английский за проф направлением. Укладач Триполець В.І. Рецензенти
 Скачать 4.04 Mb. Скачать 4.04 Mb.
|
|
2. Read the text closely and answer the following questions.
3.Fill in the blanks with the words given below. a) Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a condition in men that affects the ...gland.
f)... is a doctor who specializes in treating problems of the urinary system and the male reproductive system.  a) bacterial, b) kidney, c) urologist, d) blood, e) urinary, j) prostate, g) inflamed text 2 1. Read the text about of the most widespread urinary system problem. KIDNEY STONES A kidney stone is a solid piece of material that forms in the kidney from substances in the urine. It may be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a pearl. Men are more prone to get kidney stones than women, and around half of all people who have previously had a kidney stone will develop another one within five years. Most kidney stones pass out of the body without help from a doctor. 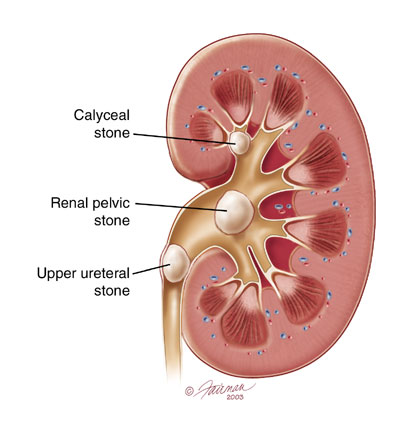 But sometimes a stone will not go away. It may get stuck in the urinary tract, block the flow of urine and cause great pain. The following may be signs of kidney stones that need a doctor's help: But sometimes a stone will not go away. It may get stuck in the urinary tract, block the flow of urine and cause great pain. The following may be signs of kidney stones that need a doctor's help:о Extreme pain in your back or side that will not go away. о Blood in your urine. оFever and chills. о Vomiting. о Urine that smells bad or looks cloudy. о A burning feeling when you urinate. Initial treatment includes pain medication and oral or intravenous fluid to help the stone pass through the urine. Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy is a procedure that uses shock waves to break up the stone without the need for surgery. Surgery may be necessary if the stone is very large and if there is blockage of the affected kidney or infection. Depending on the cause of your kidney stone, your doctor may prescribe medication or suggest dietary changes to prevent a recurrence. Also to help prevent any type of kidney stone you should drink more fluid. You should aim to drink at least three litres every 24 hours, or enough to make your urine clear rather than a yellow colour. Talk to your doctor for more advice on this. 2. Answer the following questions.
3. Say whether the sentences are true or false. 1.Kidney stone may be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a pearl.
4. Retell the text. 52. The Reproductive System. Репродуктивна система. I. Vocabulary. 1. Read and learn the topical vocabulary. ovum (pi. ova) — яйце; ovary — яєчник; uterus — матка; fallopiantubes — фаллопієві труби; fertilization — запліднення; pregnancy — вагітність; fetus — плід; pubertyperiod — період статевого дозрівання; testis (pi. testes) — яєчко; scrotum — мошонка; spermatozoon (pi. spermatozoa) — сперматозоїд; prostategland — передміхурова залоза; epididymis — придаток яєчка. 2. Match the definitions and terms.
the same pregnancy
the blood supply of the mother
3. Form word combinations.
II. Reading. Read the information about human reproduction. Get ready to comment the text. HUMAN REPRODUCTION Human reproduction is the process by which human beings create more of their own kind. A new individual develops from the joining together of two sex cells, one from a female parent and one from a male parent. The union of these cells is called fertilization. Biologists refer to sex cells as gametes. Females produce gametes called eggs or ova. Male gametes are called sperm. Fertilization may occur after a male delivers sperm to the female's egg by means of sexual intercourse. Fertilization begins a remarkable period of development in which the egg develops into a fully formed baby within the body of the female. This period of development, called pregnancy, takes about nine months. At the beginning of pregnancy, the fertilized egg is smaller than the period at the end of this sentence. The egg develops into a growing mass of cells called an embryo. Gradually, the cells rearrange themselves to form tissues. By the end of the second month of pregnancy, all the major body organs and organ systems have formed and the embryo looks distinctly human. During the rest of pregnancy, the embryo is called a fetus. The fetus grows while its systems prepare for the day when they must function outside the mother's body. Pregnancy ends when the new baby passes out of the mother's body at birth. Human beings are born with the body organs needed for reproduction. But reproduction cannot actually occur until these organs mature. This maturation process takes place during puberty, a period of several years in which a boy or girl goes through dramatic physical changes. These changes are regulated by certain hormones (chemicals produced by the body). Puberty begins during or just before the early teen-age years. The reproductive systems of females and males differ greatly in shape and structure. But both systems are specifically designed to produce, nourish, and transport the eggs or sperm. III. Post-reading activities. 1. Answer the following questions. 1.How do we call the process by which human beings create more of their awn kind?
