Учебное пособие. А. Н. Туполева (каи) кафедра восточных и европейских языков (вея) engineering английский язык для студентов технических специальностей учебное пособие
 Скачать 7.94 Mb. Скачать 7.94 Mb.
|
Part II1. GADGETSRead the following text and fill in the gaps. Use the words from the boxes below.
A gadget is a small technological (1) __________ (such as a device or an appliance) that has a particular function, but is often thought of as a novelty (= new thing). Gadgets are considered to be more unusually or cleverly designed than (2) __________ technological objects at the time of their (3) __________ . The origins of the word "gadget" trace back to the 19th century. According to the Oxford English Dictionary, there is anecdotal evidence for the use of "gadget" as a placeholder name for a technical item whose precise name one can't remember since the 1850s. The etymology of the word is still being (4)__________ . A widely circulated story holds that the word gadget was "invented" when ‘Gaget, Gauthier & Cie’, the company behind the construction of the Statue of Liberty (1886), made a small-scale version of the (5) __________ and named it after their firm; however this contradicts the evidence that the word was already used before in nautical circles, and the fact that it did not become popular, at least in the USA, until after World War I. Other sources cite a derivation from the French ‘gâchette’ which has been applied to various pieces of a firing mechanism, or the French ‘gagée’, a small (6) __________ or accessory.
Today, the term is widely used in a variety of (7) __________ and activities. It can refer to tools and toys, also to "smartphones", GPS navigation devices, key finders, USB toys, and radio controlled cars, etc. Some of them need (8) __________ (that may be included or may not be (9)__________ ) and some can be used on their own. Most of them are designed to (10) __________ people. Some of them are (11) __________ for children, some - for grown-ups, and some are (12) __________ specially for sick people to use. Gadgets may be cheap or cost much money. In the (13) __________ industry, "gadget" refers to computer programs that provide (14) __________ without needing an independent application to be launched for each one, but instead run in an environment that manages multiple gadgets. There are several implementations based on existing software development techniques, like JavaScript, form input, and various image formats. The earliest documented use of the term gadget in context of software (15) __________ was in 1985 by the developers of AmigaOS, the operating system of the Amiga computers (intuition.library and also later gadtools.library). It means what other technological traditions call GUI widget—a control element in graphical user interface. This naming convention remains in continuing use (as of 2008) since then. 2. INSPECTOR GADGET :o) :o) :o) Read the following text. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
activate gadgets character electronic humoristic adapted gadgets |
2. Match the names of gadgets from the box below with the gaps (1 - 15) in the text.
| ‘Ears’ ‘Springs’ ‘Top-Secret Gadget Phone’ ‘Tie’ ‘Helicopter’ ‘Respirator’ ‘Skates’ ‘Binoculars’ ‘Radar’ ‘Legs/Arms/Neck’ ‘Brella’ ‘Hands’ ‘Flower’ ‘Periscope’ ‘Siren’ |
‘Inspector Gadget’ is a (a) __________ animated television series developed in joint-venture between France, Canada, the United States, Taiwan and Japan about a clumsy, simple-witted detective named Inspector Gadget, who is a human being with various bionic (b) __________ built into his body. Gadget's arch-nemesis is Dr. Claw, the leader of an evil organization, known as "M.A.D." This was the first syndicated cartoon show from DIC Entertainment. It originally ran from 1983 to 1986 and remained in syndication into the late 1990s.
The series was a co-production between DIC Entertainment (now Cookie Jar Entertainment) in France (the main headquarters did not move to the US before 1987) and Nelvana in Canada; the animation work was outsourced to foreign studios such as Tokyo Movie Shinsha in Japan and Cuckoo's Nest Studio in Taiwan.
In 1999, it was (c) __________ into a live-action Disney film starring Matthew Broderick as the main (d) __________ and Rupert Everett as Doctor Claw.
The most commonly used gadgets are:
Gadget (1) ‘__________’: This lowers down out of his hat and over his eyes. It helps to watch objects at distance.
Gadget (2) ‘__________’: A hand holding an umbrella that comes out of his hat. It can be used as a parachute.
