РАЗДЕЛ VI. MICROORGANISMS
Цели раздела
В результате изучения теоретического материала по темам данного раздела вы должны
знать:
лексический минимум, необходимый для чтения и перевода профессионально ориентированных текстов о вирусах и бактериях;
лексический минимум, необходимый для устного высказывания об основных характеристиках вирусов и бактерий.
уметь:
применять знания изученного лексико-грамматического материала для чтения и перевода иноязычных профессионально ориентированных текстов по темам раздела;
извлекать необходимые сведения из иноязычных источников информации, используя изученный лексико-грамматический материал;
употреблять изученный лексический минимум в устном высказывании об основных характеристиках вирусов и бактерий.
Обучающие цели:
Изучить лексический материал, необходимый для понимания иноязычной информации по темам раздела и устного общения по ним.
Научиться применять изученный лексический материал в заданных учебных ситуациях.
Составлять устные высказывания, используя изученный лексический материал по каждой теме раздела.
TOPIC 40. MICROORGANISMS
As you know, microorganisms are very small one-celled organisms. Studying this topic you’ll learn where they can be found and how they can influence our bodies.
1.Match the words in the columns
oxygen
virulent
to invade
disease
to destroy
to occur
tissues
to fight
mucous
skin
|
болезнь
ткани
кислород
уничтожать
кожа
заразный
проникать
происходить
бороться
слизистый
|
2.Read the text and find the English equivalents of the given words.
крошечный одноклеточный организм
вредный
выживать
существующие микроорганизмы
делить на две группы
благоприятный для развития
мельчайший микроорганизм
в этом случае
защитные средства тела человека
проникать в ткань
местная или общая инфекция
Microorganisms
Microorganisms are very tiny one-celled organisms, viruses, and bacteria. They are found everywhere in the world. They are found in all living things, plants and animal. Microorganisms can live in the air, on land, and in fresh or salt water environments. Some of them can be harmful and causes diseases, but there are some microorganisms that are needed for living things to survive.
All existing microorganisms can be divided into two main groups – aerobic and anaerobic. Aerobic organisms must have atmospheric free oxygen for their life and growth. But free oxygen is not favourable for the development of anaerobic microorganisms.
Any minute virulent microorganisms may invade the human body. But due to the local protective agents of the human organism they are destroyed. In this case no disease occurs.
However the local protective agents of the human body are not always able to destroy completely the invading microorganisms. In this case a local or general infection may occur.
Most of the microorganisms produce diseases when they enter the tissue and destroy it. But the human organism can fight against microorganisms which have passed its first protective barriers, such as skin and mucous membrane.
3.Answer the questions
What are microorganisms?
Where are they found?
Where can microorganisms live?
What groups can all microorganisms be divided into?
What organisms must have free oxygen for their life and growth?
When do most of the microorganisms produce diseases?
In what case does no disease occur?
In what case may a local or general infection occur?
4.Speak English.
Микроорганизмы – это крошечные одноклеточные организмы.
Некоторые микроорганизмы могут быть вредными.
Некоторые микроорганизмы необходимы живым существам для выживания.
Мельчайшие вирулентные микроорганизмы могут проникнуть в тело человека.
Они проникают в ткань органа и уничтожают её.
Но организм может бороться с вредными микроорганизмами.
Если защитные средства организма уничтожают проникающие микроорганизмы, то болезнь не наступает.
Местная или общая инфекция может произойти тогда, когда защитные средства тела не могут уничтожить опасные микроорганизмы.
TOPIC 41. VIRUSES
You already know that viruses cause many infectious diseases that ruin the health of people. Studying this topic you’ll learn about the structure, origin and spread of these small infectious agents.
