Баракова. Первый Курс. Учебник соответствует требованиям Программы по иностранным языкам для вузов неязыковых специальностей и предназначен для студентов, продолжающих изучать английский язык после школы (12 курс технического вуза)
 Скачать 3.96 Mb. Скачать 3.96 Mb.
|
|
6. Прочитайте текст А. Назовите характерные особенности извержен ных пород: ТЕКСТ А Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks have crystallized from solidified magma.. Igneous rocks can be classified in a number of ways and one of them is based on mode of occurrence. They occur either as intrusive (below the surface) bodies or as extrusive masses solidified at the 116 Unit 5 .'"V >. Earth's surface. The terms "intrusive" and "extrusive" refer to the place where rocks solidified, The grain size of igneous rocks depends on their occurrence. The intrusive rocks generally cool more slowly than the extrusive rocks and crystallize to a larger grain size. The coarser-grained intrusive rocks with grain size of more than O.5 mm called plutonic or abyssal are referred ito as intrusive igneous rocks because they are intruded into older pre-existing rocks. Extrusive or volcanic rocks have even fitier grains, less than 0.05 nun and are glassy. Exposed igneous rocks are most numerous in mountain zones for two reasons. First, the mountain belts have been zones of major deformation. Second, uplifts in mountain belts have permitted plutonic masses to be formed. The largest bodies of igneous rocks are called batholiths (Fig. 2). Batholiths cooled very slowly. This slow cooling permitted large min eral grains to form. It is not surprising that batholiths are composed mainly of granitic rocks with large crystals called plutons. As is known, granites and diorites belong ,to the group of intrusive or plutonic rocks formed by solidification of igneous mass under the Earth's crust. Granites sometimes form smaller masses called stocks, when the occurrence has an irregular ihipe;but smaller dimensions than the batholiths. Laccoliths and sills, which are very similar, are intruded be- tween sedimentary rocks. Sills are thin and they may be horizontal, inclined or vertical. Laccoliths are thicker bodies and in some cases they form mountains. Dykes are also intrusive bodies. They ranges in JhicJmeSs from a few inches to several thousand feet. Dykes, are gerjraify much longer than they are wide. Most dykes occupy cracks and have strai&nt parallel walls. These bodies cool much more rapidly and are commonly fine-grained. For example, granite may occur 4n dykes that cut older rocks. Pegmatites (quartz, orthoclase and mica) also belong to the group of plutonic or intrusive rocks. They occur in numerous veins which usually cut through other plutonites, most often granite, or adjacent rocks. Extrusive,igneous rocks have been formed from lava flows which come from fissures to the surface and form fields of volcanic rocks such as rhyolite, andesite, basalt, as well as volcanic ashes and dust, tuff, etc. As a rule, these rocks of volcanic on|in cool rapidly and are fine-grained. It is interesting to note that basalt is the most Unit 5 117 Satellite Cone Laccolith \ V 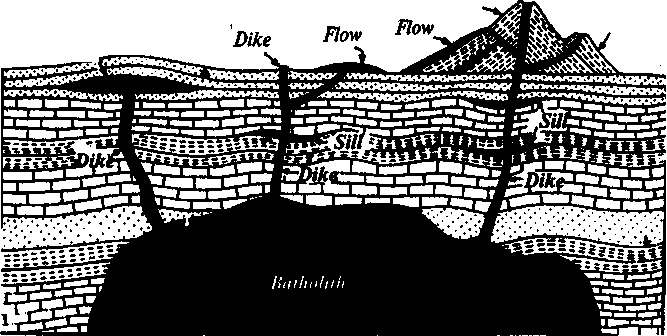 olcano olcano Fig. 2. Igneous rocks abundant of all lavatypes.lt is the principal rock type of the ocean Igneous rocks are rich in minerals that are important economically or have great scientific value. Igneous rocks and their veins are rich in iron, gold, zinc, nickel and other ferrous metals. УПРАЖНЕНИЯ 7. Укажите, какие предложения соответствуют содержанию текста. Подтвердите свои ответы фактами из текста.
