Учебнометодическое пособие для студентов первого курса медицинского колледжа специальности Сестринское дело
 Скачать 0.57 Mb. Скачать 0.57 Mb.
|
|
part ofthe trunk is the ... and the lower part is the ... . The principle organs in the chest are the ..., the ... and the ...(...). We breathe with the lungs and the heart makes beats. The principal organs of the abdominal cavity are the ..., the .... the ..., the ..., the ..., the ... and the ... . The upper extremity is connected with the chest by the shoulder. Each arm consists of the upper arm, the forearm, the elbow, the wrist and the hand. We have four fingers and a thumb on each hand. The lower extremity consists of the hip, the ..., the ..., the ... and the foot. The skin covers the body. 5. Look at the picture and share your opinion about appearance of the couple. Use adjectives:
 6. Discuss with your class mates 1. What are the principal parts of the body? 2. What does the head consist of? 3. What does ear include? 4. How do we call the upper and the lower parts of the trunk? 5. What are the principal organs of the chest? 6. What are the principal organs of the abdominal cavity? 7. What does each arm consist of? 7. In English, words connected with the body are often used in popular idioms. Match the English proverbs with their Russian equivalents. Comment on their meanings. 1. A bodyguard ---------- 1. Волноваться перед чем-либо 2. To get cold feet --------- 2. Одурачить кого-либо 3. To turn a blind eye -------- 3. Сильно рассердить кого-либо 4. To pull someone’s leg -------- 4. Держать язык за зубами 5. To be the apple of someone’s eye -------- 5. Одна голова хорошо, а две лучше 6. To make someone’s blood boil ---------- 6. Не желать иметь дело с кем- либо 7. A second-hand car ------------ 7. Телохранитель 8. To have one’s tongue in one’s cheek ----- 8. Проигнорировать кого-либо 9. To be all ears ---------------- 9. Боготворить кого-либо, быть любимцем 10. Two heads are better than one --------- 10. Старая ( подержанная ) машина 11. To be two-faced ----------- 11. Весь внимание 12. To give someone the cold shoulder------12. Быть двуликим 8. Fill in the gaps in the story Ned Clifton, the...-guard was beginning to get cold.... The reason was that he turned a blind... to the fact that a tall stranger had been pulling his... when he had told Ned that he was a veterinary surgeon who had come to see Abigail, the actress's dog. Abigail was the apple of Gloria's .... Any attempt to hurt her made the actress’s ... boil. Every day she took Abigail fara drive in her second... car. Few people recognized her in the old car. Ned decided to take a second opinion , after all , two ... are better than one. He telephoned his friend Ken, also a ... guard to another famous film star, if he would help him to solve the "veterinary surgeon" problem. Ken said: "Your trouble is that you are too naive. You will believe anything. Don't be two... If you start deceiving her, she will give you the cold... and will get rid of you because she does not trust you". These were strong words. Ned rushed into the house. The actress was lying on the floor. Dead? No. She had fainted with a shock. The vet announced that the dog must have an operation. A real tragedy. 9. Look at the abdominal cavity. What organs belong to it? Share your information with class mates. 