тест офтальма. тесты_ГАК_2020_офтальмология. Выпишу очки для дали оu 1,0DАлыса круге арналан кзілдірік оu 1,0D таайындаймын Prescribe him specs оu 0D
 Скачать 0.75 Mb. Скачать 0.75 Mb.
|
|
На прием обратился студент 20 лет, который плохо видит на оба глаза. Объективно: visusOD/OS = 0,3с корр.-1,0D = 1,0/0,4 с корр.-1,0D = 1,0. Ваши действия?/ Қабылдауға екі көзі нашар көретін 20 жастағы студент келді. Объективті: visus OD/OS = 0,3 корр.-1,0D = 1,0/0,4 корр.-1,0D = 1,0. Сіздің әрекетіңіз?/20-year old student came to with the symptoms of decreased vision in both eyes. Objectively: visusOD/OS = 0.3 cc-1.0D = 1.0/0.4 cc-1.0D = 1.0. What will you do? Выпишу очки для дали ОU -1,0D/Алысқа көруге арналған көзілдірік ОU -1,0D тағайындаймын/ Prescribe him specs ОU -1.0D Закапаю атропин, сделаю скиаскопию/Атропинді тамызып, скиаскопияны жасаймын/ Instill Atropine and make refractometry Выпишу очки для близи ОU-1,5D/ Жақыннан көруге арналған көзілдірік ОU -1,5D тағайындаймын/ Prescribe him reading specsОU -1.5D Порекомендую гимнастику для глаз, назначу витаминно-минеральный комплекс/ Көзге жаттығу жасауды және дәруменді-минеральды комплексті тағайындаймын/Recommendhim exercises for oculomotor muscles and vitamins Выпишу очки для постоянного ношения ОU+1,0D/Тұрақты киюге арналған көзілдірік ОU+1,0D тағайындаймын/Prescribe him contact lensesОU+1.0D На прием обратилась девушка 20 лет с жалобами на снижение зрения на оба глаза. Объективно: visusOD/OS = 0,09с корр.-5,0D = 1,0/0,07 с корр.-5,5D = 1,0. Ваша дальнейшая тактика?/ Қабылдауға екі көзі нашар көретін 20 жастағы қыз бала келді. Объективті: visus OD/OS = 0,09 корр.-5,0D = 1,0/0,07 корр.-5,5D = 1,0. Сіздің әрекетіңіз? /20-year old girl came to with the symptoms of decreased vision in both eyes. Objectively: visusOD/OS = 0.09 cc -5.0D = 1.0/0.07 cc -5.5D = 1.0. What will you do? Выпишу очки для близи ОU -5,0D/ Жақыннан көруге арналған көзілдірік ОU -5,0D тағайындаймын/ Prescribe her near specs ОU -5.0D Закапаю атропин, сделаю скиаскопию/ Атропинді тамызып, скиаскопияны жасаймын/ Instill Atropine and make refractometry Выпишу очки для близиOD-2,0D, OS-2,5D/ Жақыннан көруге арналған көзілдірік OD-2,0D, OS-2,5D тағайындаймын/ Prescribe her near specs OD-2.0D, OS-2.5D Порекомендую курсы трофической терапии 2 раза в год, контактную коррекцию/ Трофикалық терапия курсын жылына 2 рет және жанаспалы коррекцияны тағайындаймын/ Recommend her vitamins and contact lenses Выпишу очки для постоянного ношения ОU +5,5D/ Тұрақты киюге арналған көзілдірік ОU +5,5D тағайындаймын/ Prescribe her specs for constant wearОU +5.5D Что является причиной этого заболевания?/ Бұл аурудың себебін атаңыз? /What caused this condition?  Глистные инвазии/ Құртты инвазиялар/ Helminthicinfestations Дефицит витамина Д/ Д дәруменінің жетіспеушілігі/ Vitamin D deficiency Амблиопия/ Амблиопия/ Amblyopia Глаукома/ Глаукома/ Glaucoma Ячмень/ Теріскен/ Stye Какое лечение показано?/ Қандай ем көрсетілген?/ What treatment is indicated?  Обработка краев век антисептиками/ қабақтың шеттерін антисептиктермен өңдеу/ Application of antiseptics to eyelids margins Инстилляции кортикостероидов, внутрь – НПВС/ кортикостероидтарды тамызу, ішке – ҚҚСД/ Instillations of corticosteroids, oral NSAIDs Прием витамина Д/ Д дәруменің қабылдау/ Oral Vitamin D intake Лечение глистной инвазии/ құртты инвазияны емдеу/ Treatment of helmintic infestation Назначение системных антибиотиков/ жүйелі антибиотиктерді тағайындау/ Systemic antibiotics Какое осложнение можно ожидать у этого ребенка, если он не будет носить очки после операции?/Операциядан кейін көзілдірік кимесе, бұл балада қандай асқынуды күтуге болады?/ What complication might developinthischildifhedoesnotwearspecs after surgery?  Вторичную катаракту/ екіншілік катарактаны/ Secondary cataract Вторичную глаукому/ екіншілік глаукоманы/ Secondary glaucoma Увеит/ увеитті/ Uveitis Отслойку сетчатки/ торлы қабақтың сыдырылуы/ Retinal detachment Косоглазие/ қилылық/ Strabismus К вам обратилась мать с жалобой на наличие косоглазия у её семилетнейдочки. Проведя исследование бинокулярного зрения, врач обнаружил патологию. Какое исследование необходимо провести, чтобы установить диагноз?/Жеті жасар қызында қилылық барына, анасы шағымданып келді. Бинокулярлық көруді зерттей отырып, дәрігер патологияны анықтады. Диагнозды анықтау үшін қандай зерттеу қажет?/ Amothercomplainsonsquintinher 7-yearoldaughter. After a doctor tested binocular vision, he revealed a problem. What test is required for the diagnosis to be made? A. осмотр на щелевой лампе/саңылау лампасында қарау/ slit lamp test B. экзофтальмометрия/ экзофтальмометрия/ exophthalmometry C. пупиллометрия/. пупиллометрия/ pupillomtery D. исследование угла косоглазия/ қылилық бұрышын зерттеу/ testing deviation angle E. электроретинография и зрительные вызванные потенциалы/ электроретинография және көрермендік пайда болған потенциалдар/ electroretinography and visually evoked potentials 7. Какое лечение показано?