Учебное пособие по разговорному английскому языку для студентов всех специальностей неязыкового вуза
 Скачать 4.24 Mb. Скачать 4.24 Mb.
|
|
Read the words and say what parts of speech they belong to.   ʼExport – to exʼport; ʼimport – to imʼport; ʼincrease – to inʼcrease; ʼindustry – in ʼdustrial; ʼproduct – proʼduction. Match up the words which have a similar meaning. to obtain; to manufacture; to receive; to produce; district; products; goods; expansion; region; extention. Produce word-combinations.
7. Give Russian equivalents. Car industry, state budget, extreme expansion of the military sector, coal deposits, variety of mineral resources, have greatly increased, last decades, to obtain independence, cotton industry, everything one needs in life, to provide employment, all over the world. 8. Translate the sentences into Russian.   1. After the Second World War Great Britain has lost almost all it’s colonies. 2. During the last decades there has been a great change in the structure of British industry. 3. Now British export of machinery and electrical goods has increased greatly. 4. Many of new branches of industry have developed in the last decades. 5. One-third of the state budget has been developed to arms expenditure. Complete the sentences with English words instead of their Russian equivalents. 1. The country (известна) its car industry. 2. Clydeside and Belfast (известны) their ship-building. 3. There is no (разнообразия) of mineral resources in Great Britain. 4. Today the development of British industry is destroyed by the (чрезвычайным расширением) of the military sector. 5. Military industry (получает) more state funds. 6. The main branch of British agriculture is (молочное животноводство). 7. The main (зерновые культуры) are (пшеница) and (ячмень). In each column find nouns and give their Russian equivalents.
11. In each column find adjectives and give the Russian equivalents.
Reading 12. Study the following text.   Great Britain is highly developed industrial capitalist country. It is a member of the Common Market. Before the Second World War the country was an old naval powerful state. After the war Great Britain has lost almost all its colonies, some of them feel under the influence of the USA, others obtained independence. During the last decades there has been a great change in the structure of British industry. The main British exports were coal and textiles. But now British export of machinery, vehicles and electrical goods has greatly increased. Many new branches of industry have developed: such as the production of motor cars, radio and television sets and others. There is no variety mineral resources in the country, but coal deposits take the 6th place in the world. Coal-mining is one of the oldest industries together with ship-building and cotton industries. In the centre of England there is a district called the B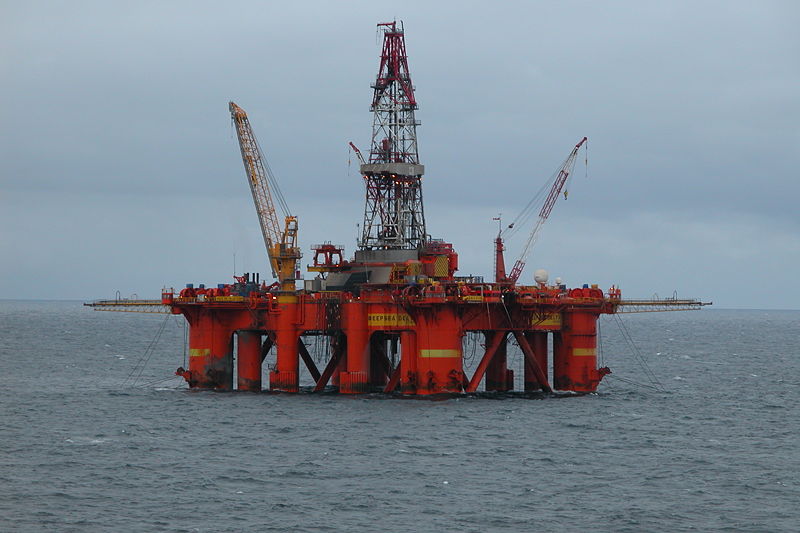  lack country. From here coal and iron are brought to many