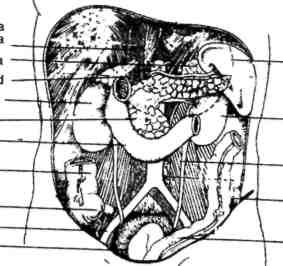 10. Read the extract from the Medical encyclopedia. In pairs discuss the contents using special questions. Use the picture of the eye for your conversation . Eye is an organ of sight and focuses an image onto the retina. Two eyes work in coordination under control of brain. Each eyeball moves by six delicate muscles. Eyeball has a tough outer coat the sclera. Sclera is a white portion of an eye. The circular part of cornea is transparent and protrudes slightly. Cornea is main lens of eye and performs most of focussing. Behind cornea is shallow chamber full of aqueous humour at the back of which is iris with its central hole, pupil. Pupil looks black and its size is altered with changes in light intensity. On the inside of the back of eye is retina, a complex structure of nerve tissue on which image is formed by the cornea. The eyeball is sealed off from the outside by a flexible membrane called conjunctiva. The conjunctiva contains many tiny tear secreting and mucus producing glands. Each eyelid contains about 30 meibomian glands opening along the lid margin behind the roots of lashes. Glands secrete an oil preventing lid margin to adhere during sleep. 11. You are a teacher of Anatomy. Be ready for your lecture translating sentences and signs to the picture from Russian into English and using the picture of an eye. Лучи света попадают внутрь глаза через зрачок. Хрусталик, как объектив фотоаппарата, собирает лучи и фокусирует изображение на задней стенке глазного яблока, сетчатке. Сетчатка буквально напичкана светочувствительными рецепторами: палочками и колбочками. Благодаря палочкам мы различаем свет и темноту, с помощью колбочек воспринимаем цвета. Зрительный центр мозга сводит воедино и воспроизводит сотни отдельных деталей, ежесекундно запечатляемых глазом. На сетчатке возникает перевёрнутое изображение. Зрительный отдел мозга возвращает его в исходное положение. Глазная мышца 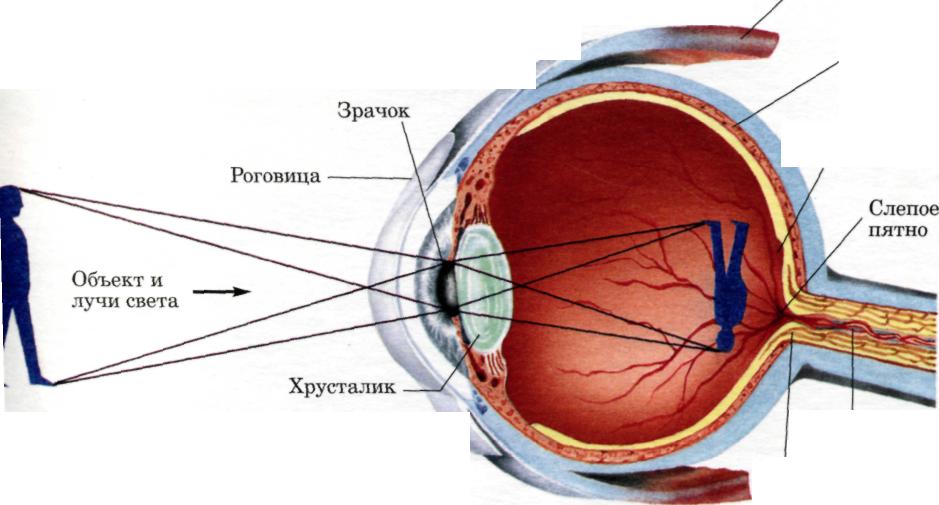 Кровеносные сосуды Зритель ный нерв Using What You’ve Learned Activity
guess the appearance of one of the students described by the other ones.
information about any organ and present your information. Topic 6. Skeleton 1. Share your ideas about the saying “Every family has a skeleton in the cupboard” 2. How would you translate the following passage from “The Final Diagnosis” by A. Hailey? Does the phrase go out on a limb have the direct meaning? Discuss it with your classmates “That is good now.” O’Donnell decided to shelve his earlier doubts. If Orden Brown had gone out on a limb like that, he would come through all right. 3. Study new words abnormal-патологический, ненормальный adult-взрослый attachment-прикрепление brain-мозг cancer-рак cause-причина, вызывать common-распространённый, характерный cranial-черепной curved-изогнутый damage-повреждать decomposition-распад, разложение excessive-излишний, чрезмерный fibula-малоберцовая кость framework-остов, каркас graft-пересаживать (орган, ткань ) inhibit-задерживать, тормозить joint-сустав limb-конечность marrow-костный мозг rib-ребро shin-голень skull-череп sternum-грудина stiff-негибкий, окостеневший thigh-бедро vertebra-позвонок vessel-сосуд weight-вес 4. Read the following pairs of words in Plural and Singular forms Singular: Plural: sternum - sterna vertebra - vertebrae corpus - corpi radius - radii 5. What are the nouns from which these adjectives are formed? bony, cranial, facial, muscular, nasal, pelvic, osseous, skeletal, spinal, thoracic, vertebral. 6. Compose pairs of synonyms 1. backbone a. clavicle 2. arm bone b. femur 3. breastbone c. fibula 4. finger bones d. foot 5. leg bone e. humerus 6. metacarpal bones f. hand 7. metatarsal bones g. phalanges 8. thigh bone h. spine 9. carpal bones i. sternum 10. collar bone j. wrist 7. Fill in the gaps of the chain (n) bres...