Gadget ‘Coat’: His trench coat inflates when he pulls one of its buttons and enables him to float — in water or in the sky.
Gadget (3) ‘__________’: Propeller blades come out of his hat and enable him to fly. Gadget has a second, "Spare" unit available in the event of failure.
Gadget ‘Cuffs’: A handcuff comes out of his forearm just above his hand.
Gadget (4) ‘__________’: Several mechanical objects can pop out of Gadget's hat. They sometimes hold various objects including a camera, a motorized fan, a spotlight, a can opener, and other useful things. Of course, there are times when they will also be holding something useless or unhelpful to the situation.
Gadget (5) ‘__________’: These parts of his body can telescope and extend to great lengths. Embedded into his left hand is a crank that can be used to retract the arm.
(6) ‘__________’: A telephone in his hand. The earpiece is in his thumb, while the mouthpiece is in his little finger. This is one of the few gadgets that is not voice activated; Instead, Chief Quimby activates it by calling Gadget. (There is also a regular telephone inside Gadget’s hat.)
Gadget (7) ‘__________’: Rollers come out of the bottom of his shoes and let him move quickly on the road. He is often very clumsy and struggles to keep his balance on the road.
Gadget (8) ‘__________’: This thing comes out of his hat, enabling him to bounce (= to jump), usually when falling head first and hitting his head against the ground. His legs can also extend with springs, which he uses often for jumping and landing.
In addition there are some other gadgets that are used by Inspector Gadget for the benefit of his mission:
Gadget (9) ‘__________’: A mechanical hand holding a big sunflower emerges from his hat and can either spray water or sleep gas towards an enemy.
Gadget (10) ‘__________’: Metal cones that deploy from his head, around his ears, allowing him to hear better.
Gadget ‘Lanyard’: A mechanical lanyard extends from his belt buckle allowing him to attach himself to various objects.
Gadget ‘Flaps’: Mechanical Flaps extend from his waist allowing him to glide smoothly, often used in conjunction with the above allowing him to attach to various forms of transport and escape precarious situations.
Gadget ‘Hat Doff’: When Gadget greets a lady, instead of doffing his hat, a mechanical hand emerges from his hat, in the hand is another hat; from this other hat emerges a second mechanical hand, which is also holding a hat. This gadget was only seen once in the film.
Gadget (11) ‘__________’: His hat opens and this thing emerges to see over high objects or when underwater. It also helps to deflect vision.
Gadget (12) ‘__________’: This thing on the Inspector’s neck becomes a lasso.
Gadget ‘Magnets’: Magnets come out of the bottom of his shoes. More often than not, the magnets end up sticking to any metallic object with a magnetic attraction, just like Captain Planet's "magnetic" personality. It is sometimes useful when attempting to avoid slipping on slippery surfaces.
Gadget ‘Mallet’: A wooden hammer held in a robotic hand that also comes out of his hat.
Gadget ‘Parachute’: A relatively small, red parachute which was used only once. He usually relies on the 'Brella.
Gadget (13) ‘__________’: A self-contained breathing mask and the only gadget that Gadget has to physically reach for and pull on as he said his "Go-Go-Gadget" command for it.
Gadget ‘Refridge-a-Gadget’: A gloved hand holding an unmarked aerosol can appears out of his hat and sprays a substance that immediately reduces the surrounding area to subzero temperatures. This gadget was only used in Gadget's Gadgets.
Gadget (14) ‘__________’: A police light and sound emerge from the top of his hat, it is used in the starting credits.
Gadget ‘Skis’: a pair of skis that extend out of the front and back of his shoes.
Gadget ‘Teeth’: Gadget's teeth deploy from his mouth and fly about.
Gadget ‘Wind Sail’: A huge wind sail emerges from his hat, which, when combined with Gadget ‘Skis’, allows him to wind sail down a snowy track.
Gadget (15) ‘__________’: It emerges from his hat and ‘feels’ the objects around.
Gadget ‘Pulley’: A mechanical hand holding a pulley on a handle emerges from Gadget's hat to allow him to travel down a gondola cable.
