Part II NUMERICAL CONTROL Read the following texts (A and B) and fill in the gaps with the following words:
steps digitalcomputer numerical controlledproductionpart Numerical Control systemsdesign component original produce
|
A.
(1) __________ (NC) refers to the automation of machine tools that are operated by abstractly programmed commands. The first NC machines were made in the 1940s and 50s. Existing tools were modified with motors. These early mechanisms were designed into (2)__________ computers, and created the modern CNC – (3) __________ machine tools - that have revolutionized the (4) __________process.
In modern CNC (5) __________, end-to-end component design is highly automated using CAD/CAM programs. The programs (6) _________ a computer file that is interpreted to give the commands needed to operate a particular machine, and then loaded into the CNC machines for (7) __________ . Since any particular (8) __________ might require the use of a number of different tools - drills, saws, etc. - modern machines often combine multiple tools into a single "cell". In other cases, a number of different machines are used with an external controller and human or robotic operators that move the component from machine to machine. In either case the complex algorithm of (9) __________ needed to produce any (10) __________ is highly automated and produces a part that closely matches the (11) __________ CAD design.
|
B.
Computer-aided manufacturing industries components CAM body design engineers programs manufacturing
|
(1) __________ (CAM) is the use of computer-based software tools that assist (2) __________ and machinists in (3) __________ or prototyping product (4) __________ (or parts). CAM is a programming tool that makes it possible to manufacture physical models using computer-aided design (CAD) (5) __________ . CAM creates real life versions of components designed within a software package. CAM was first used in 1971. The first commercial use of (6) __________ was in large companies in the aerospace (7) __________ , for example “UNISURF”, and automotive, for example “Renault” for car (8) __________ and tooling.
|
THE MINI CAR
Read the following text and fill in the gaps with the following words:
market models 1959 produced fashionable development original
buyers icon city version sold seller generation countries
|
The Miniis a small car that was (1) __________ by the British Motor Corporation(BMC) and its successorsfrom 1959 until 2000. That was the first(2) __________ of the car. The (3) __________ Mini is considered to be an (4) __________ of the 1960s. The vehicle is in some ways considered to be the British equivalent to its German competitor, the Volkswagen Beetle, which enjoyed similar popularity in North America. In 1999 the Mini was voted the second most influential car of the 20th Century, behind the Ford Model T.
Throughout the 1980s and 1990s the British (5) __________ enjoyed numerous "special editions" of the Mini, which shifted the car from a mass-market item into a (6) __________ icon. It was even popular in Japan. The ERA Mini Turbo was particularly popular with Japanese (7) __________ .
In 1994 BMW took control of the Rover Group, which included the Mini. The (8) __________ of the next generation had been done between 1995 and 2001 by two competitors - Rover Group in Gaydon, United Kingdom and BMW AG in Munich, Germany. Rover wanted an economy car, whilst BMW supported a small (9) __________ (or sport) car. After the last of the Mini production had been sold, the 'Mini' name reverted to BMW ownership. Now the name of the car's brand, MINI, is all-capitalized, that means is all written in capital letters.
The new 'BMW' MINI is technically unrelated to the old car but retains the classic transverse 4-cylinder, front-wheel-drive configuration and iconic "bulldog" stance of the original.
The 2001 - 2006 years included four hatchback (10) __________ : the basic "Mini One", the diesel-engined "Mini One/D", the sportier "Mini Cooper" and the supercharged "Mini Cooper S". In 2005 a convertible roof option was added. In November 2006 BMW released a re-engineered (11) __________ of the Mini which is unofficially known as the "Mk II Mini". The Mk II is currently[update] available as a hatchback and a wagon (Clubman). The convertible was still based on the MK 1 until January 2009. Now, it is based on the MK 2.
