Английский. английский для ИТ 1. Методическое пособие по совершенствованию навыков чтения и говорения на английском языке для студентов фксиС и фитиУ
 Скачать 0.77 Mb. Скачать 0.77 Mb.
|
|
particular application program, you'll see it in the list of files you can open with that software. A file extension is related to the file format, which is defined as the arrangement of data in a file and the coding scheme used to represent the data. Files containing graphics are usually stored using a different file format than files containing text. Most software have a native file format (.doc for MSWord, .pdf for AdobeAcrobat etc.) To designate a file’s location, you must first specify where the file is stored. Each of PC’s storage devices is identified by a device letter (A:, C:, D:) – a convention that is specific to DOS and Windows. A device letter is usually followed by a colon, so drive A could be designated as A: or as 3.5" Floppy (A:). The main hard disk drive is usually referred to as “drive C.” Additional storage devices can be assigned letters D through Z. Although most PCs stick to the standard of drive A for the floppy disk drive and drive C for the hard disk drive, the device letters for CD, Zip, and DVD drives are not standardized. A file contains data, stored as a group of bits. The more bits, the larger the file. File size is usually measured in bytes, kilobytes, or megabytes. Compared to small files, large files fill up storage space more quickly, require longer transmission times, and are more likely to be stripped off e-mail attachments by a mail server. Your computer keeps track of the date that a file was created or last modified. The file date is useful if you have created several versions of a file and want to make sure you know which version is the most recent. Comprehension сheck. Mark the following statements as True or False. 1. When you create a file, you should give it a proper name according to file-naming conventions. 2. Windows limits the length of file names up to 265 characters. 3. Users must store a file in a folder to appoint it a place in a hierarchical structure of folders and files. 4. Operating systems add special significance to certain symbols that you should avoid in file names. 5. A file extension is a compulsory file identifier separated from the file name by a period. 6. The device letters for the floppy and hard disks are standardized. Vocabulary practice 1. Match up the words that are similar in meaning.
2. Fill in the blanks choosing out of the variants given. 1. A valid file requires adhering to specific rules called file-naming … . a) conditions b) conventions c) conversions d) contents 2. Drive letter, folders, file name and extension restrict the whole file path which is referred to as a file … . a) location b) identification c) specification d) format 3. A list of files for each storage medium is defined as a … . a) scheme b) directory c) modification d) application 4. … e-mail addresses, a valid file name may contain spaces. a) instead of b) compared to c) like d) unlike 5. A native file format is supported by most …, e. g. .doc for MSWord. a) processors b) hardware c) software d) servers 6. A character generally following a device letter is a … . a) backslash b) period c) asterisk d) colon 7. If a user wants to find the most recent version of a created file, the file … will be useful. a) name b) size c) date d) extension 8. The file format means the … of data and a coding scheme representing the data. a) management b) attachment c) appointment d) arrangement 9. To pad storage space, files of a bigger size require … time than small file a) more b) less c) higher d) lower 3. Make two -word combinations using the words in columns and then fill in the gaps in the following sentences. A: root B: words maximum sensitive application attachments file directory e-mail formats reserved program case length 1. Some operating systems which allow you to use uppercase and lowercase letters in file names are not … . 2. Large files can be easily stripped off … by mail server. 3. Graphical files and files containing text are saved in different … . 4. A … of file names is restricted in file-naming conventions. 5. The … is the main directory of a disk. 6. A file with the relevant extension for a particular … will be seen in the list of files of that software. 7. There are … that represent commands or special identifiers and can’t be used alone as a file name. 4. Fill in the gaps in the text. A computer ___ is a named collection of data that exists on a storage medium, such as a hard disk, floppy disk, CD, DVD, or tape. Every file has a name and might also have a file extension. The rules that specify valid file names are called ___. These rules do not allow you to use certain characters or ___ words in a file name. A file ___ is usually related to a file format - the arrangement of data in a file and the coding scheme used to represent the data. A software program’s ___ file format is the default format for storing files created with that program. A file’s location is defined by a file ___ sometimes called a “path”, which includes the storage device, folder(s), file name and extension. In Windows, storage devices are identified by a ___ letter, followed by a colon. An operating system maintains a list of files called a ___ for each storage disk, tape, CD, or DVD. The main directory of a disk is sometimes referred to as the ___ directory, which can be subdivided into several smaller lists called subdirectories that are depicted as ___. Speaking. Discuss the following questions. What is a computer file? What are the rules for naming files? Is there a maximum length for file names? What is the purpose of folders? Why are certain characters not allowed in a file name? What are reserved words? What is the difference between e-mail addresses and file names? Are file extensions important? How can you designate a file’s location? What is the significance of a file’s size? Why is the file date useful? Text B Pre-reading. Match the English words with their Russian equivalents.