/ Қандай ем көрсетілген?/ What treatment is indicated?  Системная антибиотикотерапия/жүйелі антибиотикотерапия/ Кортикостероиды, противовоспалительные – местно/ Corticosteroids, and topical anti-inflammatory drugs Противовирусные капли и мазь местно/ Topical antiviral eye drops and eye ointment Противогрибковая терапия/ Antifungaltherapy Кровоостанавливающие, рассасывающая терапия/ Hemostatics and resorption therapy 8. Какое лечение показано?/ Қандай ем көрсетілген?/ What treatment is indicated? 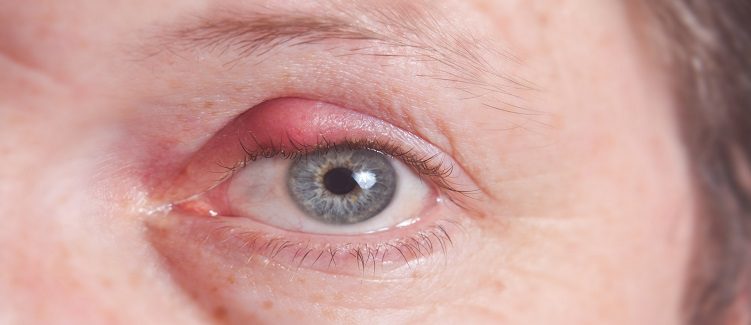 Местная антибиотикотерапия/ жергілікті антибиотикотерапия/ Topical antibiotics Кортикостероиды, противовоспалительные/ кортикостероидтар, қабынуға қарсы/ Corticosteroids, and anti-inflammatory drugs Противовирусные средства/вирусқа қарсы дәрілер/ Antiviral therapy Противогрибковые средства/ саңырауқұлаққа қарсы дәрілер/ Antifunga ltherapy Рассасывающая терапия/ сорғыш терапия/ Resorption therapy Какова этиология заболевания у этого новорожденного?/ Бұл нәрестенің ауруының этиологиясы қандай?/ What is the etiology of this disease in a newborn child? 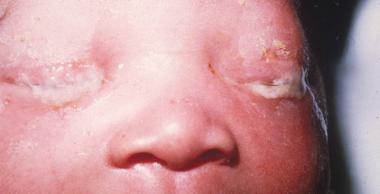 Гонококк/Гонококк/ Gonococci Стафилококк/ Стафилококк/ Staphylococcus палочка Леффлера/ Леффлер таяқшасы/ Diphtheria менингококк/ менингококк/ Meningococcus пневмококк/ пневмококк/ Pneumococcus К дежурному врачу глазного отделения обратился пациент с жалобами на резкое ухудшение зрения правого глаза. Из анамнеза: работает слесарем, обрабатывал стальную деталь на станке, что-то отлетело и ударило в глаз. Почувствовал кратковременную боль, глаз ослеп сразу. Объективно: обширное кровоизлияние под конъюнктиву в нижне-внутреннем углу глаза, на фоне которого видна рана конъюнктивы. Роговица, передняя камера глаза и зрачок не изменены, но рефлекс с глазного дна отсутствует. При пальпации глаз болезненный, мягкий. Ваша тактика?/ Көз бөлімінің кезекші дәрігеріне науқас оң көздің көруінің күрт нашарлауына шағымданып келді. Анамнезінен: слесарь болып жұмыс істейді, станокта болат бөлшекті өңдеп отырғанда, бір нәрсе ұшып, көзіне тиді. Қысқа мерзімді ауырсынуды сезіп, көзі бірден көрмей қалды. Объективно: обширное кровоизлияние под конъюнктиву в нижне-внутреннем углу глаза, на фоне которого видна рана конъюнктивы. Объективті: конъюнктиваның жыртылған жарасы көрінетін көздің төменгі-ішкі бұрышындағы конъюнктивада жайылмалы қан құйылу. Қасаң қабық, көздің алдыңғы камерасы мен қарашығы өзгермеген, бірақ көз түбінен рефлекс жоқ. Пальпациялағанда көз ауырсынбалы, жұмсақ. Сіздің тактикаңыз?/ A patient came to an ophthalmologist in charge with the symptoms of acute visual loss in his right eye. From his past history: he works as a mechanician and a steel part of the machine hit in the left eye. He felt short-term pain and his eye went blind immediately. Objective examination: extensive subconjunctival hemorrhage under localizing in the lower inner side of the eye, with visible conjunctival wound. His cornea, anterior chamber and pupil are not changed, but no red fundus reflex from is present. Eye is soft and palpation is painful. What will you do? 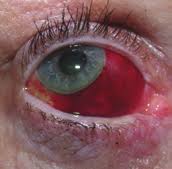 Консультация ЛОР и нейрохирурга/ ЛОР және нейрохирург кеңесі/ Refer to ENT specialist and neurosurgeon for counseling УЗИ глазного яблока/.көз алмасының УДЗ/ Оптическая когерентная томография сетчатки// торлы қабықтың оптикалық когерентті томографиясы/ Промывание слезоотводящих путей/ жас әкететін жолдарды шаю/ Исследование чувствительности роговицы/ қасаң қабықтың сезімталдығын тексеру Какое лечение показано?/ Қандай ем көрсетілген?/ What treatment is indicated? 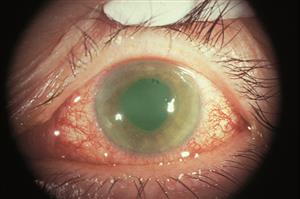 Гипотензивная терапия/ гипотензивті терапия/ Hypotensive therapy Антибиотикотерапия/ антибиотикотерапия/antibiotics Противовирусная терапия/вирусқа қарсы терапия/ Antivirals Рассасывающая терапия/ сорғыш терапия/ Resorption therapy Противовоспалительная терапия/ қабынуға қарсы терапия/ Anti-inflammatory therapy К вам на прием обратилась пациентка с жалобами на сильные боли в правом глазу и сильный туман перед глазами. Боли иррадиируют в область эпигастрия, тошнота и рвота. Объективно: застойная инъекция глазного яблока, роговица отечная, передняя камера щелевидная, зрачок черный, 5,5 мм в диаметре, на свет не реагирует. Пальпаторно Т+3. Как будете лечить?