industrial cities. lack country. From here coal and iron are brought to many industrial cities.Recently deposits of oil and natural-gas have been found in the British sector of the North Sea. Production of oil from offshore wells in the North Sea began in 1975, and the country is self-sufficient in petroleum. Other mineral resources include iron ore, tin, limestone, salt, china clay, oil shale, gypsum, and lead. The country's main exports are manufactured goods, fuels, chemicals, food and beverages, and tobacco. The main imports are manufactured goods, machinery, fuels, and foodstuffs. The United States, Germany, France, and the Netherlands are the main trading partners, and the Commonwealth countries are also important.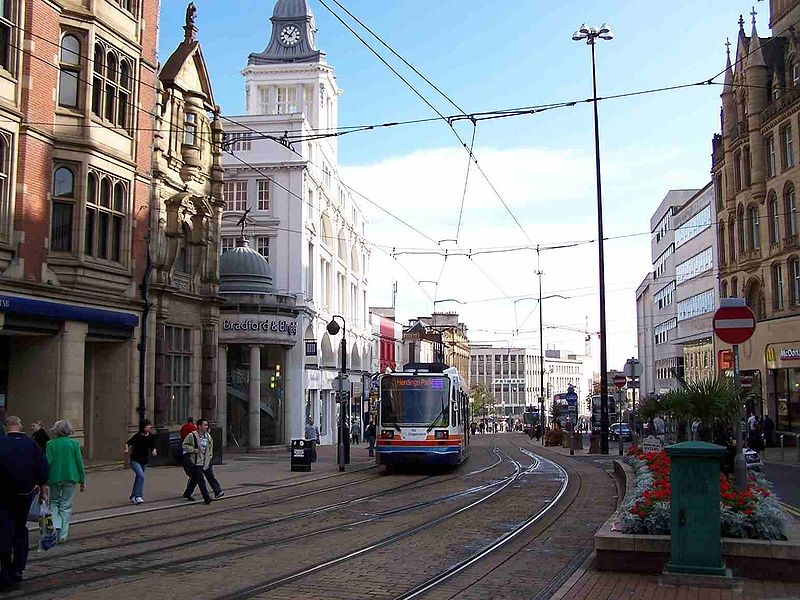  Britain has a large and sophisticated service sector. The service industries include finance, retailing, wholesaling, tourism, business services, transport, insurance, investment, advertising, public relations, market research, education, administration, and government and professional services. Telecommunications has become a dynamic growth industry, particularly with telex, facsimile, and e-mail communications Britain has a large and sophisticated service sector. The service industries include finance, retailing, wholesaling, tourism, business services, transport, insurance, investment, advertising, public relations, market research, education, administration, and government and professional services. Telecommunications has become a dynamic growth industry, particularly with telex, facsimile, and e-mail communicationsSheffield is the centre of steel industry. Everything one needs in life is manufactured in Birmingham. Manchester is a textile centre. Liverpool is an important part as well as London. Clydeside and Belfast are famous for their ship-building. Today the development of British industry is destroyed by the extreme expansion of the military sector in it. One-third of the budget has been devoted to arms expenditure. Military industry receives more state funds. Four-fifth (4/5) of the land is devoted to agriculture. It provides employment for more than 1 million people. The main branch of British agriculture is dairy-farming. Milk and milk products are famous all over the world. The main grain crops are wheat and barley. But a number of agricultural products is still imported. 13. Enumerate the main industries developed in Great Britain. 14. Scan the text. Name the cities mentioned in it. 15. Find in the text English equivalents for the following words and word-combinations. Разнообразие; все, что необходимо в жизни; зерновые культуры; наряду с; электротовары; уголь и железо; доставляют; член общего рынка; потеряла почти все колонии; молочные продукты; высокоразвитая промышленная капиталистическая страна; 4/5 земли отводится сельскому хозяйству; получили независимость; получает большие государственные фонды; большие изменения в структуре промышленности. 16. Make up sentences.
