AГЛИЙСКИЙ (1). Пособие по английскому языку для машиностроительных вузов допущено Министерством высшего и среднего
 Скачать 1.36 Mb. Скачать 1.36 Mb.
|
|
6. BEARINGS A bearing is a machine part which supports shafts and spindles. We know bearings to be classified as plain bearings and antifriction bearings and antifriction bearings. In plain bearings one friction surface slides upon another. Plain bearings may be of two classes: bearings with a continuous rotary motion and those with an intermittent motion. The first class of plain bearings is represented by journal bearings and thrust bearings. Journal bearings are bearings carrying a load which acts at right angles to the shaft axis. Thrust bearings take a load acting in the direction of the shaft axis. The second class of plain bearings embraces bearings of parts having a rocking motion, or a linear reciprocating motion. Antifriction bearings are also subdivided in two main classes depending upon the type of rolling elements: ball bearings and roller bearings. In rotating machines, noise and vibration are indications of faulty operation of ball bearings or roller bearings. A ball bearing consists of two rings: an inner ring and an outer ring between which there are hardened steel balls spaced in a ball retainer or cage. If the inner ring had been lifted to a tilt position, the balls would have been forced to climb one side of the raceway during a part of revolution, with, resulting drag on the bearing retainer, then, the balls would have accelerated down the raceway to climb the opposite side in the other part of the revolution, reversing the strains on the bearing retainer. In this instance, the balls, instead of rotating about a true horizontal axis, rush to turn from contact with the sides of the raceway and to reverse their direction of turn during the second half of the revolution. In rotating machines, the balls are spaced so that they do not touch each other, thus reducing wear and noise. They require an absolutely parallel raceway to roll upon, entirely free from eccentricity, wobble or other variations. Ball bearings may be of the following types: radial bearings, thrust bearings, and radial-thrust bearings. Intheir turn radial ball bearings which serve to take loads acting at right angles to the shaft axis, may be of two types: single- row (Fig. 44) and double-row radial bearings. All the radial bearings are used when high speeds are required. The precision-made radial bearings give the finest service together with a long bearing life. Thrust ball bearings are bearings taking axial loads and giving maximum efficiency with combined journal and thrust loads. They are also recommended for thrust duty1 at high speeds. Radial ball bearings can take both radial and axial loads. 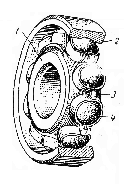 Fig. 44. Single-Row Ball Bearing: Fig. 44. Single-Row Ball Bearing:1 – inner ring or inner race; 2 — outer ring or outer race; 3 — ball retainer or cage; 4 - ball In roller bearings hardened steel rollers are used between the rings instead of balls. Roller bearings permit a larger load and have a longer bearing life in comparison with ball bearings. The rollers used in roller bearings may be of different shape: cylindrical, conical, spherical, and concave. Roller bearings, in turn, may be subdivided into single-row and double row bearings. Bearings with cylindrical rollers are intended to take radial loads, while those with conical rollers may take both radial and axial loads. _____________________________ 1. thrust duty — работа при осевых нагрузках Exercises I. Use the following words and phrases in sentences of your own: bearing, plain bearing, to support, antifriction bearing, continuous rotation, intermittent motion, to carry load, rocking motion, journal bearing, linear reciprocating motion, axial load, radial load, hardened steel balls, to touch, to reduce wear, long bearing life, precision-made radial bearings II. Answer the following questions: 1. What are bearings used for? 2. How are bearings classified? 3. How may plain bearings be classified? 4. What bearings belong to the first class of plain bearings and what loads are they intended to take? 5. How are antifriction bearings classified? 6. What bearings belong to the second class of plain bearings? 7. What are the main types of ball bearings? III. Find in the text English equivalents of: подшипник качения, подшипник скольжения, опорный подшипник, шарикоподшипник, упорный подшипник, однорядный подшипник, роликовый подшипник, сепаратор подшипника, внутреннее кольцо подшипника IV. Give derivatives from the following words and translate them into Russian: class, to move, to carry, to direct, to rock, to depend, to roll, to retain, to require, fine, axis, efficient, long, cylinder, cone, to determine, assembly V. Find the predicates and state the forms and functions of infinitives in the following sentences. Translate the sentences into Russian: 1. We know taper roller bearings to have been manufactured by many plants, in both single-and double-row types, each with plain and flanged outer rings, in a range of sizes covering bore diameters from 35 to 210 mm. 2. We also know taper roller bearings to have been designed and manufactured for use on machine tool spindles where a high degree of accuracy coupled with rigidity and cool running over a range of speeds is demanded. 3. The cage is centred on the inner ring to allow only a small proportion of the oil to flow along the bearing tracks for lubrication purposes. 4. We have noticed that some balls made of special steel increase their hardness. VI. Find the predicates and state the kind of subordinate к clauses in the following sentences and translate them h into Russian: 1. These bearings are finding other applications where similar characteristics are necessary, for example in printing machinery. 