/ Сізге қабылдауға науқас оң жақ көзінің қатты ауырсынуына және көз алдында қатты тұман болуына шағымданып келді. Ауырсыну эпигастрий аймағына таралады, жүрек айну және құсу бар. Объективті: көз алмасының іркілген инъекциясы, қасаң қабық ісінген, алдыңғы камера саңылау тәрізді, қарашық қара түсті, диаметрі 5,5 мм, жарыққа жауап бермейді. Пальпаторлы Т+3. Қандай ем тағайындайсыз?/ A patient came to your office with the symptoms of severe ocular pain and hazy vision. Her pains irradiate to gastric area, she also has vomiting and nausea. At objective evaluation you established ocular congestion, hazy cornea, very shallow anterior chamber, black pupil 5.5 mm in diameter, non-responsive to light stimuli. Her eye is as dense as stone at palpation. What treatment is indicated? А. Кератопластические средства/Кератопластикалық дәрілер/ Б. Мидриатики/ Мидриатиктер/ В. Кортикостероиды местно и системно/ Кортикостероидтар жергілікті және жүйелі түрде/ Г. Гипотензивная терапия/.Гипотензивті терапия/ Д. Антибиотики в каплях и мази/ Антибиотиктер тамшы және жақпа түрінде/ Какое лечение показано?/ Қандай ем көрсетілген?/ What treatment is indicated? 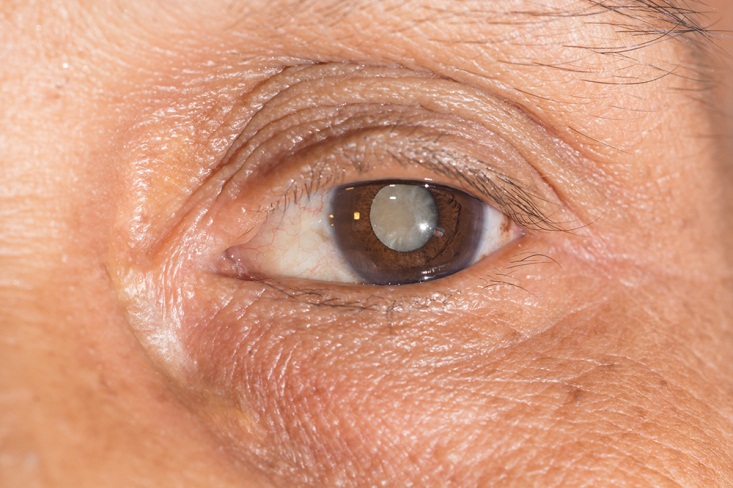 Дакриоцисториностомия/ Дакриоцисториностомия/ Синустрабекулэктомия/ Синустрабекулэктомия/ Экстракция катаракты/ Катаракта экстракциясы/ Операция по поводу отслойки сетчатки/ Торлы қабықтың сыдырылуы бойынша операция/ Удаление халязиона/ Халязионды алып тастау/ Пациент 75 лет жалуется, что все видит как в тумане. При осмотре вы установили, что глаза спокойны, роговица прозрачная, зрачок серого цвета, на свет реакция живая. Зрение снижено значительно. Пальпация глаза безболезненна, TN. Как будете лечить?/ 75 жастағы науқас бәрін тұман арқылы көретініне шағымданады. Қарағанда Сіз көздері тыныш, қасаң қабығы мөлдір, қарашығы сұр түсті, жарыққа реакциясы барын анықтадыңыз. Көру өткірлігі күрт төмендеген. Көзді пальпациялағанда ауырсынусыз, TN. Қандай ем тағайындайсыз?/ A patient 75 years of age presents with the symptoms of blurred vision. You examined her and established white eye with grayish pupil, light reactions are preserved. Her vision is significantly decreased, and ocular palpation is painless, TN. What treatment is indicated? А. Антиглаукоматозная операция/ Антиглаукоматозды операция/. Filtration surgery Б. Кератопластика/ Кератопластика/ Corneal grafting В. Дакриоцисториностомия/ Дакриоцисториностомия/ Dacryocystorhinostomy Г. Факоэмульсификация/. Факоэмульсификация/ Phacoemulsification Д. Энуклеация глазного яблока/ Көз алмасының энуклеациясы/ Enucleation of eye globe Direct ophthalmoscopy is 1.Examination of the fundus with an ophthalmoscope and a magnifying glass +13.0 D 2. Ophthalmic illumination of the sclera of the eyeball 3. Examination of the eye with a magnifying glass +13.0 D 4 Examination of the fundus with an electric ophthalmoscope 5. Examination of the fundus with a specular ophthalmoscope 2. Patient J., 30 years old, turned to the family doctor with complaints of lacrimation that appeared, especially in the cold and in the wind. What method can be used to check the patency of the lacrimal passages? 1. Collar head test (tubular and nasal) 2. Washing the lacrimal-nasal passages 3. X-ray of the lacrimal passages with contrast agent 4. Probing 5. Echography 3.A mother with a 2-month-old child turned to the polyclinic. about complaints of sticking of his eyelids after sleep, dried crusts on the eyelashes, redness of the eyes. When pressed in the area of the lacrimal sac, pus is released from the lacrimal opening. What examination is preferable in this situation to clarify the level of pathology (block)? 1.Collargol tubular test 2. Nasal collargol test 3. Washing the lacrimal ducts nat. solution 4. Contrast radiography of the lacrimal passages 5. Echography of the lacrimal ducts 4. In a patient with complaints of decreased vision, the ophthalmologist discovered a pathology of the deep optical media of the eye. What research method does NOT allow diagnosing diseases of these parts of the eye? 1. Transmitted light 2. Side lighting 3. Biomicroscopy 4. External examination 5. Echography 5 What methods are used to examine the cornea? 1. By external examination and by the method of lateral consecration 2. External inspection and transmitted light 3. Side lighting and transmitted light 4. Transmitted light and external inspection 5 Ophthalmoscopy and external examination 6 The clinical sign of damage to the optic tract is 1. Bilateral loss of the same halves of the field of view 2. Narrowing of the boundaries of the visual field (temporal, nasal, upper or lower) 3. Concentric narrowing of the visual field in both eyes 4 .. Bilateral narrowing of the boundaries of the field of view 5. Bilateral loss of opposite halves of the field of view 7 Visual acuity in a newborn, equal to 1 / ∞ p.l.c. - this is 1. Less than 0.01 2. Light perception 3.1-0.2 4.1.0 5.02-0.05 8 During the passage of the driver's commission, a young man in the study of color vision was found to have a violation of the perception of red. Make a diagnosis. 