английский за проф направлением. Укладач Триполець В.І. Рецензенти
 Скачать 4.04 Mb. Скачать 4.04 Mb.
|
|
3. Read the text. Work in pairs. Find out whether your partner has got the facts about the periodic table right. Ask him when, why and what questions. PERIODIC TABLE OF THE LEMENTS The periodic table of the chemical elements is a tabular method of displaying the chemical elements. This invention is generally credited to Russian chemist Dmitry Mendeleyev in 1869. Mendeleyev intended the table to illustrate "periodic" trends in the properties of the elements. In 1869, Mendeleyev classified 56 elements on the basis of their physical and chemical properties in the increasing order of the atomic masses, in the form of a table. Mendeleyev had observed that properties of the elements orderly recur in a cyclic fashion. He found that the elements with similar properties recur at regular intervals when the elements are arranged in the order of their increasing atomic masses. He concluded that "the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic masses". This came to be known as the law of chemical periodicity and stated: "The properties of the elements are a periodic function of the nuclear charges of their atoms". Based on this law all the known elements were arranged in the form of a table called the “Periodic Table”. D. I. Mendeleyev arranged all the elements in a table consisting of vertical groups and horizontal periods. In this table all the uncoordinated data on the properties of elements and their compounds arc collected and arranged into one well-constructed system. It enables scientists to predict the possibility of discovering new elements and their properties and to correct the errors made in previous definitions of the properties of known elements. 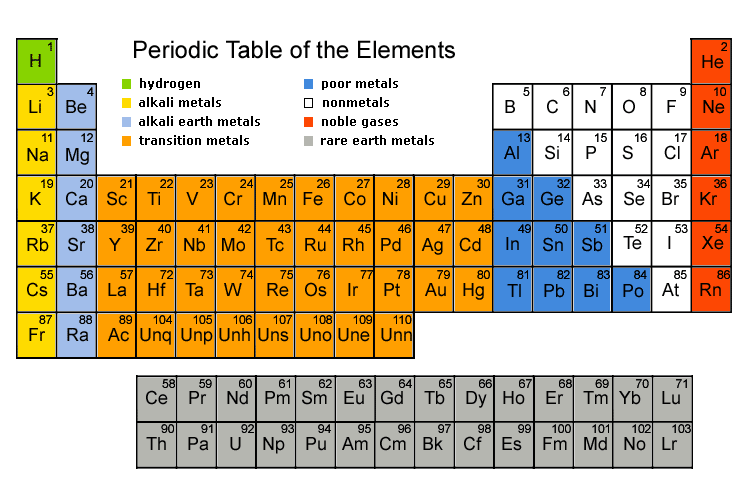 The layout of the table has been refined and extended over time, as new elements have been discovered, and new theoretical models have been developed to explain chemical behavior. The periodic table is now used within the academic discipline of chemistry, providing an extremely useful framework to classify, systematize and compare all of the many different forms of chemical behavior. The table has also found wide application in physics, biology, engineering, and industry. The table contains 117 elements as of 27 January 2008 (elements 1—116 and element 118). 4. What new information have you learned from the text? Fill in the grid.
5. Find words in the text that mean the following: a) Substance which has not so far been split up into a simpler form by ordinary chemical methods. b) List, orderly arrangement, of facts, information, etc. c) Branch of science that deals with how substances are made up, how they (their elements) combine, how they act under different conditions. 6. Are the following statements true or false? Correct the false ones. a) The Periodic Table consists of vertical periods and horizontal groups. b) The properties of the elements are a periodic function of the nuclear charges of their atoms. c) There were known 1044 elements at the time of publishing Mendeleev's Periodic Table. d) The table contains 117 elements as of 27 January 2008 (elements 1—116 and element 118). e) Mendeleyev's periodic system continues to form the basis for the most complex research. 7. Work in pairs: ask and answer questions. A. What| rnodern| cornerstones| chemistry? B. A. How many| were| in 1869| elements| known? B. A. What| predict| Mendeleyev? B. A. What| enable| Periodic Table| to predict| scientists? B. 8. Fill in the blanks using the words under the line.
IV. Supplement 1. Get more information on the topic. CHEMICAL ELEMENT The concept of chemical element is related to that of chemical substance. A chemical element is characterized by a particular number of protons in the nuclei of its atoms. This number is known as the atomic number of the element. For example, all atoms with 6 protons in their nuclei are atoms of the chemical element carbon, and all atoms with 92 protons in their nuclei are atoms of the element uranium. However, several isotopes of an element, that differ from one another in the number of neutrons present in the nucleus, may exist.  The most convenient presentation of the chemical elements is in the periodic table of the chemical elements, which groups elements by atomic number. Due to its ingenious arrangement, groups, or columns, and periods, or rows, of elements in the table either share several chemical properties, or follow a certain trend in characteristics such as atomic radius, electronegativity, etc. Lists of the elements by name, by symbol, and by atomic number are also available. Hydrogen (H) is the first element in the periodic table because it has just one proton in its nucleus. Helium (He) is second, because it has two protons, and so on. The periodic table can be coloured-coded. Often, each group is given a particular colour so that it is easy to pick out all the elements that belong to a particular group. As well as a name, each element has a symbol. Often this is the first letter or two of the element's name, but it can come from a Latin name. Each also has an atomic number and a mass number. Gallium. One element that Mendeleyev left a gap for in his periodic table was gallium (element 31). Mendeleyev called it eka-aluminium because he predicted it would have similar properties to aluminium. In 1875, French scientist Lecoq de Boisbaudran discovered gallium. It has the exact properties that Mendeleyev predicted. Gallium is a soft, silvery metal with a melting point of 29.8°C (85.6°F). 2. Read the names of the elements and identify their location in relation to other elements.