17. Answer the questions. 1. Is Great Britain a highly developed industrial country? 2. Is Great Britain a member of the Common Market? 3. What were the main British exports? 4. What are the new branches of British industry? 5. Is there a variety of mineral resources in the country? 6. What are the main industrial centres of the country? 7. What is the main branch of British agriculture? 8. Is a number of agricultural products imported to the country? 18. Complete the following sentences. Great Britain is a member of … 2. Some of the former British colonies obtained …. 3. The main British exports were … 4. One-third of the budget has been devoted to … 5. The development of British industry is destroyed by… 6. Four-fifth of the land is devoted to … Speech practice 19. Ask questions and give answers according to the model. Model: What’s the city Model: As far as I know, that city is of Manchester known for? the biggest centre of textile industry. Liverpool Clydeside Birmingham a ship-building centre a large industrial centre an important port 20. Read the dialogues in pairs, noting the most essential patterns of asking and accepting help.   This is the dialogue between Anna Smirnova, a Russian teacher of English, and Bernard Law, a London University lecturer. Anna is leaving London for Edinburgh next Saturday morning. Anna: Bernard, could you do me a favour? Bernard: Yes, sure. I'll be glad to if I can. A.: Next Saturday morning I'm going to Edinburgh by car. What cities would you advise me to see on my way there? В.: Well, it's going to be a long journey. When are you expected in Edinburgh? A.: Next Tuesday afternoon. В.: Then you should try to see Northern England with Manchester, Leeds and Bradford and Midlands with Birmingham, Coventry and Sheffield. They are the most northwest industrial cities. A.: Do you know what they are famous for? В.: Well, the wool industry is centered in Bradford and Leeds. Other industries of these cities include the making of locomotives, agricultural implements, heavy iron and steel goods of all kinds, chemicals, glass, leather goods, artificial silk and pottery. A.: And what about Manchester? В.: You see, it's the centre of cotton industry with a population of nearly one million. The University, of Manchester, founded in 1880, is famous for its modern studies. A.: Ah... that's worth knowing. And I've heard that the district of Birmingham is known as the Black Country. Is it really so heavily industrialized? В.: Oh, sure. It is a land of factories and mines and it owes its importance to iron industry. Iron goes to the steel, heavy machinery and shipbuilding industries of Newcastle and other cities. A.: I wonder do they transport all these goods to other cities and countries? As far as I know Birmingham doesn't have outlet on the sea-coast and doesn't stand on any great river. В.: You're right. The nearest port is Liverpool - the main port of western England. It is first in Great Britain in export and comes second after London in imports. But most of the goods are transported to London and then distributed to different parts of the world. A.: Oh, I'm afraid I've taken up too much of your time. Thank you very much. I really appreciate your help. 21. Speak about: а) the industrial cities of Great Britain Sheffield - steel industry; Manchester - textile industry; Clydeside and Belfast - ship-building industry; London and Liverpool - important ports; Birmingham - the city of 1500 industries. b) agriculture agriculture – 4/5 of the land; main branches – dairy-farming; wheet and barley; milk and products; employment – one million people; a number of products – to be imported. c) the main branches of industry old industries – coal, textile; ship-building; main deposits – coal and iron; new branches – motor cars, radio and television sets; today exports – machinery, electrical goods, vehicles. 22. Suppose you are to give a lecture on the current state of British economy.   I will concern myself with... I will try to outline briefly some recent data on... This is an attempt to introduce you to the... I will speak about.. 23. Role play. The group of students is divided into two teams. The first one represents businessmen from England, Wales and Scotland. The other one - journalists from Russia. They are interviewing the businessmen about the industries developed in their countries. Check list to module III Is Great Britain situated on an island or on the continent? How many parts does Great Britain consist of? By what is Great Britain separated from the continent? The climate of Great Britain is mild owing to the warm Gulf Stream, isnʾit? What do we call a group of islands situated to the northwest of Europe ? What are the most important rivers in Great Britain ? What industrial cities of Great Britain do you know? What are the capitals of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland? 9. What is the name of the Queen of Great Britain? 10. What parties are there in Great Britain? 11. Is the United Kingdom rich in mineral resources? 12. Give the names of 1) the longest river, 2) the highest mountain, 3) the largest lake, 4) the largest city outside London. 13.What is the name of the English state flag? 14.Where are most of the government offices situated in London? 15.Why is a district in the centre of England called The Black Country? 16.What is the name of one of the biggest textile industry centers in England? Module IV London – the capital of Great Britain Vocabulary training Read and remember the following words and word-combinations. 
2.Practice the reading of the proper names.
3. Find the synonyms. Fine; ancient; vast; commercial; to edit; to mean; old; enormous; to publish; trade; artisan; occupant; handicraftsman; invader; wealthy; rich; to signify; beautiful. 4. Form the derivatives.  
