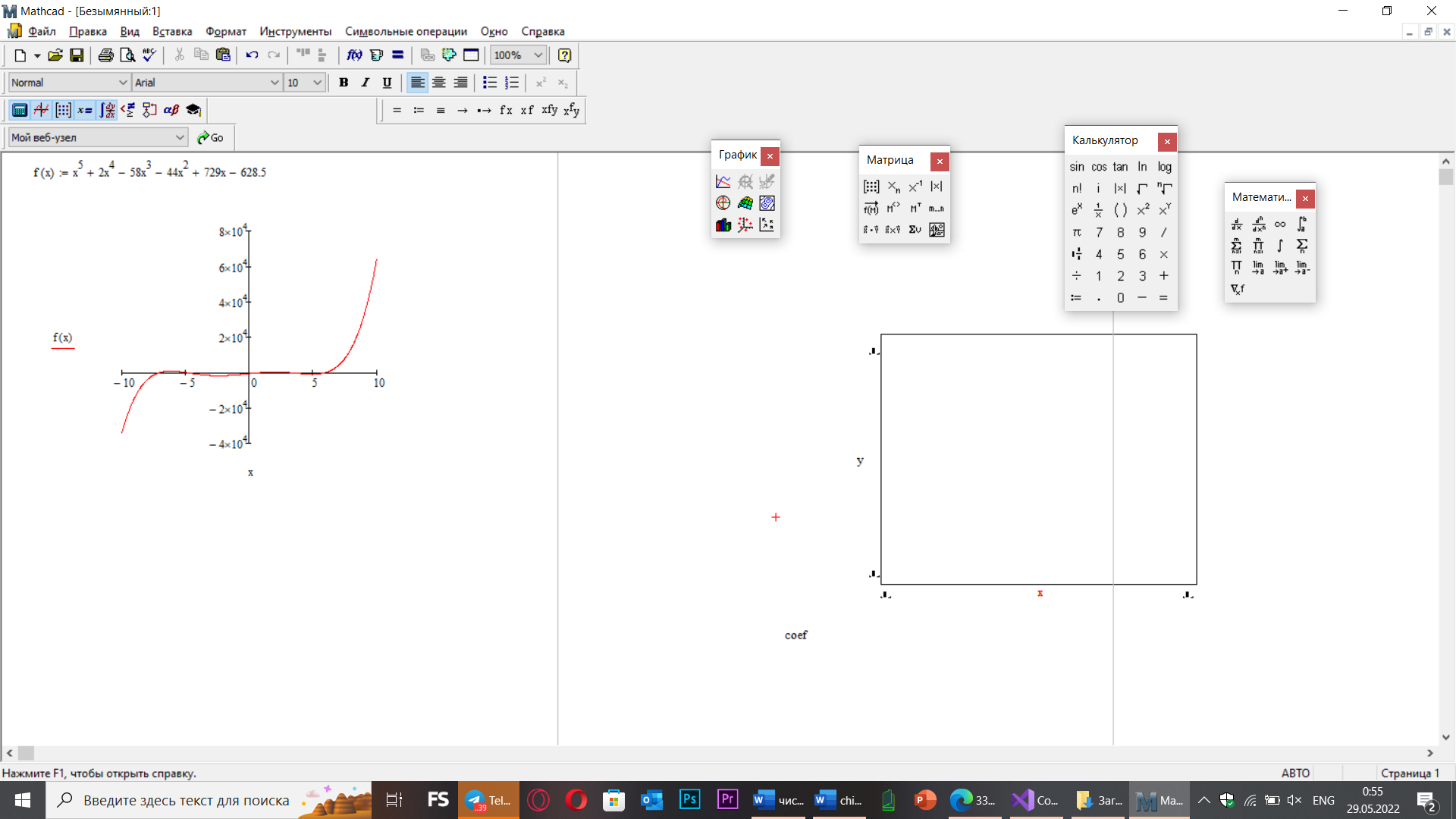
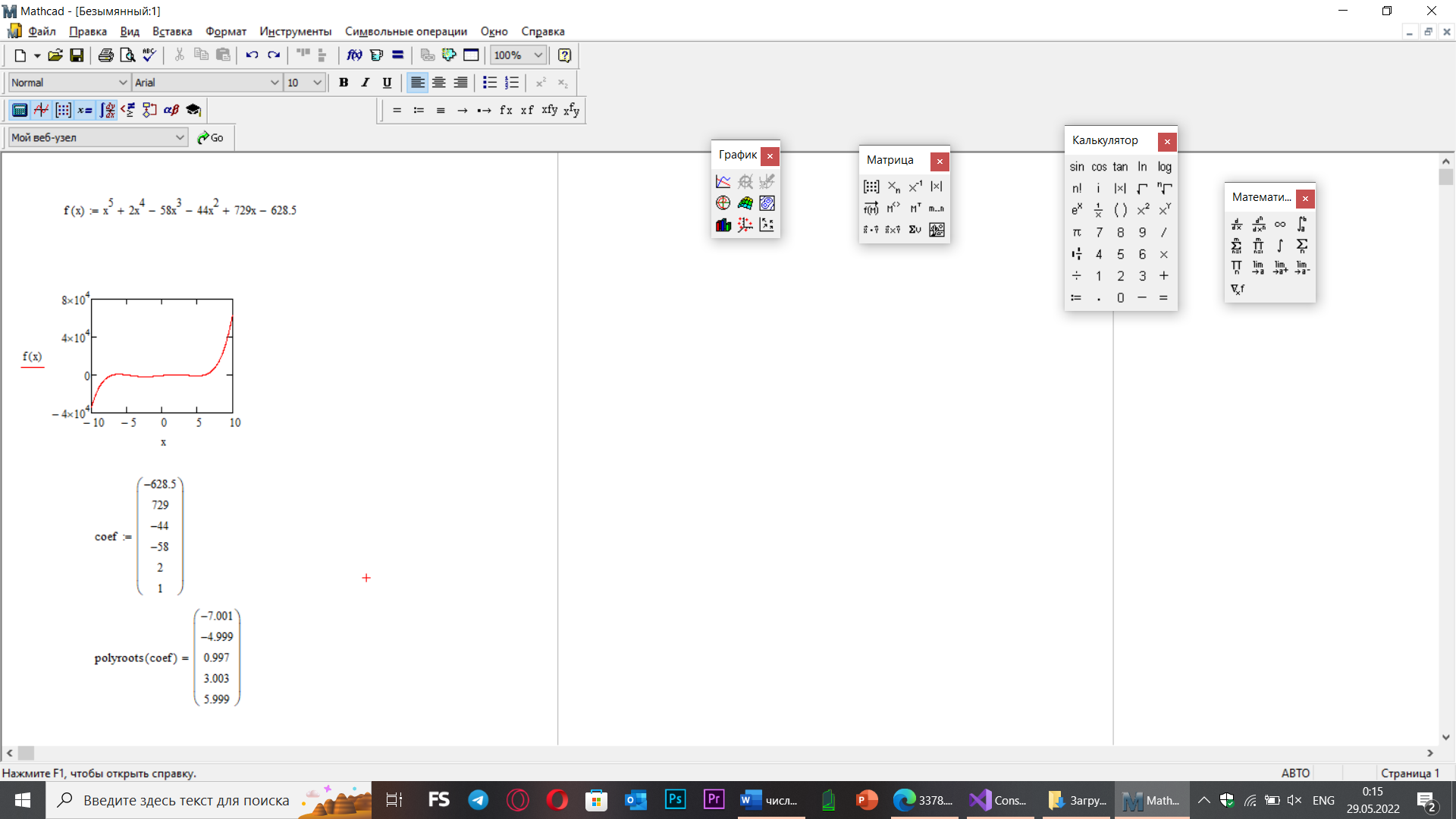
Mathcad:
№ 2

C#:
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp19
{
class Program
{
static double origfunc(double x) // интегрируемая функция
{
return Math.Asin(Math.Sqrt(x / (1 + x)));
}
static double antider(double x) // первообразная
{
return (x * Math.Asin(Math.Sqrt(x / (x + 1))) - Math.Sqrt(x) + Math.Atan(Math.Sqrt(x)));
}
static double Simpson(int n, double a, double b) // метода Симпсона
{
double s = origfunc(a) + origfunc(b);
double x = a;
double h = (b - a) / n;
double c = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
x += h;
s += (3 + c) * origfunc(x);
c = -c;
}
return s * (h / 3);
}
static double trapezoids(int n, double a, double b) // метод трапеций
{
double c = 0, x = a, h = (b - a) / n;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
x += h;