3. You've discovered a new element. What name would you like to give to the new element? Describe its properties, molecular weight, its use in chemistry, pharmacy, and industry. VIII тема: Лікарські рослини. Ліки. Класифікація та характеристика типів ліків. Рецепт. Анотація до лікарського засобу. VIII тема: Лікарські рослини. Ліки. Класифікація та характеристика типів ліків. Рецепт. Анотація до лікарського засобу. 28. Types of plants. Medicinal plants. Види рослин. Лікарські рослини. І. Vocabulary. 1. Read and learn the topical vocabulary. plant — рослина; bark — кора; leave (pi. leaves) — листок; root — корінь; seed — насіння; to collect — збирати; pollination — запилення; unripe — недостиглий; extract — екстракт; tincture — настойка; to store — зберігати; to dry — сушити; personal care — особиста гігієна. 2. Match the following English word combinations and their Ukrainian translations.
2. effective measures 3. active ingredient 4. well-being 5. medicinal plant II. READING Read, translate and discuss the following text. Write out key sentences and write a short summary of the text. MEDICINAL PLANTS A medicinal plant is any plant which, in one or more of its parts, contains substance that can be used for therapeutic рифове or which is a precursor for synthesis of useful drugs. Historically, plants have played an important role in medicine. For early people, they came easily to hand, and were intricately connected to diet and healing. Through observation and experimentation, they learned which plants promoted health and well-being. Without plants, most medicines you take would not exist. Over 40 % of medicines now prescribed in the U.S. contain chemicals derived from plants. Historically, plant medicines were discovered by trial and error. Our ancestors noticed that aches and pains went away when they drank tea made from the bark of a willow tree. Later, scientists found that willow bark contains salicylic acid, the active ingredient in aspirin. Over time, the practice of herbal medicine has grown more complex. Science has enabled us to process natural substances into pills, tinctures and powders. Throughout the world, botanists and chemists search the plant kingdom for new medicines.  Today many drug plants are cultivated and many drug plants are collected from fields and woods. Drugs are made from fruits, leaves, flowers, roots, seeds of the plants. It is very important to collect plants in proper time. Leaves are collected when they are fully developed. The time of the day is also important in the collection of medicinal plants. Flowers are collected before the time of pollination. Fruits are collected when they are fully grown but unripe. To dry plants correctly is also very important. If it is made carelessly the drug may be spoiled. The plant parts most preferred in medicinal plants are roots. Of the medicinal plants found in the shops, 61 % were in the fonn of roots, 22 % in the form of whole plant, 15 % in the form of barks, 1 % in the form of fruits and the other 1 % in the form of leaves. Medicinal plant materials should be stored in separate areas. The storage area should be well ventilated and equipped in such a way as to protect against the entry of insects or other animals, especially rodents. Effective measures should be taken to limit the spread of animals and microorganisms introduced with the plant material and to prevent cross-contamination. Containers should be located in such a way as to allow free air circulation. Special attention should be paid to the cleanliness and good maintenance of the storage areas, particularly when dust is generated. The storage of plants, extracts, tinctures and other preparations may require special conditions of humidity and temperature or protection from light; steps should be taken to ensure that these conditions are provided and monitored. The medicinal uses of plants grade into their uses for other purposes, as for food, cleaning, personal care and perfumery. Plants are used in medicine to maintain and augment health — physically, mentally and spiritually — as well as to treat specific conditions and ailments. They serve as therapeutic agents as well as important raw materials for the manufacture of traditional and modern medicine. Medicinal plants constitute an important natural wealth of a country. III. POST-READING ACTIVITIES 1. Answer the following questions.
3. What did our ancestors do when they have aches and pains? Give the example from the text.
2. Complete the sentences with suitable words.
a) medicines; b) proper time; c) plants; d) country; e) areas; J) medicine; g) cultivated 3. Translate into English.
4. Read the extracts and say, what medicinal plants are described in them. a) It is hard to believe that the fragrance of this plant comes from tiny flowers only 1/4 in long. Waxy white and bell- shaped flowers appear in April and May.It has clear green, broad leaves. This well-known plant grows from a branched horizontal rhizome. It can be found growing wild and it has been cultivated for more than 500 years. The rhizome, leaves, flowers and fruits (round red berries) are all poisonous. Its aromatic oil is used in skin lotions and perfume. In medicine it is used for the treatment of cardiac diseases. b) This plant has been spreading round the world via fields of cereals since the Neolithic about 8000 years ago. Pliny the Elder reported the medicinal power of it in the 1st century A.D. He said that the centaur Chiron used this plant to heal the wound on his leg inflicted by Hercules' arrow. It has bright blue flowers. Several hundred seed capsules ripen on a single plant. It is known not only as unwanted weed but also as one of the medicinal herbs of both folk and orthodox medicine. The bright blue flower heads of this plant are diuretic. In France a tincture made from the plant is used in eye treatment. |
