Mergers and acquisitions as an economic tool to strengthen russian banking sector evstafyeva Ekaterina Gennadyevna
 Скачать 416.42 Kb. Скачать 416.42 Kb.
|
|
MERGERS AND ACQUISITIONS AS AN ECONOMIC TOOL TO STRENGTHEN RUSSIAN BANKING SECTOR Evstafyeva Ekaterina Gennadyevna, Student of Management Department Plekhanov Russian University of Economics, Moscow Abstract: Mergers and acquisitions act is a business occasion when two or more companies join their strengths and capacities to form a larger and stronger one. The purpose of the research is to highlight the significance of M&A transactions in Russian banking sphere, where during the previous years there occurred a series of cases of financial insolvency. The results of the survey showed that M&A actions are an effective strategy to secure bankrupt industries from complete default and to ensure economic sustainability. Key words: M&A (merger and acquisition), sustainable business, banking sector, bankruptcy. СЛИЯНИЕ И ПОГЛОЩЕНИЕ КАК ЭКОНОМИЧЕСКИЙ ИНСТРУМЕНТ ДЛЯ УКРЕПЛЕНИЯ РОССИЙСКОГО БАНКОВСКОГО СЕКТОРА Евстафьева Екатерина Геннадьевна, Студент Российский экономический университет им. Г.В. Плеханова, Москва Аннотация: Сделки по слиянию и поглощению происходят в случае, когда две или более компании решают объединяют свои сильные стороны и возможности, чтобы сформировать более крупную и более сильную организацию. Целью исследования является определение уровня значимости сделок С&П в банковской сфере России, где в предыдущие годы произошел ряд финансовых банкротств банковских учреждений. Результаты исследования показали, что действия по слияниям и поглощениям представляют собой эффективную стратегию для предотвращения банкротства отраслей и обеспечения экономической устойчивости. Ключевые слова: С&П (слияние и поглощение), устойчивый бизнес, банковский сектор, банкротство. Introduction In modern market conditions companies have to search for new strategies to expand. They seek innovative ways to develop and grow, trying to discover new technologies to implement both into the production process and human resources management. This is caused by increased competition in all market segments. If the company wants to create sustainable business and increase its market share accordingly, the management should respond to these changes as quickly and effectively as possible. Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) is one of the main strategies of company development which may both influence the efficiency of operating process and increase the value of business significantly. This strategy continues to gain popularity in Russia, in particular in a situation of crisis. Therefore, M&A transactions in the banking sector of Russia can be seen as one of the options of sanitation of banking institution. Nevertheless, the risk of M&A transactions is a matter of practice - in a substantial amount of cases, it does not create added value and turns round in a failure for both companies. The aim of strategic management here is to prevent crisis which can lead to a complete disaster. Thus, the growth strategy through integration is extremely effective, but only in case of mergers and acquisitions conducted properly at all stages. We also cannot stay aside the market climate and tendencies, as the processes of M&A occur through time and space (e.g. in particular political and economic environment). In the situation of crises, the M&A deals have occurred as the most common