1. Deuteranomaly 2. Protanomaly 3. Tritanomaly 4. Erythropsia 5. Xanthopsia 9 A patient has a tumor of the right hemisphere of the brain. Visual acuity does not suffer. The fundus of the eye is normal. What changes will be detected in the field of view? 1. Cortical hemianopsia on the left 2. Homonymous hemianopsia on the left 3. Homonymous hemianopsia on the right 4. Bitemporal hemianopsia 5. Quadrant hemianopsia on the right 10. With campimetry, the patient showed an increase in the blind spot in both eyes. Visual acuity in both eyes = 1.0; refractive media are transparent. What is your preliminary diagnosis? 1. Pathology of the central retina 2. Congestive optic nerve head 3. Pathology of the peripheral retina 4. Retrobulbar neuritis 5. Optic neuritis (papillitis) 11 What intraocular changes are a manifestation of progressive myopia and require surgical treatment? 1. Posterior staphylomas 2. Myopic cone 3. Retinal detachment 4. Fuchs spot 5. Cataract 12. A 67-year-old patient came to see an ophthalmologist complaining of poor near vision; he has been using glasses for a long time, but he lost them a few days ago and now cannot read. He does not remember the strength of the glasses, he asks to pick up new ones. On examination: visual acuity of the right eye 0.5 s -0.5 D = 1.0, left = 0.2 s -1.75 D = 1.0. Diagnose the patient. 1. Mild myopia. Spasm of accommodation 2. Mild hyperopia. Astigmatism 3. Myopia is progressive. Presbyopia 4. Mild myopia. Anisometropia; presbyopia 5. Moderate myopia. Anisometropia. 13. D = 1 / F is the formula ... 1. Calculation of the volume of accommodation 2. Calculation of points for distance 3. Donders 4. Calculation of points for near 5. Calculation of points for presbyopia 14. A 25-year-old patient was prescribed glasses - 4.0 D for the right eye and -5.0 D for the left eye. Make a diagnosis. 1. Mild myopia in both eyes, presbyopia 2. Moderate hyperopia in both eyes, asthenopia 3. Moderate myopia in both eyes, asthenopia 4. Moderate myopia in both eyes, anisometropia 5. High myopia in both eyes, astigmatism 15.A = P - (± R) is a formula ... 1. Calculation of the refractive power of lenses 2. Calculation of points for distance 3. Calculation of points for near 4. Calculation of the volume of accommodation 5. Calculation of the stock of accommodation 16. The boy is 3.5 years old. The parents noticed the squint of the left eye from the age of 2. There was no treatment. Objectively: visual acuity of the right eye = 0.8 not corr., Left = 0.05 not corr. The left eye is constantly tilted inward, the Hirschberg angle is 20 degrees. When closing the right eye, the left one stands up straight, and its movement is in full. What treatment is NOT currently indicated for the patient? 1. Spectacle correction 2. Treatment of amblyopia 3. Orthopedic treatment 4. Surgical treatment 5. Pleoptic treatment 17. The boy is 3.5 years old. The parents noticed the squint of the left eye from the age of 2. There was no treatment. Objectively: visual acuity of the right eye = 0.5 does not correct, the left eye - 0.05 does not correct. The left eye is constantly deviated inward, the Hirshberg angle is 20º. When closing the right eye, the left one stands up straight, and its movements are in full. Make a preliminary diagnosis. 1.Compatible strabismus, moderate left eye amblyopia 2 .. Paralytic convergent strabismus, high grade amblyopia of the left eye 3. B. Latent strabismus, heterophoria, moderate amblyopia of the left eye 4. Concomitant convergent strabismus, high grade amblyopia of the left eye 5. Apparent alternating strabismus, very high grade amblyopia of the left eye 18 What explains the absence of diplopia in concomitant strabismus? 1. Impaired mobility of the eyeballs 2. Equality of primary and secondary deflection angle 3.Inequality of primary and secondary deflection angle 4. Impaired binocular vision 5 Preservation of mobility of eyeballs 19 Which strabismus is more common in hyperopia? 1. Divergent squint 2. Strabismus vertical up 3. Strabismus vertical downward 4. Convergent squint 5. The combination of horizontal and vertical deviation of the eye 20. The girl is 3 years old, her mother notes that she has deviations to the nose of the OS. The acuity of the right eye = 1.0, and the left eye = 0.1 not corr. Hirshberg strabismus angle = 15º. What treatment is required first of all? 1. Surgical 2. Orthoptic 3. Pleoptic 4. Pleopto-orthoptic 5. Drug treatment 21. The patient has difficulty in nasal breathing, there are periodic oily discharge from the nose. Two days ago there were pains behind the right eye, exophthalmos. Objectively: edema and hyperemia of the eyelids, limitation of eye movement, pain. What treatments and tests are NOT currently indicated? 