At its peak, the Mini was a strong (12) __________ in most of the (13) __________of the world where it was sold. A total of 1,581,887 Minis were (14) __________ in Britain only after the start of production in (15) __________ .
|
THE MORGAN CAR
|

|
Fill in the gaps in the following text:
madeCompany design was manufacturer production
founded engines Production 1952
|
The Morgan Motor (1) __________ (MMC) is a British motor car (2) __________ . The company was (3) __________ in 1909 by H.F.S. Morgan and was run by him until 1959. Peter Morgan, son of H.F.S., ran the company until a few years before his death in 2003. The company is currently run by Charles Morgan, the son of Peter Morgan.
H.F.S. Morgan's first car (4) __________was a single-seat three-wheeled vehicle which was (5) __________for his personal use in 1909. Interest in his vehicle led him to patent his design and begin (6) __________ . He initially showed single-cylinder and twin-cylinder versions of his vehicle at the 1911 Olympia Motor Exhibition. At this exhibition he was convinced that there would be greater demand for a two-seat model.
H.F.S. Morgan built his cars' reputation by taking part in competitions. One of his racing cars won the 1913 Cyclecar Grand Prix at Amiens in France. This became the basis for the Grand Prix model of 1913 to 1926, from which the Aero, Super Sports, and Sports models appeared.
These models used air-cooled or liquid-cooled variations of motorcycle (7) __________ . The engine was placed ahead of the axis of the front wheels in a chassis made of steel tubes.
Beginning in 1932, a new series of Morgan three-wheelers began with the “F-4”. The “F-4”, and the “F-Super” used a pressed-steel chassis and the four-cylinder Ford Sidevalve engine that was used in the Model Y. (8) __________ of the Ford-engined three-wheelers would continue until 1952.
Morgan's first four-wheeler was the “4-4” model (with four-cylinder engine and four wheels). The first 4-wheeled Morgan (9) __________ made in 1936 and is known as the Morgan “4-4 Series 1”. Three-wheeler production continued alongside the “4-4” model until (10) __________ .
craftsmen traditional 10 highly-skilled cars
middle unique introduced handmade list
|
The “Morgan +4” was (11) __________ to the public in 1950 as a larger-engined ("plus") car (than the “4-4”). Later the “+4+” was made in the (12) __________ of the 60-s with a contemporary fibreglass coupe body. The light weight and reduced drag characteristics improved the performance of the “+4+” over the regular “+4” in every aspect. However, the (13) __________ Morgan was loved by people more. So, only 26 “+4+” cars were built.
Also a number of other models were designed. For example, Morgan (14) __________ can be found in many areas of motorsport, including the Le Mans 24h race. Another (15) __________ Morgan race-car was the “Aero 8 GT” that took part in 2008 Britcar 24h races at Silverstone.
Morgan is based in Malvern Link, an area of Malvern, Worcestershire. Only 163 (16) __________ employees work for the company. All the cars are still (17) __________. The (18) __________ do their best to prove the quality of the car. The waiting (19) __________ for a car is approximately one to two years, although it has been as high as (20) __________ years in the past. Only 640 cars were produced by the company in 2007.
|
|
Part III
(… адрес интернет-странички с видеороликами…)
1. THE “MINI COOPER” ___________
(01:00)
Watch the video and answer the following questions:
What kind of video is this?
What is the main idea of the track?
What title can you give to the video track?
Continue the title of the video above.
2. THE MINI GREAT CARS
(01:15)
PRE-LISTENING
Do you know the words:
“decade”, “icon”, “trend”, “crowd/crowded”, “highway”, “spirit”, “to handle”?
WHILE-LISTENING
Watch the whole video and answer the following questions:
What kind of video is this?
What is the main idea of the track?
Watch the parts of the video and fulfill the tasks:
00:00 – 00:29
What is the Mini compared to in the track?
How long did it take for “the Mini” to become an “icon”?
00:40 – 00: 46
What do the fans of the Mini think of the car?
00:47 – 01:15
Fill in the gaps in the following part of the text:
-
…
There is no other (1) __________ like a (2) __________. It’s a (3) __________ car that is at (4) __________ in a crowded (5) __________ and equally happy out on a (6) __________ .