business deals. It is more convenient both for economy and businessmen not to go bankrupt, but give the company an opportunity to survive and still generate profit. Material and Methods The basic sources of information for current research were Russian laws regarding bankruptcy procedure: The Federal Insolvency (bankruptcy) law of 26.10.2002 in 2016 edition [1], in particular §4.1 The Insolvency (Bankruptcy) of credit institutions. The methodological base of the research encompasses the works of the world's leading theorists in the field of study of mergers and acquisitions: Richard A. Brealey, Stewart C. Myers, and Aswath Damodaran. Among the literature of Russian authors used, it is necessary to mention analytics of Mergers.ru (PREQVECA information-analytical agency), AK&M and RBC information agencies and “Mergers and Acquisitions” magazine. The statistical data is based on reports of consulting firms and investment banks as KPMG, as well as on data of information-analytical portals Bloomberg and Thomson Reuters. Modern trends of integration process in the banking sector of Russia Over the past twenty-five years, the Russian banking sector has undergone significant changes. According to the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, the number of credit institutions decreased from 1,686 in January 1988 to 1314 in January 2001. As for November 2016, this figure dropped to 643 operating credit institutions [5]. In banking sector of Russia the Central Bank approves the plans of emergency help by revoking the license for banking activities in an attempt to avoid bankruptcy and to strengthen the banking system. Credit institutions were eliminated, mainly through the cancellation of the license (bankruptcy) and corporate reorganization, especially through acquisition of companies. From the 1990s to the early 2000s there was a high turnover of credit institutions, which slowed down in the last decade due to the increasing number of insolvent banks. Gradually, the consolidation of banks led to an increase and amalgamation of credit institutions, their expansion through mergers and acquisitions. We can observe the trend to consolidation of assets in large credit institutions in the process of M&A over the past two decades in the Russian banking sector. Thus, as the number of credit institutions is gradually reducing, they get more public trust. Following current trends, we can predict a further potential expansion of foreign credit institutions in the Russian market; however, taking into account current economic situation and junk international ratings it is not possible yet. In recent years, the number and value of mergers and acquisitions in the banking sector around the world has been steadily declining. In the past decade, the majority of mergers and acquisitions in the financial services market have always befallen in the banking sector. The main driving forces behind the process of reduction of M&A activities on the banking market are natural growth, which is extremely weak in many countries after years of cost reduction due to the recession, so companies are not in a hurry to pour new investments in existing assets. Instead, they are looking for ways to increase the rate of profit revenue growth and further ways to reduce costs through acquisitions [3]. At the same time the global M&A market, despite the crisis, has demonstrated excellent results, broking the record 2007 of 4.6 trillion dollars [6]. According to MarketWatch the total volume of mergers and acquisitions announced in 2015 around the world, exceeded 5 trillion dollars. But despite this, many banks are still waiting significant reorganization. In order to manage credit risk effectively, different methods and tools for M&A are used. There are several ways in which to minimize these risks: convergence of interests in the process of merger of capital: thus making it possible to provide larger and more profitable loans to expand and improve its customer base; the use of high technology, capable to carry out customer service more effectively, increase the speed and efficiency of management; improving the quality of work through experienced staff recruitment policy; expansion of banking structure with increased monitoring of financial transactions. The analysis of M&A market in the Russian financial sector First of all, we have considered the current situation in the Russian banking sector, and then we have tried to identify the general trends of M&A deals in the banking sector. The slowdown in the economic growth and restrict access to international financial markets seriously complicated the situation in the Russian banking sector in 2014. The Central Bank of Russia has approved the plans of emergence help in 2014 to a number of banks and revoked the license for banking activities from 94 banks, in an attempt to avoid bankruptcy and to strengthen the banking system, which is 214% more in comparison with the previous year. Russian M&A market has shown an impressive growth during Quarter I of 2016. The total value of transactions increased in the annual comparison by 1.7 times, to $5.4 bln, compared to $3.2 billion in January-March, 2015. The number of transactions increased by 1.4 times, up to 115 transactions from 84 in the first three months of last year. The average transaction value increased in the annual comparison by 23.7% to $46.9 million from $37.9 million a year earlier. However, the increase is caused by low base effect – the crisis on the Russian market of M&A hit a peak at the beginning of last year, decreasing more or less till the second half of the year 2016. From the Table 1 below we can conclude that the ratio of current available credit institutions to all registered credit institutions is steadily declining. 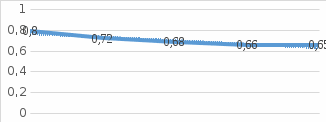 Graph 1 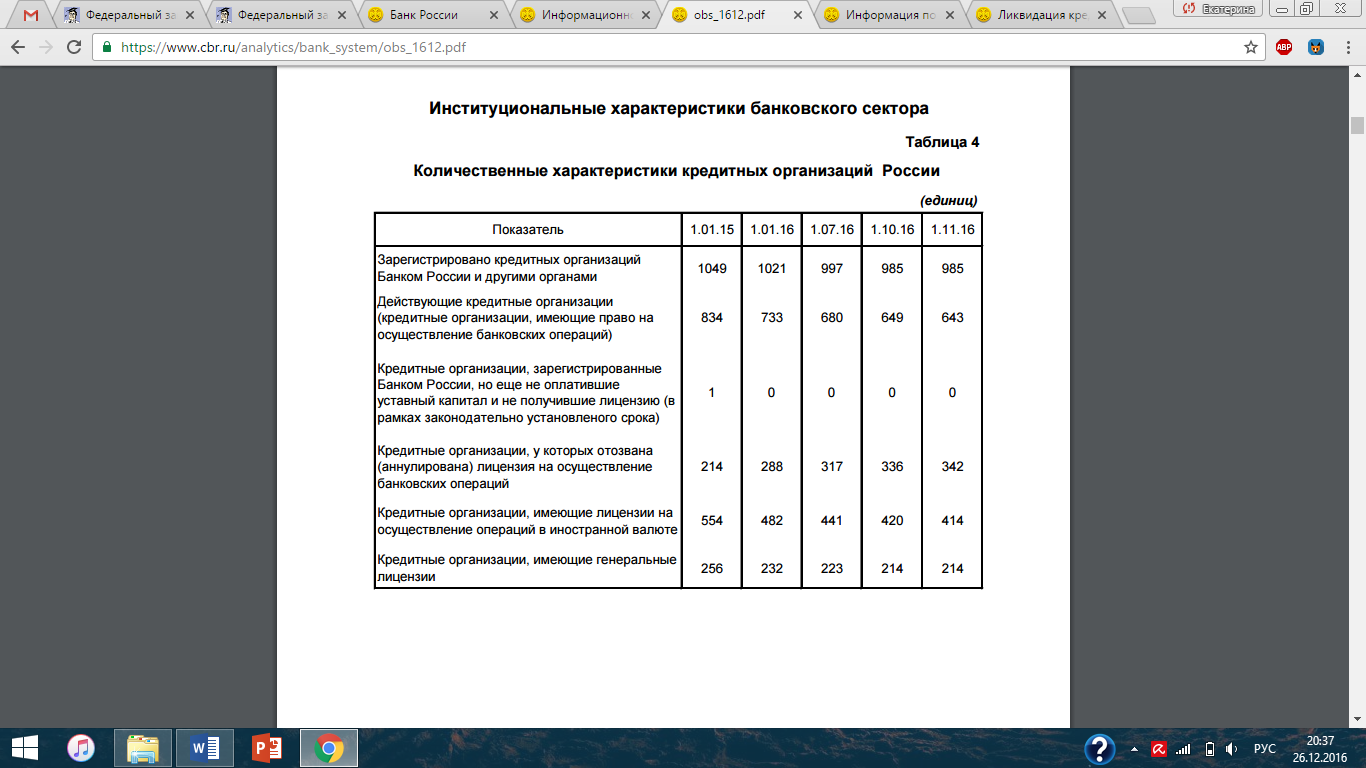 Table 1 The amount of transactions for Quarter I in 2016 was still 2-3 times lower than in the same period of previous years. In the first three months of this year is not noted any transaction over $1 billion. Thus, to talk about the full recovery of the market is still obscure, but there exist some signs of reoccurrence to pre-crisis position. According to the results of Quarter I of this year, the majority of sectors of the Russian economy showed growth of M&A-activities. The greatest growth in the number of transactions recorded finance (1.3 times). The share of all the industries on the Russian M&A market in Quarter I of 2016 is the following: as the amount of transactions 15%, of the total, the number of – 10%. The number of transactions in the Russian market of mergers and acquisitions in 2015 decreased by 19 percent to 2013 indicators. Total 504 transactions were recorded. Their monetary value fell even more - by 29 percent to 55.8 billion dollars. Based on data from AK&M Information Agency, the financial sector took the 