1.Study the new words.
reproduce – размножаться, воспроизводить
host – хозяин
be forced – быть вынужденным
at an extraordinary rate – на очень большой скорости
cells – клетки
divide – делиться
species – виды, разновидности
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – ДНК (дезоксирибонуклеиновая кислота)
RNA (ribonucleic acid) – РНК (рибонуклеиновая кислота)
protein coat – протеиновая оболочка
envelope of fat – жировая оболочка
|
vary – отличаться
helical – спиральный, винтовой
iсosahedral – двадцатигранный
spread – распространяться
vectors – переносчики инфекции
insects – насекомые
rely – полагаться, зависеть
particular – особый, особенный, индивидуальный
contaminate – заражать
21.exposure – подвергание внешнему
воздействию, незащищенность
evolve – развиваться, эволюционировать
|
2.Look through the passages. Title them using the given titles.
Structure of viruses
|
General characteristics
|
Spread of viruses
|
Origin of viruses
|
Treatment of viral diseases
|
|
1.____________________________. A virus is a biological agent that reproduces inside the cells of living hosts. When infected by a virus, a host cell is forced to produce many thousands of identical copies of the original virus, at an extraordinary rate. Unlike most living things, viruses do not have cells that divide; new viruses are assembled in the infected host cell. Over 2,000 species of viruses have been discovered.
2.____________________________ .A virus consists of two or three parts: genes, made from either DNA or RNA, long molecules that carry the genetic information; a protein coat that protects the genes; and some viruses have an envelope of fat that surrounds and protects them when they are not contained within a host cell. Viruses vary in shape from the simple helical and icosahedral to more complex structures. Viruses are about 100 times smaller than bacteria.
3.____________________________ .Viruses spread in many different ways. Plant viruses are often spread from plant to plant by insects and other organisms, known as vectors. Some viruses of animals are spread by blood-sucking insects. Each species of virus relies on a particular method. Influenza viruses are spread through the air by people when they cough or sneeze, noroviruses are transmitted by the faecal-oral route, contaminate hands, food and water. Rotavirus is often spread by direct contact with infected children. Human Immuno-deficiency Virus HIV, is transmitted during sexual contact and by the exposure of infected blood.
4._____________________________.The origins of viruses is unclear: some may have evolved from plasmids—pieces of DNA that can move between cells—while others may have evolved from bacteria.
5._____________________________.Viral infections often cause disease in humans and animals, however they are usually eliminated by the immune system. Examples of common human diseases caused by viruses include the common cold, influenza, chickenpox and measles. Many serious diseases such as AIDS and hepatitis are caused by viruses. Antibiotics have no effect on viruses, but antiviral drugs have been developed to treat life-threatening infections. Vaccines that produce lifelong immunity can prevent some viral infections.
3.Translate the 1st passage into Russian.
4.Read the 2d passage and do the tasks A and B.
A. Name three parts of a virus.
1.______________________ 2.________________________ 3._____________________
B. Complete the sentences and translate them.
Genes are made of __________________________________________________
Genes are __________________________________________________________
A protein coat ______________________________________________________
An envelope of fats __________________________________________________
Viruses may be ______________________________________________________
5.Read the 3d passage. Say if the statements are true or false. Correct the mistakes. Translate the sentences.
Viruses spread in different ways.
Plant viruses are often spread by vectors.
Some viruses of animals are spread by butterflies.
Influenza viruses are spread through the food by people when they cough or sneeze.
Noroviruses are transmitted by the faecal-oral route, contaminate hands, food and water.
Rotavirus is often spread by indirect contact with infected children.
Human Immuno-deficiency Virus HIV is transmitted during sexual contact and by the exposure of infected blood.
6.Read the 4th and 5th passages. Answer the questions. Translate the answers.
Where have viruses evolved from?
What do viral infections cause?
What system eliminates viruses?
What diseases are caused by viruses?
What drugs can help to treat viral infections?
What can prevent some viral infections?
7.Fill in the gaps using the given words.
long molecules / helical / eliminate / viral infections / protects / influenza / protein coat / measles / genetic / complex / prevent / surrounds / antiviral drugs
A virus consists of two or three parts: genes, a _____________ and an envelope of fat. DNA or RNA are _________ that carry the ___________ information. A protein coat ________ the genes. An envelope of fat __________ and protects viruses. Viruses may be __________ and icosahedral or have more _________ structures. __________________ cause diseases in human and animals. Common colds, ___________, chicken-pox and _____________ are caused by viruses. The immune system helps to ______________ viruses. ________________ treat viral infections. Vaccines can ____________ some viral infections.