The new Mini was (7) __________ to capture the spirit of the (8) __________. It had to be (9) __________, handle well and be (10) __________ no matter where it’s driven.
|
POST-LISTENING
Summarize the idea of the track in 4–6 sentences and present your summary to the class.
3. THE MINI CAR
(05:45)
PRE-LISTENING
1. What do you remember about the Mini from the previous videos?
2. Do you know the words: “significant”, “to launch”, “mile”, “influence”?
WHILE-LISTENING
Watch the following parts of the video and fulfill the tasks:
00:45 – 01:39
3. What cars did the Mini leave behind?
01:40
4. How many cars were being produced a day in September and October 1959?
01:50-02:28
5. What was the original Mini-prototype’s speed?
What month was the Mini introduced to people?
What year did it happen?
02:40 – 03:13; 03:38 - 04:08
6. The 1st interview: the name of the interviewee _______________
the job of the interviewee _______________
what does the interviewee think of the Mini? _____________
03:45
7. What can you see on the screen? Continue the following sentences:
This is a …
There are …
A Mini is …
A new model ….
04:27 – 04:55; 05:23 - 05:33
8. The 2nd interview: the name of the interviewee ______________
the job of the interviewee ______________
what does the interviewee think of the Mini? ____________
04:54 – 05:24
9. What is the name of the most famous Mini prototype model?
10. Fill in the gaps in the following text:
00:45 – 01:39
The Mini is the car that more than any other has changed the pace of motoring for ever. One can not (1) __________ the city scope without a Mini being in present.
The most significantly it is impossible to look at the small car today without seeing very real evidence of the influence (2) __________ has had.
In (3) __________the Ministry of Experts called the Mini “the most significant car of the century”. This sentiment was reflected by the leadership of the old-car (4) __________ in the (5) __________ , who also named it “the most (6) __________ car of the century. The Mini left behind such cars as VW Beetle, Ford model “T” and (7) __________ .
01:50 – 02:28
From the area of the first (8) __________ to the cars launch in (9) __________ only a few major (10) __________ changes were made. A reduction in (11) __________ size from (12) __________ cc to (13) __________ cc was ordered as a direct result of the fact that early prototype’s speed was (14) __________miles per (15) __________ , which was considered far too fast for the market.
The new capacity was arrived at power reducing the stroke from (16) __________ mm in a 948cc version to (17) __________ mm in final 848cc.
04:09 – 04:27
When (18) __________ saw the car, it was not shy to praise it. The Mini is a (19) __________ , exceptional space efficiency and relatively good performance.
04:54 – 05:24
After showing some strong points of the Mini, (20) __________ began to notice it. And the most notable was (21) “__________”. Cooper was aware of the car’s basic strengths, and such drivers as (22) __________ Braden and (23) __________McCara liked it.
|
POST-LISTENING
11. The whole text is:
instructions on how to use the car;
background information about the history of the car;
- interviews with craftsmen.
8. ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT
Part I
1. Complete the statements below for you. Then compare your answer with the rest of the class. Which is the most popular way to learn?
When I learn to do something practical, I prefer …
a) … to see someone demonstrating it.
b) … someone to help me do it.
c) … to follow a diagram.
d) … to try and ask for help if things go wrong.