2. Complete the sentences with suitable words. 1. A new individual develops from the joining together of two ....
 a) shape, b) reproductive, c) sex cells, d) organs, e) structure, f) pregnancy,g) organ systems IV. Speaking. Make up a dialogue between a gynecologist/urologist and a patient. Here is vocabulary for you to speak about reproductive system problems.
INSTRUCTIONS I am afraid you need a course of treatment with medications, both tablets and injections. There is recommended administration of estrogenic preparations. Don't live sexual life while treatment. Don't forget to use condoms while sexual intercourse. V. Supplement. Text 1 1. Match the following English word combinations and the Ukrainian ones. 1. external organs a) хвилеподібні скорочення 2. pear-shaped b) велика кількість 3. menstrual cycle c) зовнішні органи 4. wavelike contractions d) грушоподібний 5.large amount e) менструальний цикл 2. Read and translate the following text. Get ready to speak on the female reproductive system. THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In females, the reproductive system consists primarily of a group of organs located within the pelvis. A woman or girl has external organs called the vulva. The outer parts of the vulva cover the opening to a narrow canal called the vagina. The vagina leads to the uterus, a hollow, pear-shaped, muscular organ in which a baby develops. Two small, oval organs called ovaries lie to the right and left of the uterus. The ovaries produce, store, and release eggs. These organs also produce two types of hormones — progesterone and estrogens. Eggs from the ovaries reach the uterus through tubes called fallopian tubes or oviducts. Females produce eggs as part of a monthly process called the menstrual cycle, which begins during puberty. Each menstrual cycle, the female reproductive system undergoes a series of changes that prepares it for fertilization and pregnancy. If the egg is not fertilized, a shedding or loss of tissue in the uterus called menstruation occurs. Bleeding is associated with this process and lasts three to seven days. Menstruation marks the beginning of each menstrual cycle. Each cycle lasts about 28 days. Other changes during a menstrual cycle involve cells in the ovaries called oocytes. Eggs develop from these cells. At birth, each ovary has about 400,000 oocytes. These cells remain inactive until the first menstrual cycle. Thereafter, many oocytes grow and begin to mature each month. Normally, only one oocyte in either of the ovaries reaches full maturity. This fully developed cell — the mature egg — is released from the ovary in a process called ovulation. This process occurs at about the midpoint of the menstrual cycle. After ovulation, the egg travels toward the uterus through one of the fallopian tubes by means of wavelike contractions of muscles and the beating of cilia (hairlike structures) located on cells in the walls of the oviduct. Fertilization may occur in one of the tubes. An unfertilized egg lives for about 24 hours after it leaves the ovary. Important changes also occur in the endometrium (lining of the uterus). During the first half of the menstrual cycle, the ovaries release relatively large amounts of estrogens, which cause the endometrium to thicken. The endometrium reaches its maximum thickness at about the time of ovulation. After ovulation, the ovaries release relatively large amounts of progesterone. This hormone maintains the thickness of the endometrium, so that a fertilized egg can attach to the uterus. If fertilization occurs, the endometrium continues to develop. If fertilization does not occur, the egg breaks down and the production of progesterone decreases. The thickened endometrium also breaks down and passes out of the body during menstruation. Most women produce eggs until the ages of about 45 to 55, when the menstrual cycles become increasingly infrequent and then stop. This period of a woman's life is called menopause. The completion of menopause marks the end of a woman's natural childbearing years. 3. Answer the following questions.
4. Find in the text definitions of anatomical terms denoting the female reproductive system. | ||||