8. Ответьте на следующие вопросы: 1. Have igneous rocks crystallized from magma or have they been formed by sedimentation? 118Unit 5
9. а) Найдите в правой колонке руссжше эквиваленты следующих слов в сочетаний слов:
б) Найдите в правой колонке английские эквиваленты следующих сочетаний слов:
10. Переведите сочетания слов, обращая внимание на место причастия прошедшего времени по отношению к определяемому существительному: accelerated process weathered fragments of rocks crystallized magma generally applied method successfully improved design unconsolidated and consolidated rocks \ weakly deformed minerals unfrozen ground rapidly cooled rocks detailed studies of the Earth's crust utilized equipment dissolved minerals minerals dissolved by the consolidated rocks action of water rocks consolidated by some substances rocks formed by solidification stratified sediments rocks exposed on the Earth's exposed rocks surface transformations caused by new conditions... Unit5119 11. Найдите предложения, • которых имеются причастия прошедшего времени. Определите их функцию. Переведите предложения:
12. Замените определительное придаточное предложение определитель ным причастным оборотом. Образец: The igneous rocks which have crystallized from magma may rise through fissures to the surface of the Earth as lava. ->• The igneous rocks crystallized from magma may rise to the surface of the Earth as lava.
13. Найдите в тексте Л и выпишите: 1) причастия прошедшего времени в функции левого определения вместе с существительными, которые они определяют; 2) причастия прошедшего времени, входящие в определитель ный причастий оборот; 3) причастия прошедшего времени, используемые для образования глагольных форм группы Perfect; 4) причастия прошедшего времени, используемые для образования страдательного залога. 120 UnitS 14. Сосдввште главные предложения с придаточными: 1. Abyssal rocks belong to the a) that are economically important. group of intrusive rocks 2. Uplifts in mountain belts 6) which usually cut through have permitted erosion to plutonites. the depths 3. Granites and dioritcs occur в) because they are intruded into as batholiths pre-existing rocks. 4. Pegmatites (quartz, orthoclase r) at which plutonic masses are and mica) occur in numerous formed, veins 5.Extrusive igneous rocks have д) where the changes in temperature been formed as lavas are great. 6. Igneous rocks are rich in e) which come from fissures to minerals the surface of the Earth's crust. 7. Physical weathering occurs ж) which are large irregular masses. in the deserts and in high mountains 15. Закончите следующие предложения подходящими по смыслу словами из текста А:
16. Выразите несогласие со следующими высказываниями. Подт свои ответы фактами из текста, используя предлагаемые разговорные формулы: It seems to be wrong; I don't agree with yon; I don't think so; on the contrary; that's not quite so; as far as I know
Unit 5121 17. Суммируйте содержание текст» А, используя слон в скобках.
18. Расскажите об изверженных породах. (См. рнс. 2, с. 118.) В своем рассказе дайте ответы на следующие вопросы:
ГРАММАТИКА 1. Степени сравнения прилагательных и наречий Односложные и некоторые двусложные прилагательные и наречия образуют сравнительную степень прибавлением к своей основе суффикса -ег, а превосходную степень — при-бавлением суффикса -est. Многосложные и большинство дву-сложных прилагательных образуют сравнительную степень при помощи слова more более, а превосходную — при помо-щи слова most самый, наиболее. Перед прилагательными в превосходной степени употребляется определенный артикль. 122 Unit 5
Особые случаи
Для усиления сравнительной степени перед прилагательными и наречиями употребляются слова much, far, still, a great deal, которые переводятся на русский язык словами: намного, значительно, гораздо, еще. far more favourable conditions far better results much more work much more successfully гораздо (намного) более благоприятные условия гораздо лучше результаты значительно (гораздо) больше работы гораздо более успешно Прилагательные выражением by far. в превосходной степени усиливаются Unit 5123 Open-cast mining is by Разработка открытым спосо- far the most efficient. бом наиболееэффективна. 1. Место наречий в предложении Наречия неопределенного времени always всегда, often часто, seldom редко, already уже, usually обычно, sometimes иногда, soon скоро, never никогда и т.