5. Produce word-combinations. ancient: castle, city, manuscript, church. wealthy: people, family, district. original: name, language, tradition. fine: theatre, palace, city, concert hall. commercial: centres, part, people, business. historical: place, associations, part, museum, building. fashionable: part, restaurant, mansion, apartment. 6. Read and translate the following word-combinations and phrases. The largest part in Europe; the territory of 400 square miles; more than 20 centuries old; the Celts gave London its name; to destroy the city; the Germanic invaders; Llyn-din means a «lonely port»; vast urban area; Greater London; governmental office; is famous for its historical associations; the finest Renaissance church; fashionable part; a densely populated district; smog hangs dark in the sky. 7. Fill in prepositions if necessary. 1. London is situated … the river Thames. 2. London covers … the territory of 400 square miles. 3. Modern London is a number … cities, towns, villages. 4. Every block of the City is famous … its historical associations. 5. Londoners are proud … being called Cockneys. 6. Karl Marx lived … many years in London. 7. Lenin visited London … several times. 8. Fill in articles if necessary. 1. London is the capital of … Great Britain. 2. London is one of … biggest port in the world. 3. London is situated on … river Thames. 4. … Romans made the city the centre of their colony. 5. … main traditional parts of … London are…City, … West End and East End. 6. … many banks, offices are situated in … City. 7. … St. Pau’s Cathedral is … finest Renaissance church. Paraphrase the italicized words.   1. London is themajor tradecentre of the country. 2. London occupiesthe territory of 400 square miles. 3. Modern London consists of several cities, towns, villages, that have grown together. 4. The Tower of London is an old fortress. 10. Translate the following sentences into Russian. 1. London is the largest city in Europe. 2. London is the main political, commercial, transport centre of Great Britain. 3. The population of London is about 9 million. 4. London is more than 20 centures old. 5. Modern London is a number of cities, towns, villages that have grown together to make one urban area. 6. «Great London» consists of many parts but the main parts are: the City, the West End and East End. 7. The City is the commercial and business centre of London. 8. The West End is the richest, fashionable and most beautiful part of London. 9. The East End is the poorest district of London, its industrial part. Reading 11. Study the following text.   London London, the capital of Great Britain, and the largest city in Europe, is situated on the river Thames. It is the main political, commercial, transport centre of the country and one of the biggest ports in the world. London covers the territory of 400 square miles. It’s population is about 9 million people. London is a very old city. It is more than 20 centuries old. The old Celts gave London its name. The Romans made the city the centre of their colony, the Germanic invaders tried to destroy it and the Normans made London the capital of the country. Llyn-din was the original name of the settlement which means a «lonely port». M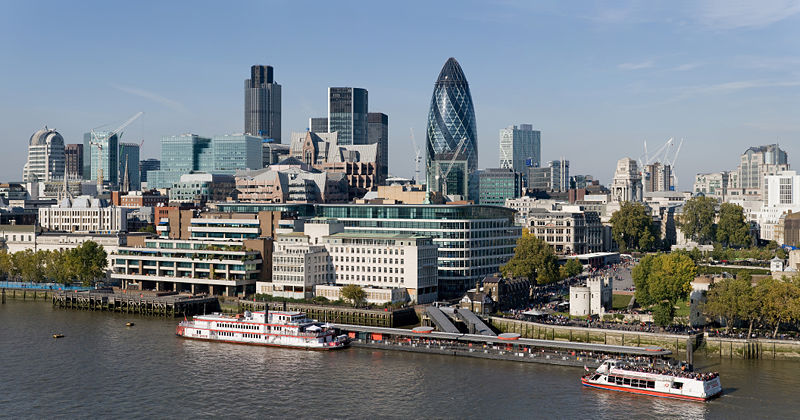  odern London is not one city. It is a number of cities, towns and villages that have grown together to make one vast urban area. «Great London» consists of many parts but the main traditional parts are: the City, the West End and the East End. odern London is not one city. It is a number of cities, towns and villages that have grown together to make one vast urban area. «Great London» consists of many parts but the main traditional parts are: the City, the West End and the East End.The City is an oldest and very important part of the capital, it’s commercial and business centre. Many banks, governmental and newspaper offices are situated in the City. People do not live in the City, they only work there. The heart of the City are 3 buildings: the Manshion House, the Royal Exchange and the Bank of England. Every block in the City is famous for it’s historical associations. St. Paul’s Cathedral, the finest Renaissance church in Europe, and the Tower of London, an ancient castle, are the most famous places of interest in the City. T  he West End is a symbol of wealth, the richest, fashionable and most beautiful part of London. It is situated between the City and Hyde Park. Here you can see wide streets, fine theatres, cinemas and concert halls, the best hotels and restaurants. Among all historical places of the West End