4th place in the number of mergers and acquisitions in 2015, analysts of the AK&M agency estimated: 37 transactions at $1.89 billion [2]. During the recession it is always the dilemma of how to grow better: in a natural way or differently. If we talk about non-organic growth: it makes it possible for one or two years to pass a way that, when organic growth takes five years. Most of M&A transactions today occur through sanitation. The share of such transactions related to clean-ups has increased considerably this year: 19% of all M&A transactions in the financial sector and 32% of transactions amongst the banks. In the last months, sanitation actually became the main method of transferring the ownership of banks, claim the analysts of AK&M. This trend became more visible in 2014 already. The market is a growing number of banking business sellers with a deficit of buyers. But the proportion of transactions related to bank sanitation is steadily increasing [4]. 643 credit organizations are now working in Russia, according to the data of the Central Bank on 1 November 2016; even in 2008 this figure was 1136. During 2015 the Central Bank revoked the licenses of 89 credit institutions. The regulator has already sent 10 banks to the sanitation in the first half of this year, by spending 267 billion rubles [6]. The most expensive and largest procedure was The Bank of Moscow sanitation in May, 2016. Sanitation gives a huge amount of money inflow to the bank. Therefore, the main motive of consolidation today, unfortunately, is getting money from the state. The consolidation of the banking sector can be divided into healthy and unhealthy, and unhealthy is widely spread. Most of the profits of the banking sector in 2014 were not provided by the main activity: 220 billion rubles from 160-170 billion rubles. This is the effect of the recognition in the income money, received from the state funds for improvement of sanitation transactions. This means that some banks get instant profit and see this as the purpose of consolidation. The law allows banks, which are on financial recovery, to violate the mandatory regulations of the Central Bank. For sanators it is an excellent opportunity to clear balance, transferring bad or low-yielding assets on the rehabilitated banks. The major advantage here is that in the process of sanitation, banks have a chance to rectify the situation and to keep the business. 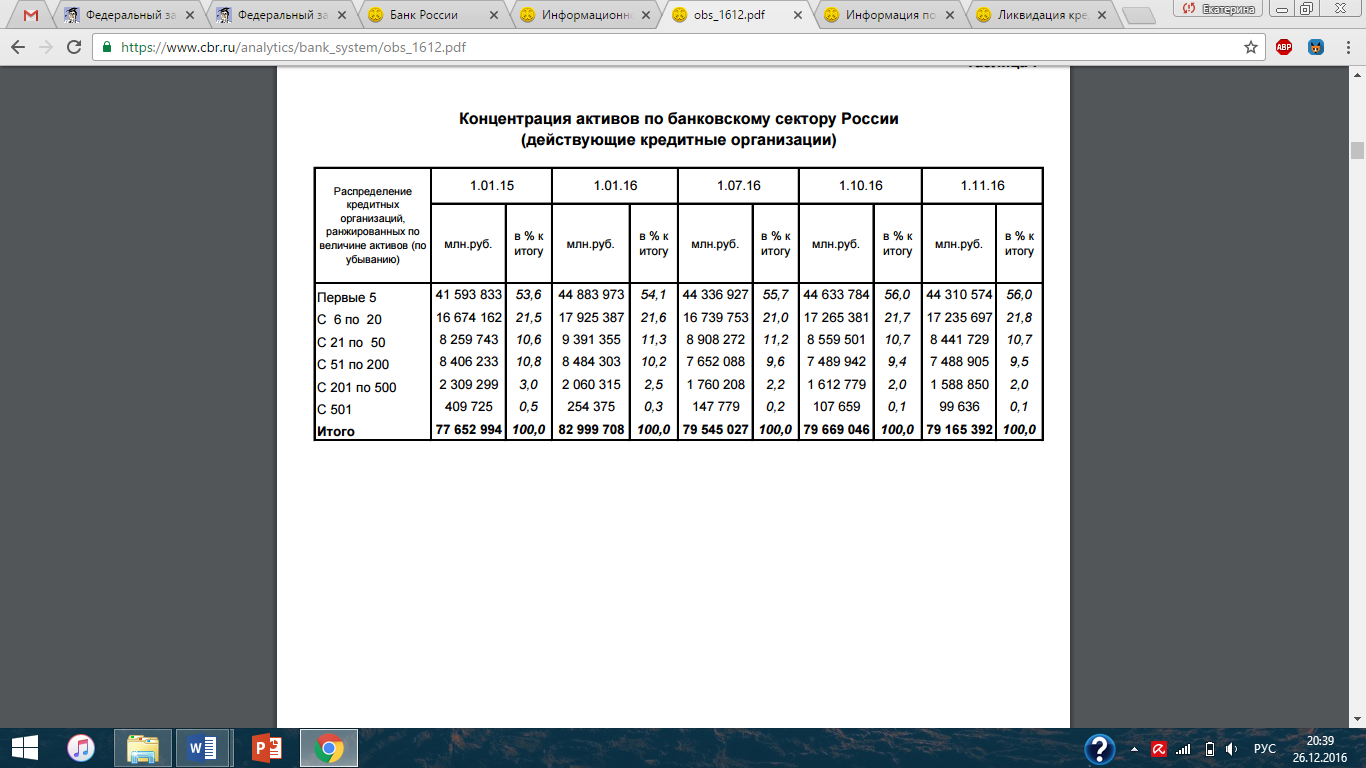 Table 2 There are about 500 banks, which do not contribute to the qualitative growth of the industry now. Banks outside the top 150 almost have no prospects of survival, because the banking is very tech-consuming, very expensive, and most of these organizations serve the interests of a few shareholders, collecting money for deposits and rearranging them in the related loans. We can see from Table 2 above that more than a half of the resources are concentrated in the top-5 according to the size of assets of credit institutions. But all in all we can say that the leavers are non-viable unhealthy banks with flawed business models. In general, the process of consolidation is a logical and correct. This makes the market more transparent: still there are many banks engaged in questionable activity or maintaining another shareholder business. In some cases, shareholders no longer have the financial capacity or the desire to develop the bank. But most of all in a role of subject to consolidation