‘Finger’ Gadgets: There are several gadgets inside his fingers, accessed by taking the end off his finger to expose the gadget. These include a flashlight, skeleton key, laser, pen, screwdriver, drill bit, snow gun, corkscrew, water pistol, and whistle.
The Inspector can (e) __________ each of his gadgets by calling its name, "Go-Go-Gadget Arms!" (for example), but there are times when gadgets appear to be activated by reflex rather than being called. The Inspector also activates some of his (f) __________ (such as a third hand in his hat, and his extending neck) by simply thinking about it, which is accompanied by a "thinking" or "computer is busy" (g) __________ sound effect.
PartIII
(… адрес интернет-странички с видеороликами…)
1. THE LATEST TECHNOLOGY GADGETS
(02:40)
PRE-LISTENING
What is a gadget?
What latest gadgets can you name? Make a list.
Which from your list is the most important for you? Why?
Study the following words and phrases:
“to project”, “to magnify”, “(to) clip”, “magnetic field”.
WHILE-LISTENING
Watch the whole video-track and answer the following questions:
5. How many gadgets are described in the text?
Watch the video-track a part by part and answer the following questions:
00:00 – 00:47
What gadget is described?
What can you do with this gadget?
Why is it so useful?
Which synonym is used instead of the word ‘comfortable’?
How does it work? Fill in the gaps in the following text with the words you hear:
| The keyboard (1) __________ by projecting red diode laser (2) __________ through the refracting field shaped like a (3) __________ . A lens magnifies and (4) __________ the light … into any flat surface … and (5) __________ the motion of user’s (6) __________ and communicates the (7) __________ wirelessly to the receiving (8) __________ . |
00:48 – 01:10
What gadget is described?
What is its capacity?
How is it connected to a computer?
How does it work?
01:11 – 01:47
15. What gadget is described?
16. How many elements are included in this gadget?
17. What is the capacity of a clip?
18. What can you do with this gadget?
19. How is it connected to a computer?
20. How does it work? Fill in the gaps in the following text with the words you hear:
-
__________ on the pen’s tip (2) __________ a radio (3) __________ to the clip on the (4) __________ of the page. It (5) __________ the position of the (6)__________ .
01:48 – 02:32
21. What gadget is described?
22. What is its capacity?
23. What can you do with this gadget?
24. How small are the capsules inside the display screen?
25. What makes negatively charged black sides and positively charged white sides in capsules inside the display screen change their position?
POST-LISTENING
26. What gadgets shown in the track, do you think, are of great importance?
27. Why do people design gadgets?
28. What kind of gadget would you like to be designed?
2. VW TOUAREG GADGETS
(02:30)
PRE-LISTENING
What is a gadget?
What gadgets do cars usually have?
WHILE-LISTENING
Watch the whole video-track. Match the phrases from columns A, B and C in the table below to form sentences in order to answer the following question:
What can you do with the VW Touareg gadget that is shown in the track?
You can…
| A | B | C |
| set | the disposition of a virtual picture | to choose options. |
| see | the parameters | in front of your car. |
| project | temperature | while navigating your car. |
| use | the road | on the road. |
| watch | sensor display | for a driver and a passenger. |
| set | the Russian language | behind your car. |
| navigate | the virtual position of your car | of climate control. |
| use | the direction of wheels | of you car, moving along the road. |
| change | the road | on the road. |
| watch | your car | of your car. |
POST-LISTENING
Think of similar sentences about other car gadgets. What can you do with … ?
You can … .
3. THE BEST JAMES BOND GADGETS
(04:52)
PRE-LISTENING
Do you know James Bond? Do you remember any of films with him? Do you remember any of gadgets that he used?
Do you know the following words and phrases:
“mission”, “to crack”, “a missile”, “spectrum”, “a gun”, “space”,
“to discover”, “to prevent”, “to break out”, “to accompany”,
“to identify”, “to seize a control”, “water supply” .
WHILE-LISTENING
Watch the whole video-track and answer the following question:
How many gadgets that were used by James Bond are described in the text?