1.R-graphy of the paranasal sinuses 2. Consulting otorhinolaryngologist, dentist 3. Opening and drainage of the orbit, antibacterial therapy. 4. Absorbent therapy 5. Consultations with a therapist, neuropathologist 22. During the game, the child was hit by an arrow in the left eye. Objectively: hematoma of the upper eyelid of the left eye, the sensitivity of the eye is reduced, ptosis, the palpebral fissure is narrowed. There is a deep wound on the upper eyelid. Exophthalmos, apple mobility is absent. Conjunctival injection of the sclera, the pupil is wide, does not react to light Refractive media are transparent. The fundus of the eye is normal. Visual acuity = 0. What structures of the orbit are damaged by the indicated clinical symptoms? 1. Nerves and vessels passing through the lower orbital fissure 2. Nerves and vessels passing through the superior orbital fissure 3. Nerves and vessels passing through the lattice openings 4. Nerves and vessels passing through the round hole 5. Nerves and vessels passing through the optic opening. 23. A patient was admitted to the regional hospital, who had weakness, chills, headache, temperature 37.8º C, runny nose, nasal congestion for 2 days. There was pain in the right eye, they began to see worse. Was treated with herbs, no improvement was observed. On examination, the doctor noted edema and hyperemia of the eyelids on the right, mild exophthalmos and limitation of eye mobility, decreased vision. The left eye is healthy. Make a diagnosis. 1. Phlegmon of the lacrimal sac on the right 2. Sinusitis, abscess of the eyelids of the right eye 3. Phlegmon of the orbit on the right 4. Pansinusitis 5. Thrombophlebitis of the orbit on the right 24. What treatment is NOT prescribed for orbital phlegmon in the acute period? 1. Large doses of broad-spectrum antibiotics i / m or i / v 2. Sulfonamides inside, i / v - 40% urotropine solution, topically drops of 30% albucid 3. When fluctuating - wide and deep incision, wound drainage with rubber turunda, dressings with hypertonic solution 4. General resorption therapy without opening the phlegmon 5. Emergency inpatient treatment 25. The patient has a fresh wound in the upper eyelid, going deep into the orbit. The visual acuity of this eye = 0.0 (from the anamnesis - was good). On examination: subconjunctival hemorrhage on the sclera, an eyeball without pathology. What is the reason for this patient's blindness? 1. Ruptured retina 2. Dislocation of the lens 3. Hemophthalmos 4. Subconjunctival hemorrhage of the sclera; 5. Damage to the optic nerve 26. A 4-year-old boy with mumps has edema, hyperemia, soreness in the outer part of the upper eyelid, the eyelid is S-shaped, the eyeball is displaced downward and inward, its mobility is limited upward and outward. The preauricular lymph nodes are enlarged and painful. Make a preliminary diagnosis. 1. Acute dacryocystitis 2. Phlegmon of the lacrimal sac 3. Abscess of the upper eyelid 4. Acute dacryoadenitis 5. Panophthalmitis 27. A newborn has a congenital narrowing of the palpebral fissure for tons of adhesions between the eyelids. Make a diagnosis. 1. Ectropion 2. Entropion 3. Ankyloblefaron 4. Simblefaron 5. Blepharophimosis 28. The patient was diagnosed with fungal canaliculitis on the right. What are the results of the study of the patency of the lacrimal duct on the right in the patient? 1. Nasal collargol test positive 2. Tubular collargol test is positive 3. Tubular and nasal collargol tests (-) 4. Tubular and nasal collargol tests (+) 5. Fluorescein test is positive 29 A child was admitted to the department who hit the back of a chair with his left eyebrow 2 days ago. Yesterday the temperature rose to 38.3 ° С, the child is lethargic, there is a swelling of the upper eyelid of the left eye. Objectively: the eyelid does not rise well, its skin is tense, hyperemic, painful on palpation along the entire length of the eyelid. From the side of the eyeball, there are no deviations from the norm. Make a complete clinical diagnosis. 