Reading. Read the text and try to guess the meaning of the words in bold. Check your variants in the dictionary. FILE MANAGEMENT File management encompasses any procedure that helps you organize your computer-based files so that you can find and use them more efficiently. Depending on your computer’s operating system, you can organize and manipulate your files from within an application program or by using a special file management utility the operating system provides. Application-based file management Applications, such as word processing software or graphics software, typically provide a way to open files and save them in a specific folder on a designated storage device. Take a look at an example of the file management capabilities in a typical Windows application — Microsoft Word. As you type the document, it is held in RAM. If you want to save the document, you click File on the menu bar, and then select the Save As option. The Save As dialog box opens and allows you to specify a name for the file and its location on one of your computer’s storage devices. The difference between the two options is subtle, but useful. The Save As option allows you to select a name and storage device for a file, whereas the Save option simply saves the latest version of a file under its current name and at its current location. If you want to save a new file without a name, your application displays the Save As dialog box, even though you selected the Save option. Windows explorer As an example of a file management utility, take a closer look at Windows Explorer, a utility program bundled with the Windows operating system and designed to help you organize and manipulate the files stored on your computer. The Windows Explorer window is divided into two “window panes” (see figure 5 on the following page). In addition to locating files and folders, Windows Explorer provides a set of procedures that help you manipulate files and folders in the following ways: - Rename - Copy. - Move. When you move a file, it is erased from its original location, so make sure you remember the new location of the file. - Delete. File management tips The following tips pertain to managing files on your computer. -Use descriptive names. Give your files and folders descriptive names, and avoid using cryptic abbreviations. -Maintain file extensions. When renaming a file, keep the original file extension so that you can easily open it with the correct application software. - Group similar files. Separate files into folders based on subject matter. - Organize your folders from the top down. When devising a hierarchy of folders, consider how you want to access files and back them up. - Do not mix data files and program files. Do not store data files in the folders that hold your software. 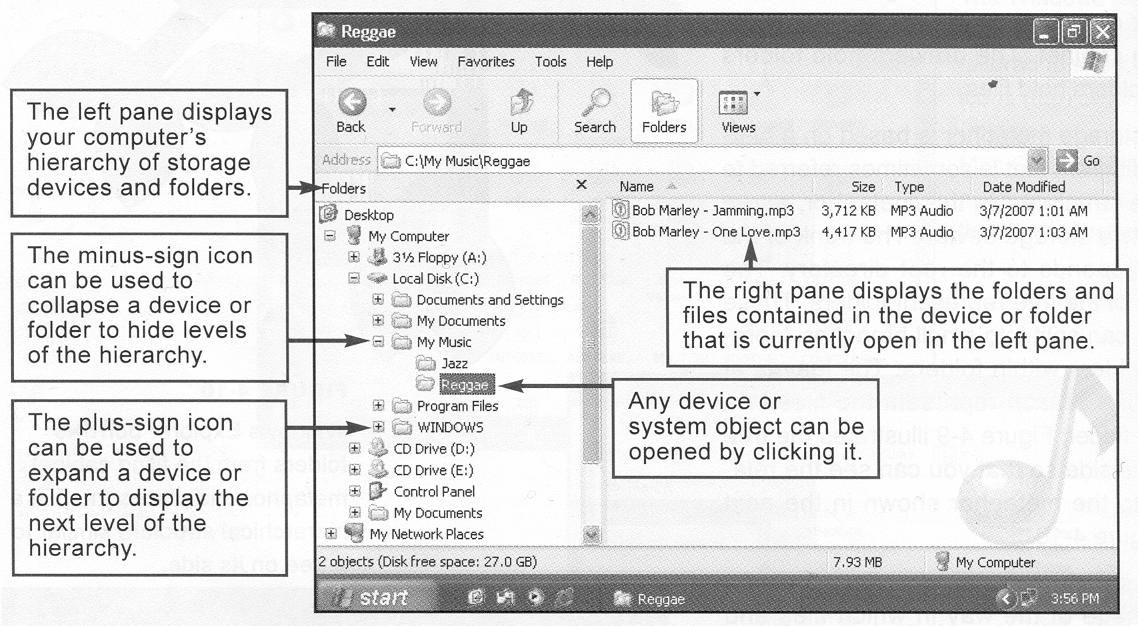 Fig. 5: The Windows Explorer window - Don’t store files in the root directory. Although it is acceptable to create folders in the root directory, it is not a good practice to store programs or data files in the root directory of your computer’s hard disk. - Access files from the hard disk. For best performance, copy files from floppy disks or CDs to your computer's hard disk before accessing them. - Delete or archive files you no longer need. Deleting unneeded files and folders helps keep your list of files from growing to an unmanageable size. - Be aware of storage locations. When you save files, make sure the drive letter and folder name specify the correct storage location. - Back up! Back up your folders regularly. Physical file storage Before a computer can store a file on a disk, CD, or DVD, the storage medium must be formatted. The formatting process creates the equivalent of electronic storage bins by dividing a disk into tracks and then further dividing each track into sectors. Tracks and sectors are numbered to provide addresses for each data storage bin. The numbering scheme depends on the storage device and the operating system. On floppy, Zip, and hard disks, tracks are arranged as concentric circles; on CDs and DVDs, one or more tracks spiral out from the center of the disk. To speed up the process of storing and retrieving data, a disk drive usually works with a group of sectors called a cluster or a “block”. The number of sectors that form a cluster varies, depending on the capacity of the disk and the way the operating system works with files. A file system's primary task is to maintain a list of clusters and keep track of which are empty and which hold data. This information is stored in a special index file. If your computer uses the FAT32 file system, for example, this index file is called the File Allocation Table (FAT). If your computer uses NTFS, it is called the Master File Table (MFT). When you save a file, your PC’s operating system looks at the index file to see which clusters are empty. It selects one of these empty clusters, records the file data there, and then revises the index file to include the new file name and its location. Comprehension check. Indicate the paragraph where the following ideas are found in the text . 