What are they?
Watch the video-track a part by part and answer the following questions:
00:00 – 00:20
How did James Bond complete his missions?
What helped James Bond to complete missions?
00:21 – 00:25
Complete the following sentence with the words you hear:
| Let’s take a (1) __________ at some of the (2) __________ Bond (3) __________ and how they were worn over the last (4) __________ years. |
00:26 – 01:05
Complete the following with the words you hear:
… Early car (1) __________ had been around for (2) __________ years. But these were essentially (3) __________-wave (4) __________ with the (5) __________ to the existing lane-line grid because it (6) __________ in the same spectrum as most ‘walky-talkies’. …
When did car phones become commercially available?
01:06 – 01:47
Complete the following with the words you hear:
… The safe (1) __________ was the (2) __________ of (3) __________ . Real (4) __________ crackers at the time used listening (5)__________ , (6) __________and other more destructive (6) __________ . …
When and where was an auto-dialer designed?
What was the most advanced lock ever built?
01:48 – 02:08
When did ray-guns stop being simply fictional toys?
What company began manufacturing laser weapons?
02:09 – 02:27
Where is the scene of ‘The Moonraker’ set?
02:28 – 02:52
What is special about the boombox shown in the track?
When did German police discover the hand guns?
What were these hand guns like?
02:53 – 03:35
What did James Bond have to do in ‘Tomorrow never dies’?
03:57 – 04:31
What mission is James Bond completing in the film mentioned in this part of the track?
What is the name of organization that accompanies the idea of creation of implants to identify pets and human?
Watch the video-track again and complete the following table:
Fill in the gaps in the following table:
| year | gadget | name of the film | name of an actor as James Bond |
| 1963 | | | Sean Connery |
| | a safe-cracker | On Her Majesty’s Secret Service | George Lazenby |
| | laser | Moonraker | Roger Moore |
| 1987 | | The Living Daylights | |
| | a remote-controlled car | | Pierce Brosnan |
| 2008 | | Quantum of solace | |
POST-LISTENING
Which of these gadgets is/are of most importance? Why?
Which of these gadgets is/are widely used nowadays?
16. BRIDGES
Part I
Why do people build bridges? Where are bridges usually built?
Read the text quickly and choose the correct answers to the questions below. Don’t pay attention to the gaps.
-
1
Where is the text from?
a
An engineering book about bridges
b
A tourist guidebook
2
Which is the best title for the text?
a
The Clifton Suspension Bridge
b
Isambard Kingdom Brunel
| The CLIFTON SUSPENSION BRIDGE is a (1) __________ bridge which means it doesn’t open or move to allow boats through. It was (2) __________ in the 1830s by one of Britain’s greatest nineteenth-century (3) __________ , Isambard Kingdom Brunel. The bridge was actually (4) __________in the 1860s. (5) __________ analysis of the design shows that many of the ideas are almost (6)__________ . When the bridge opened it was for carriages pulled by horses but 150 years later it carries 12,000 cars and lorries a day, that’s over four million (7) __________ a year. Strange but true:
* (the text is from: “Engineering” Workshop by Lindsey White, OUP; Unit 19, pg.22, ex.2) |
Read the text again and complete the gaps with the words from the box below.
| aeroplane built computer designed engineers fixed parachute perfect pilot vehicles |
* (“Engineering” Workshop by Lindsey White, OUP; Unit 19, pg.22, ex.3)
Read the text again and find the English equivalents to the following expressions:
… что означает…
… он был разработан…
… он предназначался для…
… спустя…лет…
… в день…
…в год…
…безопасно приземлилась…
… до 70 с лишним лет…
…летевший со скоростью …
Read the text again and decide if the sentences (1-5) are true (T) or false (F).
-
1
The Clifton Suspension Bridge is a moveable bridge.
T
F
2
It was designed and built in the twentieth century.
T
F
3
The designer was a famous British engineer.
T
F
4
The design of the bridge is very good.
T
F
5
Pilots fly under the bridge every day.
