Учебнометодическое пособие для студентов первого курса медицинского колледжа специальности Сестринское дело
 Скачать 0.57 Mb. Скачать 0.57 Mb.
|
|
Example: I’d like to be able to help my relatives and it gives me much satisfaction. I’d rather have flexible working hours in a hospital than stay in the office from 9to 5. - holidays - satisfaction - salary - additional benefits - leisure time - family practice - to practice medicine - to examine a patient - massage - perform duodenal intubations - apply mustard plasters 4. Study new words
среды 5. Fill in the gaps with the new words from Ex. 1
6. Translate sentences using the words from Ex.1
7. Read the text and do the tasks after the text Every year many young people who really care for medicine enter our medical college and become students. A new life begins – it is the life of the adult who has the responsibility for all his actions before the society. Some students live at the hostel, others – with their relatives. Many students get stipends. Our medical college is one of the oldest educational establishments of the region with its own traditions. Its graduates are considered to be the most highly trained specialists of the region. There are 4 departments in our school. “Nursing Affair” department gives qualification of a nurse of general practice. A medical nurse is a chief assistant of a doctor who provides uninterrupted medical help, including preventive and rehabilitation measures. Our graduates work in the polyclinics, hospitals, kindergartens, schools and houses for aged people. “Curative Affair” department is for those who want to become doctor’s assistants. A doctor’s assistant of general practice is a highly-trained specialist who works independently in the polyclinics, emergency ambulances and hospitals. His main task includes prescription and performance of preventive, curative and diagnostic measures. The graduates of this department are waited for at the stations of emergency medical help, in the country-side hospitals and in the military hospitals. “Pharmacy” department offers qualification of a pharmacist. Pharmacy is the science which treats of medicinal substances. The students work much in classes and libraries. As the students want to become not ordinary but good professionals they must pay attention to modern medical literature. 8. Say which skills and abilities from the list you’ve made in Ex.2 are necessary for each specialty 9. Ask seven special questions trying to know more information than having been mentioned in the text 10. Look at the picture. Students are at the Information Sciences lesson. Match a student and his description.  TRoFESgcR AKBRWS COMPUTER SCI 30t: INTRO TO BASIC PAgCM^ FORTRAN Jane is interested in the subject because she cares for Information Sciences. Paul is frightened. He spent his time at the disco last night so he is not ready for the lesson. Nick is depressed because he doesn’t know the matter of discussion. Mary is excited because she has found the answer to her question. Ann is bored. She doesn’t take interest in the subject. And you? Tell what makes you interested (bored, excited, frightened, depressed) in the medical school. And how is Information technology connected with medicine? 11. Life of the medical school student is connected not only with medicine and medical subjects. Students participates in activity of different groups and societies. Look through the steps of the table below and write the purpose of each step taking into consideration work of your medical school.
12. Prove that at the medical college it is necessary to study not only special medical subjects. Discuss your choice with other students. 13. Make the list. What qualities\ abilities and conditions help you to be more successful as a future medical worker. Using What You’ve Learned a) Make a description of yourself as a student of the medical school. b) Think of ways to improve yourself as a student of the medical school. Language support: * that I will always * I promise * that under no circumstances will I } be * I solemnly undertake * that I will never do * I swear * to be ... (adj.) ... * I will * (to) be * (to) do }... * I’ll do my best * (to) become Раздел II Development of Medicine. Topic 2. Early Medicine. 1. Share your information by answering these questions about the picture
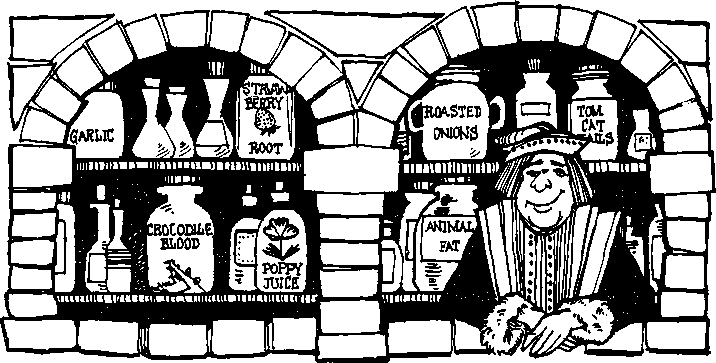 2. Study new words - recent times - недавние времена - barbers -парикмахер - a guessing game - (зд.) нечто приблизительное - remedy -лекарство - poppy juice -сок мака - animal fat -животный жир - poor eyesight -плохое зрение - bleeding -кровотечение - a common practice -общая практика - to let out ‘bad blood’ -выпускать«плохую кровь» - skull -череп - wound -рана - to relieve pressure -облегчать давление - incurable -излечимый - drill -сверлить - reliable science -надёжная наука 3. Read the text and say which of the following is true: 1 People believe medical myths 2. Medicine was a reliable science 3. Dangerous medical practices were commonly used. 4. There was nothing unusual in medicine of the Middle Ages. 5. Astrology and medicine were equal Medicine and pharmacology are two sciences that have changed a great deal in recent times. Long ago, medicine was a guessing game. Medical care was given by doctors, pharmacists, and even barbers! All of them experi mented freely on their