2. Among the features of these bearings are the hollow rollers which, together with special cage construction, ensure that full use is made of the oil flow for lubricating and cooling purposes. 3. A light alloy cage, the surface of which has oil retaining properties, is employed and almost entirely encloses the rollers occupying practically the whole space between the inner and outer rings. VII. Change the following sentences using, the subordinate clauses instead of the complex objects and translate them into Russian: Example: We know bearings to be subdivided into several classes. We know that bearings are subdivided into several classes. 1. We know a bearing to be a machine part for supporting shafts and spindles. 2. We know bearings to be classified as I plain bearings and antifriction bearings. 3. I find in plain I bearings one friction surface to slide upon another. 4. I have I noticed thrust bearings to take a load acting in the direction of the shaft axis. 5. I know antifriction bearings to have been subdivided into two main classes. VIII. Translate the following sentences into English using the complex object: Example: Мы предполагаем, что они окончили новую конструкцию сепаратора подшипника. We suppose them to have completed a new design of the bearing retainer. 1. Мы знаем, что опорами валов и шпинделей служат подшипники. 2. Мы знаем, что подшипники подразделяются на подшипники качения и подшипники скольжения. 3. Мы предполагаем, что подшипники скольжения получили свое название из-за вращения вала по внутренней поверхности вкладыша. 4. Мы ожидаем, что трение, нагрев и износ подшипников уменьшится при применении обильной смазки. 5. Общеизвестно, что, для того чтобы обеспечить различные условия работы шпинделя, вкладыши подшипников изготовляются из различных материалов. IX. (a) Read and translate the text without using a dictionary: Automatic assembly and inspection machine for antifriction bearings. The range of air-operated gauging equipment made by some plants for checking ball and roller bearings is being extended to include fully- and semi-automatic machines for carrying out assembly' as well as inspections on most types of precision antifriction bearings. One of the new machines for automatic assembling and inspecting taper roller bearings is discussed below. On this machine, the inner-race is automatically checked for diameter, and rollers of the required size are selected. Assembly of the race, rollers and cage is next carried out to produce a bearing with predetermined clearance. The bearing is then checked for torque, noise level,1 and assemblies which are not acceptable are automatically rejected. ________________________ I. noise level — уровень шума (b) Retell the text. X. Using the following words and word combinations describe the construction of the ball bearing shown in Fig. 44: single-row bearing, to be represented, this picture, to consist, two rings, an inner ring, an outer ring, there are, these rings, hardened steel balls, to be placed, each other, to reduce, this feature, wear and noise, balls, to require, to roll upon, parallel raceway, free from wobble 7. CLUTCHES A clutch is a device for connecting two parts, such as shafts or a shaft and a pulley. The difference between a coupling and a clutch is that a coupling is used to connect two shafts permanently, while a clutch may ensure easy and quick connection and disconnection of two shafts. Clutches used in lathes are subdivided into several types, such as rigid couplings and disengaging clutches. A rigid coupling serves for connecting coaxial shafts which are not disengaged in the process of operation. Fig. 45 shows a rigid coupling, which consists of a solid bushing connecting electric motor and lathe shafts by means of a key. Disengaging clutches are applied, in lathes for temporary engagement and disengagement of a shaft and parts connected with it. They are divided into friction clutches and jaw clutches. Friction clutches serve to connect a stationary machine part to transmit the required power. Sometimes friction clutches are intended as safety devices to prevent the breakage of parts in the trans-emission train. Friction clutches may be divided into two groups, according to the direction of the acting, force: axial clutches and radial or rim clutches. In axial clutches the contact pressure is applied in a direction parallel to the axis of rotation, while in rim clutches the contact pressure is applied upon a rim in a radial direction. Axial clutches can be subdivided into cone clutches, and combined cone and disc clutches. Fig. 46 shows a cone clutch. By moving a movable wheel the cone 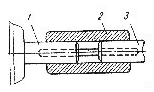 Fig. 45. Rigid Coupling: Fig. 45. Rigid Coupling:1 — electric motor shaft; 2 — solid bushing; 3 — lathe shaft disc connected with the toothed wheel by a key may engage the cone located in the movable wheel. Thus the cone disc is pressed against the inside cone of the movable disc, friction necessary fur transmitting rotary movement to the movable 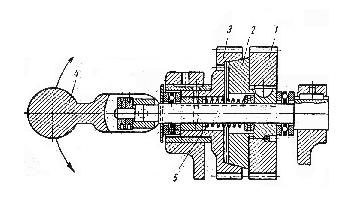 Fig. 46. Cone Clutch: Fig. 46. Cone Clutch:1 — toothed wheel; 2 — cone disc; 3 — movable wheel; 4 —eccentric clamp; 5 — spring wheel being created between the two cones. The outside cones are meshed by an eccentric clamp. By turning the eccentric clamp to 90° the friction clutch is disengaged, a spring pressing out the toothed wheel from the friction disc. Radial or rim clutches may be classified as band clutches, block clutches, and as external, internal, and combined internal and external clutches. Jaw clutches consist of two half-clutches—a fixed one and a movable one which have jaws on their faces. The fixed half-clutch is rigidly fastened on one shaft, the movable one being keyed to another shaft. The shafts