* (“Engineering” Workshop by Lindsey White, OUP; Unit 11, pg.12, ex.1)
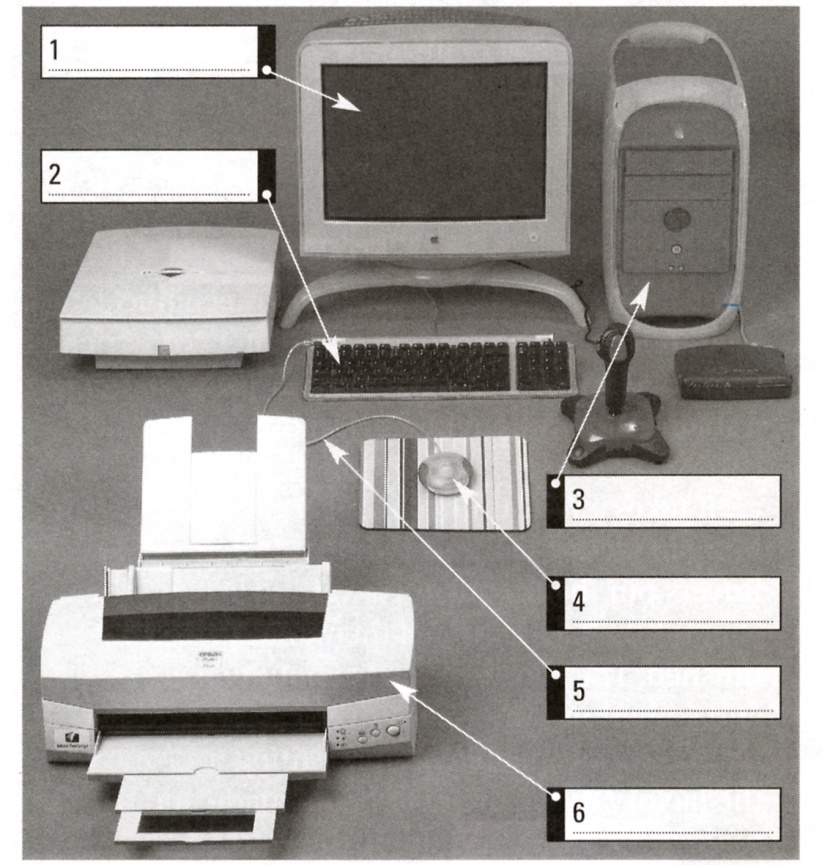
2. Look at the picture and study the words in the box below. Label the computer components.
-
cable central unit keyboard monitor (screen, display) mouse printer
|
-
* (“Engineering” Workshop by Lindsey White, OUP; Unit 11, pg.12, ex.2)
3. Study the verbs in the box below and complete the sentences (1 – 5). There is one extra verb that you do not need to use.
-
connect disconnect loosen plug in tighten unplug
|
-
1.
|
If you don’t pay the bill, the electricity company will __________ the supply.
|
2.
|
__________ the screws before you take the plug out.
|
3.
|
It’s sensible to __________ your computer if there is a bad storm.
|
4.
|
If you don’t __________ the TV, it won’t work!
|
5.
|
__________ the video cable to the TV.
|
* (“Engineering” Workshop by Lindsey White, OUP; Unit 11, pg.12, ex.3)
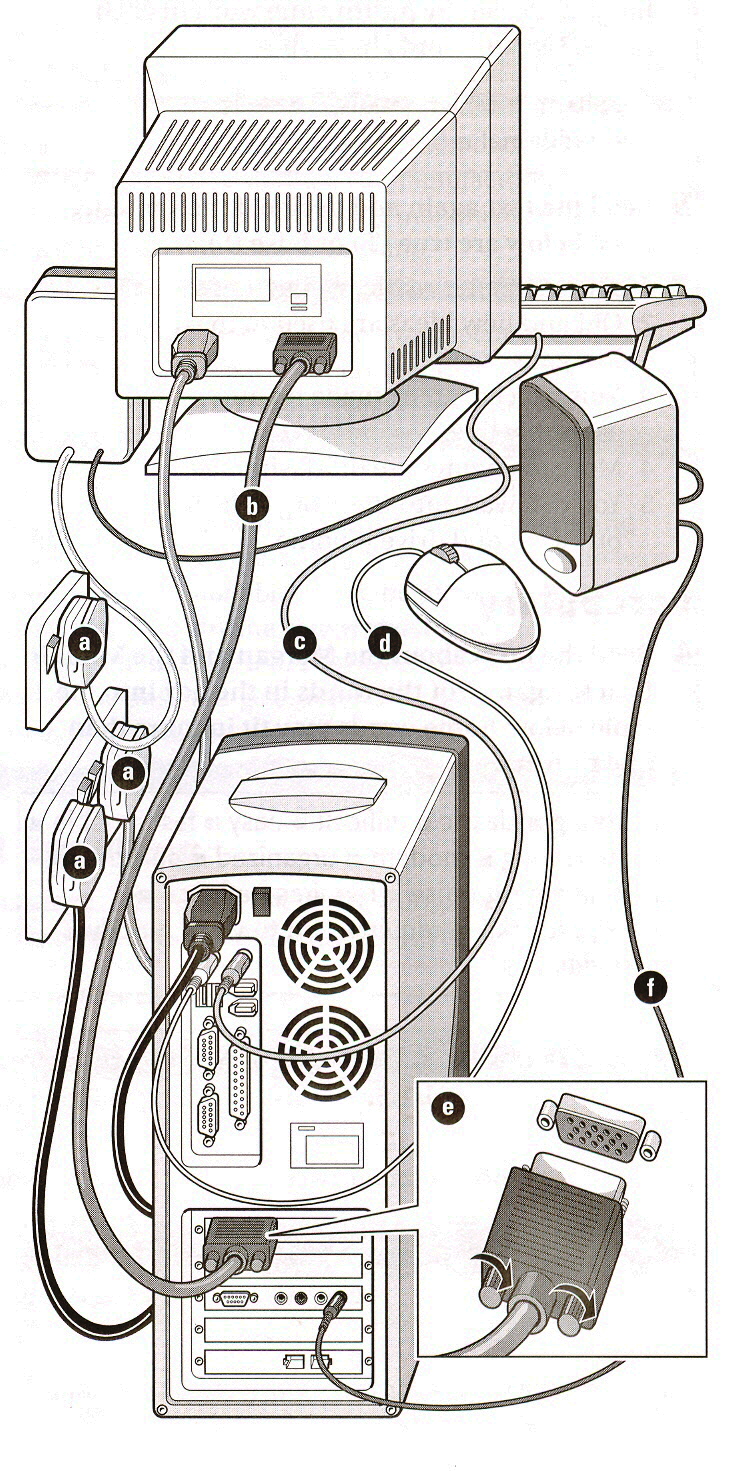
4. Read the following instructions (1 – 6) and match them with the diagram.
1.
|
Connect the keyboard cable to the back of the computer.
|
|
2.
|
Connect the mouse cable to the back of the computer.
|
|
3.
|
Plug in the monitor cable; be careful not to bend the pins.
|
|
4.
|
Tighten the screws.
|
|
5.
|
Connect the speakers to the back of the computer.
|
|
6.
|