1. External barley of the upper eyelid of the left eye in the stage of infiltration 2. Abscess of the upper eyelid of the left eye in the stage of infiltration 3. Traumatic edema of the upper eyelid of the left eye 4. Abscess of the upper eyelid of the left eye in the stage of necrosis 5.Internal barley of the upper eyelid of the left eye in the stage of infiltration 30. The child is 4 months old. 2 days high fever. In the first days after birth, he had discharge from both eyes and occasionally red eyes. Since yesterday, there has been redness, swelling of the eyelids and skin at the inner corner of the palpebral fissure of the left eye. Objectively: the left palpebral fissure is narrowed, edema of the eyelids, hyperemia in the lacrimal sac region, edema, pain on palpation, when pressing on this area both on the left and on the right, mucopurulent discharge from the lacrimal openings is released. Make a diagnosis. 1. Phlegmon of the lacrimal sac in both eyes 2. Dacryocystitis of the newborn in both eyes 3. Dacryocystitis of the newborn in both eyes, phlegmon on the left 4. Phlegmon of the eyelids of both eyes 5. Acute dacryocystitis of newborns in both eyes 31 A patient with trachoma has moderate infiltration and hyperemia of the conjunctiva, hypertrophy of the papillae, immature follicles; changes in the cornea: edema, infiltration and vascularization of the upper segment. What stage of the process is indicated? 1.1 stage 2. Stage 2 3.3 stage 4.4 stage 5. 1-2 stage 32. The main treatment for pterygium ... 1. Disinfecting antibacterial agents locally 2. Local cytostatic drugs 3. Instillation of corticosteroid drugs 4. Surgical treatment 5. Resorption therapy 33. In a 40-year-old woman, a medical examination found insignificant mucous discharge from the palpebral fissure, on the conjunctiva of the eyelids, a small amount of light gray translucent grains (follicles) and a large number of linear white stripes, located unevenly, some parts of the conjunctiva are hyperemic and edematous. Make a diagnosis. 1. Trachoma 1 tbsp 2. Trachoma 4 tbsp 3. Trachoma 2 tbsp. 4. Trachoma Z Art. 5. Paratrachoma 34 The boy was again brought to the appointment with complaints of itching in the eyes, pronounced tearing. Objectively: the upper eyelids of both eyes are thickened, the palpebral fissure is narrowed. On the mucous membrane of the cartilage of the upper eyelid, tuberous growths of tissue are visible, the conjunctiva is hyperemic. Make a clinical diagnosis and prescribe treatment. 1. Acanthomebic keratoconjunctivitis; alomide or lecrolin drops, spersallerg 2. Spring Qatar; antihistamines - drops, ointments, general therapy 3 .. Adenoviral conjunctivitis; antiviral agents (general and local); 4. Morax-Axenfeld conjunctivitis; zinc drops 0.5-1%, 1-5% zinc oxide ointment 5. Polynous conjunctivitis; alomid or spersallerg in drops, immunotherapy 35 When examined in kindergarten, three children from the group were found on the conjunctiva in the lower fornix numerous translucent grains (follicles). The mucous membrane around is not hyperemic. Your diagnosis. 1. Allergic conjunctivitis 2. Herpes of the conjunctiva 3. Folicullosis of the conjunctiva 4. Adenoviral conjunctivitis 5. Suspected trachoma 36. A 18-year-old patient is discharged from the hospital after treatment for keratitis of the right eye. Objectively: the eye is calm, a rounded opacity is visible in the optical zone of the cornea, through which the pupil is not visible, 3x3 mm in size, the visual acuity of the eye is 0.01 not corr. There is no corneal sensitivity. Make a diagnosis by classification. 1. Acute herpetic deep discoid keratitis of the right eye 2. Cicatricial opacity of the cornea such as the spot of the right eye 3. Acute metaherpetic deep keratitis of the right eye 4. Cicatricial opacity of the cornea such as the eyesore of the right eye 5. Acute bacterial deep keratitis of the right eye, corneal ulcer 37. A 5-year-old girl was admitted to the department, she was thin, her face was pasty. Mom the girl suffers from tuberculosis. The child's eyes turned red for about a week and photophobia appeared. Directed for inpatient treatment. Objectively: in both eyes there is a pronounced mixed injection, with a dark purple tinge outward from the cornea, the sclera in this area is painful when palpated through the eyelid. What is your presumptive diagnosis? 1. Scleritis of tuberculous etiology 2. Keratitis of tuberculous etiology 3 Iridocyclitis of tuberculous etiology 4. Keratoscleritis of tuberculous etiology 5. Keratoconjunctivitis of tuberculous etiology 38. A boy growing up without parents complains of poor distance vision. and on examination, you notice a pericorneal injection of both eyes, the cornea is cloudy, does not shine, its sensitivity is preserved. Against the background of turbidity, vessels are visible, which are rectilinear, almost without branching and without anastomosing each other, go from the periphery to the center. Make a diagnosis. 1. Deep diffuse herpetic keratitis 2. Deep diffuse tuberculous keratitis 3. Parenchymal syphilitic keratitis 4. Scrofulous keratitis 5. Flictenular keratitis 39. What is NOT related to the complications of a purulent corneal ulcer? 