МУ РЭТ. Unit Telecommunications. Basic Concepts
 Скачать 334.5 Kb. Скачать 334.5 Kb.
|
|
Unit 2. Transmission Media Start-up What does the efficiency of the transmission medium depend on (discuss with your partner)? Do you believe that fiber optic is more efficient than copper cable? Is the word “media” singular or plural? Write the following words in singular: data, media, criteria, syllabi, phenomena, crises, analyses, theses. Text A. Transmission Media Transmission media are the highways and arteries that provide a path for telecommunications devices. There is a general tendency to say that one transmission medium is better than another. In fact, each transmission medium has its place in the design of any communication system. Each has characteristics which will make it the ideal medium to use based on the particular set of circumstances. It is important to recognize the advantages of each and develop a system accordingly. Factors to consider when choosing the transmission media include: cost, ease of installation and maintenance, availability, and most important, efficiency of transmission. It is important to recognize the advantages of each and develop a system accordingly. Transmission efficiency is generally viewed as the amount of signal degradation created by the use of a particular transmission medium. The transmission medium presents a "barrier" to the communication signal. The "barrier" can be measured by many different factors. However, one common question is asked about all communication media. How far will the communication signal energy travel before it becomes too weak (or distorted) to be considered unstable? There is equipment available to extend the distance for transmitting a signal, but that adds to the overall cost and complexity of deployment. 2.1 Match the words in column A with their synonyms in column B: A B Circumstances difficulty Degradation conditions Barrier placement Distorted attenuation Deployment obstacle Complexity weakened 2.2 Translate this sentence into Russian: Transmission efficiency is generally viewed as the amount of signal degradation created by the use of a particular transmission medium. 2.3 Answer the following questions: 1) What factors should be considered when choosing the transmission media? 2) Why is a transmission medium called a “barrier” to the communication signal? 3) What common question is usually asked about all communication media? 4) How can you explain the term “transmission efficiency”? Text B. Transmission lines The most common types of transmission media used today are: Copper Wire; Fiber Optics; Radio Frequency (Wireless); Free Space Optics. Many engineers will argue that one transmission medium is the best, or better than some of the others. The reader should keep in mind that each medium has advantages and disadvantages. Which medium is best depends upon the purpose of the communications system and the desired end results. In fact, most systems are a hybrid. That is, two or more media are combined to effect the most efficient communication network infrastructure. There are many traffic signal systems that combine a twisted copper pair infrastructure with wireless links to serve part of the system. The decision to create this type of system may have been based on economics, but that is certainly one of the reasons to choose one medium over another, or to combine the use of several. Coaxial cable (coax): Flexible coax has a copper wire core surrounded by copper braid. The core and braid are insulated from each other by a dielectric material such as polyethylene and covered by a PVC sheath. i 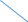 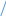 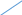 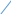 nner conductor nner conductorcopper braid dielectric PVC sheath (outer conductor) The braid helps to screen the signals from interference. Coax can carry a large number of signals over long distances up to 1000 Hz. It is used to connect telephone exchanges and for cable television. Advantages of coaxial cable: - low cost; - easy to install, easy to expand; - up to 10Mbps capacity; - moderate level of EMI immunity. Disadvantage: - single cable failure can take down the entire network. Twisted pair. Two insulated copper wires are twisted together to reduce interference effects and are enclosed in an insulating polyethylene sheath. Because the wires are twisted, unwanted stray signals picked up by one tend to be cancelled by similar signals picked up by the other. They are used for communications over longer distances, for example to connect telephones to their local exchange. i  nsulator (e.g. polyethylene) sheath nsulator (e.g. polyethylene) sheath   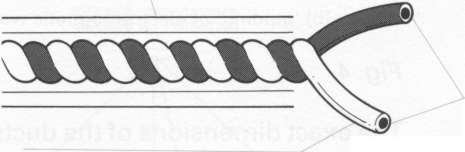 copper wire conductors copper wire conductorsinsulator (e.g. polyethylene) covering wire There are two types of twisted pairs cabling: 1) Unshielded twisted pair (UTP). 2) Shielded twisted pair (STP). 1. Unshielded twisted pair is more common. It can be either voice grade or data grade depending on the condition. Advantages of UTP: - easy installation; - high speed capacity; - low cost. Disadvantage of UTP: short distance due to attenuation. 