д. ставятся перед смысловым глаголом или после первого вспомогательного глагола в сложных глагольных формах: Combustible shales often Горючие сланцы часто зале- occur as horizontal гают горизонтальными beds. пластами. Coal isusually usedas Уголь обычно используется fuel. в качестве топлива. Не doesn 'tever playОн никогда не играет в tennis. теннис. Наречия, выполняющие в предложениях функцию обстоятельства места и времени, стоят либо в начале предложения перед подлежащим, либо в конце предложения: Yesterday a group of Вчерагруппа студентов посе- students visited the тила обогатительную фаб- concentration plant. рику. I was very busy yesterday. Я был очень занят вчера. Наречия, определяющие прилагательное, причастие или другое наречие, обозначают признак или степень качества и всегда стоят перед словом, к которому относятся: a chemically pure substance химически чистое вещество; a highly developed industry высокоразвитая промышленность. 3. Наречия на -1у От многих прилагательных можно образовать наречия, прибавив к ним суффикс -ly: nice — nicely, great — greatly, careful — carefully, definite — definitely, excellent — excellently и Др. Некоторые наречия, образованные от прилагательных с помощью суффикса -1у, отличаются по значению от соответствующих прилагательных: 124 UnitS Прилагательные Наречия
действительно сразу, непосредственно едва быстро, легко очень, в основном Некоторые наречия имеют две формы: одну без суффикса, совпадающую с прилагательным, другую — с суффиксом -Yy. Последние часто не совпадают по значению с соответствующими прилагательными: Прилагательные Наречия без суффикса higb — высокий high — высоко close — близкий close — близко, рядом wide — широкий near — близкий late — поздний wide — широко near — близко late — поздно Наречия с суффиксом bight — весьма, очень, чрезвычайно widely — очень, значительно nearly — почти lately — недавно, за последнее время closely — тщательно, внимательно ПРЕДТЕКСТОВЫЕ УПРАЖНЕНИЯ 19. а) Прочитайте вслух следующие слова: [i:] — be'neath, mean, heat, cleave, 'easy, 'easily, 'medium [л] — some, run, such, a'bove, 'structure, 'other [ei] — 'nature, 'slate, 'layer, 'flaky, 'trace, great [ai] — 'mica, 'primary, de'fine, 'crystalline [ou] — show, low, slow, com'pose, 'process, know [э:] — third, Earth, oc'cur, 'surface [a:] — marble, large б) Прочитайте следующие слова и запомните их произношение: gneiss (nais], chlorite ['kb:rait], phyllites ['filaits], quartzite [ 'kwo:tsait] в) Прочитайте слитно следующие сочетания слов: the nature of pre-existing rock and the mechanism of the meta- morphic deformation an opportunity of analysing the causes of its metamorphism to be subjected to pressure, heat and chemically active fluids beneath the Earth's surfaqe Unit 5 125 to consist of quartz, orthoclase and mica to be determined by at least four variable geologically related parameters 20. Прочитайте следующие слом и сочетания слов 1-2 раза про себя, затем вслух и постарайтесь запомнить их. at least по крайней мере to give an opportunity (of) давать возможность (кому-л., чему-л.) In such a way таким образом 21. а) Определите по словообразовательным элементам (суффиксам и префиксам), какой частью речи являются следующие слова. Переведите их: known — unknown; differ — different — difference; found — founder — foundation; mean — meaning; difficult — difficulty б) Переведите на русский язык прилагательные с суффиксом -able: changeable, understandable, valuable, variable, breakable •) Заполните пропуски прилагательными, образованными от выделенных глаголов или существительных: 1. Under the action of pressure and high temperature rocks change their composition and structure. One may say that the structure and composition of rocks are .... band [btend] л слой; полоса; прослоек (породы); synlayer cleave [kli:v] v расщепляться; трес-• каться, отделяться по кливажу; cleavage nкливаж constituent [kan'stitjusnt] л составная часть, компонент define [di'fain] v определять, давать определение [dis'tnbjurt] v (among) распределять (между); раздавать s'ta:b] v нарушать; смещать excess [ik'scs] л избыток, излишек; ant deficiency [di 'fi/(s)nsi] flaky ['fleiki] а слоистый; похожий на хлопья fluid [ 'flu(:)id] л жидкость; жидкая или газообразная среда foliate [Toulieit] v расщепляться на тонкие слои; foliated а листоватый, тонкослоистый; synflaky marble [ 'ma:bl] л мрамор mention ['теп/(э)п] v упоминать, ссылаться; л упоминание plate [pleit] nпластина; полоса (металла) pressure ['рге/э] л давление; rock pressure (underground pressure) горное давление, давление горных пород relate [ri'leit] v относиться; иметь отношение; related а родственный; relation л отношение; relationship л родство; свойство; relative а относительный; соответственный run [глп] (ran [ran], run) v бегать, двигаться; течь; работать (о машине); тянуться, простираться; управлять (машиной); вести (дело, предприятие) schistose ['Jistous] aсланцеватый; слоистый sheet |Ji:t] л полоса slate [sleit] л сланец; syn shale split [split] (split) v раскалываться, расщепляться, трескаться; syn cleave trace [treis] л след; tracing л про слеживание 126 Unit 5 2.Everybody understands that metamorphic rocks have been developed from earlier igneous and sedimentary rocks. It is quite ... that these changes take place in texture, in mineral composition and in structural features of rocks.