are connected through the coupling of jaws on f both half-clutches. The following factors are decisive in selecting the type of clutch to be used: torque, rotative speed, available space, and frequency of operation. When a heavy torque should be transmitted a clutch must have sufficient gripping power, which is usually ensured by multi-disc clutches. For low-speed service cone and rim clutches are used. For high rotative speeds light, compact and internally balanced clutches of the multi-disc type may be applied. Space being limited, multi-disc, twin-cone and double-cone clutches are used because of their greater compactness in comparison with other types of clutches. Single-disc clutches with metal contact surfaces and cone clutches are the most suitable ones for frequent or continuous operation. Exercises I. Use the following words and phrases in sentences of your own: clutch, coupling, rigid coupling, disengaging clutch, coaxial, key, friction clutch, transmission train, axial clutch rim clutch, jaw clutch, to engage, fixed clutch, eccentric clamp, suitable II. Retell the text giving answers to the following questions: 1. What is the difference between a clutch and a coupling? 2. How are clutches subdivided? 3. What does a rigid coupling serve for? 4. What is a disengaging clutch applied for? 5. What is a friction clutch? 6. How are friction clutches classified? 7. What is the difference in application of the contact pressure in axial clutches and in radial clutches? III. Choose synonymical groups out of the following list rigid, to connect, frequently, different, to engage, tendency, to join, various, hard, to gear, often, direction, rotation, transmission, revolution, transferring IV. Choose antonymical groups out of the following list to divide, movable, to engage, external, to connect, immovable, to disconnect, to unlink, to stop, internal, to start, to combine V. Underline the suffixes and prefixes and translate into Russian the following words: engage, engagement, engaging, disengaging, disengagement; determination, predetermination; station, stationary; intensity, intensive; rigidly, rigidity VI. Connect the following sentences using the absolute participle construction and translate them into Russian: Example: A rigid coupling connects coaxial shafts. Coaxial shafts are not disengaged in the process of operation. A rigid coupling connecting coaxial shafts, they are not disengaged in the process of operation. 1. The construction of some new clutches has already been completed. We ordered some of them. 2. Numerous experiments have been carried out. The design of the new jaw clutches was approved. 3. The clutches used in lathes are subdivided into several types. The friction clutches are subdivided into two groups. 4. A spring presses out the wheel from the disc. Ву turning the eccentric clamp, the cone clutch is disengaged. 5. Clutch constructions are based on the positive-action and friction principles. Couplings are made in two main types: rigid and flexible. VII. Translate the following sentences into English using the absolute participle construction: Eхатр1е: Когда расстояние между валами ограничено, используются многодисковые муфты. The distance between shafts being limited, multi disc clutches are used. 1. Так как некоторые валы имеют небольшое отклонение от соосности, применяется упругое соединение. 2. Схематическое устройство конусной фрикционной муфты показано на рис. 46; конический диск может при перемещении подвижного колеса входить во внутренний конус. 3. Когда кулачковая муфта включена влево, вращение от ведущего вала передается ведомому валу через колеса. 4. Если кулачковую муфту включить вправо, то вращение передается ведомому валу через зубчатые колеса. 5. Так как кулачки легко повреждаются, кулачковые муфты переключаются только при остановленном станке. VIII. Translate the following sentences into Russian observing different meanings of the word "part": 1. The part of the work was completed in time. 2. The second part of London's complete works has been published. 3. This part of the machine was worn due to bad lubrication. 4. They part when he goes to sea. 5. They took part in a discussion on the manufacture of new clutches. IX. Translate the following text in written form using a dictionary: The multi-disc clutch is usually equipped with automatic cone brake. Moving the clutch control handle to the left compresses the clutch driving discs to set the lathe driving shaft in motion. To disengage the clutch, the clutch control handle should be moved to the right. The clutch driving discs then automatically separate and the brake takes hold to stop the lathe driving shaft with a smooth, quick stop, holding it rigid for ease in locking work in chuck or other operations requiring a fixed spindle. When necessary to turn the spindle by hand, it may be entirely disconnected from the driving shaft by throwing the lathe's regular gearshift handles into their neutral position.1 The speed with which the brake will stop the lathe is affected by weight of the workpiece that is in the lathe. ___________________ 1. throwing... into neutral position — переключением ... их в нейтральное положение X. Using the following words and word combinations describe the clutches in Figs 45 and 46: a rigid coupling, to be represented, Fig. 46, to consist, a solid bushing, to connect, electric motor, lathe shafts, a key, axial clutches, to be subdivided, cone clutches, disc clutches, to be shown, the cone disc of the cone clutch, to be connected, the toothed wheel, to engage the cone, to be located, the movable wheel, friction necessary, to transmit rotary motion, to be created, the two cones, to be meshed, an eccentric clamp, the friction clutch, to be disengaged, the eccentric clamp, to be turned to 90°, a spring, to press out, friction disc |