Plug the computer, monitor, and the speaker cables (in that order) into the mains supply.
|
|
|
|
* (“Engineering” Workshop by Lindsey White, OUP; Unit 11, pg.12, ex.4)
5. Read the instructions below and match the spoken instructions (1 – 3) with the written instructions (a – c).
-
1
|
Put some water and turn on the gas.
|
|
a
|
Refer to diagram 1. Button A releases the locking mechanism.
|
2
|
If I were you, I’d put the bulb in first.
|
|
b
|
Remove the lid and fill from the cold tap. Place the kettle on the centre of the gas ring making sure that it is stable before turning on the gas.
|
3
|
You press that and the back opens.
|
|
c
|
Insert a 60 W bulb before putting the plug in the socket.
|
* (“Engineering” Workshop by Lindsey White, OUP; Unit 11, pg.12, ex.5)
6. Read the instructions in ex.5 again. Which instructions are about:
- a new kettle?
- a new desk lamp?
- a new camera?
* (“Engineering” Workshop by Lindsey White, OUP; Unit 11, pg.12, ex.6)
7. Complete the instructions for connecting a DVD recorder to a TV set. Use the words in the box.
aerial insert (= put in) cable mains switch plug (n) socket TV
|
INSTRUCTIONS FOR CONNECTING THE DVD TO THE TV
(1)__________off your TV set.
Remove the aerial cable (2)__________ from your TV set. Insert it into the ANTENNA socket at the back of the DVD recorder.