small regional banks are evolved which have to run a stable network of well-established clientele and positive reputation. The main risk of consolidation is to reduce competition. Due to the consolidation of the position of small and medium-sized market participants may get worse, because they can begin to lose their competitive edge. Small banks are used to be difficult to offer corporate customers a competitive rate, compared to large private and state-owned banks. And now it is more difficult to increase the attraction of deposits from individuals in such an unstable and unpredictable economic environment. According to Moody's, the share of assets of the five largest private banks (FC “Otkritie”, Alfa-Bank, Promsvyazbank, B&NBANK and Credit Bank of Moscow) by the end of Quarter II of 2015 rose to 12.5% from 10.8% at the end of 2014, and 8.4% at the end of 2013. The share of small and private banks accordingly declined from 23.4% in 2013 to 18.9%. The presence of strong private banks promotes competition in the banking sector. For the banking system as a whole, the consolidation of the risk may mean the increase of the state's share. But the situation is far away from monopolizing. Banks-consolidators need time to connect the acquisition, and it is not so easy. For example, each bank has its own set of IT-solutions, making it difficult to move to a single platform, and failures in the operation of the system will be a serious threat to the business. There is also the risk that management will focus on the integration process, not on the main activities of the bank, and it cannot affect the financial results. In some cases, consolidation significantly reduces the quality of management, as management loses independence and should pay more attention to the formal aspects of the management process. The sanitation of problematic banks may adversely affect the credit quality of the sanatorium-banks, and the more the savable banks, the higher the risk for a savior. The risks of participation in rehabilitation in the long run may outweigh the benefits and lead to downgrading of the sanatorium-banks. Hence, we see the trend of increasing the number of credit institutions in Russia going bankrupt. In 2015, the Bank of Russia continued to work on the withdrawal of credit institutions that are actively involved in money laundering, illegal withdrawal of funds abroad (the number of such credit institutions was 34 and remained almost at the level of 2014 - 36 credit institutions) from the market of banking services. But at the same time, the number of credit institutions, from which the licenses were revoked due to their poor financial situation increased. So, the cases of revocation of licenses for the loss of the capital in 2015 was 29 (31%) versus 14 (16%) in 2014. At the same time the proportion of credit institutions whose licenses were withdrawn due to sustainable insolvency were 30% (26) of the credit organization in 2014 to 14% (13) of the credit organization in 2015. During 2015 the Bank of Russia appointed 93 temporary administrations in connection with the withdrawal of banking licenses from the credit institutions. On the basis of materials, based on the results of temporary administrations functioning, they serve credit institutions to determine the presence in their work the signs of bankruptcy, premeditated bankruptcy, misconducted bankruptcy, as well as other facts and information that, under the identified