the most interesting are: Westminster Abbey and Westminster Palace, known as the Houses of Parliament, with 2 towers: the Victoria Tower and the Clock Tower with Big Ben. he West End is a symbol of wealth, the richest, fashionable and most beautiful part of London. It is situated between the City and Hyde Park. Here you can see wide streets, fine theatres, cinemas and concert halls, the best hotels and restaurants. Among all historical places of the West End the most interesting are: Westminster Abbey and Westminster Palace, known as the Houses of Parliament, with 2 towers: the Victoria Tower and the Clock Tower with Big Ben.The East End is the poorest district of London, it’s industrial part with many plants, factories, workshops. It is a densely populated district. Workers, dockers, handicraftsman live in the East End. They produce the wealth of the West End and are proud of being called true Londoners. The port of London is also in the East End. The smog hangs dark in the sky over the East End. It is often said: «The City is the money of London, the West End is it’s goods, the East End is the hands of London». The main industries of London are shipbuilding, textile and machine-building industries. Many famous people lived in London: Heinrich Heine, the German poet; Mozart, the German composer; Alexander Herzen, the Russian writer; Ivan Pavlov, the famous Russian physiologist and many other scientists, artists, writers, painters. Karl Marx worked and lived for many years in London and is buried in the Highgate Ceremony. 12. Find in the text the words which have an opposite meaning. The richest district; narrow streets; modern; to build; unknown; unimportant; the worst hotels; old. 13. Find in the text English equivalents for the following words and word-combinations. Лондон занимает территорию; прекрасная церковь эпохи возрождения; издательства газет, которые слились вместе; пытались разрушить; «одинокий порт»; первоначальное название; плотно населенный район; гордятся; похоронен на Хайгетском кладбище. 14. Translate the following sentences into English.   1. Лондон, столица Великобритании и самый большой город в Европе, расположен на реке Темзе. 2. Лондон занимает территорию в 400 кв. миль. 3. Древние кельты дали Лондону его название. 4. Лин-дин было первоначальное название поселения, которое означало «Одинокий порт». 5. Современный Лондон – это ряд городов, городков и деревень, которые слились вместе, чтобы образовать один огромный мегаполис. 6. Сити – старейшая и очень важная часть столицы, ее торговый и деловой центр. 7. Вест Энд – это символ богатства, самая богатая, фешенебельная и наиболее красивая часть Лондона. 8. Ист Энд – беднейший район Лондона, его промышленная часть. 9. Ист Энд – это очень плотно заселенный район. 10. Ист Энд – это руки Лондона. 11.Главными отраслями промышленности Лондона являются кораблестроение, машиностроение и текстильная промышленность. 15. Answer the following questions. 1. Is London the main political, commercial, transport centre of the country? 2. How old is London? 3. What are the main traditional parts of London? 4. What part of London is the oldest? 5. What offices are situated in the City? 6. What are the most interesting places of interest in the West End? 7. What people lave in the East End? 8. Where is the port of London? 9. What famous people live in London? 16. The information given below contains different points of view of the American students on some aspects of social life in Great Britain.  The British and the Americans speak the same language. But life in two nations can be very different.... 'The police. They're very friendly and they don't carry guns.' Claude, Trenton. 'The weather is awful. You don't seem to get any summer heat. It's winter all year round.' Toni, San Francisco. 'The tourists! The streets are so crowded. I think you should do something about them. And 1 can't stand the litter everywhere. It's a very dirty place.' Jose, Washington. 'Walking and sitting on the grass in the parks, especially on a hot summer's day. Oh, and the green countryside. But why is the beer warm? Max, Houston. 'Well, they certainly seem rather unfriendly. Nobody ever talk on the buses. But maybe we haven't met any real English people yet' Eva, Niagara Falls. 'Feeling safe when you walk the streets. Oh, and the polite drivers who stop at a street crossing if they see someone waiting there.' Moon, Los Angeles. 