Экология. НОВ.2019_Сборник_контрольных_работ_для_заочников_ФЗО_1. Технологический университет
 Скачать 1.02 Mb. Скачать 1.02 Mb.
|
Вариант 1 для направления подготовки 15.03.05 Конструкторско-технологическое обеспечение машиностроительных производствПрочитайте и устно переведите текст на русский язык. AN AVERAGE AUTOMOBILE An average automobile is made of roughly 14000 parts, which can be divided into several structural and mechanical subsystems. The most basic of these is the body of the automobile, which contains the passenger and storage space as well as the engine compartment. It is usually classified according to the number of doors and the type of roof it has (e.g., two-door hardtop) and is made of molded steel, which is painted and treated to retard corrosion. The body sits upon the chassis, a steel frame that also supports the engine, wheels, axle assemblies, transmission, steering mechanism, brakes, and suspension members. The internal-combustion gasoline engine, with reciprocating pistons and a fourstroke cycle, is the most widely used power plant. In the United States in the 1940s engines were developed in size and design from four cylinders to the more powerful configuration of eight cylinders in a "V" shape. Since the 1970s, however, the trend has been toward smaller, less powerful and more efficient engines. A transmission comprised of shafts, gears, and a clutch-is installed between the engine and the driving wheels to allow the engine to be disconnected when the engine is started and idling and to make the most efficient use of the engine's power varying loads. Transmissions are of two types: those in which the gears are shifted manually by the driver and those where the gears are shifted automatically by such a device as a hydraulic torque converter. To control it once it is in motion, a car is equipped with steering and braking systems. The steering system consists of a series of linkages and gears that transmit the movement of the steering wheel to the front wheels. One braking system employs two semicircular "shoes" at each wheel that when activated press outward against the inner surfaces of drums attached to each wheel. More recently disk brakes, in which a clamp squeezes a disk attached to the wheel, have been used. Automobiles have complex electrical systems that consist of a storage battery, alternator (alternating-current generator), devices for starting the engine and for vehicle operation (e,g., headlights and windshield wipers), and such accessories as heaters and radios. The battery provides enough power to engage the starting motor and to activate the ignition system. Once the engine is started, the alternator continually recharges the battery and supplies power to the other electrical equipment. There are several other important subsystems. The fuel system provides storage space for the fuel, transports it to the engine, and mixes it with air for combustion in the engine. The exhaust system