22. Переведите наречия, образованные от прилагательных с помощью суффикса -1у. chief главный — chiefly ..., general общий, основной — generally ..., common общий — commonly ..., original первоначальный — originally ..., particular особенный — particularly ..., practical практический, фактический — practically ..., usual обычный — usually ..., wide широкий — widely ... 23. Прочитайте следующие сочетавм слов. Переведите их: cleavage distribution the definition of rocks geological disturbances schistose structure schistose coal low-grade metals medium-grade coals high-grade oil the most common metamorphic exposed igneous rocks rocks single oithoclase crystals chemically active fluids scientific value rock pressure water pressure excess of water thin sheets foliated and non-foliated the Earth's surface metamorphic rocks separate plates 24. Определите значения выделенных слов по сходству их корней с соответствующих слов в русском языке: metamorphic rocks; some changes in texture; in mineral composition and structure; the description of metamorphism; schistose structure; the role of water; four variable geologically related parameters; flaky materials; the mechanism of metamorphic deformation; crystalline schists; the great dislocations of the Earth's crust; during normal progressive metamorphism 25. Прочитайте текст Б и найдите в нем ответы на следующие вопросы:
Unit 5 127 ТЕКСТ Б Metamorphic Rocks The problem discussed concerns metamorphic rocks which compose the third large family of rocks. "Metamorphic" means "changed frop". It shows that the original rock has been changed from its primary form to a new one. Being Subjected to, pressure, heat and chemically active fluids beneath the Earth's surface, various rocks in the Earth's crust undergo changes in texture, in mineral corhpositioh and structure and are transformed into meta-morphic rocks. The process describeci is called metamorphism. As is known, metamorphic rocks have been developed from ear lier igneous and sedimentary rocks by the action of heat and pressure. ^ Gneisses, mica schists, phyllites, marries, slate, quartz, etc. belong to the 7sarhe group of rocks,having the same mineral com- position as granite, gneisses consist chiefly of quartz, orthoclase and mica^. However unlike granite, they have a schistose structure. It means that their constituents are diatributed in bands or layers and rar^ parallel to each other in one 'Direction. If disturbed the rock Cleaves easily into separate plates. The role of water in rnetamorphism is deterrnine^ by at least four variable 'geologically refuted parameters: rock pressure, tempera- ture .water pressure, and the amount of water present. ? During a normal progressive metamorphism rock pressure and temperature are iriterciependent, and the amount of water and the pressure of water are related the sediments and to the degree of metamorphism in' such a way that,generally. speaking, the low-grade metamorphic rocks are characterized by the excess of water. The medium-grade rocks defined by some deficiency of water and the high-grade metamorphic rocks are characterized by the absence of water. Many of the metamorphic rocks -mentioned above consjst,of flaky materials such as mica and chlorite. These minerals cause the' rock to split into thin sheets, and rocks become foliated.сг-оисъи Slate, phyllite, schist and gneiss belfcng to the group of foliated metamorphic rocks. Marble and quartzite are non-foliated metamor phic rocks, The structure of metamorphic rocks is of importance because it shows the nature of pre-existing rocks and the mechanism of metamorphic deformation. Every trace ofc original structure is of great importance to geologists. It gives an opportunity of analysing the causes of its metamorphism. 128 Unit 5 Being often called crystalline schists, metamorphic rocks such asi gneisses and mica have a schistose structure. Metamorphic rocks represent the oldest portion of the Earth's crust. They are mostly found in the regions of mountain belts where great dislocations on the Earth once took place. УПРАЖНЕНИЯ 26.Укажите, какие предложен» соответствуют содержанию текста Б. Подтвердите свои ответы фактами из текста.
