Английский язык
 Скачать 1.02 Mb. Скачать 1.02 Mb.
|
POST-LISTENING1. Consider the following points. Share your ideas with a partner or a small group. Be prepared to explain your answers to the class.a) How could Ambrose Harper’s importance in the company be defined? b) What are the advantages of J.Martin’s membership in the Board? c) What do the Rules of Association drawn up by Harper and H.G.’s father state? d) What are the reasons for Wentworth to be invited to join the board? e) Prove that John Martin would be a useful counter to Wentworth. 2. Recount the situation as if you were Hector Grant. 3. Suppose you are Alfred Wentworth, are you satisfied with the situation in Harper & Grant Ltd. and the number of its shares you own? What do you plan for the future? 4. Give a lecture on the structure of the share capital in Harper & Grant Ltd. before and after Ambrose Harper’s death. (See Illustration 1 below) 5. Answer the following questions as if you were William Buckhurst: a) Why should the accounts be done every month in your opinion? b) What are the disadvantages of doing accounts every quarter? c) What is the essence of breaking down the activity of the company into cost centres? 6. Act out: a) a conversation between Peter Wiles and John Martin. Discuss the pro and contra of the introduction of monthly accounting by cost centres; b) a talk between Hector Grant and William Buckhurst before the Board meeting about the changes in the board that are to be made. Illustration 1 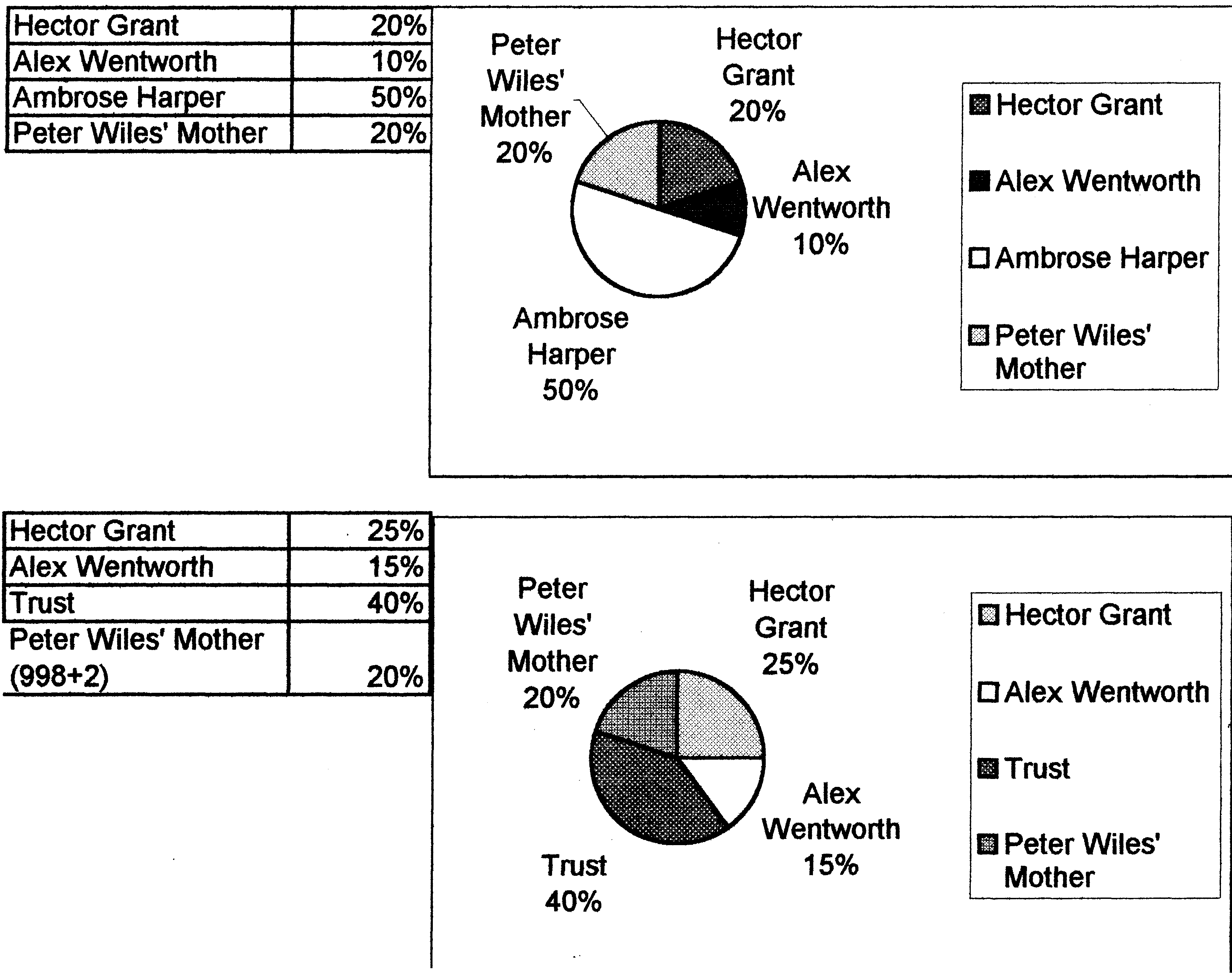
Phrase listListen to the tape and practise the pronunciation of the following words and word combinations, quote the sentences in which they are used in the unit. Consult a dictionary and translate them into Russian. to approve the accounts to ensure that somebody is reporting correctly to be in private practice to be exempt from having to publish the accounts Profit Statement (a Trading and Profit and Loss Account) Balance Sheet Director’s Report to deduct overhead charges depreciation on plant and buildings the capital employed issued share capital retained earnings fixed assets trade investments compilation of net current assets less liabilities The totals must agree. current liability stock valuation to go into things to be listed as goods paid for to find no/the record of payment to buy something on a sale or return basis to make out cheques to somebody to total up the value of the cheques to pay in the staff member’s cheques to draw out an equivalent sum of cash with the cheque a withdrawal on the bank statement a paying-in voucher for the date to be a fiddle to query the figure to draw somebody’s pay in advance PRE-LISTENING Task I Consider the introduction to the unit. Answer the following questions and be ready to give a story line. Use the word combinations in brackets. 