'Driving on the left. It's very confusing. I keep looking the wrong way.' Paula, San Diego. Speech practice 17. Use the following words to speak about а) London – the capital of Great Britain the capital; the largest city in Europe; the main political; commercial centre; the biggest port; the population of 9 million; a number of towns; to be situated; to cover the territory; to grow together; to make one vast urban area. b) the history of London: a very old city; 20 million centuries old; the old Celts; the Romans; the Germanic invaders; the Normans; the original name Llyn-din; a «lonely port»; to give; to make the centre of the colony; to destroy; to mean; to make the capital. c) the parts of London: the main traditional parts; the City; the West End; the East End; banks; governmental offices; newspaper offices; a symbol of wealth; wide streets and fine theatres; cinemas and concert halls; workers; dockers; handicraftsmen; the smog; many plants; factories; workshops; to live; to be situated; to work; to hang; to produce the wealth. 18. Learn the dialogues.  1. – Which are the most interesting picture galleries in London? – Well, the National Gallery, to begin with, then comes the National Portrait Gallery. – Yes, but what about the British Museum? I’ve heard a lot of it. – Oh surely, you ought to go there, but the British museum is not a museum of Fine Arts. It’s a museum of history, archeology and ethnography. It’s also one of the largest libraries in the world. 2. – This is Fleet Street. – It’s name suggests a sea voyage. – Nothing of the kind. It suggests journalism. – Why? – Because all the big British daily newspapers are edited here. 3. – Why, it’s № 10 Downing Street: – Exactly so. Here the Prime Minister of Britain lives. – And where’s the residence of the Queen? – The London residence of the British kings is Buckingham Palace. When the Queen is in the residence the Royal Standard is flown at mast head (флагшток). 19. In groups, hold a discussion on the following situation: You are a guide. Give a short commentary on any well-known place of interest in London.  - Big Ben is a tower clock. It is famous for its accuracy and for its 13-ton bell, designed by Edmund Beckett, Baron Grimthorpe. Big Ben is housed in the tower at the eastern end of the Houses of Parliament. The clock was named after Sir Benjamin Hall, commissioner of works at the time of its installation in 1859. Originally applied only to the bell, eventually it came to indicate the clock itself. - Many important events in the history of Great Britain are connected with the Tower of London. It has served as citadel, palace, prison, mint, and menagerie. Now it is a museum. In 1078 William the Conqueror built the White Tower to defend the city. The Tower is famous for its illustrious prisoners. Many great people lost their heads on the executioner's block. The Yeoman Warders known as 'Beefeaters' guard the Tower. They wear traditional Tudor costumes. 20. Comment on the following proverbs and sayings. (Explain their meaning, give their Russian equivalents.) East or West, home is best There is no place like home. So many countries, so many customs. When at Rome, do as the Romans do. 21. Role play A group of guides suggests possible sightseeing routes about London to their office director commenting on the peculiarities of different historical places. Each one speaks in favour of his/her suggestion trying to convince both the director and the guides that the route is the best. In the end the participants of the talk choose the most appropriate route. Check list to module IV What's the City, the West End, the East End? What are English buses called? What is the name of the tower which contains the famous Big Ben? What is the name of London underground? Can you name the person of England whose final Battle was at Trafalgar? What is the famous place in Hyde Park where people can say anything they like? Who was the famous English general and statesman who won the victory of Waterloo? Module V The Russian Federation Vocabulary Training 1. Read the words and the expressions below.  Norway, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Kaliningrad Oblast, Poland, Belarus, Ukraine, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, China, Mongolia and Democratic People's Republic of Korea, mineral and energy resources, unfrozen fresh water 2. Group the words into subject groups republic, country, land borders, energy, minerals, water, land 3. Work with your partner.   semi-presidential republic, the eighth of the Earth’s land area, federal subjects, the ninth largest by population 4. Read English sentences choosing one of the Russian words in brackets with the proper meaning. This time work in small groups.   