Учебник для бакалавров. Учебник для бакалавриата по направлению Юриспруденция
 Скачать 1.2 Mb. Скачать 1.2 Mb.
|
UNIT 2. THE SYSTEM OF COURTS OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATIONTEXT 1The Structure of the RF Courts (Part I) Vocabularyto reflect – отображать, отражать to interpret – интерпретировать, истолковывать, трактовать to be consistent with – согласовываться с чем-либо, не противоречить to adjudicate – судить; решать, выносить решение the court of cassation – кассационный суд the highest court of appeal – высший апелляционный суд the court of supervisory instance – суд надзорной инстанции a tier – ярус a district court – районный суд, окружной суд (в США) the implementation of domestic law – исполнение закона, действующего внутри страны legally binding – юридически обязывающий a provision of the law – положение закона fleet – флот garrison – гарнизон military formation – военное формирование anti-aircraft defenсe – противовоздушная оборона an integral part – неотъемлемая часть economic dispute – экономический спор 1. Прочитайте текст и ответьте на вопросы.How are judges appointed to all federal courts? What is the jurisdiction of the Constitutional Court? What is the jurisdiction of the Supreme Court? What is the jurisdiction of Military Courts? What is the jurisdiction of the Higher Arbitration Court? What is the extra duty of the Supreme Court and the Higher Arbitration Court? The judicial system of the Russian Federation consists of courts at the federal level and regional courts: COURTS AT THE FEDERAL LEVELThe Constitutional Court.This is the highest judicial body in the Russian Federation. It is made up of 19 judges, proposed by the President of the Russian Federation and approved by the Federation Council. Since June 2008 the Constitutional Court has been located in St Petersburg. The Constitutional Court has jurisdiction to interpret the RF Constitution; to decide whether a federal law is consistent with the country’s Constitution; and to adjudicate whether or not laws regulations and normative acts passed by the President of the Russian Federation, the Council of the Federation, the State Duma, the Government of the Russian Federation, constitutions of republics, charters and other normative acts of the subjects of Russian Federation are consistent with the Constitution of the Russian Federation; Courts of General Jurisdiction.The Supreme Court of the Russian Federation. This is the supreme judicial body for all courts of general jurisdiction on civil, criminal and administrative matters. As of today the Supreme Court consists of 123 judges. Judges for the Supreme Court are proposed by the President of the Russian Federation and approved by the upper house of the legislature, the Federation Council. The Supreme Court is located in Moscow. It has jurisdiction as a court of cassation, i.e. it is the highest court of appeal in the land. It is a court of supervisory instance over the courts of the subjects of the Russian Federation and over the tier of district courts below that level. There are three chambers in the structure of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation: Judicial Chamber on Civil Cases; Judicial Chamber on Criminal Cases; and Military Chamber. The Plenary Session of the Supreme Court can issue regulations. Regulations are a unique element of the machinery for the implementation of domestic law in the Russian legal system. Enacted by the Plenary Session, they are “explanations on issues of judicial practice”, based on the overview and generalization of the jurisprudence of the lower courts and Supreme Courts of subjects of the Federation. Regulations are abstract opinions but legally binding on all lower courts. They summarize the judicial practice of lower courts and explain how a particular provision of the law shall be applied. These regulations are employed to ensure the consistent application of Russian law by explaining how the law shall be interpreted. Regulations have their legal basis in Article 126 of the RF Constitution. Military Courts.The basic tier of military courts is the military courts of the armed forces, fleets, garrisons and separate military forces. The middle tier of military courts consists of military courts of the branches of the armed forces, the seven Military Districts into which the country is divided, and the districts of anti-aircraft defense, navy and individual armies. They consider disputes involving military personnel. Three-tiered system of the military courts is an integral part of Courts of General Jurisdiction Arbitration Courts.Arbitration courts form a system with jurisdiction over economic disputes that, as a rule, arise between companies and individual entrepreneurs, both Russian and foreign. 