patients, who often died as a result. Early pharmacists depended on plant remedies that had been developed over the centuries. One popular remedy during the Middle Ages was poppy juice, which contains opium (a narcotic). Other remedies were animal fat and even crocodile blood, which was considered to be a "cure" for poor eyesight. Other common practices were dangerous and sometimes fatal. For instance, bleeding patients to let out "bad blood" often resulted in the death of the patient. A common practice that was equally dangerous involved drilling a hole in the patient's skull. Perhaps this was done to treat head wounds or to relieve pressure inside the head. People whose diseases were "incurable" often looked for help from the spirit world, astrology, and magic. Astrology, which was valued as a method of diagnosis, was even taught in many medical schools. Medicine has become a reliable science only in recent times. Even now, however, it still involves a certain amount of experimentation. 4. Find in the text the following: 1. The description of fatal treatment 2. The things that can struck modern people 3. Drilling a hole in the patient’s skull was approved. Work with grammar Clauses with Who and Which. Replacement of Subjects To form adjective clauses from simple sentences, who may replace subjects that refer to people. Which may replace subjects that refer to things or ideas. Examples: Two simple sentences: The physician was Dr. Andrews. He treated the patient. One complex sentence with WHO: The physician who treated the patient was Dr. Andrew. 5.Use the cues to form sentences with adjective clauses with who. Add a or an where necessary and use appropriate singular or plural verbs in your adjective clauses. examples: orthopedist / treat bone, joint, or muscle problems An orthopedist is a doctor who treats bone, joint, or muscle problems. orthopedists / treat bone, joint, or muscle problems Orthopedists are doctors who treat bone, joint, or muscle problems. 1. radiologist / read / X-rays 2. surgeons / perform / operations 3. pediatrician / take care of / children 4. ophthalmologist / treat / diseases or injuries of the eye 5. internists / specialize in / diagnosis and treatment of diseases in adults 6. gynecologist / specialize in / functions and diseases of women 7. neurologist / take care of / patients with nerve or brain disease 8. psychiatrists / treat / mental problems 6. Use the following cues to form sentences with adjective clauses with which (or that). Be sure to add articles where necessary. example: rubber hammer / tool / be used for testing reflexes A rubber hammer is a tool that is used for testing reflexes. 1. stethoscope / instrument / be used for listening to a person's heart 2. scalpel / instrument / be used for cutting during surgery 3. opium / narcotic / produce a feeling of great happiness 4. anesthetic / drug / put people to sleep before surgery 5. aspirin / drug / relieve pain 6. thermometer / instrument / measure temperature 7. Combine the following sentences about early medical practices with who or which. Make the second sentence of the two into an adjective clause when you combine them. Change words where necessary. example: Some prehistoric people performed brain operations. These people lived in Europe in about 10,000 B.C. Some prehistoric people who lived in Europe in about 10,000 B.C. performed brain operations. These brain surgeons used simple knives. The knives were made of stone. Many skulls have been found in Europe. The skulls had small holes cut into them. The surgeons probably removed pieces of bone. They operated on the head. In early times, however, some people went to magicians rather than doctors. These people had physical problems. People would ask for help from a magician. They thought spirits or magic caused illness. During the Middle Ages, some doctors used different cures. These cures did not treat the body at all. For example, a swordsman was not treated with medicine. The swordsman had been hurt in a fight. (The sword was treated instead!) Another remedy was to wear a card with the word "abracadabra" on it. This remedy became very popular in the Middle Ages. Clauses with Whose: Replacement of Possessives Whose may also be used to form adjective clauses. It does not act as the subject of a clause. Instead, it replaces a possessive noun or adjective that modifies the subject of the clause. examples Two Simple Sentences One Complex Sentence with whose The woman thanked the doctor. His treatment had cured her. The woman thanked the doctor whose treatment had cured her. 8. Combine the following sentences with whose. Make the second sentence into the adjective clause. example: The villagers gave a gift to the pharmacist. His secret medicine had cured their mysterious disease. The villagers gave a gift to the pharmacist, whose secret medi cine had cured their mysterious disease. A person sometimes gets well unexpectedly. His or her will to live is very strong. Another person might die unexpectedly. His or her belief in witchcraft is strong. Some doctors can be successful. Their treatments are not always scientific. Some people refuse to see a doctor. Their condition is serious. People may be afraid of doctors. Their faith in modern medicine is not very strong. Restrictive Versus Nonrestrictive Clauses In some cases, commas come before and after adjective clauses. Commas are used with adjective clauses that give additional information. These clauses often modify proper nouns (Dr. Nie, Athens, the Tower of London)or names of unique people, places, or things (the sun, vitamin C, the equator). Who, which, whom, and whose (but not that) may be used in these clauses. They are called nonrestrictive clauses. In contrast, commas are not used with adjective clauses that specifically identify the word(s) they modify. That may be used in this type of clause only; who, which, , whom, and whose may also be used. These clauses are called restrictive clauses. 