T
F
* (“Engineering” Workshop by Lindsey White, OUP; Unit 19, pg.22, ex.4)
Look at the diagram below and write the dimensions in the correct places.
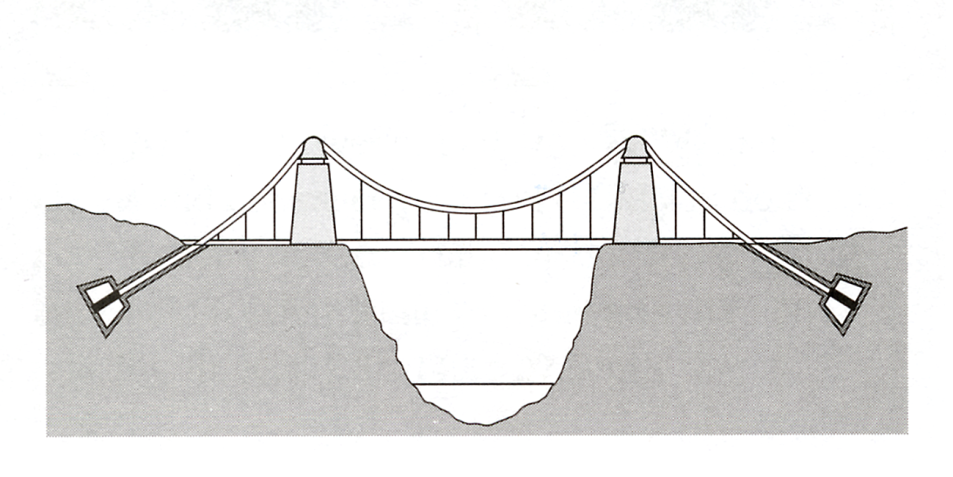 | Dimensions: span - 214m height above the river - 75m height of towers - 26m |
* (“Engineering” Workshop by Lindsey White, OUP; Unit 19, pg.22, ex.5)
Look at the words in the box below. Check the meaning of any new words in the glossary. What do you think the next text will be about?
| bridge collapse cracked disaster enquiry killed substandard |
* (“Engineering” Workshop by Lindsey White, OUP; Unit 20, pg.23, ex.2)
Read the following text. What is it about?
| The TAY BRIDGE in Scotland was designed and built by Sir Thomas Bouch in the nineteenth century. The bridge, which was over 3km long, opened in 1878 and fell down in a winter storm in 1879. A train carrying 70 people was on the bridge at the time and all people were killed. There was an enquiry into the Tay Bridge disaster to find out why the accident happened. One of the conclusions was that the design and construction were based on how quickly and cheaply it could be built; safety and strength were not thought about properly. Another conclusion was that it was a very cold winter and the iron may have cracked when it contracted. Also, the design was based on experience rather than the more scientific and accurate calculations used today. During the twentieth century engineers used computers to do a detailed structural analysis of the design used for the Tay Bridge. The results confirm that the design of the bridge was definitely substandard. * (the text is from: “Engineering” Workshop by Lindsey White, OUP; Unit 20, pg.23, ex.3) |
Read the text again and find the English equivalents to the following expressions:
…был разработан и построен …
… длиной свыше … километров …
… в это время …
… чтобы выяснить …
… были основаны на …
… следующий вывод …
… научный и точный расчет …
… детальный структуральный анализ …
… результаты доказывают, что …
… абсолютно непригоден …
Now find the English equivalents to the following phrases. Mind that the phrase given can easily replace the phrase used in the text without any change in meaning:
… to get to know…
… the reason of the accident…
… spending less money…
… were forgotten …
… absolutely not acceptable …
Read how the Tay Bridge collapsed. Match the sentences (1-5) with the diagrams (a-e) below.