circumstances, led to the bankruptcy of credit institutions. So, in 2015 some law enforcements were addressed to the Bank of Russia, which evidence the presence of some steps of management and owners of 62 credit organizations breaking the law which need to be prosecuted (under Art. 159 “Fraud”, Art. 159.5 “Fraud in insurance”, Art. 160 “Misappropriation or embezzlement”, Art. 172.1 “Falsification of financial accounting and financial institution reports”, Art. 195 “Misconduct in bankruptcy, Art. 196 “Deliberate bankruptcy” and Art. 201 “Abuse of power” of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). Conclusion M&A act is an economic tool that helps to increase efficiency through getting synergy effect. Some of benefits may be expressed in the increase of market share, usage of consolidate database of clients and others. The process of combining the resources of banks as a result of M&A transactions is initially an advantage that allows the new organization to obtain certain economic benefits, and has a purpose to protect the credit institution from bankruptcy. In Russia there is a mode called sanitation to help banks with troubles. But, as it is figured out above, some organization going bankrupt purposely, have an aim to get money from the government, and some just cannot cope with big changes in economy. As we see, it is difficult for the Central Bank to fight with the two big shadows from which banking system is suffering. They are illegal, “black” financial transactions market and unpredictably changing political environment. Consequently, we cannot treat the current situation as a complete result of economic crisis: the huge amount of all the failures in the banking system are caused by the players themselves. References 127-FZ Of October 26, 2002 On Insolvency (Bankruptcy) [electronic resource] - http://fin-lawyer.ru/2015/127-fz-of-october-26-2002-on-insolvency-bankruptcy/. AK&M: информационное агентство [electronic resource] - http://www.akm.ru/. PwC: the decrease of mergers and acquisitions deals in the banking sector [electronic resource] - http://www.pwc.ru/ru/press-releases/2013/banking_m_a_apr_2013.html. Russian mergers and acquisitions market review – 2015 [electronic resource] - http://www.kpmg.com/ru/ru/issuesandinsights/articlespublications/press-releases/pages/ma-2015-survey.aspx. Количество кредитных организаций [electronic resource] - http://www.cbr.ru/statistics/. Крупнейшие слияния и поглощения 2015 года [electronic resource] - https://lenta.ru/articles/2016/02/01/big_kush/. Sources Richard A. Brealey, Stewart C. Myers, Franklin Allen, Principles of Corporate Finance, McGraw-Hill Publ. Company, New York, 2007. Kim S. Cameron, Robert E. Quinn, Diagnosing and Changing Organizational Culture: Based on the Competing Values Framework, Jossey-Bass, University of Michigan, 3rd edition, 2011. A. Damodaran, The Value of Synergy, Stern School of Business, 2005. A. Roberts, W. Wallace, Mergers and Acquisitions, Edinburgh Business School, 2010. Teerikangas S., Very P. The Culture-Performance Relationship in M&A: From Yes/No to How // British Journal of Management. — Vol. 17, 2006. Timothy J. Galpin, M. Herndon, The Complete Guide to Mergers and Acquisitions: Process Tools to Support M&A Integration at Every Level, Oxford University Press, 2007. Молотников А., Слияния и поглощения. Российский опыт, Вершина, Москва, 2006. Файншмидт Е. А., Кризис-менеджмент, Учебное пособие, Москва, 2014. |
