Посібник з інтенсивного навчання англійської мови (для студентів внз спеціальності початкова освіта) Частина перша Київ 2013 удк ббк
 Скачать 5.32 Mb. Скачать 5.32 Mb.
|
|
Help: Narrow path – вузька стежка Immense – величезний Frightened – наляканий Branch – гілка Jaw - щелепа 3  . Conversational Topic . Conversational Topic ‘Educational Space’ 3.1. Pre-text work. Invitation to the conversation a). Discuss the following questions:
b). Instructions for the reading: You are going to read some paragraphs about education. Skim the suggested ideas to get the understanding. Then read and translate one paragraph after another (use ‘help’ after the text and a dictionary). Retell the text, you can suggest your ideas and add the information from your own experience. 3  .2. Text A. Changes in Education .2. Text A. Changes in EducationThe world has changed, it has become technologically more developed and its different cultures and traditions have become closer to Ukraine. As a result, philosophy of education is changing too. The main task of it is to bring up a new personality both positive and open to the world. Also he should be educated enough to bring the culture of his country to the world and accept other cultures. A person should be good at computers and foreign languages as well. What for? – For having wide and profound knowledge? Meeting new friends? Working in different spheres? Discovering the world? Getting good employment, professional growth or promotion at work? Every variant is possible and leads to success. Study at university should be more motivated than before. Seek for difficulties. If you learn, for example, a foreign language, you should clearly understand a final goal and the importance of this process. You will see that it is not enough to learn some new words or grammar rules but it is more important to develop communicative skills. Try new knowledge in practice. The more you speak, the more projects you can realize. You should also acquire skills how to learn, how to adapt to changes. A great wish to socialize with people of different cultures is also typical in our time. In which way can you develop it with your friends? Lifelong learning has become a popular notion in education. This strategy is defined as an all-round learning activity in order to improve one’s knowledge, skills and professional competence. It includes: development of new basic skills for all (e.g. social skills such as self-confidence, self-direction and risk-taking); investment in human resources to create conditions for learning; innovation in teaching and learning – teachers and trainers become guides; bringing learning closer to home – to provide lifelong learning opportunities as close to learners as possible. Help: Satisfied – задоволений Enough - достатньо Knowledge – знання Suggest – пропонувати Source - джерело Profound – глибокий Paragraph – абзац Bring up – виховувати Acquire – набувати Socialize – спілкуватися Notion – поняття Competence – компетенція Opportunity – можливість Personality – особистість Employment – робота, заняття (праця) Skill – вміння Investment - інвестування LESSON TWO. Part two 4. Grammar  Practice - Grammar in use Task 1: Read, translate and write three forms of the following irregular verbs: Become, buy, come, drive, get, forget, keep, leave, say, find, speak, take, think, understand, write, build, be, begin, sit, choose, drink, give, run, lie, meet, show, spend, teach, learn, win. Task 2: Write sentences with the underlined verbs from the task 1 in the past simple and the past continuous. Task 3: Review all the learnt tenses in the table of grammar tenses given below. 4.1. Past Perfect Tense 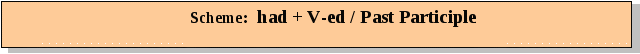 Revision 1: Study the sentences in the past perfect tense.
Revision 2: Study the situations when the past perfect tense is used.
I had done my work by 5 o’clock. I had cleaned my flat before I watched TV. When I arrived, they had finished lunch. We felt much safer after Denis had locked all the doors. He had never flown before. b) The action happened in the past. The result was also visible in the past. He had repaired his car. He could drive again. The flat was empty – everyone had gone out. He had fixed an old armchair. It looked brand new. Compare the situations presented above with those of the present perfect tense: He has repaired his car. Now he can drive again. The flat is empty – everyone has gone away. He has fixed an old armchair. Now it looks brand new.  Practice – Grammar in use Task 1: Read and translate more examples with the past perfect and other past tenses. Try to feel the situations. a). She had watered all the flowers by five o’clock in the afternoon. After she had cleaned the house, she called her friend. When Henry arrived at the theatre, the play had already started. Had they bought tickets before they left? What had you studied before you entered the University? When he arrived at the party, Ann wasn’t there. She had gone home. The man sitting next to us on the plane was very nervous. He hadn’t flown before. The house was dirty. They hadn’t cleaned it for weeks. b). - I was at the cinema. I was watching a great film when a fire broke out. Someone had dropped a match into a waste-paper basket. - By the time he arrived, I had (I’d) opened the mail; I’d sorted it; I’d answered the most important letters; I’d typed two reports and I’d made a cup of tea. - A woman walked into the room. She was a complete stranger to me. I had never seen her before. - We were driving along the road when we saw a car which had broken down, so we stopped to see if we could help. Task 2: Underline the correct tense. 1. Lynne was singing / had sung as she was cleaning the windows. 2. Jo was happy. He was winning / had won the first prize in the competition. 3. It was raining / had rained while they were playing the football match. 4. We bought / had bought the tickets before we went to the theatre. 5. She broke the glass while she was washing / had washed it. 6. People used to work / had worked very long hours in those days. Task 3: Choose the correct answer. 1. The play had started _________ we got to the theatre. A while B until C by the time 2. Tom has __________ had some good news. A still B just C yet 3. __________ did you move to Poltava? A How long ago B How long C While 4. George was washing the car __________ Sue was cutting the grass. A while B as soon as C before 5. She __________ eats beans because they make her ill. A ever B never C always 4.2. Past Perfect-Continuous Tense  Study the table of the English tenses above and grammar references. Revision 1: Study the situations when the past perfect-continuous tense is used.