9. In the passage "Early Medicine" reread the sentences with Adjective clauses. Try to explain why commas are or are not used with each clause. 10. In the following pairs of sentences, underline the adjective clause. Then indicate whether the clause gives essential or additional information. Next, add commas where necessary. example: Typhoid and cholera, which have been common problems for thousands of years, have now disappeared from some areas. (Additional information—commas are used.) The bubonic plague which is a contagious disease is carried by rats. This plague which was also called the "black death" killed half the population of Europe in the fourteenth century. Physicians who treated plague victims never found a cure for the disease. During the plague, many people who touched the sick or the dead died after a short time. People who lived in major seaports were more likely to become plague victims. Thousands of people died in Marseilles which was the major seaport. 11. Combine the sentences here and on the next page with who, which, or whose. Change the second sentence into an adjective clause. Be sure to use commas where necessary. example: Mumps and chicken pox are not treated with antibiotics. They are diseases caused by viruses. Mumps and chicken pox, which are diseases caused by viruses, are not treated with antibiotics. 1. Certain illness cannot be treated with antibiotics. These illnesses are caused by viruses. 2. The ordinary cold is a viral infection. The cold is our most common sickness. 3. A careful diet can be a good treatment for people. Their internal organs do not function properly. 4. People can be treated effectively with drugs. These people suffer from tuberculosis. 5. People must take hormone pills very day. Their thyroid glands have been removed. 6. Many people take vitamin C every day. These people are trying to avoid colds. 7. Antibiotics are chemicals. These chemicals are produced from microorganisms. 8. Antibiotics can kill or control some bacteria. Some bacteria cause diseases. 9. Sir Alexander Fleming received the Nobel Prize in 1945. Hediscovered penicillin. 12. Work in pairs and make two lists
13. What in your opinion was the most dangerous in treatment during the Middle Ages? Discuss it with your class mates 14. Read this extract from a medical newspaper article and be ready to complete the mind map Charaka (200 AD) the most popular name in Ayurvedic medicine was a court physician to Buddhist king Kaniska. Based on the teachings of Atreya, Charaka compiled his famous treatise on medicine, “Charaka Samhita”.Susruta of Benaras compiled his surgical knowledge in his classic 'Susruta Samhita' between 800 BC and 400 AD. Early Indians set fractures, performed amputations, excised tumours and repaired hernias. Egyptian medicine dates from 2000 BC. The best known medical manuscript is the Ebers Papyrus (1500 BC) which was found with mummy on the banks of Nile. It contains 800 prescriptions with 700 drugs. An early leader in Greek medicine was Aesculapius (1200 BC) whose daughter Hygiea was worshipped as a goddess of health. Hippocrates (460-370 BC) is described as father of medicine. He studied and classified diseases. His famous oath is the basis of medical ethics of today. His book Airs, Water and Places is considered a treatise on social medicine. He was born in Greece. Medical man of Rome (25 BC-50 BC) was Celsus who gave us the cardinal signs of inflammation. Another Roman medical scientist Galen (130-205 A.D.) was a pioneer of experimental medicine. He noted that diseases were due to three factors : (i) predisposing factors, (ii) exciting factors, and (iii) environmental factor, a truly modern fact. He was a medical dictator of his own time. Arabs developed Unani system of medicine. Two arab physicians Rhazes (865-923) who differentiated between smallpox and measles and Avicenna (980-1037) who was the first to describe guineaworm. Medicine was revived by Paracelsus (1490-1541) who publicly burnt the works of Galen and attacked superstitions and dogma in medicine. Fracastorious (1843-1553) enunciated the "Theory of contagion' and explained the cause of epidemics. He became the founder of epidemiology. Vasallus (1514-1564) did lot of dissection on human body and demonstrated some of Galen's error. Pare (1517-1590) revived surgery and became and father of modern surgery. Fracastorius of Verona (1546) in his book on contagious disease pointed out that the agent of communicable disease was contagium vivum. He told that infection itself consists of minute particles, too small to be seen by naked eye. He further defined infection and expressed that infectious diseases were transmitted per contactum, by direct contact, per fonitem by fomites or inanimate objects.