1.4. The Higher Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation.Judges for the Higher Arbitration Court are proposed by the President of the Russian Federation (Article 127 of the Constitution) and approved by the Federation Council. It exercises original jurisdiction over disputes between the Russian government and commercial parties, the government and subjects of the Russian Federation, or between subjects of the Russian Federation. The Plenary Session of the Higher Arbitration Court can also issue Regulations. Прочитайте утверждения и скажите, соответствуют ли они содержанию текста. Исправьте неверные утверждения.The present Russian judicial system follows the structure of courts of the USA. The Higher Arbitration Court acts only as a court of original jurisdiction. The Supreme Court is the supreme judicial body for all courts of general jurisdiction on civil, criminal and administrative matters. The Constitutional Court has jurisdiction to interpret the RF Constitution; to decide whether a federal law is consistent with the country’s Constitution; and to adjudicate whether or not laws and regulations passed by the Republics and Regions of the Russian Federation are consistent with the RF Constitution. The Plenary Session of the Supreme Court can issue laws. Military Courts consider disputes involving military personnel. There are two chambers in the structure of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation: Judicial Chamber on Civil Cases and Judicial Chamber on Criminal Cases. Regulations are abstract opinions (not decisions in exact disputes) but legally binding on all lower courts. Judges for all courts are approved by the State Duma. The judicial system of the Russian Federation consists of courts at the federal level and regional courts. TEXT 2The Structure of the RF Courts (Part II)Vocabulary to constitute – составлять a challenge – претензия, оспаривание, проблема rural – деревенский, сельский overwhelming – непомерный, подавляющий to handle – разрешать, заниматься (каким-либо делом), syn. to try, to consider petty – мелкий, незначительный a review – пересмотр, обзор 3. Прочитайте текст и ответьте на вопросы.What is the jurisdiction of Constitutional Courts (or Charter Courts) of the Subjects of the Russian Federation? What courts does the three-tiered system of courts of general jurisdiction at the regional level consist of? What disputes do courts of the subjects of the Russian Federation consider? What disputes do district courts consider? What disputes do justices of the peace deal with? What courts does the system of arbitration courts at the regional level consist of? What are the jurisdictions of all? REGIONAL COURTSConstitutional Courts (or Charter Courts) of the Subjects of the Russian Federation with the jurisdiction to interpret Regional Constitutions and Charters and decide whether local statutes are consistent with Regional Constitutions and Charters. Courts of General Jurisdiction.Courts of the subjects of the Russian Federation. These include the Supreme Courts of the Republics, the highest Courts of each Region, the Moscow and Saint-Petersburg City Courts, and the courts of autonomous districts. Courts of the subjects of the Russian Federation serve as courts of cassation and extraordinary appeal from their subordinate district courts. Their original jurisdiction constitutes challenges to normative laws and regulations of the regional authorities, and adoption of regulations. There are district courts located in the country’s smaller towns and rural administrative areas including groups of villages; cities have several courts of that kind. District courts are the basis of the system of courts of general jurisdiction, with jurisdiction over the overwhelming majority of civil and criminal cases, unless otherwise provided by law. As courts of appeal, district courts decide appeals from justices of the peace. Justices of the peace form an integral part of the system of courts of general jurisdiction, although they are considered to be regional judges. They handle minor civil disputes, petty administrative and criminal offences. Appeals against decisions of justices of the peace go to district courts, the decisions of which are final. In each district there may be several justices of the peace. Arbitration Courts.Ten Federal District Arbitration Courts act as courts of cassation. The Appellate Courts consider appeals as a rehearing with new evidence. The Arbitration Courts of the subjects of the Russian Federation consider the absolute majority of economic disputes. Объедините предложения так, чтобы получились связные высказывания.
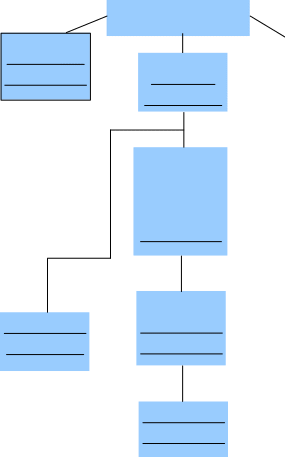 Заполните схему и расскажите о системе судов в России. Заполните схему и расскажите о системе судов в России.
 | ||||||||||||||||