vents exhaust gases by way of a muffler, which helps reduce engine noise. The lubrication system keeps friction from wearing out moving parts. Relatively lightweight motor oils are used in the engine, and heavier weight oils and greases are used in such parts as transmissions and wheel bearings, the cooling system keeps the engine from overheating, generally by means of liquid coolant, although many engines are air cooled. The suspension system, comprised of coil or leaf springs and shock absorbers, is combined with the tires to cushion the vehicle from the shock caused by driving over irregular surfaces. In addition, tires come in a variety of tread designs to provide traction in all driving conditions. 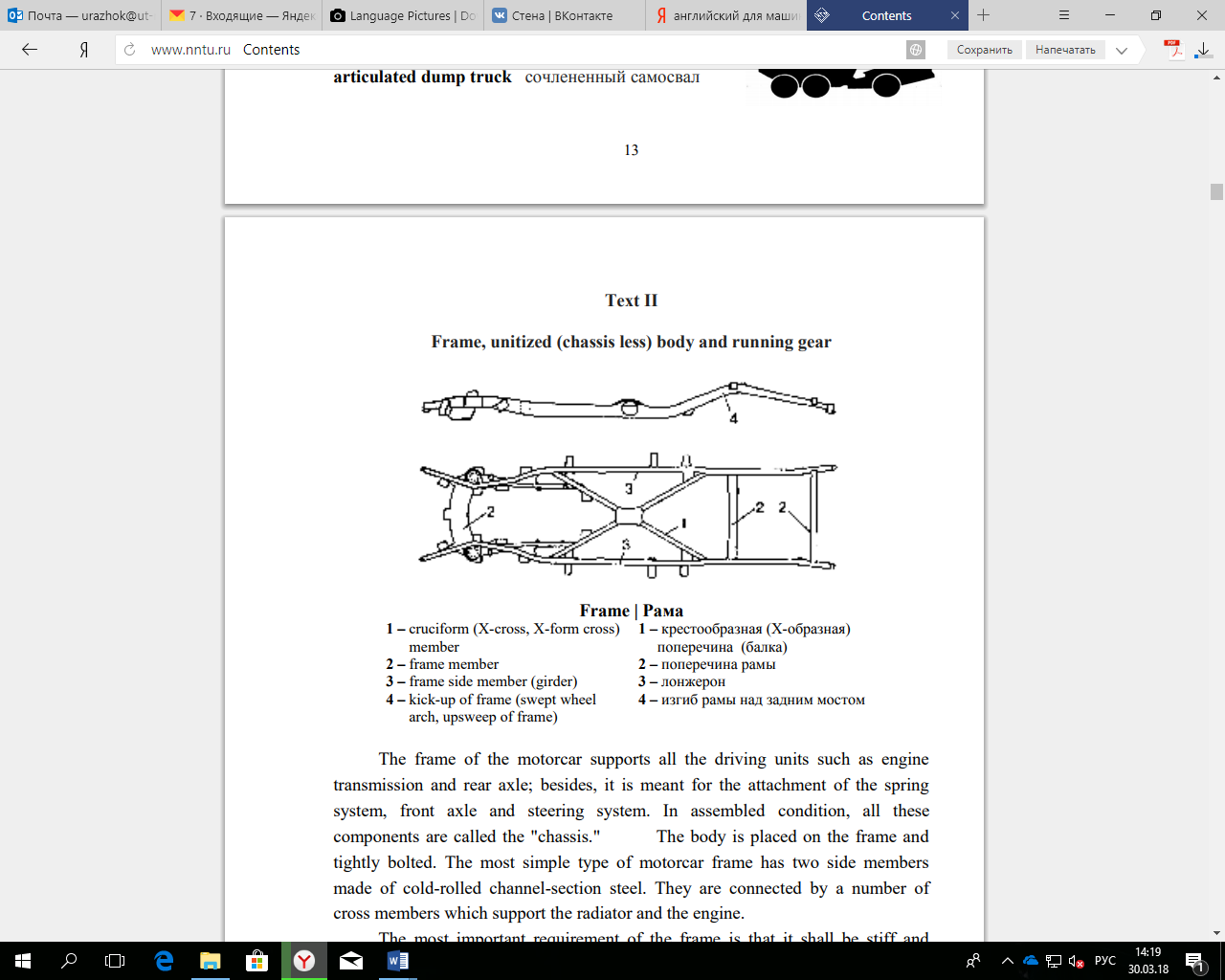 Frame, unitized (chassis less) body and running gear Frame, unitized (chassis less) body and running gearThe frame of the motorcar supports all the driving units such as engine transmission and rear axle; besides, it is meant for the attachment of the spring system, front axle and steering system. In assembled condition, all these components are called the "chassis." The body is placed on the frame and tightly bolted. The most simple type of motorcar frame has two side members made of cold-rolled channel-section steel. They are connected by a number of cross members which support the radiator and the engine. The most important requirement of the frame is that it shall be stiff and strong enough to resist the twisting and bending forces to which it is subjected, particularly when the vehicle is traveling over rough roads. Since the introduction of the independent wheel suspension by transverse springs etc., the shapes of the frames have changed considerably. For some modern passenger cars and buses, the frameless construction, the so-called "chassis less body" is now used. In this case, the body is designed so stiff that it replaces the frame. All the units, such as engine, transmission, axle casing, springs and steering, otherwise arranged on the frame, are attached to the body. Therefore, only a limousine or bus body can be used for a chassis-less construction 15 since only these bodies may be built sufficiently resistant to torsion due to their particular type of construction. A special type of frameless construction is the platform construction; in this case, the frame has been replaced by a corrugated continuous bottom plate. This construction can be used only for independent wheel suspension with front-wheel drive or rear-mounted engine since it has no oscillating universal shaft. It combines the advantages of light-weight construction and the possibility to attach various bodies. In addition, the continuous bottom plate offers a good protection against dirt and it permits convenient clearing. (Атрохин А.М. Сборник текстов по дисциплине «Иностранный язык (деловой)» (английский язык)) II. Письменно переведите 4 и 5 абзац. III. Найдите абзац, где выражается основная идея текста. |