c += origfunc(x);
}
return (2 * c + origfunc(a) + origfunc(b)) * h / 2;
}
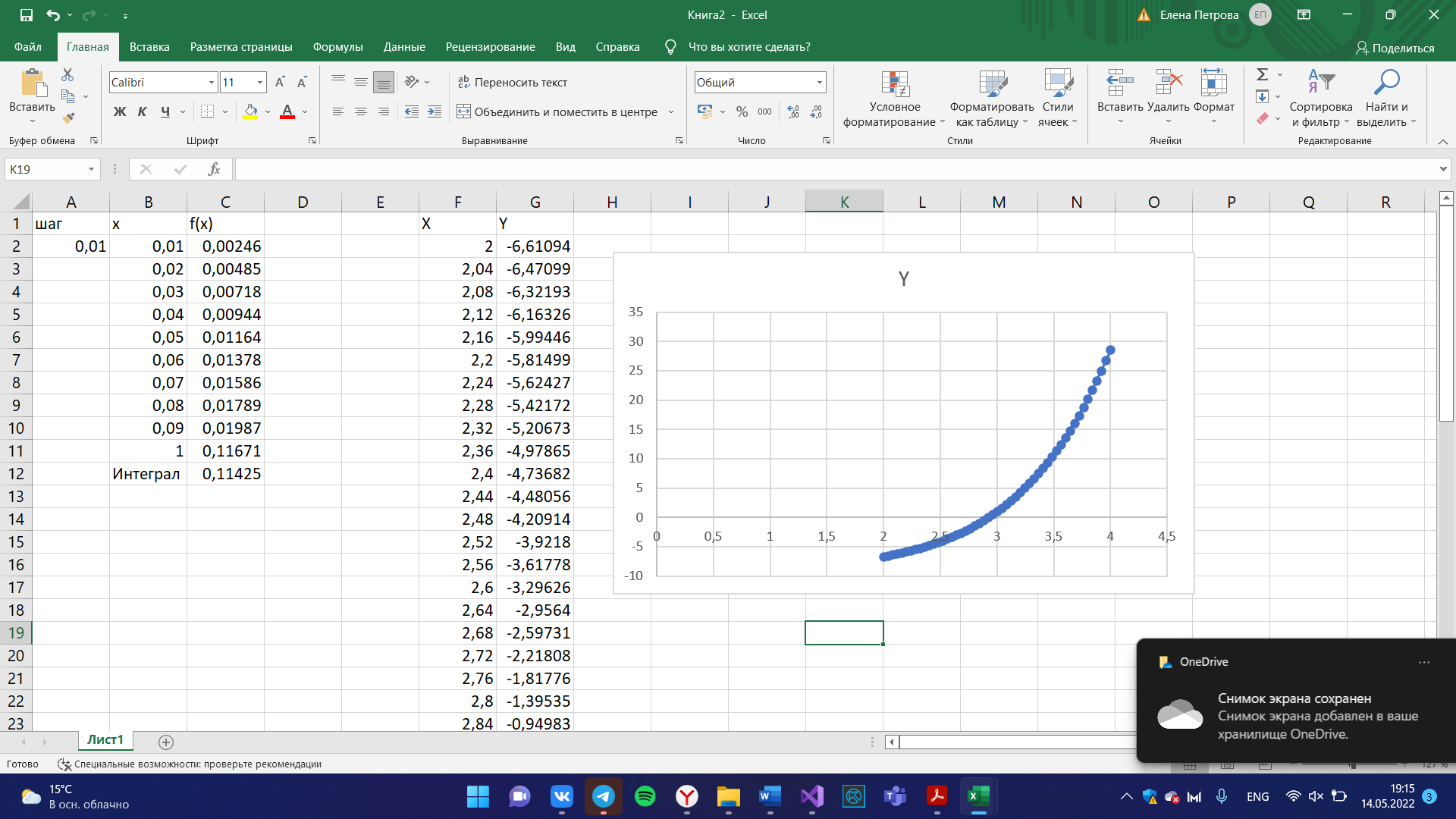
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int n = 2;
double eps = 0.001, error, integral;
double a = 0, b = 3;
double result = antider(b) - antider(a);
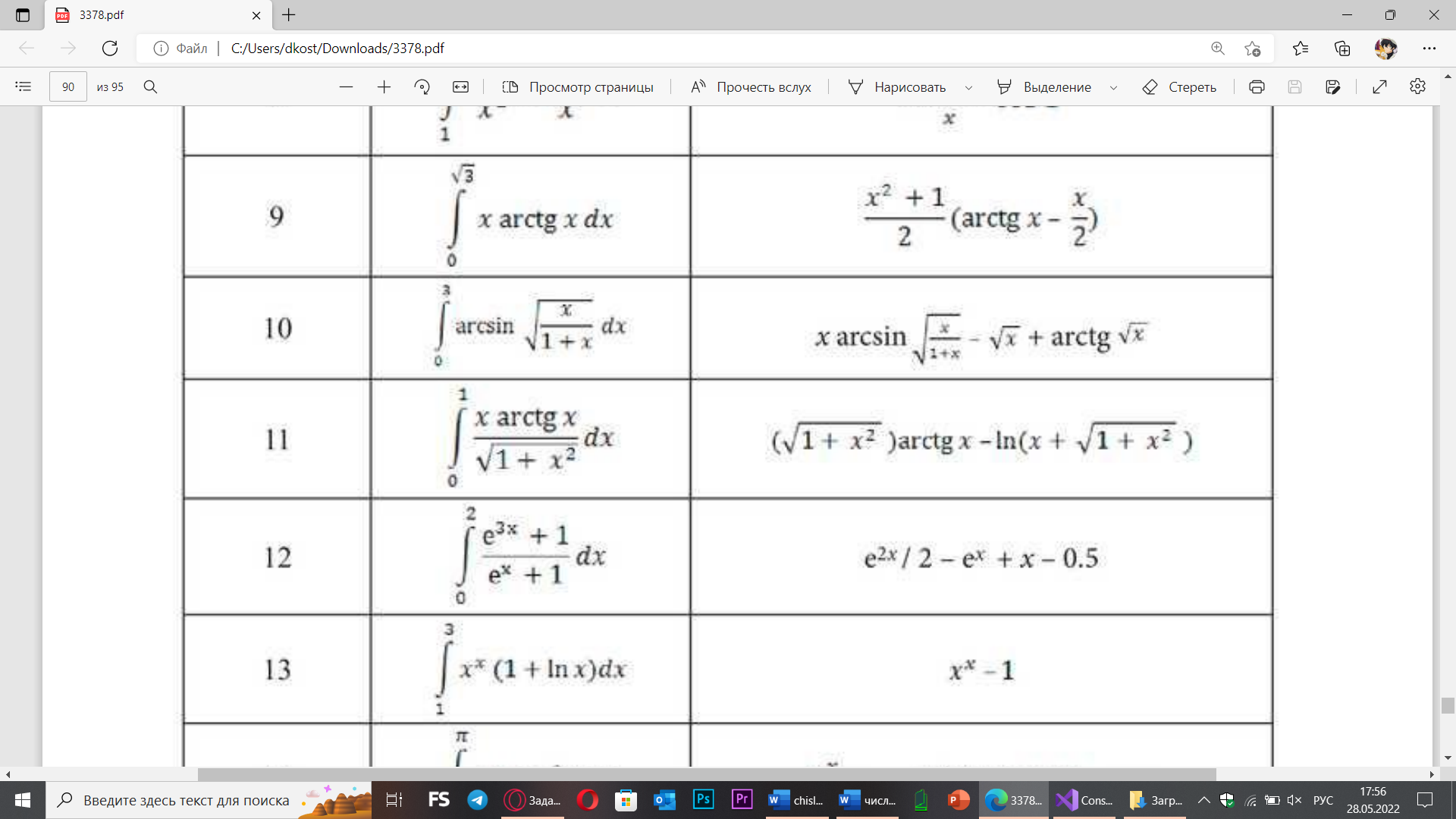
Console.WriteLine("По Ньютону-Лейбницу: {0:f3}\n", result);
do
{
integral = trapezoids(n, a, b);
error = Math.Abs(result - integral);
n++;
} while (error > eps);
Console.WriteLine("Метод трапеций");
Console.WriteLine("Результат: {0:f3}", integral);
Console.WriteLine("Абсолютная погрешность: {0:f3}", error);
Console.WriteLine("Относительная погрешность: {0:f3} %", error / result * 100);
Console.WriteLine("Количество итераций: {0}\n", n);
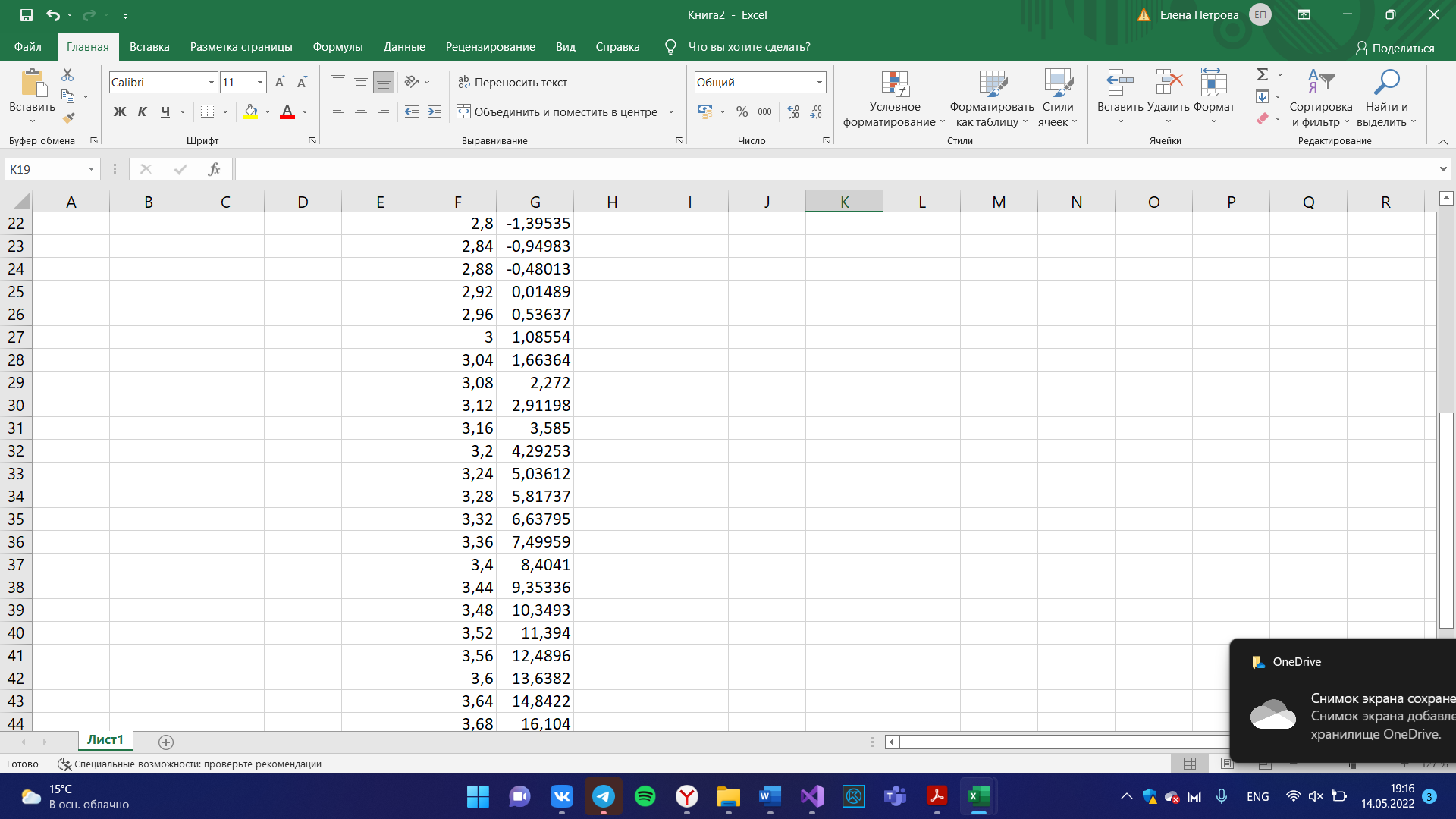
n = 2;
do
{
integral = Simpson(n, a, b);
error = Math.Abs(result - integral);
n++;