She had been working on the computer for an hourbefore he came to help her. She had been writing an article since morning by the time he came. How long had you been waiting for the bus before it arrived? Had Peter been driving for two hours before he had an accident? We had been playing tennis for half an hour when it started to rain.
- At last the bus came. I’d been waiting for 20 minutes. - She was tired. (Why? Because) - She had been working hard all day yesterday. (Compare this situation with the Present Perfect Continuous: She is tired. She has been working hard all day.) - She was wet. (Why? Because) - She had been walking in the rain. (Compare: She is wet. She has been walking in the rain.) 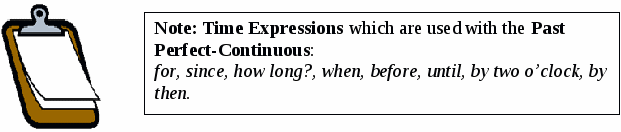 Revision 2: Compare and study the sentences with two actions in past tenses. Past simple: When Jim came, they watched a film on TV. (Jim came home and then they watched a film together – actions happened immediately one after the other in the past.) Past Continuous: When Jim came home, Mary was watching a film on TV. (She was still watching TV when Jim came home – one longer action was interrupted by a shorter one.) Past Perfect: When Jim came home, Mary had already watched the film on TV. (She watched the film first. Jim came home afterwards – a past action which preceded another past action.) Past Perfect-Continuous: By the time Jim came home, Mary had been watching the film on TV for an hour. (Mary started and finished the action in the past before Jim came – emphasis was put on the duration of an action which started and finished in the past before another past action.) Practice – Grammar in use Task 1: Put the verbs in brackets into the correct form of the past perfect-continuous. 1. Sophie ________ (paint) the walls all day before she finished her work. 2. _________ (you / wait) for long when the boss announced that he couldn’t see you? 3. Tom ________ (look) for a job for six months by the time he found one. 4. They ________ (sunbathe) for an hour when it started to rain. 5. They were tired. They_______ (discuss) business problems for an hour. 6. Jim gave up smoking two months ago. He ________ (smoke) for 30 years. Task 2: Put the verbs in brackets into the present / past perfect-continuous. 1. What you (to do) for the past two weeks until today? 2. Suddenly she understood that she (to speak) for a long time and it was time to stop. 3. He (to paint) this picture for two years and I don’t know when he is going to finish it. 4. The children (to fight) for some time when the door opened and the teacher came into the classroom. Task 3:Past Perfect or Past Perfect Continuous in this dialogue? A: Are you alright? You look tired. B: Yes, I am. I didn’t sleep very well. I ________ (just / go) to sleep last night when a lot of noise outside woke me up. I got up and went to the window. I ________ (stand) there for a few minutes when two police cars stopped outside the house. I went downstairs and a policeman told me that two prisoners ________ (escape) from prison and were hiding in the area. A: Did they catch them again? B: Yes, but I didn’t t sleep very well after that. Task 4: Complete the sentences about yourself.
5  . Supplementary reading: Discover the world with us. . Supplementary reading: Discover the world with us.You are going to read the text about Drahomanov National Pedagogical University and about Mykhailo Drahomanov himself. 5.1. Text B. Your University is Your Future. T  his year you have entered Drahomanov National Pedagogical University and you have become a student. It is a real event in your life. You have made a good step into your future. Now much will depend on your study and your attitude to it. his year you have entered Drahomanov National Pedagogical University and you have become a student. It is a real event in your life. You have made a good step into your future. Now much will depend on your study and your attitude to it.The University has a long history. It was founded as an educational establishment in 1834. Throughout the years there were changes in its name, in its status but it has always followed the traditions of preserving Ukrainian culture and national features. Now it is the university which helds a special place in Ukraine. It fulfils its main task to educate young people and prepare highly qualified specialists for Ukraine. The University is Pedagogical. During its history it has prepared more than 150 thousand teachers for work in the kindergartens, schools and universities. In accordance with the changes in the world students are being taught new methods of bringing up a new generation familiar with new technologies and open to the world. The more knowledge they get in different spheres of life and science, the better teachers they are. The University is National. It both meets the recognition from the state and guarantees the rights of its students. The university is called after Mykhailo Drahomanov. Born in 1841 in Poltava gubernia, Mykhaylo Drahomanov was a great patriot of Ukraine. He was known as a scholar, civic and political leader. All his life he was fighting for independence of Ukraine, for preserving its national treasures, culture and traditions. For his political views M. Drahomanov was dismissed from the Kyiv University. Later he moved to Switzerland and then to Bulgaria. He accepted a professorship at Sofia University. The historical-comparative method was the basis of his scholarly work. He dealt mostly with constitutional, ethnic, cultural and educational issues. Living abroad M. Drahomanov devoted his life to Ukraine, he propagated national ideas of his country. On the whole he was an ambassador of Ukraine abroad. |