1. It is preferable to maintain file extensions and not to store files in the root directory. 2. There is a slight difference between the Save option and the Save As option. 3. A special index file is required to keep track of a file’s location. 4. This program is related to the Windows operating system and exemplifies a file management utility. 5. The way to open and save a file on a specified storage medium depends on software applications. 6. Apart from locating files, it enables users to rename, copy, move and delete them. Vocabulary practice 1. Match up the words that are opposite in meaning. save distinct empty display additional include subtle erase hide basic retrieve full 2. Fill in the blanks choosing out of the variants given. 1. To make storing and finding data fast, a disk drive deals with a … which is a group of sectors. a) track b) bin c) cluster d) junction 2. You had better … cryptic abbreviations in files and folders. a) give b) avoid c) access d) accept 3. You can avoid growing your list of files to an unmanageable size by … unnecessary files and folders. a) saving b) deleting c) renaming d) moving 4. File … facilitates the process of organizing and manipulating your computer-based files. a) location b) extension c) performance d) management 5. The operating system revises the index file to … the new file name and its location. a) erase b) include c) number d) exclude 6. … a file is stored on a disk, CD, etc., the storage medium should be formatted. a) before b) after c) while d) since 7. The pattern of … tracks and sectors is dependent on the storage medium and your PC’s operating system. a) dividing b) selecting c) numbering d) arranging 3. Make three-word combinations using the words in columns and then fill in the gaps in the following sentences. A: file B: sign C: option save storage utility master management table data file bin plus as icon 1. If you want to select a name and a storage device for a file, the … should be used. 2. … are designated addresses by numbering tracks and sectors. 3. A special … provided by the operating system helps you manage your files efficiently. 4. The … is used to display the next level of your computer’s hierarchy of storage devices and folders. 5. The … is the index file supported by the NFTS file system. 4. Fill in the gaps in the text. File ___ provides any procedure that can help you organize your computer-based files so that you can find and use them more ___. File management uses tools provided with a software program to open and save files. Additional tools might enable you to ___ new files and folders, rename files, and delete them. The Save and Save As ___ boxes are examples of these file management tools. Before a computer stores data on a disk, CD, or DVD, it creates the equivalent of electronic storage ___ by dividing the disk into ___, and then further dividing the disk into ___. This dividing process is referred to as ___. Each sector of a disk is numbered, providing a storage address that the operating system can track. Many computers work with a group of sectors, called a ___, to increase the efficiency of file storage operations. Speaking. Discuss the following questions. 1. What does file management mean? 2. How does a software application help users manage files? 3. What is the difference between the Save option and the Save As option? 4. What is the example of a file management utility? 5. What is Windows Explorer designed for? 6 What can be done with the files and folders that are listed in Windows Explorer? 7. What file management tips should be followed while manipulating files? 8. What does the formatting process involve? 9. What is a cluster? 10. Is a file system’s primary or secondary task to keep track of which clusters keep data and which clusters don’t? 11. How does the operating system use an index file to help you save a file? |