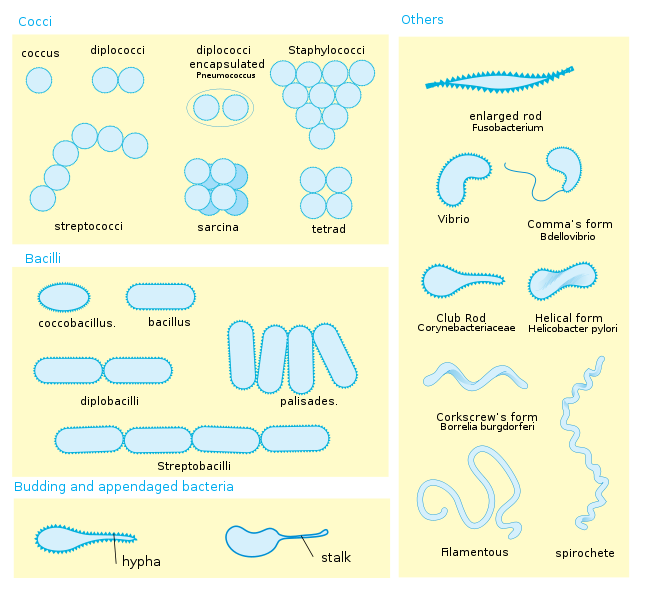
TOPIC 42. BACTERIA
Do you know that the term bacteria was introduced in the 19th century by the German botanist Ferdinand Cohn (1828-98)? Studying this topic you’ll be able to enrich your knowledge about bacteria, their shapes, habitant and influence on the living organisms.
1.Arrange (расположите) the sentences according to the given titles. Translate the sentences.
General characteristics
……………………………………………………………………………………….
Shapes of bacteria
……………………………………………………………………………………….
Habitat (среда обитания) of bacteria
………………………………………………………………………………………
Harmful bacteria
………………………………………………………………………………………
Beneficial bacteria
………………………………………………………………………………………
curved – изогнутый
comma-shaped – имеющий форму запятой
cluster of grapes – гроздь винограда
anthrax – сибирская язва
fertile – плодородный
inhibit – останавливать, подавлять
lactic acid – молочная кислота
Some types of bacteria can cause diseases and become harmful to the environment, animals and humans.
Bacteria in our digestive system help to convert milk protein into lactic acid and inhibit the growth of potentially harmful bacteria.
Bacteria is commonly found in the ground, water and in other living organisms.
Bacteria (bacterium) are a large group of minute single-celled microorganisms.
Bacteria help produce the food we eat and keeps the soil fertile, it also helps us digest our food.
Some rod-shaped bacteria, called vibrio (вибрион), are slightly curved or comma-shaped; others, can be spiral-shaped, called spirilla.
Some bacteria offer benefits that we likely could not live without.
Many bacteria exist as single cells, others form pairs, chains and group together in "cluster of grapes".
There are typically 40 million bacterial cells in a gram of soil and a million bacterial cells in a milliliter of fresh water.
Bacteria vary in shapes.
They cause infectious diseases, including cholera, syphilis, anthrax, leprosy and bubonic plague.
Most bacterial species are spherical (cocci), rod-shaped (bacilli).
Bacterial infections are treated with antibiotics.
They are among the oldest living organisms on the Earth.
РАЗДЕЛ VII. THE MEDICAL EDUCATION IN GREAT BRITAIN AND THE USA
Great Britain and the USA have their own systems of medical education and health service. This unit will give you a chance to know about medical education in these countries.
Цели раздела
В результате изучения теоретического материала по темам данного раздела вы должны
знать:
лексический минимум, необходимый для чтения и перевода профессионально ориентированных текстов о системах медицинского образования в Великобритании и США;
лексический минимум, необходимый для устного высказывания об этапах медицинского образования в Великобритании и США.