27. Ответьте на следующие вопросы:
28. i) Найдите в правой колонке русские эквиваленты следующих слов и сочетаний слов: 1. as a result of the chemical а) полоса (или прослоек) угля and physical changes б) составляющие пород 2. constituents of rocks в) расщепляться на отдельные слои Unit 5 129 3. to be subjected to constant development
10. generally speaking г) вообще говоря д) в результате химических и физических изменений е) избыток воды ж) изменяться з) находиться в постоянном развитии и) низкосортные руды к) следы первоначальной структуры б) Найдите в правой колонке английские эквиваленты следующих слов и сочетаний слов:
а) unlike granite б) to be of importance в) r) mentioned above д) schistose structure е) to give an opportunity (of doing smth) ж) to define (determine) rock texture з) deficiency of water и) flaky rocks к) marble and slate л) gneiss 29. Заполните пропуски в предложениях, используя следующие слова: cleave cleaves cleavage
relate related relationship relating (to)
30. а) Переведите следующие сочетания слов и предложения, обращая внимание на перевод прилагательных в сравнительной степени: to observe the higher temperature at day time and the lower temperature at night to become wider and deeper 130 • Unit 5 to cause more complex and varied changes to penetrate deeper to become more and more destroyed to decompose at a slower rate There are deeper and wider cracks. The action of plants is even more destructive. 6) Переведете сочетаем слов с врвлагателшшв в варешмв в сравветелыюй стевевв, обравша вввмавве ва случав усвяеввл сраввеввв: to be more than 0.5 mm to intrude into older pre-existing rocks to have even finer grains less than 0.5 mm to form smaller rock masses to be much longer to cool much more rapidly to cool more slowly to crystallize to a larger-grain size coarse-grained intrusive rocks 31. а) Подберете вз сввсков А в Б блвзкве во звачеввю слова: А. 1. band Б. a) allow (let)
10. dimension к) be similar to б) Подберете вз сввсков А в Б протввоволожвые во эвачеввю слова. А. 1. deep Б. a) cleavage
10. foliated к) heat л) uncommon Unit 5131 32. а) Прочитайте следующие сочетания слов с причастием прошедшего времени в функции правого определения и переведите их. Образец: The equipment used is ...— используемое оборудование является ...
6) Прочитайте следующие предложения. Найдите в каждом из них группу «подлежащее-сказуемое». Определите функции слов с суффиксом -ed: l.The prospecting party provided with new equipment planned to begin its work in spring. 2. The prospecting party provided new data on useful minerals discovered in the region. З.Тпе prospecting party is provided with new equipment. 4. The rocks described represented the oldest portion of the Earth's crust. 33. Заполните пропуски в предложениях, употребив данный в скобках глагол в соответствующем времени н залоге: 1. Scientists and engineers ... computers in their work. Computers ... in different fields of science and engineering, (to apply) 1. Materials for sedimentary rocks ... fragments of pre-existing rocks. Conglomerate, sandstone and shale ... into the group of sedimentary rocks, (to include)
34. Определите, какие функции в предложении выполняют совпадающие по форме выделенные слова. Переведите предложения: 1. The term "prospecting" includes the whole range of geological work directed to discovering deposits of valuable minerals. The Moscow Mining Academy directed the activities of the Academy's research institutions. Ш Unit 5
35. Переведите предложения, обращая внимание на перевод причастия прошедшего времени. Образец 1: The mining method used depends on many factors. -» Используемый метод разработки зависит от многих факторов.