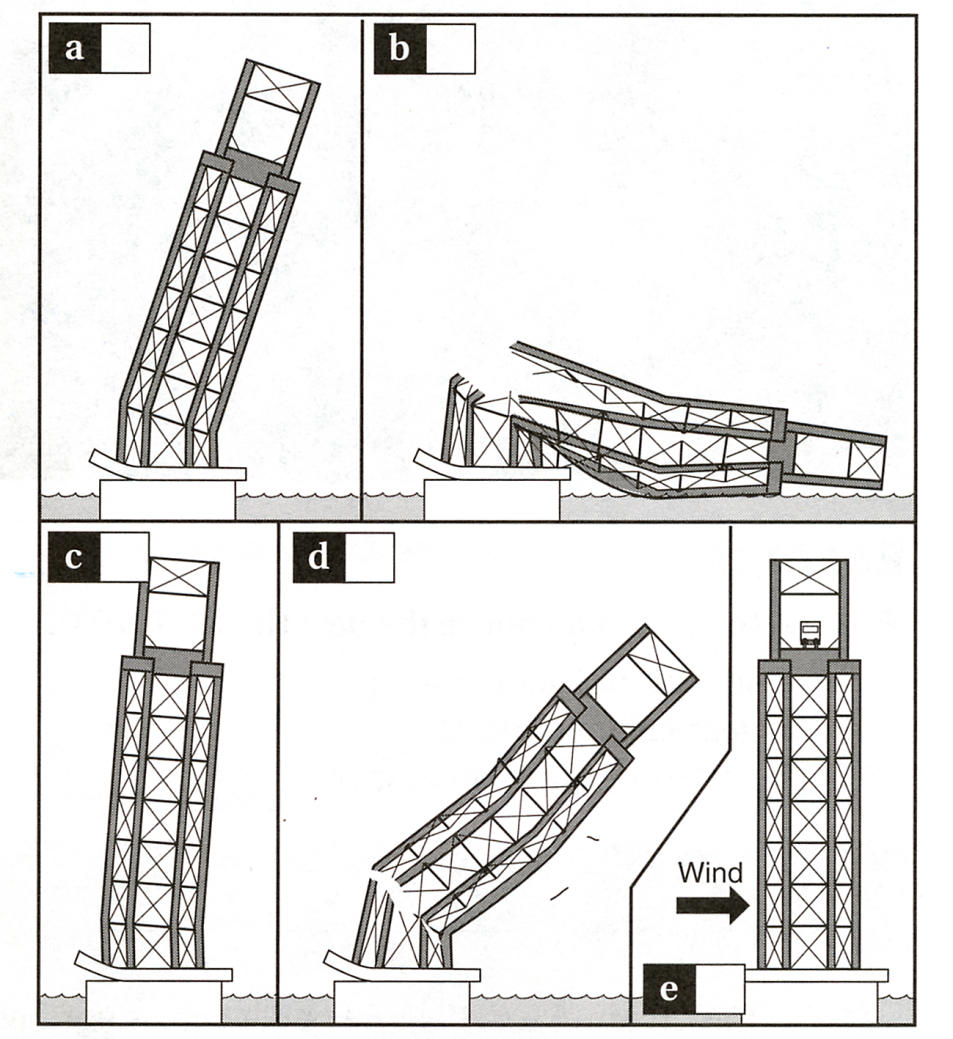 |
|
* (“Engineering” Workshop by Lindsey White, OUP; Unit 20, pg.23, ex.4)