1. Corneal perforation 2. Endophthalmitis 3. Panophthalmitis 4. Purulent iridocyclitis 5. Trichiasis, madarosis 40. A 4-year-old girl was brought in for photophobia, lacrimation and blepharospasm, more pronounced on the left. The day before, I had acute respiratory infections. On the surface of the cornea there is a dull, rounded opacity located in the optical zone, rough, like a thorn. The sensitivity is sharply reduced. The cornea is not stained with fluorescein. Diagnose: 1 Avitaminosis A, corneal keratomalacia 2. Acute neuroparalytic deep keratitis 3. Acute tuberculous-allergic keratitis 4. Acute herpetic deep discal keratitis 5. Acute deep keratomycosis 41. The patient complained of pain in OD, decreased vision. Objectively: mixed injection of the sclera of the right eye, the cornea is transparent, large "greasy" precipitates, the pupil is narrow, the reaction to light is sluggish; iris color changed; fundus reflex weak pink; the fundus is not detailed; visual acuity = 0.1 not corr., T-1; palpation of the eye is sharply painful. A history of contact with a tuberculosis patient. What is your diagnosis? 1. Tuberculous-allergic keratitis 2. Tuberculous scleritis 3. Tuberculous metastatic keratitis 4. Tuberculous iridocyclitis 5. Tuberculous choroiditis 42. A patient suffering from chronic iridocyclitis of the right eye complains of deterioration of vision in it. Objectively: the eye is calm, somewhat smaller than the left one. The pupil is scalloped, inhomogeneously gray. T + 1. In the fundus - the optic disc is hyperemic, the borders are blurred, the retina around it is swollen. 42. A patient suffering from chronic iridocyclitis of the right eye complains of deterioration of vision in it. Objectively: the eye is calm, somewhat smaller than the left one. The pupil is scalloped, inhomogeneously gray. T + 1. In the fundus - the optic disc is hyperemic, the borders are blurred, the retina around it is swollen. Which of the following complications of uveitis does NOT explain the visual impairment in this patient? 1. Complicated cataract 2. Secondary uveal glaucoma 3. Subatrophy of the eyeball 4. Retrobulbar neuritis 5. Optic neuritis (papillitis) 43. What does NOT apply to the principles of treatment of iridocyclitis ... 1. Etiotropic therapy (general and local) 2. Mydriatics 3. Corticosteroid therapy 4. Dry heat 5. Pathogenetic therapy 44. The boy complains of watery eyes, redness of the right eye. According to the parents, the child wakes up at night during the week due to pain in the eye, eats poorly, rubs the eye. Objectively: OD insignificant photophobia, weak pericorneal injection, transparent cornea, narrow pupil, sluggishly reacts to light, iris pattern is indistinct, color is darker than on the left, floating opacities in the vitreous body. Your diagnosis. 1. Acute keratitis 2. Acute dacryocystitis 3. Acute conjunctivitis 4. Acute iridocyclitis 5. Acute dacryoadenitis 45. A patient had a pain in his right eye at night, in the morning he turned to SVA. On examination: mixed injection of the eye, sharp pain on palpation, T + 3; the cornea is edematous, the iris is changed in color, the pupil is pinpoint, there are no reactions to light. There is no fundus reflex. Visual acuity = light perception. Frequent instillation of pilocarpine and reos diacarb were prescribed. An hour later, the pains in the eye and head intensified. Make a diagnosis by classification. What was required to prescribe this patient to reduce eye pressure? 1.Acute attack of glaucoma in the right eye; carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, hot foot baths 2. Angle-closure glaucoma IV "c" of the right eye; carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (general and topical) 3. Acute iridocyclitis of the right eye, secondary glaucoma; topical corticosteroids 4. Acute iridocyclitis of the right eye, secondary glaucoma; mydriatics 5. Open-angle glaucoma IV "c" of the right eye; β-blockers, prostaglandins 46. During your night shift in the surgical department, the nurse had an attack of sharp headaches radiating to the right eye. On examination, you found a narrowing of the right palpebral fissure, redness of the eye, dilated pupil that does not respond to light. On palpation, the eye is hard as a stone. Visual acuity = 0.05 Make a diagnosis according to the classification. 