Образец 2: When burnt, coal produced heat. -> При сжигании уголь выделяет тепло.
to be formed; to belong to; to be like; to be of value; to give an opportunity Unit 5133 of; unlike; to be of importance; pre-existing rocks; schistose structure; to determine
4. Вообще говоря, описанные метаморфические породы имеют большое значение, так как их структура дает возмож ность установить следы существовавших ранее пород. 38. Задайте вопросы по образцу. Образец: Metamorphic rocks are mostly found in the regions of mountain belts, (where?) -> Where are meta-morphic rocks mostly found?
39. Закончите предложения подходящими по смыслу слотами из текста Б:
40. Суммируйте содержание текста Б, используя слова в скобках:
134 UnitS
41. Расскажите коротко (8-10 предложений), что вы знаете о горных породах в земной коре, об их происхождении, залегания н минералах, которыми они богаты. Используйте данную ниже схему н следующие разговорные формулы: as for as I know; as is known; as for; I'd like to say a few words about...; it should be noted that...; as a rule; generally speaking и др. Rocks of the Earth's Crust I I sedimentary rocks igneous rocks metamorphic rocks I I I mechanical, chemical intrusive rocks, rocks structure and organic extrusive (volcano) | sediments rocks water in metamorphism I I I Practical value of each type of rocks (metals they are rich in) 42. Прочитайте текст В без словаря и скажите, о чем ои. Слова для понимания текста: profit — прибыль; польза residual — осадочный alloy — сплав cast iron — чугун ТЕКСТ В Minerals that make up rocks, are defined as inorganic substances which occur naturally and have a definite chemical composition and physical properties which vary within known limits. The major properties are colour, crystal form, hardness, cleavage and others. Cleavage is one of the most diagnostically useful mineralogi-cal properties which can be found throughout the mineral. Minerals of use to man can be grouped into two broad categories: 1) metals, such as aluminium, copper, gold, silver, iron, tin, platinum, chromium, nickel, lead and zinc, and 2) non-metallic minerals, such as diamonds, salt, limestone, cement, sulphur, and asbestos. When minerals occur so that they can be worked at a profit they are called ore deposits. Mineral deposits are seldom equally rich throughout. Unit 5135 Economic minerals are those which are of economic importance and include both metallic and non-metallic minerals. Most minerals consist of several elements. Such elements are oxygen, silicon, titanium, aluminium, iron, magnesium, calcium, sodium, potassium and hydrogen. They make up more than 99 per cent by weight of all the rock-forming minerals. Of these, aluminium, iron and magnesium are industrial metals. The other metals are present in small quantities, mostly in igneous rocks. For example, iron is one of the most abundant metals in the Earth's crust. There are three important classes of iron deposits: deposits associated with igneous rocks; residual deposits and sedimentary deposits. Iron deposits associated with igneous rocks are usually small but very rich bodies either of haematite or magnetite. Large concentrations have been successfully mined in Pennsylvania (the USA) and in the Russian Federation. Residual deposits of iron minerals are formed wherever weathering occurs. Iron deposits formed this way are very widespread. It should be stressed that the residual deposits were among the first to be exploited by man. Sedimentary iron deposits make up most of the world's current production. As the essential component of every variety of steel, iron is obviously the most important of all industrial metals. It has played a large part in the development of our modern civilization. Iron ores are mainly used for producing cast iron, steels and ferro-alloys. From a scientific point of view, iron's most important property is that it becomes magnetized. The magnetic iron ore is the main wealth of the Kursk Magnetic Anomaly (KMA). It is necessary to say that only in the last century was the secret of the unusual magnetism of enormous iron ore masses discovered underground. Iron fields are worked by surface mining which is more economical. But the KMA is rich not only in iron ores. Its deposits contain bauxite, phosphorite, cement, sand and clays. 43. Разделите текст В м логические части. В каждой иста текста вайднте предложение, передающее ее основную мысль. Озаглавьте каждую |