} while (error > eps);
Console.WriteLine("Метод Симпсона");
Console.WriteLine("Результат: {0:f3}", integral);
Console.WriteLine("Абсолютная погрешность: {0:f3}", error);
Console.WriteLine("Относительная погрешность: {0:f3} %", error / result * 100);
Console.WriteLine("Количество итераций: {0}", n);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
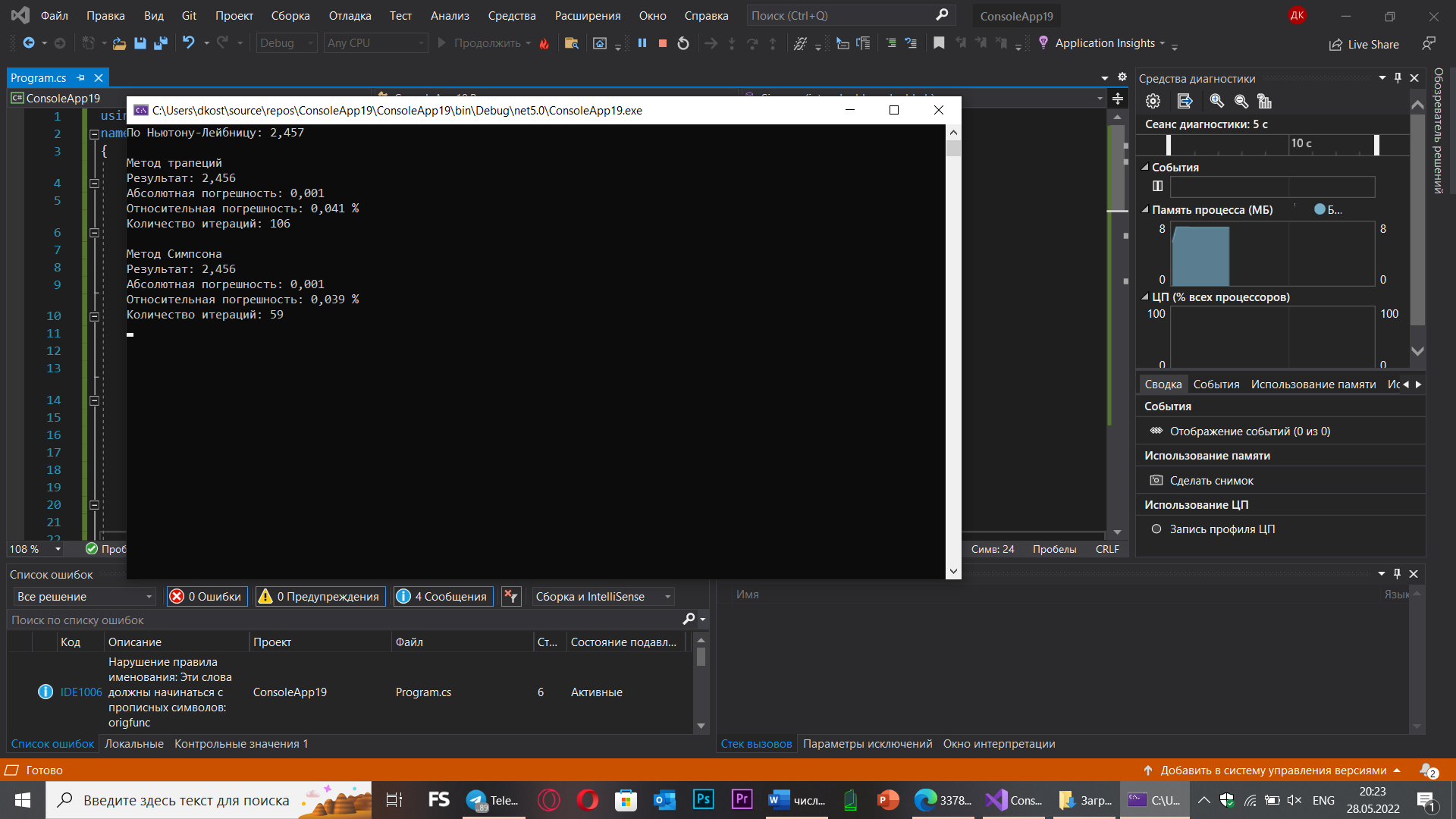
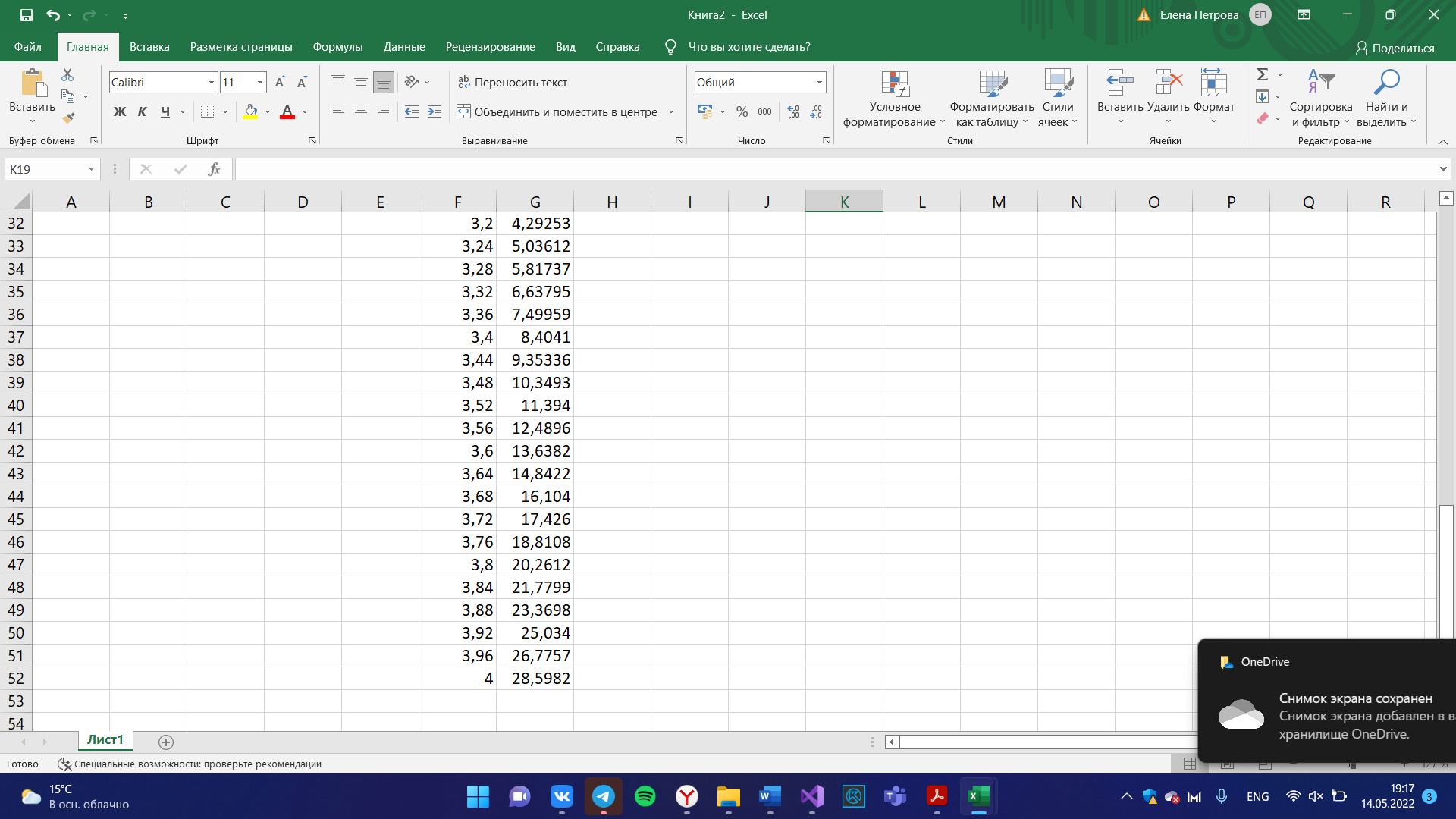
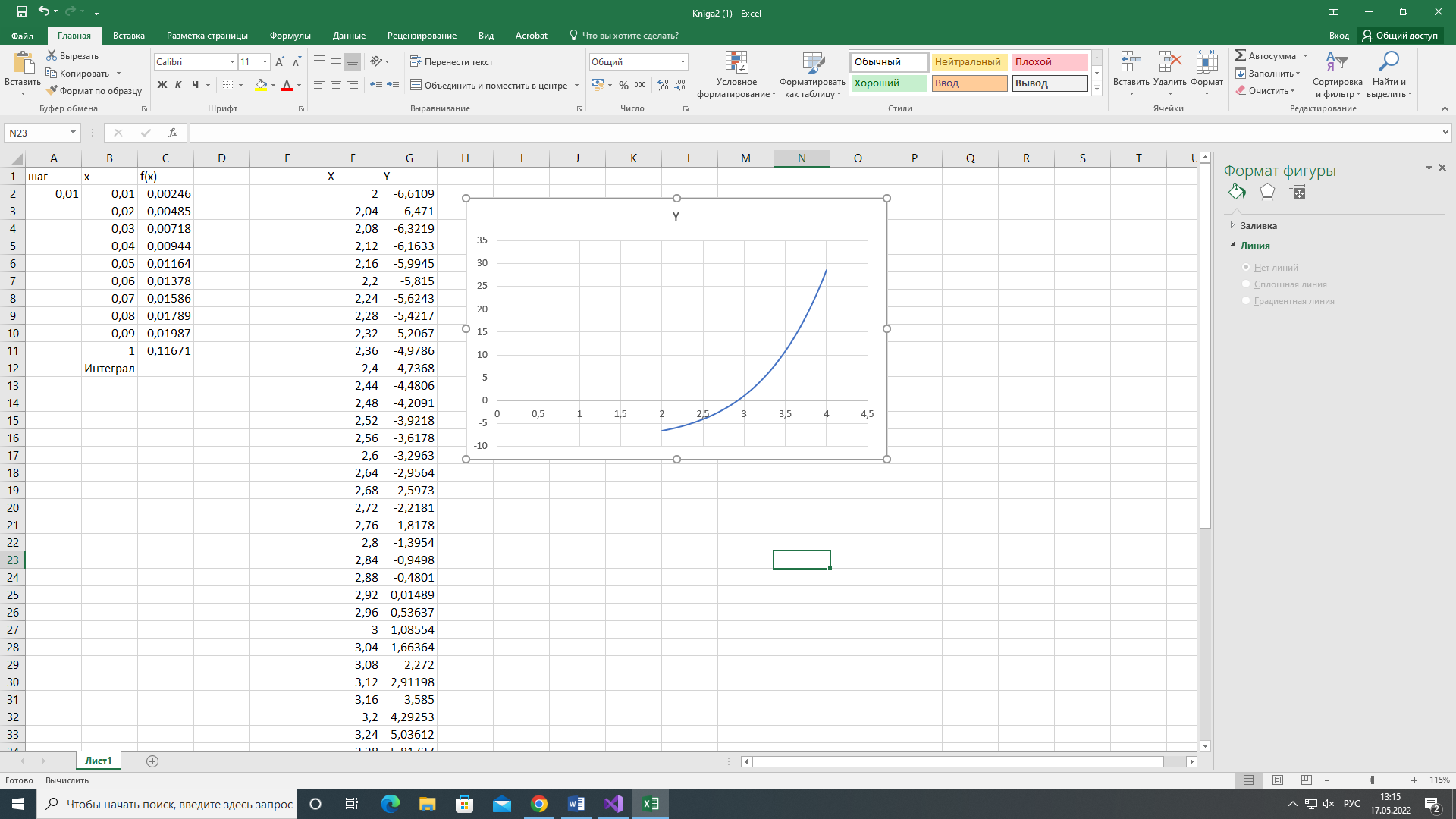
Excel:
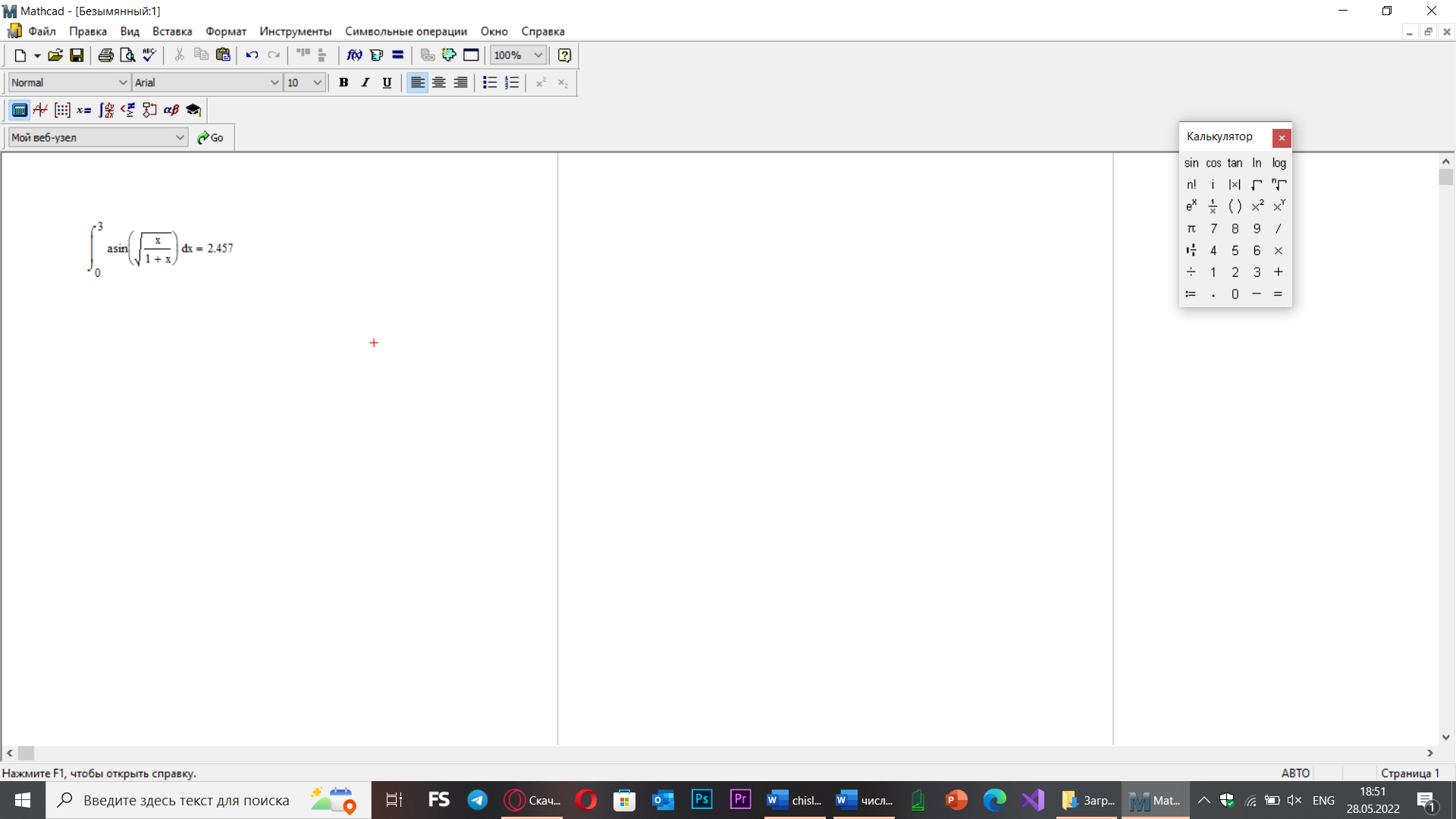
Mathcad:
№3

C#:
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp19
{
class Program
{
public static double lagrange(double[] x, double[] y, double xt) // интерполяция полиномом Лагранжа
{
double yt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < x.Length; i++)
{
double temp = y[i];
for (int j = 0; j < x.Length; j++)
{
if (i != j)