уметь:
применять знания изученного лексико-грамматического материала для чтения и перевода иноязычных профессионально ориентированных текстов по темам раздела;
извлекать необходимые сведения из иноязычных источников информации, используя изученный лексико-грамматический материал;
употреблять изученный лексический минимум в устном высказывании об этапах медицинского образования в Великобритании и США.
Обучающие цели:
Изучить лексический материал, необходимый для понимания иноязычной информации по темам раздела и устного общения по ним.
Научиться применять изученный лексический материал в заданных учебных ситуациях.
Составлять устные высказывания, используя изученный лексический материал по каждой теме раздела.
TOPIC 43. MEDICAL EDUCATION IN GREAT BRITAIN
Studying this topic you'll learn about the education and training of medical doctors in the United Kingdom, from entry-level training through to continuing education of qualified specialists.
1.Read about the entry requirements to a medical school and find English equivalents of these words.
поступать в медицинскую школу
сдавать тест
тестировать общие способности и знания
Сертификат о среднем образовании
оценка «хорошо» и «отлично»
изучать химию на повышенном уровне
конкурс на место
персонал медицинской школы
выбирать кандидатов для интервью
взимать плату
получать финансовую помощь
покрывать расходы
Entry Requirements (требования для поступления)
To enter a medical school in Great Britain candidates must be 18 years of age. They must take BMAT (Biomedical Admission Test) which lasts 2 hours. It tests their general abilities and knowledge. All candidates must have GCSE (General Certificate of Secondary Education) at grade B or A in Mathematics and English. They also must study Chemistry, Biology and Physics at advanced level (A level) before entering any medical school. The competition for places is very high. The staff of the medical school selects candidates for interview and makes the best ones offers of places.
Medical schools charge tuition fees for education. Most students receive financial assistance in the form of grants, which cover their expenses wholly or in part.
2.Read about the curriculum and fill in the table
Subjects
|
Activities
|
Human anatomy
|
attend lectures
|
The Curriculum (учебный план)
Students spend five years studying different medical sciences: Human anatomy, Biology, Physiology, Biochemistry, Statistics, Genetics, the Methods of Clinical Examinations, History Taking, General Pathology, Microbiology, Pharmacology, Community Medicine and others. Students attend lectures, do dissections and practical work in labs. They follow up their patients and attend wards rounds. After five years of studies students obtain degrees of Bachelor of Medicine (B.M) and Bachelor of Surgery (B.S.). These degrees give the right to registration as a medical practitioner.
3.Read about the examination and answer the questions.
What do students do at the end of the term?
What do most exams include?
What must students do before finals in Surgery?
What must students do before finals in Obstetrics and Gynaecology?
Examinations
The academic year is divided into 3 terms. At the end of each term students take exams. Most of the exams are written. They include academic and practical problems. The final exams are in Medicine, Surgery, Obstetrics, Gynaecology and Pathology. Before final exams in Surgery students assist in operations. Before final exams in Obstetrics and Gynaecology they must assist during the delivery of at least 20 babies. These examinations are both written and oral.
4.Say if the statements are true or false
Before finals students work in a hospital for a year.
During the period of internship students work in a hospital for a year.
After internship a young doctor obtain the degree of Bachelor of Medicine.
A young doctor can work as a medical practitioner after residency.
During the period of residency students must work in a hospital in a definite field of medicine.
The period of residency lasts 3 years of work.
Students can obtain the degree of Doctor of Medicine by performing an operation.
Further Education (дальнейшее обучение)
After the finals graduates work in hospitals for a year. This period is called internship. Students work under the supervision of the medical school. After internship a young doctor obtains a “Certificate of Experience” from medical school and he or she can work as medical practitioner. Further specialization requires training in residency. It takes 1-2 years of work in a hospital in some definite field of medicine: Gynaecology, Urology, Neurology and so on. Students also can obtain the degree of Doctor of Medicine by writing a thesis.
5.Match two parts of the sentences together. Translate them into Russian.