2. Shielded twisted pair is similar to UTP but has a mesh shielding that protects it from EMI which allows for higher transmission rate. Characteristics of STP: - medium cost; - easy to install; - higher capacity than UTP; - higher attenuation, but same as UTP; - medium immunity from EMI; - 100 meter limit; Advantages of STP: shielded; faster than UTP and coaxial. Disadvantages of STP: - more expensive than UTP and coaxial; - more difficult to install; - high attenuation rate. Optical fibers. An inner core made from very pure silica fiber is surrounded by a similar glass sheath, known as cladding. This is covered by a protective plastic sheath. Non-visible light from lasers or LEDs can travel along the fiber by reflection from the surface where the core and cladding meet. Although the optical fiber has a smaller diameter than a human hair, it can be used to transmit tens of thousands of signals at high speed with very low loss and no interference from other signals. Optical fiber cable can be used in corrosive environments and is light, flexible and cheap. This type of cable is gradually replacing conventional copper wire for connecting telephones and computer networks. Advantages of Fiber Optic Cable: fast; low attenuation; no EMI interference. Disadvantages: very costly; hard to install. Wireless Media. Since the invention of the Wireless Telegraph in 1896 communication system designers have sought to use wireless because of the reduced infrastructure cost and complexity, when compared to wireline communication systems. There is no need to construct miles of telephone line poles or cable trenches. Simply put in a few strategically positioned radio towers and transmit around the world. Today, wireless systems are significantly more complex because we want to allow millions of users to make telephone calls or receive feature length movies via wireless systems. There are four general types of wireless (radio) communication systems: - Cellular Telephone. - Basic 2-Way Radio. - Point-to-point. - Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity), and recently, Wi-Max. Traffic signal and freeway management systems use three of the variants to support operations, and are considering the use of Wi-Fi. The Wi-Fi/Wi-Max systems are becoming increasingly ubiquitous in their deployment, and a part of most telecommunication deployment strategies. 2.4 Read text B again and find a word or phrase that means: - the communications channel or path over which a signal propagates; - a type of wiring in which two conductors of a single circuit are twisted together; - the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation, a form of luminescence; - a type of cable that has an inner conductor surrounded by a tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield; - a form of cable that uses a single center conductor with two shields; - anything which alters, modifies, or disrupts a message as it travels along a channel. 2.5 Make up a list of terms you can find in the text. Find definitions to the terms. Make up 10 questions with the terms used in the text. 2.6 TranslatethefollowingphrasesorsentencesusinginformationfromtextB: экранированная витая пара; высокая пропускная способность; это позволяет увеличить дальность передачи с уменьшением потерь из-за воздействия внешних электрических сигналов. 2.7 Read the following terms and translate them into Russian: Media, copper wire, cable, transmission, high-speed data transmission, data communications, customer premises, high frequency, coaxial cable, bandwidth, telephone channel, local loop, long-distance network, capacity, traffic, transmission medium, wireless system. 2.8 Find all the abbreviations in the texts. Give their meanings. 2.9 Discuss the text with your neighbor in the form of a dialogue. 2.10 Find English equivalents for the following: Одномодовый кабель (одномодовое волокно); затухание сигнала; техническая характеристика; передача данных на большие расстояния; скорость передачи данных; низкочастотные радиосигналы. 2.11 Answer these questions: 1) What are the main types of fiber cables? What is the difference between them? 2) Why is fiber considered to have the best overall characteristics for transmission efficiency? 3) What factors, besides highest transmission speed, may influence the choice of transmission media? 2.12 Compare transmission characteristics of fiber, copper, radio and infrared. Text D. Среды передачи информации Средой передачи информации называются те линии связи (или каналы связи), по которым производится обмен информацией между компьютерами. В подавляющем большинстве компьютерных сетей (особенно локальных) используются проводные или кабельные каналы связи, хотя существуют и беспроводные сети. Передача на большие расстояния при любом типе кабеля требует сложной передающей и приемной аппаратуры: для этого надо формировать мощный сигнал на передающем конце и детектировать слабый сигнал на приемном конце. Промышленностью выпускается огромное количество типов кабелей, которые можно разделить на три большие группы: - кабели на основе витых пар проводов, которые делятся на экранированные и неэкранированные; - коаксиальные кабели; - оптоволоконные кабели. Каждый тип кабеля имеет свои преимущества и недостатки. Витые пары проводов используются в самых дешевых и на сегодняшний день, пожалуй, самых популярных кабелях. Они довольно гибкие и удобные для прокладки. Неэкранированные витые пары характеризуются слабой защищенностью от внешних электромагнитных помех, а также слабой защищенностью от подслушивания с целью, например, промышленного шпионажа. Для уменьшения излучений кабеля, защиты от внешних электромагнитных помех и снижения взаимного влияния пар проводов друг на друга (cross-talk - перекрестные наводки) применяется экранирование. Основные достоинства неэкранированных витых пар — простота монтажа разъемов, на концах кабеля, а также простота ремонта любых повреждений по сравнению с другими типами кабеля. Все остальные характеристики у них хуже. Коаксиальный кабель - это кабель с центральным медным проводом, который окружен слоем изолирующего материала для того, чтобы отделить центральный