1. Open-angle glaucoma III "c" of the right eye 2. Angle-closure glaucoma IV "c" of the right eye 3. Open-angle glaucoma IV "a" of the right eye 4. Acute attack of glaucoma of the right eye 5. Subacute attack of glaucoma of the right eye 47. A 52-year-old man accidentally noticed that he could not see with his right eye. Visual acuity of the right eye = 0.0 and left = 0.8 does not correct. On examination: the right eye is calm, the reflex from the fundus is pink, uniform, on the fundus is a gray disc, marginal excavation. The left eye is calm. The fundus of the eye is normal. Intraocular pressure of the right eye = 32 mm Hg, left = 27 mm Hg. The anterior chamber is medium. Make a diagnosis by classification. 1. Open-angle glaucoma III "c" of the right eye, open-angle glaucoma I "c" of the left eye 2. Open-angle glaucoma III "c" of the right eye, open-angle glaucoma I "c" of the left eye 3. Open-angle glaucoma IV "c" of the right eye, open-angle glaucoma I "a" of the left eye 4. Open-angle glaucoma IV "c" of the right eye, suspicion of glaucoma of the left eye 5. Open-angle glaucoma IV "c" of the right eye, open-angle glaucoma I "a" of the left eye 48. A 60-year-old patient complains of a gradual painless decrease in vision in both eyes, within 2 years: visual acuity in both eyes = 0.4 does not correct; the field of vision is narrowed from the nasal side to 15 º from the fixation point, the optic nerve head is gray with marginal IOP excavation = 33 mm. rt. Art. The anterior chamber is medium. Make a diagnosis by classification. 1. Open-angle glaucoma ІІІ "in" both eyes 2. Angle-closure glaucoma II "in" both eyes 3. Open-angle glaucoma II "in" both eyes 4. Angle-closure glaucoma II "c" in both eyes 5. Open-angle glaucoma ІІ "c" in both eyes 49. The patient complains of periodic appearance of iridescent circles before the eyes when looking at a light bulb, blurred vision, sometimes pain in the eyes and in the head. On examination: visual acuity of the right eye = 0.7 does not correct, the left = 0.5 does not correct. The field of view of the right eye is narrowed from the nasal side to 10º, in the left - to 35º degrees from the fixation point. Disc of the optic nerve in both eyes with marginal excavation. Intraocular pressure of the right eye - 30 mm Hg, left = 41 mm Hg. Art. Make a diagnosis by classification. 1. Open-angle glaucoma II "c" of the right eye, II "c" of the left eye 2. Open-angle glaucoma III "c" of the right eye, III "c" of the left eye 3. Closed-angle glaucoma III "c" of the right eye, II "c" of the left eye 4. Closed-angle glaucoma III "c" of the right eye, II "c" of the left eye 5. Angle-closure glaucoma II "c" of the right eye, III "c" of the left eye 50. On examination, the doctor noticed enlargement of both eyes and cornea of the newborn. In addition, there is a scleral injection on the left eye, the cornea is cloudy, but a dilated pupil that does not react to light is visible through it. The right eye is calm, the pupil is 3 mm in diameter, its reactions are weakened. There is a general motor reaction and irritation with the light of the right eye (the left is not). Make a diagnosis. What are the tactics? 1. Congenital corneal pathology (macrocornea). Ophthalmologist consultation 2. Congenital glaucoma. Surgical treatment by an ophthalmologist. 3. Congenital macrophthalmos. Palpation tonometry. Ophthalmologist consultation 4. Congenital paresis of the third pair of FMN. Consultation with a neurologist. 5. Congenital thorn in the left eye. Keratoplasty. Ophthalmologist consultation 51. A 65-year-old patient 3 years ago had a cataract of the right eye removed. There is now a decrease in vision in the left eye. Objectively: visual acuity of the right eye = 0.05 s + 12.0 D = 0.8 and the left eye - 1.0. The right eye is calm, the anterior chamber is deep, the pupil is black, round, basal coloboma of the iris at 12 o'clock. The fundus reflex is uniform pink. The fundus of the eye is normal. The left eye is healthy. Make a diagnosis. What is the treatment? 1.Afakia of the right eye, contact lens 2. Aphakia of the right eye, intraocular lens 3. Aphakia of the right eye, keratoprosthesis (biolens) 4. Amblyopia of the right eye, occlusion 5. Artifakia of the right eye, glasses for near Мальчику 3,5 года. Косоглазие левого глаза родители заметили с 2-х летнего возраста. Лечение не проводилось. Объективно: острота зрения правого глаза =0,5 не корригирует, левого - 0,05 не корригирует. Левый глаз постоянно отклонен кнутри, угол по Гиршбергу равен 20º. При закрывании правого глаза, левый встает прямо, а движения его в полном объеме. Поставьте предварительный диагноз. Бала 3,5 жаста. Қылилықты ата-анасы 2 жасынан байқаған. Ем жасалмаған. Объективті: оң көзде көру өткірлігі = 0,5 түзетілм., сол көзде = 0,05 түзетілм. Сол көз үнемі ішке қарай ығысқан, қылилық бұрышы Гиршберг бойынша 20 градусқа тең. Оң көзді жапқанда,сол көз тура тұрады, және оның қозғалысы толық көлемде. Диагноз қойыңыз. |