1. What is the main task of the auditors? (to approve the accounts of a limited company; to act on behalf of the shareholders; to ensure that the directors are reporting correctly; the state of affairs of the company; to judge whether the directors are managing the company efficiently; to judge for themselves) 2. Why has H.G. changed the firm auditing the firm’s accounts? (to audit the accounts of Harper & Grant; to be in private practice as an accountant; to be appointed; a privately owned limited company; to be exempt from something; to publish accounts; to have the accounts audited by independent auditors; to be connected with the company) 3. What is W. Buckhurst responsible for? (to be Company Secretary; to be responsible for something; the period in question; to be ready for checking; to make a bad impression; the accounts department; to supply immediately any information wanted by the auditors) 4. Which three documents are in the focus of the auditors’ attention? (to be satisfied; the Profit Statement; the Balance Sheet; the Directors' Report; a Trading and Profit and Loss Account; to arrive at the profit for the year; to start with net sales or income; to deduct the cost of materials, work and overhead charges; to leave a trading surplus; depreciation on plant and buildings; auditors' fees; administration and selling costs; to produce the net profit or loss; a summarised statement; the amount of funds employed in the business; to derive the funds from some sources) 5. What does the Balance Sheet show? (to list the capital employed; the issued share capital plus reserves and retained earnings; the total cost of fixed assets; trade investments; a breakdown of net current assets; cash and stocks, plus what the firm is owed by its customers, less its liabilities; to be shown as a trade investment; a current liability; an item in the compilation of net current assets) 6. Why is stock valuation a mixed blessing? (to prepare accounts; to put a value on all goods in the hands of the company; to check against the suppliers' invoices; the value of commodities; to fluctuate; a company's stock; work in progress; finished stock; the volume of all stock is changing daily, if not hourly; to be taken at cost price or market price, whichever is the lower) Task 2Give the English equivalents for the following word combinations:
LISTENING Exercise 1 You are going to hear a talk between William Buckhurst and Mr. Brent. Before you listen to the conversation look at these statements, which you will mark T (True) or F (False) after you have listened to the tape.
|