temp *= (xt - x[j]) / (x[i] - x[j]);
}
yt += temp;
}
return yt;
}
static double quadratic(int i, double testx, double[] x, double[] y) // квадратичная интерполяция
{
double A, B, C, D, E, F;
A = testx - x[i - 1];
B = testx - x[i];
C = testx - x[i + 1];
D = x[i - 1] - x[i];
E = x[i - 1] - x[i + 1];
F = x[i] - x[i + 1];
return y[i - 1] * B * C / (D * E) - y[i] * A * C / (D * F) + y[i + 1] * B * A / (F * E);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double y = 0;
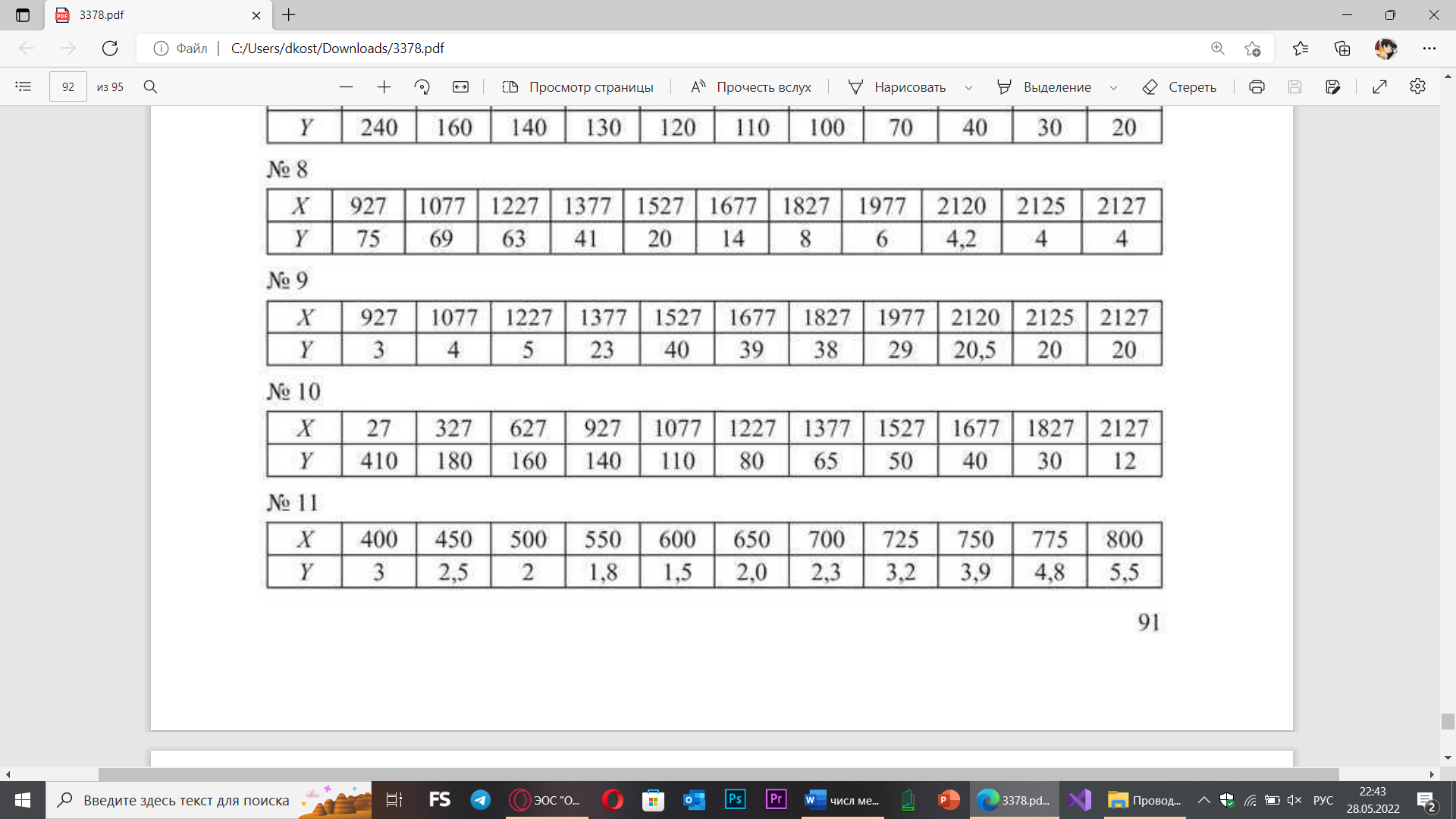
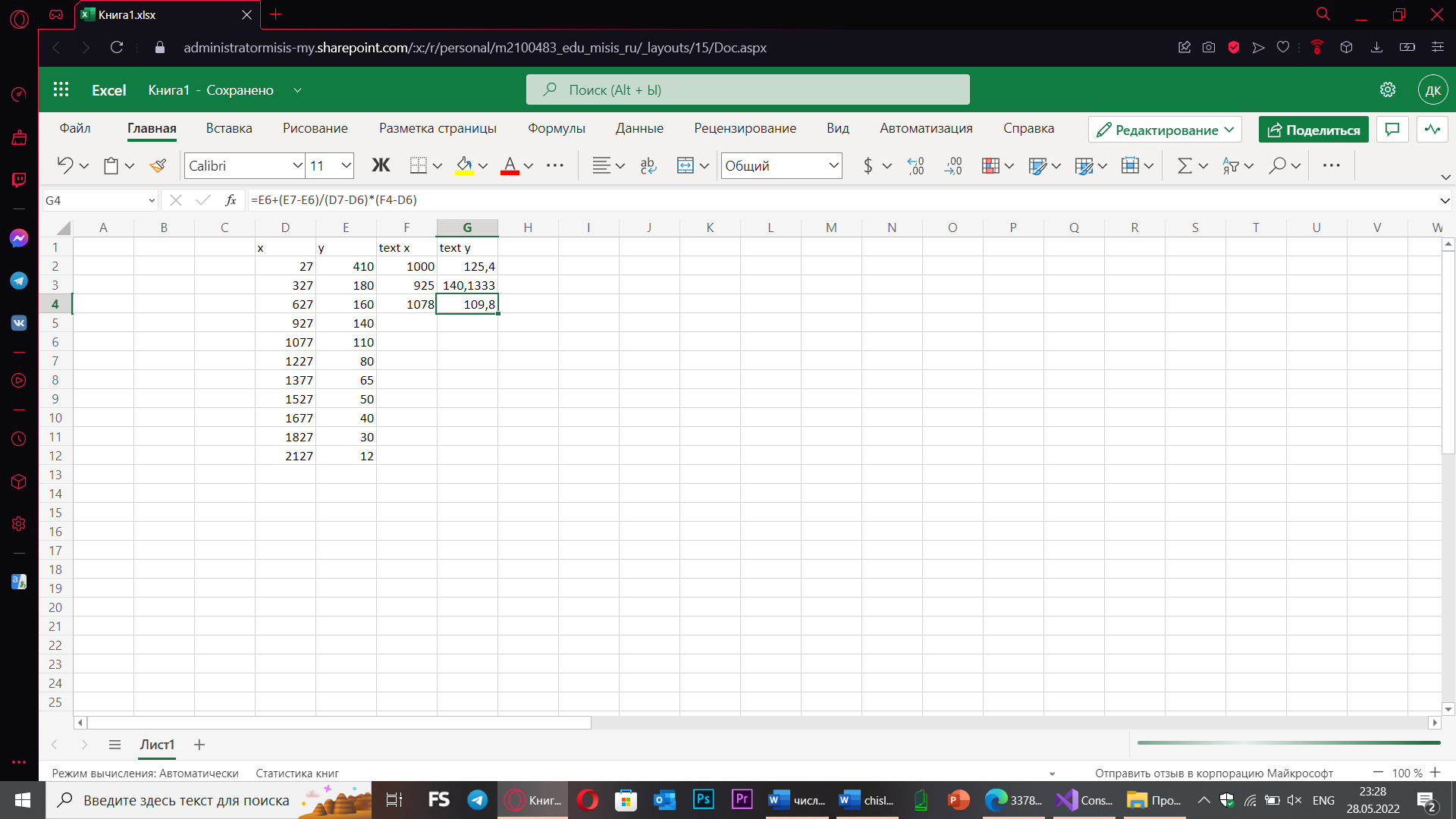
double[] xvalues = new double[] { 27, 327, 627, 927, 1077, 1227, 1377, 1527, 1677, 1827, 2127 }; // значения x
double[] yvalues = new double[] { 410, 180, 160, 140, 110, 80, 65, 50, 40, 30, 12 }; // значения функции Y(x)
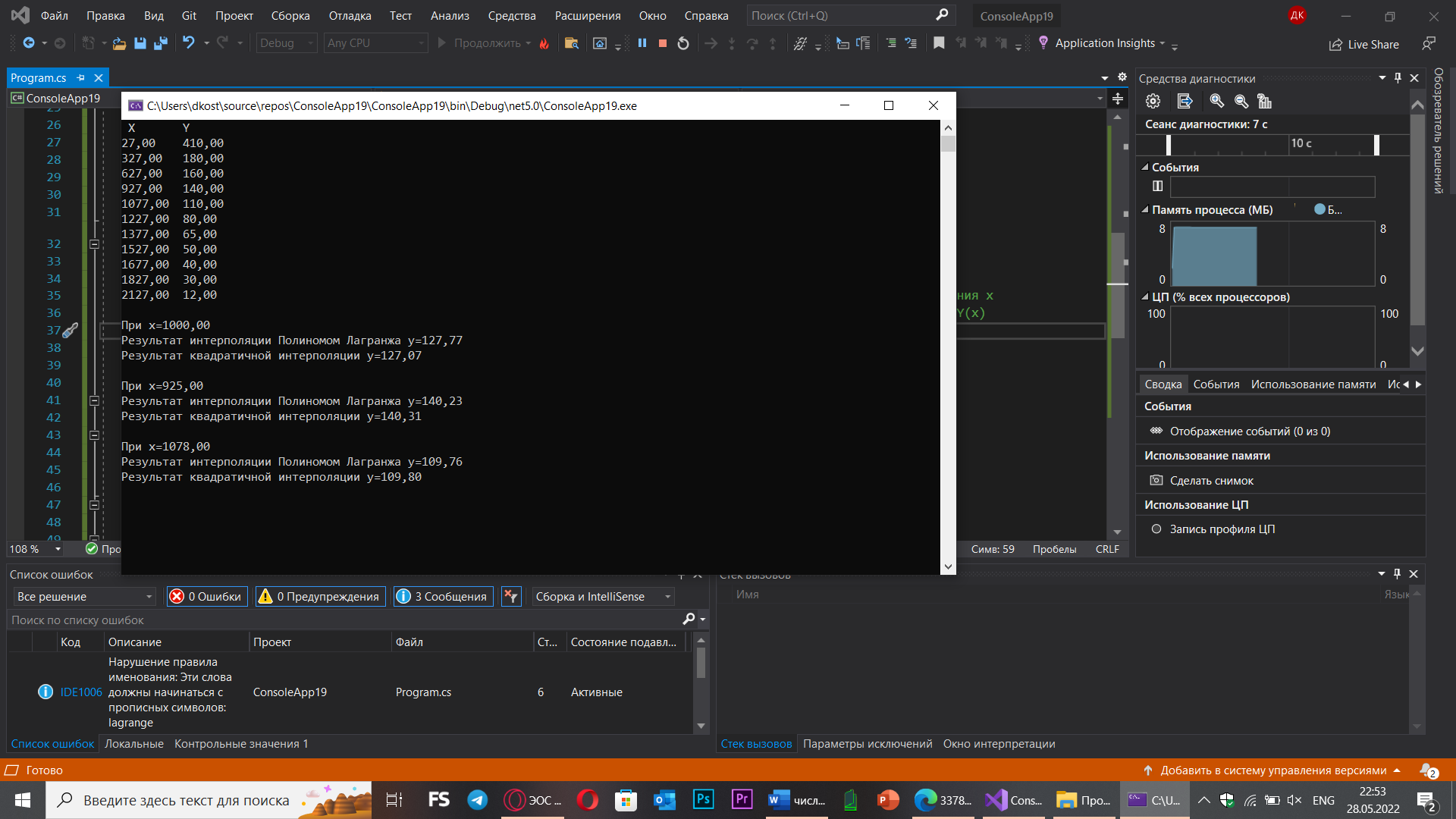
double[] testvalues = new double[] { 1000, 925, 1078 }; // контрольные точки