-...hig...-...i...-...ai...-...os...-.....xtremity (v) perfor...-...en...-...amage (a) crania...-...ight. 8.Give translation of the logical combinations of the word “bone” with the following words transplanted, broken, curved, deformed, damaged, enlarged, misshapen 9.Look through the words and select the meanings to the figures clavicle, femur, fibula, humerus, patella, radius, ribs, skull, sternum, tibia, ulna 10. Select descriptions to the pictures and discuss it with your class mates
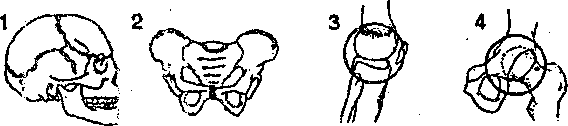 11. Read the text and do the tasks after it The Human Skeleton The human skeleton consists of more than 200 bones that are the organs of the skeletal system. The distribution of bones is as follows: Skull-29 bones Vertebrae-26 bones Ribs and sternum-25 bones Upper extremities-64 bones Lower extremities-62 bones Besides forming the framework of the body, the skeleton serves as a means of attachment for the skeletal muscles. It also protects delicate structures, such as the brain, the heart and the lungs. The marrow, or internal soft tissue, present in some bones is responsible for the formation of red blood cells (erythropoiesis) as well as the formation of certain kinds of white blood cells. Erythropoietic marrow is found only in the cranial bones, the vertebrae, the sternum, the hip bone, and the proximal ends of the thigh and arm bones. Bones also acts as a storehouse for calcium and phosphorus, releasing these minerals to the blood when they are needed. 12. Fill in the logical scheme of the content of the text 1. Composition (a) and Function (b-f) a. Complete adult skeleton-206 bones b. c. d. e. f. 2. Divisions of the skeleton a. Axial skeleton-80 bones 1. 2. 3. b. Appendicular skeleton-126 bones 1. 2. 13. Read the title of the text, its annotation and the text itself. Give your own version of annotation. Prove your opinion to your class mates Заголовок. Mend one broken leg with the other Аннотация.An American surgeon has found the way to replace the damaged bone Текст.Sometimes broken legs don’t mend properly. This may be the result of bone cancer, or an accident which has damaged the soft tissue in the leg very badly. An American surgeon, Mr. Harold Dick, has found the way to avoid amputating the damaged leg – and even get the patient walking again quite normally.He takes the thin shin bone, the fibula, from the undamaged leg and grafts it. 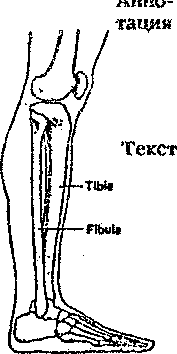 The fibula can be removed without affecting the leg in place of the damaged bone. The fibula can be removed without affecting the good leg. The thin fibula isn’t strong enough to support the damaged leg immediately. The patient has to wear a splint for several month after the operation. The amazing thing, however, is that during this time the transplanted fibula grows in size until it becomes as thick as the damaged bone ( the tibia ) it has replaced. Topic 7. The Major Systems of the Body 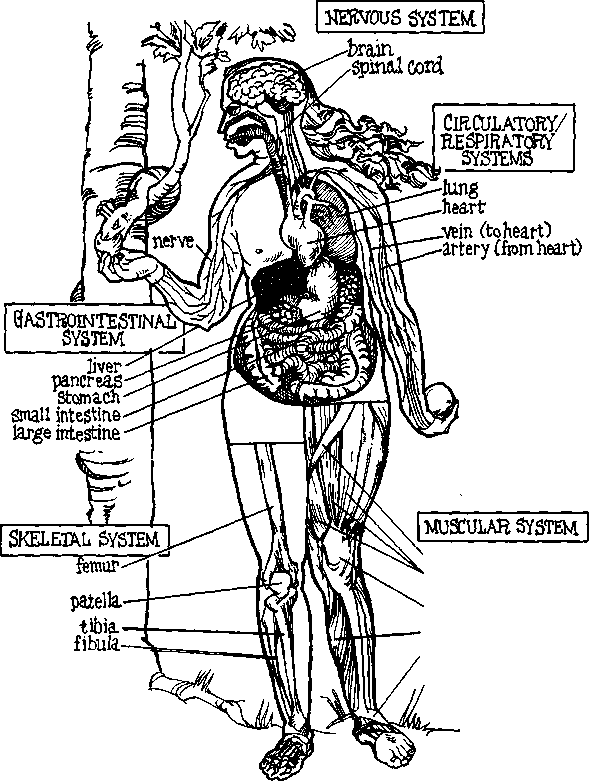 sartoriusquadri ceps tendon gastrocnemius ligament 1. Study new words. Skeletal -скелетный muscular -мышечный digestive -пищеварительный respiratory -дыхательный urinary -мочевой endocrine - эндокринный reproductive - репродуктивный structural - структурный alimentary - пищеварительный spinal cord - позвоночный столб ligament - связка cartilage - хрящ discharge - удалять, выводить из организма urinary bladder - мочевой пузырь hormone - гормон join - связывать vessel - сосуд 2. What do you know about the way your body works? Share your ideas and opinions by answering the following questions about the picture. * What are the major systems of the body? * How does your blood move through your body? * What are nerves? Do they extend throughout your body? 3. Read the text and do the tasks after the text The Major Systems of the Body During the last one hundred years, medical researchers have discovered a great deal about the way the human body works. We now know about the various systems of the body that keep us alive. The systems that are most important include the circulatory, respiratory, nervous, musculoskeletal, and gastrointestinal systems. Each of these systems controls major body functions. The system that controls the flow of blood through the body is the circulatory system. It includes the heart, the arteries, the capillaries, and the veins. The nervous system connects the brain to the rest of the body through the spinal cord and the nerves. The system that supports the body and allows it to move is the musculoskeletal system. The system that controls breathing is the respiratory system. It includes the nose, mouth, throat, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. Finally, the gastrointestinal system, the part of the body that controls digestion and elimination, consists of the esophagus, the stomach, and the small and large intestines. Two of its most important organs are the liver and is the pancreas. 4. Quote the sentences in which the following words and word combinations are used in the text. The way the human body works, the various systems, that are most important, major body functions, controls the flow of blood, to connect the brain to the rest of the body, to support and allow it to move, to control digestion and elimination, to control breathing, most important organs. 5. Make up sentences using the following words.
human.
6. Insert the missing words given below.
acid in the body liquids. - The brain is the … centre for regulating and coordinating body activities. - Respiration is the … process of breathing. - The blood and lymphatic systems have many … . - Joints are the places where … come together. - The endocrine system is composed of … located in different regions of the body. (main, proper, functions, mechanical, bones, glands) Work with grammar Clauses with THAT: Replacement of Subjects To form an adjective clause, that may replace the subject of a simple sentence. It may be used to refer to ideas, things and people. Note that who(m) is usually used for people, however. examples Two The body is like a complex machine. This machine automatically Simple repairs itself Sentences One The body is like a complex machine that automatically Complex repairs itself. Sentence With that 8. Underline the adjective clauses (that clauses) in the opening passage, "The Major Systems of the Body." Circle the words that the clauses modify. 9. Combine the following sentences. The second sentence should become a clause beginning with that. Omit words and change a or an to the where necessary. example: Blood is a liquid. This liquid circulates through the body. Blood is the liquid that circulates through the body. 1.The heart is an organ. This organ pumps blood through the body. 2.Blood is a liquid. This liquid carries food and oxygen through the body. 3.Blood is carried in vessels. The vessels are called arteries and veins.
responsible for body posture and movement.
