УЧЕБНИК 1 КУРСА. Learningenglis ru learningenglis ru
 Скачать 18.07 Mb. Скачать 18.07 Mb.
|
to prepare for living in society
to increase IQ
to develop your body
to make connections
to prepare for tests
to learn job skills
to have fun |
Discuss the following questions in groups.
| e) performed f) examined g) gave to a person in charge | h) communicated i) started j) remained |
D. Complete these sentences with the phrasal verbs from Exercise C in the correct form.
1) Haven't your notes … yet? Perhaps they are in your coat.
2) Are you … after class tonight or going home?
3) Who's going to … that experiment?
4) It is time I … marking the papers.
5) … your answers carefully.
6) I haven't … my homework yet. It is still in my bag.
7) I can't … all the latest technology.
8) Come and … your old coursework from my office.
9) He didn't really … his meaning … to the students.
10) We are trying to … the best way to meet students' needs.
E. Read these tips for exam success and match phrasal verbs from a) – h) with their definitions from 1) – 8).
Six tips for exam success
Keep your reading up (a) during the term so that you have less to read just before the exam.
Brush up on (b) some of the things you learnt a long time ago; they may possibly come up (c) in the exam.
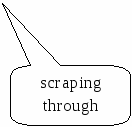
Don't just mug up (d) on the key points you need for the exam and hope that you'll scrape through (e) with little effort.
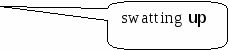
On the other hand, don't try to do everything. Swatting up (f) on everything you have done all term means you will have to revise a lot of useless things too.
Concentrate on polishing up (g) the most important areas and your best skills.
Don't fool yourself that you'll pass the exam on the basis of what you've picked up (h) during the lectures and classes. You will need to revise!
continue to do something
practice and improve your skills or your knowledge of something, usually something you learned in the past but have partly forgotten
if a question or a subject comes up in an exam, that question is asked or questions about that subject are asked in the exam
quickly try to learn the main facts about a subject, especially before an exam
manage with a lot of difficulty to succeed in something
learning as much as you can about something, especially before exam
practicing and improving your skills or your knowledge of something
learnt by absorbing it rather than studying it
F. Choose phrasal verbs you have known to complete this letter.
| Cambridge, 20 June Dear Auntie Meg, At last my first year exams are over. It's such a relief. I feel as if I've done nothing but (1) for them for ages. Although, I'd (2) with work quite well during the year, I still needed to (3) everything that we had covered, of course. Fortunately, everything that I hoped would (4) in the exam paper did. So I hope I've, done OK and haven't just (5). Now all I have to do is (6) one course assignment, which I need to hand in by the end of term. We don't (7) till the end of the month and so I won't be home till then. We don’t (8) until the end of September, so it’llbe a lovely long break. I look forward to seeing you soon. Love, Suzanna. |
Which of these would make most students happy and why?



READING 1: HIGHER EDUCATION IN RUSSIA
Study the vocabulary.
arrears
задолженность
on a competitive basis
на конкурсной основе
Certificate of Secondary
Complete General Education
аттестат о среднем образовании
comprehensive knowledge
всесторонние познания
curriculum
курс обучения, учебный план
to be dismissed
быть отчисленным
educational establishment
образовательное учреждение
expenses/expenditures
расходы
precious
совершенный
to raise funds
привлекать капитал, средства
to sign a decree
подписывать указ, приказ
Before you read, answer these questions.
What do you know about higher education system in Russia?
Is it different from other systems of higher education?
Read and translate the text.