1. The Russian Federation is a transcontinental (пересекающийся, трансконтинентальный, трансматериковый) country. 2. Democratic People's (национальный, народный, общественный) Republic of Korea is our eastern neighbour. 3. Russia`s lakes contain approximately (приблизительно, приближенно, точно) one-quarter of the world's unfrozen fresh water. Reading 5. Read this text quickly and define the main idea of this text.    Russia or the Russian Federation is a transcontinental country. It is a semi-presidential republic comprising 83 federal subjects. Russia shares land borders with the following countries: Norway, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania (via Kaliningrad Oblast), Poland (via Kaliningrad Oblast), Belarus, Ukraine, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, China, Mongolia and Democratic People's Republic of Korea. At more than 17 million square kilometres, Russia is the largest country in the world, covering more than an eighth of the Earth’s land area; with 142 million people, it is the ninth largest by population. Russia has the world's greatest reserves of mineral and energy resources, and is considered an energy superpower. It has the world's largest forest reserves and its lakes contain approximately one-quarter of the world's unfrozen fresh water. 6. Using the information from the text above, complete these sentences. 1. Russia is a … . 2. Russia shares its borders with … . 3. Russia is the largest … . 4. Russia has the world’s greatest … . 5. Russia is considered … . 6. Russia’s lakes contain … . 7. forest reserves are … . 7. Work with your partner. Compose 4 or 5 questions to the text.   Vocabulary Training 8. Read the following words and word combinations.  AD (Anno Domini) – от Рождества Христова Emerge - появляться Byzantine Empire – Византийская империя Ultimately – в конце концов Principality – княжество cultural and political legacy – культурное и политическое наследие annexation - аннексия (присоединение) successor state – государство – правопреемник Grand Duchy of Moscow – Великое княжество Московское 9. Read the following words and expressions and guess their meaning.  nation's history, a noble Viking warrior class, Byzantine Empire, many small feudal states, reunification process, independence struggle 10. Scan the text quickly and find the English equivalents of the following words and word expressions. восточные славяне, различимая группа, государство – правопреемник, посредством завоеваний, простираясь от Reading 11. Read and translate the text about early days of Russian history. E 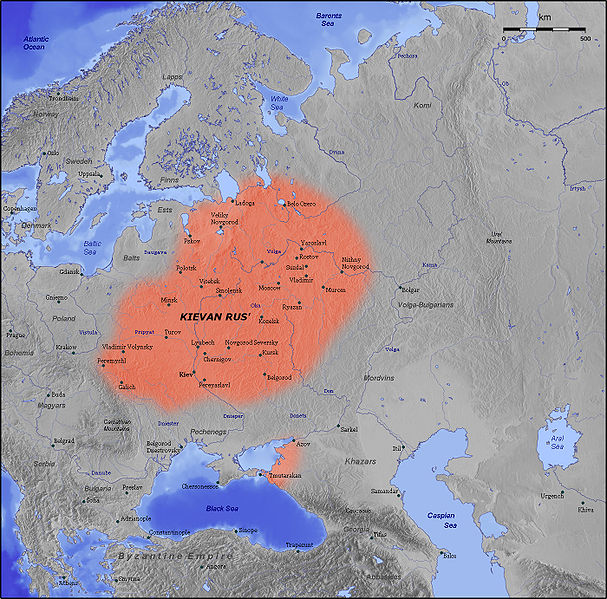 arly History of Russia arly History of RussiaT  he nation's history began with that of the East Slavs. They emerged as a recognizable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries AD (Anno Domini). The first East Slavic state was Kievan Rus'. It arose in the 9th century and was founded and ruled by a noble Viking warrior class and their descendant. Kievan Rus' adopted Christianity from the Byzantine Empire in 988. It was the synthesis of Byzantine and Slavic cultures and that defined Russian culture for the next millennium. Kievan Rus' ultimately disintegrated and the lands were divided into many small feudal states. The most powerful successor state to Kievan Rus' was Moscow (or Grand Duchy of Moscow). Moscow served as the main force in the Russian reunification process and independence struggle against the Golden Horde. he nation's history began with that of the East Slavs. They emerged as a recognizable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries AD (Anno Domini). The first East Slavic state was Kievan Rus'. It arose in the 9th century and was founded and ruled by a noble Viking warrior class and their descendant. Kievan Rus' adopted Christianity from the Byzantine Empire in 988. It was the synthesis of Byzantine and Slavic cultures and that defined Russian culture for the next millennium. Kievan Rus' ultimately disintegrated and the lands were divided into many small feudal states. The most powerful successor state to Kievan Rus' was Moscow (or Grand Duchy of Moscow). Moscow served as the main force in the Russian reunification process and independence struggle against the Golden Horde. Moscow gradually reunified the surrounding Russian principalities and came to dominate the cultural and political legacy of Kievan Rus'. By the 18th century, the nation had greatly expanded through conquest, annexation and exploration to become the Russian Empire. And it was the third largest empire in history, stretching from Poland eastward to the Pacific Ocean and Alaska. |