12. Match the following words with their definitions (1-10).
| disaster analysis bridge to crack girder span height to collapse enquiry dimension |
| 1 | The measurement from the bottom to the top. | |
| 2 | A structure that carries a road or railway across a river. | |
| 3 | The length of something from one end to the other. | |
| 4 | The careful examination of the different parts or details of something. | |
| 5 | To fall down or break into pieces suddenly. | |
| 6 | To break or to make something break so that a line appears on the surface without breaking into pieces. | |
| 7 | An event that causes a lot of harm or damage; terrible situation. | |
| 8 | A question or number of questions that you ask about something in order to get more information. | |
| 9 | A long heavy piece of iron or steel that is used in bridge (or building) construction. | |
| 10 | A measurement of the length, width or height of something; the size of something. | |
Match the following words:
-
construction disaster calculation of tower the design
on experience direction designed bridge(x3) analysis (x2) dimensions
| 1 | moveable | | | 8 | 2 or 3 | |
| 2 | height | | | 9 | be based | |
| 3 | accurate | | | 10 | opposite | |
| 4 | detailed | | | 11 | suspension | |
| 5 | analysis of | | | 12 | structural | |
| 6 | bridge | | | 13 | fixed | |
| 7 | was | | | 14 | natural | |
Answer the following questions about bridges in the texts above:
| 1. | What are the main dimensions of a bridge? |
| 2. | What kind of bridge is the Clifton Bridge? |
| 3. | What does the word ‘fixed’ mean? |
| 4. | Which word is the opposite to the word ‘fixed’? |
| 5. | What should be done before the beginning of a bridge construction? |
| 6. | What happened to the Tay Bridge construction? |
| 7. | What does the word ‘substandard’ mean? |
| 8. | Why did the Tay Bridge in Scotland collapse? |
| 9. | What do we call such events as the Tay Bridge collapse? |
| 10. | What was organized after the Tay Bridge collapse? |
| 11. | What was the aim of this enquiry? |
| 12. | What were the conclusions of the analysis of the Tay Bridge disaster? |
| 13. | What may happen to people during a disaster? |
| 14. | What are girders usually made of? |
15. Translate the following sentences into Russian. Translate the idea, not a word for word:
| 1. | Let’s check your height and weight. |
| 2. | The height of this bridge is about 50m. |
| 3. | Some people are afraid of height. |
| 4. | The height of this building is over 75 metres. |
| 5. | What is the height of this construction? |
| 6. | The height is one of 3 dimensions of an object in space. |
| 7. | Where is the Clifton Suspension Bridge situated? |
| 8. | How long is the Clifton Bridge? |
| 9. | How many bridges over Kazanka river are there? |
| 10. | What is the span of the Millennium Bridge in Kazan? |
| 11. | What is the span of wings of this bird? |
| 12. | Find out the span of this bridge and write it in the correct place on the picture. |
| 13. | Send this water to the laboratory for analysis. |
| 14. | This plastic should be sent for analysis. |
| 15. | A group of highly-skilled engineers were asked to do a professional analysis of the bridge construction. |
| 16. | The equipment was not of good quality and was sent for analysis. |
| 17. | Analyse the situation and design a solution. |
| 18. | A lot of buildings collapsed during the earthquake. |
| 19. | There was a collapse of the motorway bridge 2 days ago. |
| 20. | Suddenly the construction collapsed. |
| 21. | At first constructions crack and then crash. |
| 22. | A crack could be seen on a wall of the building. |
| 23. | Plastic may crack in cold. |
| 24. | Metal contracts in cold. |
| 25. | Earthquake is a natural disaster. |
| 26. | Always put on your safety equipment at work in order to avoid the disaster. |
| 27. | The fall of the Tay Bridge in Scotland was a serious disaster. |
| 28. | Accurate calculations must be done in order to prevent disaster. |
| 29. | I’d like to make an enquiry about the place of a welder. |
| 30. | Before you start a course you should make an enquiry about it. |
| 31. | Make an enquiry into the Internet resources. |
| 32. | Girders are normally used in constructions. |
| 33. | What are girders made of? |
| 34. | Girders in a construction may crack if accurate calculations were not done properly. |
16. Translate the following sentences into English. Translate the idea, not a word for word:
| 1. | Этот мост был построен в 1950 году. |
| 2. | Этот мост был спроектирован известным инженером. |
| 3. | При проектировании этого здания научными расчетами занимались высококвалифицированные специалисты. |
| 4. | До начала строительства этого здания был проведен детальный анализ. |
| 5. | Для проведения детального анализа сегодня используют компьютерные технологии. |
| 6. | В Санкт-Петербурге много «подвижных» мостов. |
| 7. | «Разводные» мосты строят для того чтобы пропускать судà. |
| 8. | «Подвесной» мост является разновидностью мостов. |
| 9. | Протяженность этого моста составляет более 3х километров. |
| 10. | Неожиданно здание рухнуло. |
Check the knowledge of active vocabulary from this module with the help of
“ACTIVE VOCABULARY” section.