проводник от внешнего проводящего экрана. Внешний проводящий экран кабеля покрывается изоляцией. Стоимость коаксиального кабеля выше стоимости витой пары и выполнение монтажа сети сложнее. Коаксиальный кабель применяется, например, в локальных сетях с архитектурой Ethernet, построенных по топологии типа “общая шина”. Коаксиальный кабель более помехозащищенный, чем витая пара и снижает собственное излучение. Пропускная способность – 50-100 Мбит/с. Допустимая длина линии связи – несколько километров. Несанкционированное подключение к коаксиальному кабелю сложнее, чем к витой паре. Кабельные оптоволоконные каналы связи Оптоволоконный кабель – это оптическое волокно на кремниевой или пластмассовой основе, закрытое внешней оболочкой. Оптическое волокно передает сигналы только в одном направлении, поэтому кабель состоит из двух волокон. На передающем конце оптоволоконного кабеля требуется преобразование электрического сигнала в световой, а на приемном конце обратное преобразование. Основное преимущество этого типа кабеля – чрезвычайно высокий уровень помехозащищенности и отсутствие излучения. Несанкционированное подключение очень сложно. Скорость передачи данных 3 Гбит/c. Основные недостатки оптоволоконного кабеля – это сложность его монтажа и небольшая механическая прочность. 2.13 Match the words on the left with the words on the right to make pairs of words that often go together. 1  coaxial a) twisted pair cable, cord coaxial a) twisted pair cable, cord2 unauthorized —— b) medium, speed, line 3 unshielded с) cable 4 copper d) communication, processing, security 5 data e) access, distribution, use of property 6 transmission f) wire, cable, ore 2.14 In your vocabulary notebook, write out all the terms and expressions related to the topics of the specialty, with definitions (in English) showing the exact meaning in the above text. Read the text again, take notes and render it in English. Unit 3. Communication Systems and Networks Start-up Think of the following. What are the main parts of a communication system? What is a modem used for? What are the main types of a telecommunication channel? Text A. Basic communication systems Data communications are the transfer of data from one device to another via some form of transmission medium. A data communications system must transmit data to the correct destination in an accurate and timely manner. The five components that make up a communications system are the message, transmitter, receiver, medium, and protocol. Text, numbers, images, audio, and video are different forms of information. The transmitter injects a signal into the channel that delivers it to the receiver. The receiver must recover the information contained in the receiver signal despite the limitations introduced by the channel. The channel can be a physical one, like a copper cable and an optical fiber, or simply air or even vacuum that transmits electromagnetic waves. Any channel is subject to some kind of electromagnetic “noise” and interference. In order to transmit a digital signal at a reasonable distance it has to be processed by a modulator. The modulator can: Select the frequency at which the signal will be transmitted over the channel. Allow for different signals to share the same modulation channel, in a process known as multiplexing. Adapt the signals parameters to suit the requirements of a given channel (bandwidth, spectral properties, noise robustness, etc.). Provide the flexibility to exchange spectral efficiency for robustness, as needed. Of course, at the receiving end, the inverse operation, called demodulation, needs to be performed. So in bidirectional systems a single device will perform both operations and therefore be called a modem. The word modem is a combination of the words modulation and demodulation which is precisely what a modem does. A modem can also be viewed as a device that takes information, transfers it on to a medium to allow transportation of the information, and at the other end, removes the information from the medium and restores it to its original form. This brings up two distinguishing characteristics of a modem, the type of information it accepts and the media that it operates upon. The type of medium employed by the modem dictates the type of modulation it will employ. The medium can be a copper cable, an optical fiber or an electromagnetic wave in free space. Although the modem is a separate building block, it is often embedded in a laptop or in a wireless router. Multiplexing is the sharing of a single communication channel among different users. The communication channel can be a copper wire, an optical fiber or the space between a transmitting and a receiving antenna. Different users can be distinguished by means of different frequencies, time slots, codes or regions of space. 3.1 In the text above, find English equivalents for the following: Обеспечить надежность (прочность); информация, содержащаяся в сигнале; отличительная особенность (свойство); встроенный в компьютер блок; временной интервал. 3.2 Answer the questions: 1) What are the five components of a data communications system? 2) What functions do transmitters and receivers have? 3) What does the process known as multiplexing consist in? 4) What is a modem and what is it designed for? 3.3 Translate into Russian: 1) The type of medium employed by the modem dictates the type of modulation it will employ. 2) Any channel is subject to some kind of electromagnetic “noise” and interference. 3) A modem can also be viewed as a device that takes information and transfers it on to a medium. 4) Of course, at the receiving end, the inverse operation, called demodulation, needs to be performed. |