Using What You've Learned Activity a) Giving Definitions. In small groups, test your skills at a vocabulary game. The object of this game is for one person to describe people, places, objects, ideas, and so forth. The other people in the group must guess who or what they are. In this version of the game, the clues must include adjective clauses with that, who, which, or whose. examples: a: I'm thinking of an instrument which is used to listen to a person's heart. b: A stethoscope. a: I'm thinking of a physician whose specialty is treating children. b: A pediatrician. b) Read the two opinions on Early medicine. Which of them do you share? 1.Early medicine is full of prejudices. And it must be excluded from modern medicine. 2. Early medicine is a basis of modern medicine. Join a group supporting one of the opinions. Add more arguments to your part of the chart. Topic 3. Medical Myths. 1. What are “medical myths”? How do such myths originate? Share your ideas and opinions about the picture by answering these questions
 2. Study new words
- germ -микроб 3. Make the plural form of the nouns and translate them. What origin do some of the words have? Earache, century, bacterium, germ, virus, cold, faith, people. 4. Read the text and do the tasks after the text In the past, people believed a number of medical myths that we laugh at today. During the Middle Ages, for example, many people believed the bubonic plague was caused by arrows that Christ had shot. In the eighteenth century England, even people whom others considered sophisticated had faith in strange remedies. They believed they could cure an earache by sleeping with a roasted onion in the aching ear. The same people thought a growth on the eyelid could be cured by rubbing it with the tail of a male cat. Since then, we have learned many things: bubonic plague is caused by bacteria, roasted onions cannot cure earaches, and cats do not cure growths. Nevertheless, there are medical myths that people still believe today. There are many misconceptions about the common cold, for example. People believe they will catch a cold if they sit in a draft or become chilled. Yet, we know a cold is due to a virus which is passed on through personal contact with peo ple who have the germ. There is no myth about this! 5. Make these sentences interrogative and give an emotional colour using the phrases To be honest…, It makes me feel…, Not to mention the fact that…., Contrary to popular belief…., I feel very strongly that….. 1. Many diseases are caused by bacteria. 2. We have learned about bacteria and germs. 3. People believed a great number of medical myths. 4.There were many misconceptions about origin of bubonic plague. 5.We know that virus passes from one sick person to another. Work with grammar Clauses with That and Which: Replacement of Objects That and which may replace objects of verbs to form adjective clauses. Which refers To things or ideas. That may refer to things, ideas, or people ,although who(m) is Generally preferred for people. That may be used only in restrictive clauses (clauses Without commas) and is preferred in these clauses. Both that and which can also be omitted from restrictive clauses. Examples Two simple Many people believe in predictions. Sentences Astrologers make them. One complex Many people believe in predictions that (which) Sentence with astrologers make. That or which. One complex Many people believe in predictions astrologers make. Sentence with No relative Pronoun. Clauses with Who(m): Replacement of Objects Who(m) may replace objects of verbs to form adjective clauses. Who(m) refers to people. In this type of clause, whom is correct and preferred in formal English. However, who is very frequently used,especially in conversation. Both who and whom can also be omitted from restrictive clauses. examples Two simple The woman believed the astrologer. She had consulted him. Sentences. One complex The woman believed the astrologer who(m) she had consulted. Sentence With who(m). One Complex The woman believed the astrologer she had consulted. Sentence With No Pronouns. 6. Underline the adjective clauses in the passage “Medical Myths”. Indicate whether the clause is restrictive or nonrestrictive. Also note whether the subject or the object of the original clause has been replaced. 7. Add adjective clauses to the sentences. Use commas where necessary. In sentences with restrictive clauses ( without commas ), write both possibilities: using the relative pronoun and omitting it. Remember that you cannot omit the relative pronoun from a nonrestrictive clause. example: Every society has myths, (which people believe in) Every society has myths which people believe in. Every society has myths people believe in.