Console.WriteLine(" X \t Y");
for (int i = 0; i < xvalues.Length; i++)
Console.WriteLine("{0,1:f2}\t {1:f2}", xvalues[i], yvalues[i]);
for (int i = 0; i < testvalues.Length; i++)
{
if (testvalues[i] <= ((xvalues[1] + xvalues[2]) / 2))
{
y = quadratic(2, testvalues[i], xvalues, yvalues);
}
else
{
for (int j = 2; j < xvalues.Length - 1; j++)
{
if ((testvalues[i] >= (xvalues[j - 1] + xvalues[j]) / 2) & testvalues[i] <= ((xvalues[j] + xvalues[j + 1]) / 2))
{
y = quadratic(j, testvalues[i], xvalues, yvalues);
break;
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("\nПри x={0:f2}", testvalues[i]);
Console.WriteLine("Результат интерполяции Полиномом Лагранжа y={0:f2}", lagrange(xvalues, yvalues, testvalues[i]));
Console.WriteLine("Результат квадратичной интерполяции y={0:f2}", y);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Excel:
Mathcad: 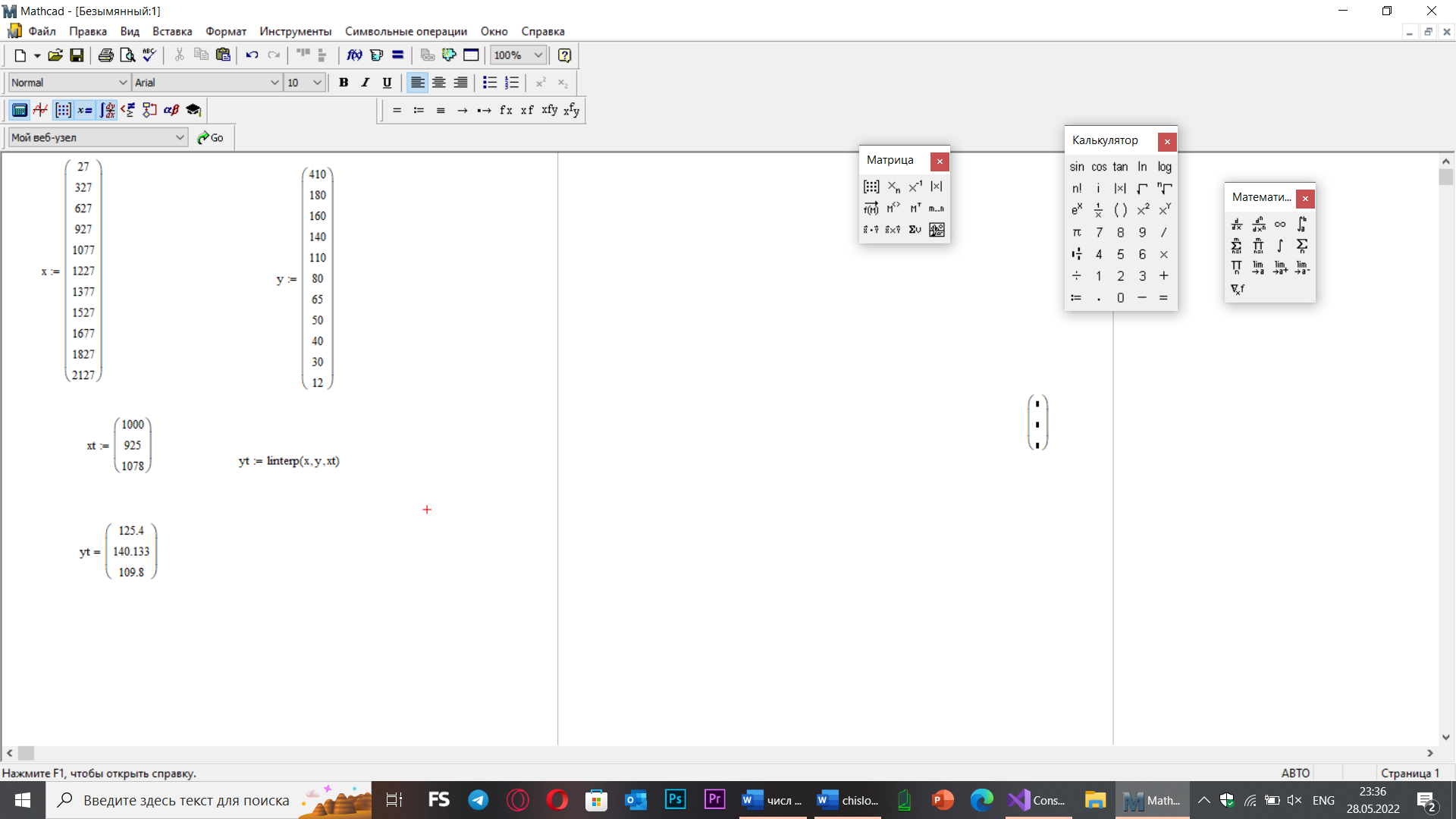
№4
Построение графика



using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WindowsFormsApp2
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
static void Coordinates(Graphics g, int Height, int Width)
{
int wdth = Width / 2;
int hght = Height / 2;
g.TranslateTransform(wdth, hght);
g.DrawLine(new Pen(Color.Red, 2.0f), -200, 0, 200, 0);
g.DrawLine(new Pen(Color.Red, 2.0f), 0, -180, 0, 180);
}
private void Form1_Paint(object sender, PaintEventArgs e)
{
Graphics g = e.Graphics;
Coordinates(g, Height, Width);
for (double x = 2; x <= 4; x += 3.5 / 50)
{
double y = Math.Exp(x) - Math.Pow(x, 2) - 10;
g.DrawEllipse(new Pen(Color.Blue, 2.0f), (int)(x * 2), (int)(-y * 2), 1, 1);
}
Font font = new Font("TimesNewRoman", 15);
SolidBrush brush = new SolidBrush(Color.Black);
string s1 = "y = e^x - x^2 -10"; float x1 = 155.0F; float y1 = 110.0F;