And from the body. 8. Digestion of food is an essential process. This process is taken place in the intestine. 10. Combine the following sentences to form one sentence with a clause with that. Omit words where necessary. example: In Ancient Egypt, there were many doctors. These doctors cured patients with the help of magic and spirits. In Ancient Egypt, there were many doctors that cured patients with the help of magic and spirits.
and evil.
spirit had caused the person's illness.
certain way.
wild animals. 5. In addition, these doctors used a large number of drugs. These drugs included minerals, vegetables, and even beer. 6. The ancient Greeks practiced a different kind of medicine. This kind of medicine was based on the study of symptoms. 7. Ancient Greek doctors trained in medical schools. These schools were located all over Greece. 8. Aristotle, the famous Greek philosopher, wrote three important books. These books discuss medical problems that we still face today. 11. Adjective clauses with that are often used to define words. Use the following cues to define various parts of the body. Be sure to use appropriate singular or plural verbs in the adjective clauses and to add articles or pronouns where necessary. example: heart / organ / pump blood / through / body The heart is the organ that pumps blood through your body.
12. In pairs, use the diagram at the beginning of the chapter to help you to make definitions of the following terms. Complete each sentence in column A with one of the items in column B. example: Your brain is the organ that controls the body through nerves. а в 1. Your brain is the organ a) that carry blood back to the heart 2.Your heart is the organ b) that brings oxygen to your blood 3.Your lungs are the organ c) that controls the body through nerves 4.Your intestine is the organ d) that connects the upper arm and forearm 5. Your bones and muscles are the structures e) that digest your food 6. Your arteries are the blood vessels f) that carry blood from your heart to your organs 7. The veins are the blood g.) that receives vessels food you eat 8. The elbow is the joint h) that support the body and provide movement 9. The pancreas is the organ i) that pumps blood through the body 10. The stomach is the organ j) that makes insulin Topic 8. Cardiovascular System 1. Study new words
node узел nourishment питание outfit снабжать output выброс oxygen кислород pacemaker водитель ритма pump насос septum перегородка rate частота, скорость suction всасывание ventricle желудочек 2. Read the following pairs of words and translate them.
3. Read and translate the words and word combinations. Chamber: the heart consists of two separate chambers; the right atrium and the right ventricle are the right chamber. Thick: a thick wall; thick layer; the walls of the left atrium are thick; the left ventricle has thick walls. Pulmonary: pulmonary artery; pulmonary circulation; pulmonary disease; pulmonary function; pulmonary valve. Dilate: dilated; to be dilated: the vessels dilate: the heart dilates and contracts. 