Магистры-экономисты. Английский язык english for masters of economics
 Скачать 4.55 Mb. Скачать 4.55 Mb.
|
|
Economic environment influences the ________ to a great extent. The economy comprises millions of people and thousands of firms as well as the ________ and local authorities, all taking decisions about prices and wages, what to buy, sell, ________, export, import and many other matters. The economy is complicated and difficult to ________ and predict, but it is certainly important to all businesses. Economic environment is very dynamic and ________ in nature. Any improvement in the economic ________ such as standard of living, purchasing ________ of public, demand and supply, distribution of income affects the size of the market. Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and ________ of goods and services. There are a ________ of modern definitions of economics. The two main ________ of economics are microeconomics and macroeconomics. Money is a ________ of final payment for goods in most market economies. Government ________ are usually responsible for setting the terms of importing and exporting goods in the economic ________.
A business organization. Something that is used as a medium of exchange; money. The act or process of functioning. A relatively large group of people organized under a single, usually independent government. Frequently or repeatedly. The branch of economics dealing with the broad and general aspects of an economy Property or another possession acquired for future financial return or benefit. A business enterprise; a firm. An organized group of people associated together for religious, benevolent, cultural, scientific, political, patriotic, or other purposes. Match the beginnings and the endings of the sentences. Put the sentences in the correct order to have a passage about economic factors. Translate the passage.  Economic They may be… Economic factors create…  3. The same factor can have… 3. The same factor can have… 4. The success or failure of any company… 5. Economic factors are variables that… 6. It depends on its current status or…  Factors a. … either a positive or negative impact. b. … influence a company's capacity to successfully do business. c. … the climate in which a business operates. d. … the type of business it is affecting. e. … beneficial or detrimental. f. … strongly depends on its own resourcefulness and ability to adapt to these external economic factors.
Answer the questions. W  hat are economic factors? hat are economic factors?What impact do economic factors have on? What do economic factors create? What influences the success or failure of a company? Is it true that economic factors make up the economy of the nation? TEXT 2 TYPES OF ECONOMIC SYSTEMS 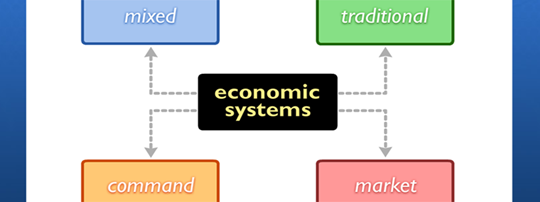 An economic system refers to the way in which the resources of a country are used to produce goods and services, and the manner in which these goods and services are distributed for consumption. There are four basic types of economic systems: traditional, command, market, and mixed. An economic system refers to the way in which the resources of a country are used to produce goods and services, and the manner in which these goods and services are distributed for consumption. There are four basic types of economic systems: traditional, command, market, and mixed. Traditional Economy. The traditional economic system forms around a society's past patterns of production, distribution and exchange. Economic decisions are based on customs and beliefs—often religious—handed down from generation to generation. Positions within society are already established and life is generally predictable. While predictable, this system does not allow much room for an individual's financial or career movements. Instead, traditional economic systems are more concerned with community stability. In this system, each member of the society knows early in life what his or her role in the larger group will be. Since jobs are handed down from generation to generation, there is very little change in the system over generations. In a traditional economy, people are depended upon to fulfill their traditional role. If some people are not there to do their part, the system can break down. An advantage of living in a traditional economy is that you know what is expected of you. In addition, family and community ties are usually very strong. Disadvantages include an economy in which change is discouraged and perhaps even punished, and in which the methods of production are often inefficient. Consequently, choices among consumer goods are rare. Also, people living and working in traditional economies rarely experience an increasing level of material well-being. Things tend to stay the same. Traditional economies exist in very limited parts of the world today. The Inuit of North America, the Mbuti of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and the Aborigines of Australia are organized into traditional economic systems. Command Economy. A command economy is sometimes called a planned economy. The most important aspect of this type is that all major decisions related to the production, distribution, commodity and service prices, are all made by the government. The planned economy is government directed, and market forces have very little say in such an economy. Individuals and corporations generally do not own businesses; the government owns these. Workers at a business are told what to produce and how much to produce in a given time. This is called quota. The government’s goal is to assign quotas to all workers. This type of economy lacks the kind of flexibility and because of this, the planned economy reacts slower to changes in consumer needs and fluctuating patterns of supply and demand. On the other hand, a planned economy aims at using all available resources for developing production instead of allotting the resources for advertising or marketing. Disadvantages of such a command economy also include a lack of incentives to work hard or to show inventiveness, as well as a lack of consumer choices. Because the government sets workers’ salaries, there is no reason to work efficiently. The former Soviet Union was an example of a command economy. Only a few countries in the world today still have much of a command economy. North Korea and parts of the People’s Republic of China are the two main examples because so much economic activity there is government-planned. Market Economy. Other names for market economy are free enterprise and capitalism. In a market economy, national and state governments play a minor role. Instead, consumers and their buying decisions drive the economy. Market decisions are mainly dominated by supply and demand. The role of the government in a market economy is to simply make sure that the market is stable enough to carry out its economic activities properly. The advantages of a pure market system are many. People have freedom – to choose a career, to spend their income how they wish, to own property, and to take risks and earn profits. Also, the existence of competition provides consumers with a wide array of goods and services from which to choose, as well as an efficient system of determining costs. A disadvantage of a pure market system involves concern about those too young, too old, or too sick to work. Many fear that survival for these people would be difficult unless the government, family members, or other organizations stepped in to provide goods and services for them. So this system leads to great inequalities as the few rich get richer and the many poor get poorer. Since the making of profits is the dominant motive of the private sector, only goods and services that yield the highest profit will be produced. There is no real life example of a purely free market economy, this only exists in theory. Mixed Economy. A mixed economy combines elements of the planned and the market economies in one cohesive system. This system prevails in many countries where neither the government nor the business entities control the economic activities of that country – both sectors play an important role in the economic decision-making of the country. In a mixed economy there is flexibility in some areas and government control in others. http://www.economywatch.com/world_economy https://lessons.engrade.com/economicsystems TEXT COMPREHENTION Answer the questions. 1. What is an economic system? 2  . What are the basic types of economic systems? . What are the basic types of economic systems? 3. What does traditional economic system form around? 4. What does the term «command economy» mean? 5. What other names for «market economy» do you know? 6. What features of market economy can you name? 7. Will you characterize the mixed economy? 8. What economic system is used in most countries? VOCABULARY PRACTICE Match the English words with their Russian equivalents.    распределение товар поколение   goal consumption     flexibility distribution потреблениееение  гибкость   inventivenesss generation     спрос предложение цель community  supply     общество demand изобретательность commodity   profit competition   прибыль конкуренция |