g.DrawString(s1, font, brush, x1, y1);
string s2 = "y"; float x2 = 5.0F; float y2 = -180.0F;
g.DrawString(s2, font, brush, x2, y2);
string s3 = "x"; float x3 = 185.0F; float y3 = 0.0F;
g.DrawString(s3, font, brush, x3, y3);
string s4 = "0"; float x4 = 0.0F; float y4 = 0.0F;
g.DrawString(s4, font, brush, x4, y4);
font.Dispose();
brush.Dispose();
}
}
}
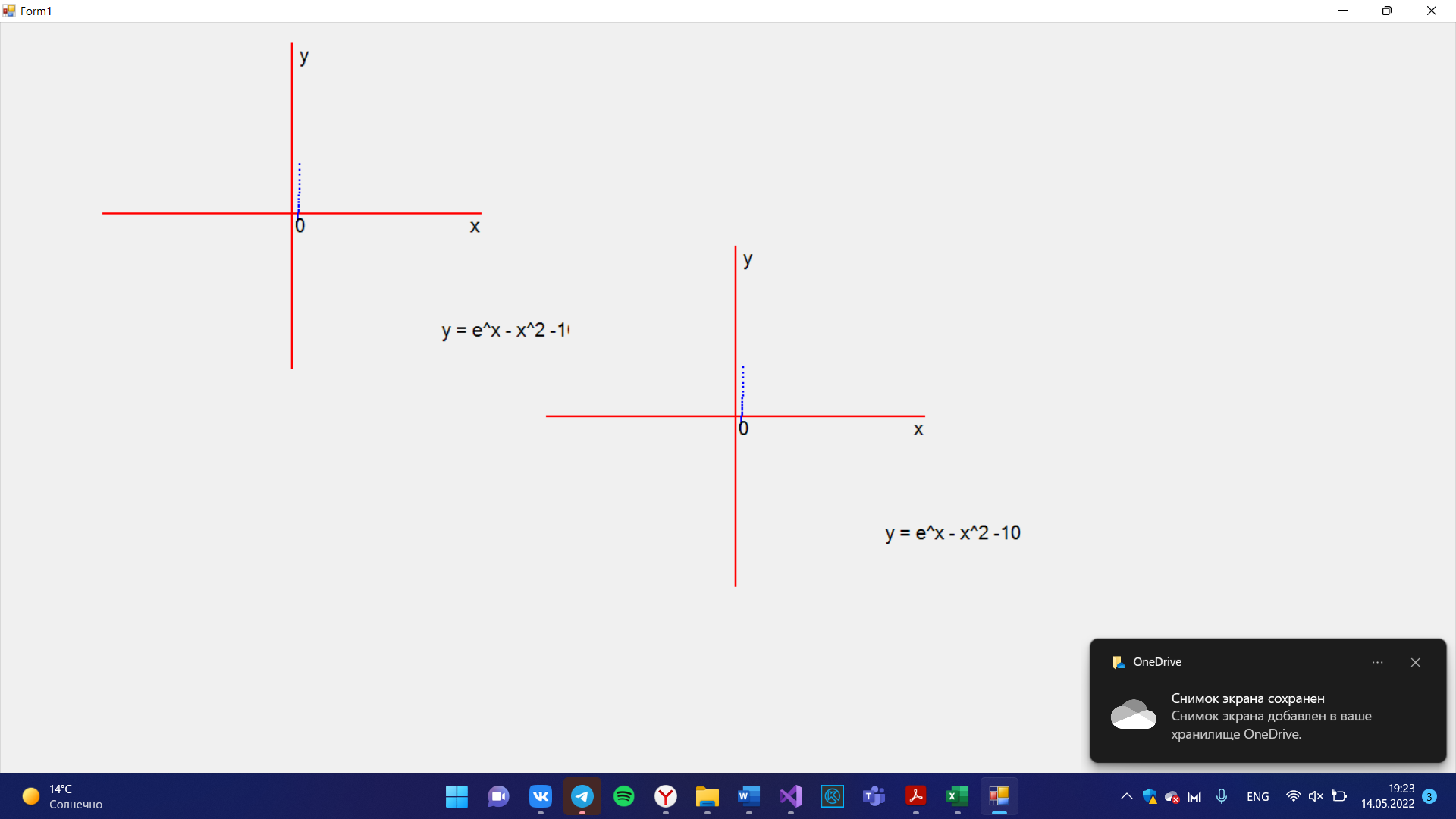
Excel:
Mathcad:
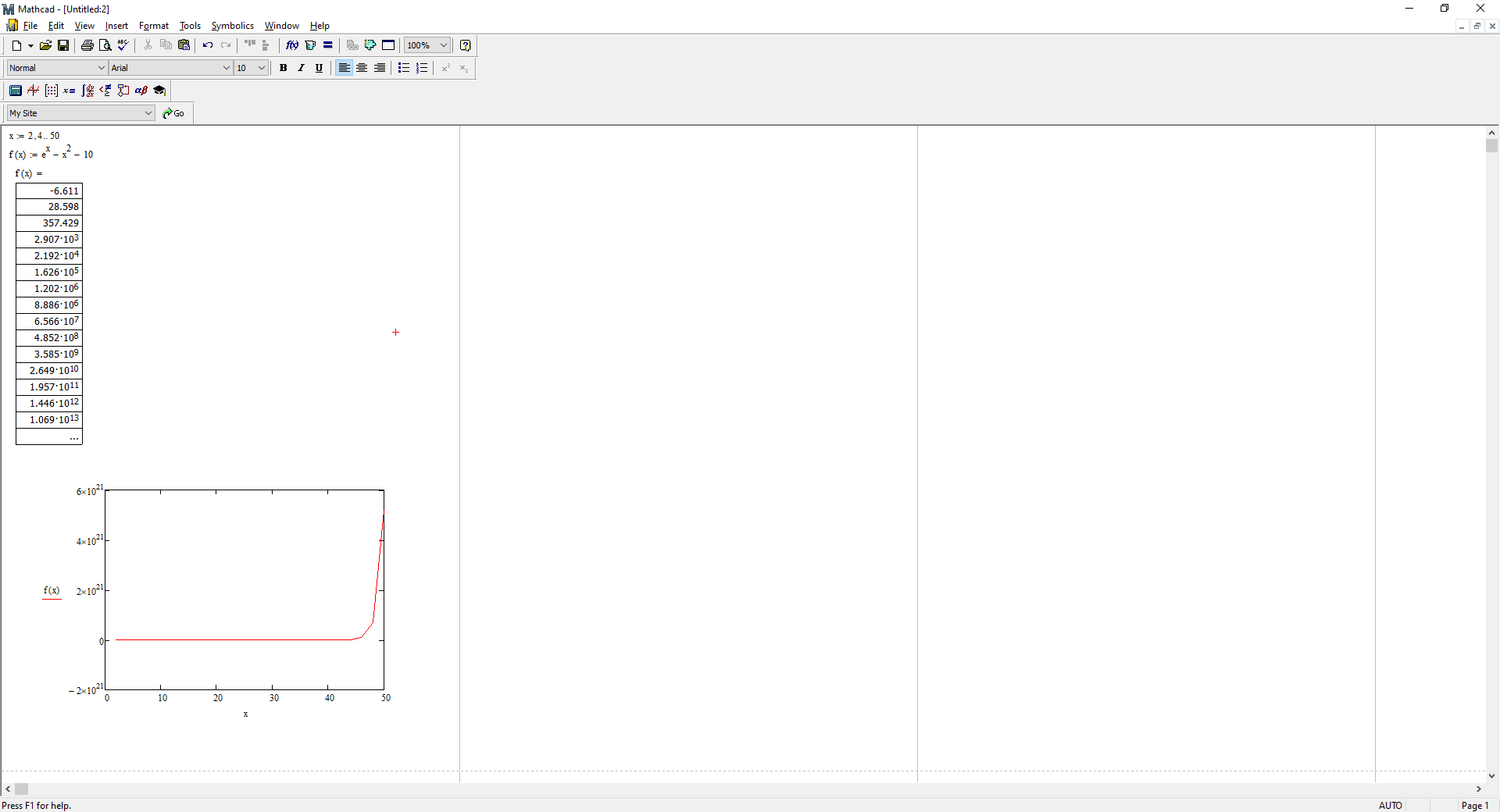 |
|
|
 Скачать 6.25 Mb.
Скачать 6.25 Mb.
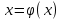 , где
, где 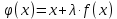 ,
, 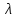 является произвольно подобранной константой. Значения на интервале близ корня подставляются в преобразованное уравнение и сравниваются между собой, пока их разность не станет меньше заданной точности.
является произвольно подобранной константой. Значения на интервале близ корня подставляются в преобразованное уравнение и сравниваются между собой, пока их разность не станет меньше заданной точности.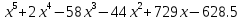 непрерывна на отрезке [-10;10], ее производная 5x4 + 8x3 – 174x2 – 88x + 729 – тоже.
непрерывна на отрезке [-10;10], ее производная 5x4 + 8x3 – 174x2 – 88x + 729 – тоже.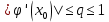 ;
;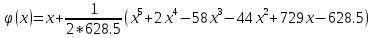 .
.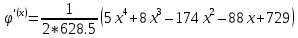 .
.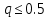 – для того, чтобы пользоваться соотношением
– для того, чтобы пользоваться соотношением 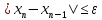 , где
, где 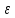 – точность расчетов (это соотношение используется в коде).
– точность расчетов (это соотношение используется в коде).


