The system of higher education in Russia started with the foundation of the universities in Moscow and St Petersburg in the middle of the 18th century. In 1724 the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, founded by Peter I, established the university and a grammar school. However, these educational establishments didn’t fulfill the task they took on. It was Michail Lomonosov who suggested the idea of establishing university in Moscow. In 1755, on 25 January, Empress Elizaveta Petrovna signed a decree of university foundation. According to Lomonosov’s plan, there were originally three faculties. First, all the students acquired a comprehensive knowledge in the field of science and humanities at the faculty of Philosophy. Then they could specialize and continue at the faculty of Philosophy or join either the Law faculty or the faculty of Medicine. Lectures were held either in Latin, the language of educated people at that time, or in Russian. Originally, tuition at Moscow University was free for all students; later only poor students were exempt from tuition fees. The state funding didn’t cover all the University expenses; thus the administration had to find ways to raise additional funds.
In general, the system of higher education in Russia was constructed similar to that of Germany. Due to demands of the international educational organizations, the higher education system began to change over the past ten years. Universities began transitioning to a system similar to that of Britain and the USA.
There are presently four basic types of higher education institutions (HEIs):
Universities (responsible for education and research in a variety of disciplines);
Academies (responsible for education and research. They differ from universities only in that they restrict themselves to a single discipline (Academy of Arts, Academy of Architecture);
Institutes (multi-discipline oriented);
Private Institutions (offer degrees in non-engineering fields such as business, culture, sociology, and religion).
Entry requirements. The Constitution and the Russian Federation Law on Education guarantee open and free access to higher education on a competitive basis. Currently the Certificate of Secondary Complete General Education is required for admission to all kinds of HEIs. Applications are accepted from citizens of both sexes who have completed secondary education and passed a competitive entrance examination. The academic year lasts from September 1 to June everywhere, with long summer vacations from July to August 31. It is divided into two terms. The evaluation of student’s performance is designed in such a way that the progresses of the latter in mastering subjects included in the curriculum are monitored closely and objectively. The number of tests and examinations to be taken during every academic year is strictly formulated by the head of the institutions. Student performance on test is evaluated as “passed” or “failed” and on examinations as “excellent”, “good”, “satisfactory” and “unsatisfactory”. Some HEI have already introduced a system of continuous assessment which helps to evaluate student’s progress during the whole academic year. Students who accumulate a number of arrears in their new academic year would be dismissed from their educational institutions. The final state examinations are also very important part of the higher educational assessment process in Russia. These methodologies constitute a comprehensive evaluation system by which the knowledge and the skills of specialists are brightened and the qualification obtained becomes invaluable and precious.
Answer the questions.
When did the system of higher education start in Russia?
Who suggested the idea of establishing university in Moscow?
What are the basic types of higher education institutions in Russia? And what are they responsible for?
What are the entry requirements to the HEI?
What evaluation system do HEIs have?
When does the academic year begin in Russia?
What is higher education for you?
Are the following statements true or false? Correct the false ones.
The first University and grammar school were established in 1724 by the St. Petersburg Academy of science.
Peter I suggested the idea of establishing the university in Moscow.
Moscow University had originally four faculties: Philosophy, Theology, Law, and Medicine.
Administration had not to raise additional funds to cover all the university expenses.
The system of higher education has not change over the last century.
The Russian Federation Law on Education guarantees open and free access to higher education.
All HEIs have already introduced a system of continuous assessment.
Find words in the text that mean:
money that you must pay a university for teaching you
a department within a university or institute
to gradually get more and more over a period of time
the subjects of study concerned with human culture, esp. language, history or philosophy
the action or process of making a formal request
talks given by a university tutor to a large number of students
short examination of knowledge or ability, consisting of questions that must be answered or activities that must be carried out
subjects included in a course of study or taught at a particular HEI
Choose the correct answer to the following.
1) A decree of university foundation was signed by …
a) Michail Lomonosov
b) Peter I
c) Empress Elizaveta
2) The system of higher education in Russia was initially constructed similar to that of …
France
Germany
Britain
3) Academy is responsible for education and research …
a) in a single discipline
b) in a variety of disciplines
c) in three disciplines
4) The academic year is divided into …
three terms
two terms
four terms
5) The number of tests and examinations to be taken every year is strictly formulated by …
lecturers
the head of institution
the examiner