4. Match the columns to find correct explanation and translate them 1.At heart ( or in one's heart of hearts) crush him with grief 2. (Be) sick at heart In one's inmost feelings 3. Break somebody's heart oppressed with grief or despair 4. Take something to heart show one's feelings for all to see 5. Open (uncover) one's heart to somebody cheerfully, free from sorrow 6. Search one's heart heavily, with sorrow 7. With a heavy heart examine carefully one's own beliefs and conduct 8. With a light heart expand or enlarge it 9. Wear one's heart on one's sleeve consider seriously 10. Lose heart be hard-hearted enough (to do ) 11. Not to have the heart lose courage 12. Take heart with all one's energy and devotion 13. Heart and soul cheer up 5. Do you remember the Latin language? Translate the following English words vascular inter space atrium fibrous pericardium costal ventricle systematic apex septum valve pulmonary 6.Translate explanations, make up scheme, entitle it and give definitions in Russian A-Heart B-Pulmonary Arteries C-Systemic Veins D-Pulmonary Veins E-Systemic Arteries F-Lung Capillaries G-Systemic Capillaries 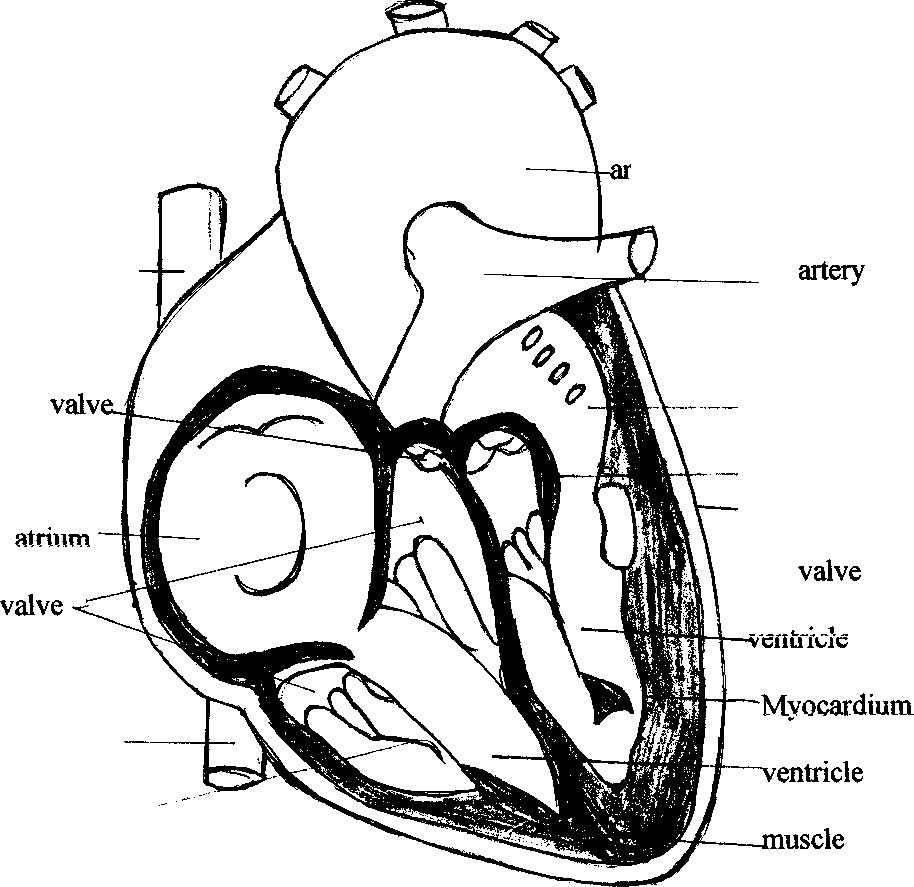 ch of aorta vena cava —-atrium valve Pericardium vena cava Chordae tandinae Scheme 1 7. Insert the necessary words given below. - The aorta … from the upper part of the ventricle. - The shape of the vessels … when they dilate. - The right lung is … than the left one. - The lungs are … with the pleura. (varies, covered, extends, heavier) 8. What is the meaning and function of the words 'examined', 'changed' in each sentence. Translate them A1. The therapeutist examined the patient yesterday. 2. The patient was examined by the therapeutist attentively. 3. The patient examined by the therapeutist yesterday felt bad. 4. The examined patient was ill with a heart disease. B.1. The doctor saw the changed condition of the patient. 2. That was why he changed the administrations (назначения) to the patient. 3. The administrations were changed to restore his health rapidly. 4. The nurse did not forget to carry out the administrations changed by the doctor. 9. Read the text and the tasks after the text Evolution of the Heart Beginning with the invertebrates, the lowest members of the animal kingdom, the heart is a simple propulsive muscular tube. In the fish the heart has evolved into a chambered organ with an atrium, or receiving chamber, and a ventricle, a thick-walled pumping chamber. This development was necessary because the vertebrates, of which the fish are the lowest class, have a more complicated structure and are generally large than the invertebrates, and require more oxygen. With the development of lungs in the higher vertebrates, the atrium became divided into two parts by the formation of a dividing wall called septum. Thus, in man and other animals with a four-chambered heart, blood from the body cells enters the heart at the right atrium, and from here it passes into the right ventricle from which the blood is pumped through the pulmonary artery towards the lungs. The oxygenated blood is carried back to the heart through the pulmonary veins, which empty into the left atrium. From the left atrium, the blood passes into the aorta for the distribution throughout the body. 10. Choose five nouns from the text which characterize the heart and compose three sentences of your own. Consult with anatomy plates (see the application №7). Discuss it with your class mates 11. Give definitions of the following terms. E.g.: The heart is a pumping organ. Atrium, ventricle, septum. 12. Answer the questions using this scheme 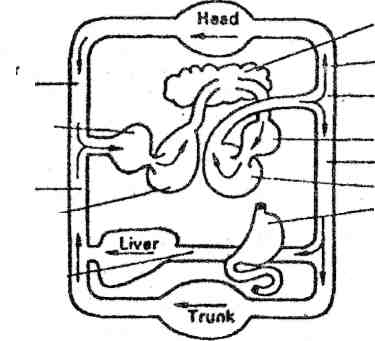 Lungs Carotid and vertebral arteries Aortic arch Left atrium Aorta Left ventricle Gastrointestinal tract Superior vena cava Right atrium Interior vena cava Right ventricle Portal vein 1. How many circulatory systems are there in the body? 2. What does the systemic circulation supply? 3. What is the main function of the pulmonary circulation? 4. What organs receive arterial blood?