Insert one end of the aerial (3)__________ into the TV socket at the back of the DVD recorder and the other end into the (4) __________ input socket at the back of the (5) __________ set.
Plug a special scart cable into the scart (6) __________ at the back of the DVD recorder and the corresponding scart socket at the back of the TV set.
Switch on the TV set.
(7)__________ one end of the supplied mains cable into the (8) __________ socket at the back of the DVD recorder and the other end into the wall socket.
|
* (“Engineering” Workshop by Lindsey White, OUP; Unit 11, pg.12, ex.9)
8. Find the mistakes in spelling of the following words and correct them. Three words are correct:
-
1.
|
keybord
|
|
2.
|
conect
|
|
3.
|
tihten
|
|
4.
|
printe
|
|
5.
|
losen
|
|
6.
|
unplug
|
|
7.
|
caible
|
|
8.
|
computer
|
|
9.
|
monitor
|
|
10.
|
mous
|
|
9. Find the names of computer components in the following table (6 words). They may be written diagonally, horizontally or vertically:
-
|
a
|
b
|
c
|
d
|
e
|
f
|
g
|
h
|
i
|
j
|
1
|
A
|
B
|
T
|
K
|
P
|
U
|
T
|
M
|
M
|
Q
|
2
|
K
|
E
|
Y
|
B
|
O
|
A
|
R
|
D
|
O
|
W
|
3
|
A
|
S
|
D
|
F
|
W
|
Z
|
X
|
G
|
U
|
E
|
4
|
X
|
P
|
C
|
V
|
B
|
N
|
M
|
F
|
S
|
R
|
5
|
S
|
W
|
R
|
T
|
G
|
S
|
C
|
D
|
E
|
T
|
6
|
M
|
O
|
N
|
I
|
S
|
Q
|
A
|
S
|
H
|
Y
|
7
|
L
|
H
|
M
|
O
|
N
|
I
|
T
|
O
|
R
|
U
|
8
|
O
|
P
|
R
|
I
|
N
|
T
|
S
|
J
|
J
|
I
|
9
|
Q
|
A
|
C
|
A
|
B
|
L
|
E
|
K
|
K
|
O
|
10
|
Z
|
S
|
P
|
E
|
A
|
K
|
E
|
R
|
L
|
P
|
10. Guess the word from its explanation:
1.
|
A place in a wall where you put a plug into in order to connect a piece of electrical equipment to an electrical supply.
|
|
2.
|
A small plastic object with 2 or 3 metal pins that connects a piece of electrical equipment to the main supply.
|
|
3.
|
To make something tight.
|
|
4.
|
To separate (or to remove) a piece of electrical equipment from electrical supply.
|
|
5.
|
To make something less tight or less firmly fixed.
|
|
6.
|
To remove the plug of a piece of electrical equipment from the electrical supply.
|
|
7.
|
To join together two or more things (ex. a video camera and a TV).
|
|
8.
|
A set of “buttons” that people use to manage a computer
|
|
9.
|
A screen that shows information from a computer.
|
|
10.
|
A machine that prints information from a computer on paper.
|
|
11. Translate the following sentences into Russian. Give the idea, not a word for word translation:
1.
|
Connect the printer to the computer.
|
2.
|
Loosen the screw first and then disconnect the cable.
|
3.
|
You must change the plug of your TV, it’s not working.
|
4.
|
Unplug the phone if the battery is full.
|
5.
|
Disconnect the keyboard and clean it!
|
6.
|
The central unit is working but the screen isn’t showing any picture.
|
7.
|
I plugged in the radio but it’s not working.
|
8.
|
Please, turn on the radio – I want to listen to the news.
|
9.
|
Could you switch the light off – I’m trying to relax.
|
10.
|
Something is wrong with the cable; I think you should change it to a new one.
|
Check the knowledge of active vocabulary from this part with the help of “ACTIVE VOCABULARY” section.
Part II
1. PLUGS AND SOCKETS
|
 Скачать 7.94 Mb.
Скачать 7.94 Mb.