8.Combine the following sentences by using that, who(m),or which. Use commas where necessary. For each sentence, write all possible combinations. Then tell which sentences preferred in formal English. example: Many cultures still have healers or magicians. Sick people consult the healers or magicians. Many cultures still have healers or magicians whom sick people consult. (Preferred in formal English.) Many cultures still have healers or magicians who sick people consult. Many cultures still have healers or magicians that sick people consult. Many cultures still have healers or magicians sick people consult. There are many medical myths. Even educated people believe them. A common saying is "An apple a day keeps the doctor away." Mothers repeat this saying to their children. Most of us think of doctors as special people. We can trust doctors with our most personal problems. In many places there are no doctors. Sick people can consult doctors. In my town there was one old woman. Everyone asked her about their health problems. This woman always made herbal tea. She gave the tea to the sick. 9. Use the following cues to form questions with adjective clauses beginning with who(m), which, or that. Work in pairs and take turns asking and answering the questions. Many answers are possible. example: medicine / you take most often a: What is the medicine that you take most often? b: Aspirin.
10. Following the example as a model, use the cues to write definitions. Add connect ing words, articles, prepositions, and any other necessary expressions. example: flu / illness / many people get / in the winter The flu is an illness that many people get in the winter.
11. Make up sentences of your own using the following. To become chilled, to have germ, to catch a cold, to cure different diseases, to be caused by bacteria, through personal contact, misconceptions about. 12. Work in pairs and discuss the following 1.What problems do the medical myths cause ? 2.What are the roots of these problems? 3.Have you ever met people who believed different myths? Exchange your impressions. 13. In groups discuss these statements and express your opinion by giving your arguments. Try to persuade your opponents
Using What You've Learned Activity 1. Comparing Traditional Beliefs. Are there foods that people believe have special effects? For example, are there foods that make people live longer, have more children, see better, and so forth? Discuss these questions in small groups. Find out if there are foods that are recommended for a certain purpose in more than one culture. Does science support the idea that these foods are effective for these particular purposes? Activity 2. Describing Myths and Superstitions. This activity concerns several "medical myths" and folk remedies that people have believed in. Look at the list of medical problems. Do you know any medical myths about their causes or cures? Where did you hear about them? In small groups, share your stories and information. colds skin rashes flu allergies rheumatism headaches hiccups depression Topic 4. Changes in Medical Care 1. What do you know about medical care in other countries? Share your ideas and experience by answering these questions about the picture.
 2. Study new words. - expensive equipment -дорогое оборудование - hospital stay - пребывание в больнице - discovery - открытие - facilities - оборудование - bulb - лампа - cardboard - картон - guess - догадываться - currant - электрический ток - penetrate - проникать - metal salts - металлическая стружка - fracture -перелом - to destroy cancer cells -разрушать раковые клетки - laboratory assistant -лаборант - available medical care -доступная мед. помощь - health insurance -страховка - private -частный - small-pox -оспа - typhus -тиф - scarlet fever -скарлатина - measles -корь - to be widely spread -быть широко распространённым - to be established -быть основанным - disease prevention -предотвращение болезни - scientific -научный 3. What do the words below mean in Russian? Try and find a purely Russian equivalent
4. Study the meaning of the underlined words
5. Which of these questions from the list below you can answer before reading the text? 1. How has medical science changed? 2. How is the physician’s office equipped? 3. Why do specialists work together? 4. How much time do the patients stay in a hospital? 5. What is the result of medical technology? 6. Read the text and say which of the questions from Ex. 2 you can answer after reading. Medical care has changed greatly since the days when the family doctor treated all family members for every type of medical problem. Today's physician is usually a specialist who treats only problems within his or her specialty. Today's specialists often work together in a large group in order to share costs. The group will buy expensive equipment for its own offices rather than use hospital facilities. The physician's office usually has a laboratory where a variety of medical tests can be done. So, unlike the family doctor, who often visited patients at home, today's doctors normally see patients in their offices, where they can use specialized equipment. Likewise, many changes are taking place in hospitals, where the cost of medical equipment and care is skyrocketing. Because of the high costs, patients now spend a limited number of days in the hospital, depending on their illness. Even new mothers, who used to have a five-to-ten-day hospital stay after the birth of their babies, are now being sent home in twenty-four hours. Medical technology certainly has led to great advances in the diagnosis and cure of many illnesses. However, some people want to bring back the "good old days" when the family physician was also a family friend. 7.What was medical care like in the past? How is it different now? Why? Are changes also taking place in our country? Why or why not? |