13. Analyze the following sentences in pairs 1 . The invertebrates are the lowest members of the animals. 2. The fish are the lowest class of the invertebrates. 3. The vertebrates have a more complicated structure and are generally larger than the invertebrates, and require more oxygen. 14. Listen to the text. The Human Heart. The bigger person, the bigger the heart. Thus, there is the great variation in the size and weight of the human heart. The normal weight of the heart in both children and adults is approximately half of one per cent, or a little less, of the total body weight. The professional athlete's heart is a little heavier, with slightly more muscle. Just as the size and weight of the heart vary, so does the rate at which the heart beats. In some persons, especially trained athletes, the heart beat may be as slow as 45 beats per minute, when the person is at rest. Under the stress of vigorous exercise, the heart rate may reach as high as 170 or 180 beats per minute. The normal heart beat is considered to be about 72 beats per minute. At this average rate the heart contracts 4.320 times in an hour, 103.680 times in a day, 58.597.200 times in a year, and 4.100.544.000 times in a lifetime of 70 years. 15. Give the English equivalents of the following Russian words and expressions and quote the sentences with them. - человеческое сердце - вес сердца - взрослый человек - мышцы - процент - биение сердца - 45 ударов в минуту - человек на отдыхе - сокращения сердца 16. Discuss the following in your group
17. Compose the sentences from the words. 1. acts, The, pump, a, heart, as. 2. the, doctor, out, varying, pulse, in, John Floyer, an, men, rate, the, English, was, scientist, to, first, find. 3. tons, blood, pumped, the, daily, Ten, of, are, through, heart. 18. Translate the sentences into English. 1. Физиологи определили, что у взрослого сердце совершает от 60 до 72 ударов в минуту. 2. Исследовательская работа показала, что уровень сердечных ударов возрастает в зависимости от различных эмоций. 3. За каждым ударом сердца следует пауза. 4. Каждое сокращение и пауза составляют сердечный цикл. 5. Каждый сердечный цикл состоит из трёх фаз. Раздел IV. Texts for Reading Text 1. Pediatrics. Pediatrics is a science about a child's development and his diseases. Pediatrics originated from a Greek word: pais is a child, iatreia is treatment. In Russia the science began to develop at the beginning of the 19th century. The first hospital for children was opened in St. Petersburg in 1834. Now it is named after the famouse Russian pediatrician Filatov. The names of Khotovitski, Filatov, Gundobin, are well - known, not only in our country, but abroad. There is a Pediatric institution in St. Petersburg in which such famous doctors as Tur, Volovik, Speranskiworked. Russian scientists have contributed much to the problems of Pediatrics. They help children suffering from allergy, infectious and other diseases. Text 2. Nursing of Children During Illness It is very important for a sick child to have a good nursing. When we speak of nursing in illness we mean first of all cleanness of the child's room, bed and clothing. When a child is ill he needs more fresh air. You must air the room no less than three times a day: in the morning, after the midday meal and at bed-time. When you air the room cover the child warmly not to chill him. It is good to have a small nursing table near the child's bed. You can keep different things on the table which you need in the care of the patient. A soft towel for his hands and face is placed on it. The patient's hands are washed several times a day. The nails are cut very short. Dirty clothes are put immediately into a disinfectant. It is especially important in the case of dysentery or other infectious diseases. Text 3. Heart Disease Risks Certain risk factors can increase anybody’s chances of developing heart disease. These risks include life style and family history. Some risks are: Age. The older you get the more likely you are to develop heart disease. Sex. More men develop heart disease and develop it earlier than women do. The gap begins to narrow after the menopause and women "catch up" with men around 65. Heredity. If members of your family have had heart disease, you are more likely to develop it. Race is also a risk factor: Black Americans have a greater risk of heart disease than white Americans mainly because they have higher average blood pressure levels. Text 4. Accessory Aids of Blood Circulation It was obvious even to primitive man that the pulsating heart was a pump distributing to the brain and all other parts of the body important substances, including nourishment from the gastrointestinal tract and liver. However, i twas not until the middle ages and later that the details of circulation were discovered.' In later years it was found that certain accessory aids help the heart in maintaining an optimal circulation of the body. Undoubtedly the most important aid is that of the large muscles of the leg, which on contracting, squeeze the veins in the legs and thus relieve the heart of about one third of its work when the legs are used actively, as in cycling, running, swimming or jogging. A second important aid is that of the elasticity of the aorta. When hardening of the aorta wall develops as a result of arteriosclerosis, the advantage of natural elasticity is lost. A third aid is a freely moving diaphragm. When the diaphragm moves up and down, the chest cavity becomes a suction pump that help to bring blood up from below as well as to bring air into the lungs. A fourth aid is the arterial system's ability to adjust to the changing demands of different organs. During the process of active digestion the blood supply to the gastrointestinal tract has greater priority than that to the skeletal muscles, which are at rest. During exercise, the situation is normally reversed, with skeletal muscles receiving priority over the gastrointestinal tract. Text 5. Heart Failure As the heart has only one function, to pump all the blood it receives from the veins into the arteries, so in a sense it has only one disease, failure to do so. But heart failure has many causes. As fast as blood arrives from the veins a healthy heart pumps it into the arteries. The heart is in "failure" when it does not pump the blood quite as fast as it arrives. As a result the veins become congested with blood and the pressure in them rises. The circulation then goes on as before, but with a constant accumulated blood. The heart no longer empties itself with each beat. The heart failure is divided into two groups; those due to poor output (forward failure) and those due to congestion on the veins (backward failure). Forward failure affects the whole body: all tissues need an adequate supply of fresh blood, and when the supply is reduced nothing in the body functions quite as well as it should be. The symptoms of congestion are due not so much to overfilling of the veins as to leakage of water into tissues, causing edema (dropsy). At least three mechanisms operate in heart failure. The roost obvious is the raised pressure in the capillaries which prevent them from absorbing water from the tissues. Secondly, poor circulation deprives the capillaries of their full quota of oxygen and causes them to leak. Thirdly, poor circulation in the kidneys causes too much salt to be retained in the body. The relation to other disease is very complex, for on the oik; hand heart failure lowers the efficiency of other organs and on the other hand chronic disease, especially the lungs and kidneys can lead to heart failure. Text 6. Heart Block Heart block improper formation of sinoatrial impulse and its propagation through the junctional tissues of heart is known as heart block. It may be SA block, A V block, bundle branch block or arborisation or Purkinje block. It leads to dizziness, stroke or fainting attacks. It may be caused by coronary heart disease, myocarditis, overdose of digitalis drug. The rate of ventricle beat is slower than normal and in complete heart block the rate does not increase after exercise. Pulse becomes lesser than 50 per minute. Mild block does not require treatment. In severe case pace maker is fitted. Text 7. Heart Burn It is the burning pain in epigastrium and may be caused by overeating, spicy prickles, and alcohol consumption. This pain is generally mistaken for heart attack. Antacid and anticholinergic drugs are helpful. Heart transplant is a complex form of surgery undertaken to replace a patient's diseased heart either with ahealthy one from donor or a mechanical one. Close matching has to be done. Text 8. Heat Exhaustion It is caused by overexposure to heat, when person it not accustomed to work in hot environment. Insufficient water intake and diminished consumption of salt precipitate it. Symptoms include faintness, fatigue, headache, restlessness and heat cramps. Skin it pale and clammy. Breathing is shallow and fast. Pulse is rapid and weak. Glucose saline intravenous drip and antipyretics help the patient. Patient should be shifted to cooler place and whole body sponging will relieve the fever. Литература
communicative grammar. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 1996г.
Books Centre SDN. BHD., [ T – 142884 ]
Высш. шк., 1985. 160с. 10. Францева Л.Ф.Самоучитель английского языка для медиков. Москва 2002. |