To enter a medical school in Britain
For entrance the candidates must study
The staff of the medical school
Medical schools charge
Medical students follow up patients and
After 5 years of studies the students obtain
Written and oral exams include
During internship medical graduates must
After internship graduates can
During residency students get
|
work as medical practitioners.
degrees of Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery.
candidates must take an admission test.
work in a hospital for a year.
a specialization in a definite field of medicine.
selects students for interviews and offers places for the best ones.
tuition fees for education.
Chemistry, Biology and Physics at advanced level.
practical and academic problems.
attend wards rounds.
|
TOPIC 44. THE MEDICAL EDUCATION IN THE USA
Studying this topic you'll learn about the education and training of medical doctors in the USA, from entry-level training through to continuing education of qualified specialists.
Task : Study the information about medical education in the USA according to your variant.
Variant 1. Admission to an USA Medical School
1.Find the English equivalents in the text below.
начальное школьное образование
средняя школа
пройти курс подготовительного (домедицинского) обучения
длиться 3 года
подавать заявление в медицинскую школу
учебная успеваемость
отбор студентов
вступительный тест
приемная комиссия
оценивать общие способности
конкурс на место
2.Translate the sentences into Russian
Primary school education generally takes the pupils from the age of 6 to the age of 14 years, and secondary school – to the age of 18.
After finishing his secondary school the candidate for medical school must take a course of premedical studies in a college or university.
This course lasts for 3 years and prepares the candidates for a medical school.
A student applies for admission to a medical school when he has completed premedical studies.
Academic achievement is the most important factor in the selection of students. In most medical schools candidates are required to pass the admission test.
This is a national multiple choice test.
The test lasts about 8 hours over a one day period and includes questions in biology, chemistry, physics, mathematics and English.
Then, the special admission committees have personal interviews with the candidates in order to assess the candidates’ general abilities, his character and his abilities to study medicine.
The competition for places is very difficult and only about half of the students who apply to a medical school are accepted and begin their medical education.
Variant 2. Curriculum
1.Find the English equivalents in the text below.
основные медицинские предметы
состоять из клинических предметов
проходить практику
участвовать в лечении пациентов
получать степень
работать в больнице интернами
интернатура
ординатура
обязателен для всех выпускников-медиков
специальность врача
лицензия на практику
2.Translate the sentences into Russian
Curriculum
The basic medical sciences are presented largely during the first two years of medical studies.
The students study anatomy, biophysics, biochemistry, physiology, bacteriology, histology and other subjects.
In the second year they study microbiology, pathology, physical diagnosis, pharmacology and laboratory diagnosis.
During the final two years the curriculum consists of clinical subjects.
Medical students have practical work at teaching hospitals affiliated to the medical school.
Students in small groups meet their teachers in the wards and in the out-patient departments where they participate in the treatment of the patients.
At the end of 4 years all students receive the Degree of Doctor of Medicine.
Then they must work in the hospital for one year as interns. This course of work at the hospital is called internship.
The period of residency is obligatory for all medical graduates.
The period depends on the specialty of the doctor and may be 3 or 4 years.
After the residency the graduate is granted a license to practice and he may work either in government service or private practice.
Variant 3. Medical Colleges and Universities in the USA
1.Find the English Equivalents in the text below.
аспирантский уровень
законченное университетское образование
получить университетскую степень
обучение в ординатуре
основные медицинские науки
методы осмотра пациента
приобретать опыт
обязательные и элективные курсы
выбирать специальность
получать лицензию на практику
2.Translate the sentences into Russian
In the USA medicine is taught only at the postgraduate level after an undergraduate university education.
You must first receive an undergraduate degree.
Medical education in the US is generally considerably longer than medical education in the UK.
Four years of undergraduate study (pre-medical education) are followed by four years of medical school, then three to seven years of residency training.
After successful completion of the four-year medical school curriculum and exams, the Doctor of Medicine (MD) degree is conferred (присуждать).
The entire process can take anywhere from 11 to 15 years.
In general, during the first two years you will study basic medical sciences: anatomy, biochemistry, physiology, microbiology, pathology and pharmacology and examination techniques.
In the third year, you will gain experience with patients in hospital, clinics in the fields of pediatrics, obstetrics and gynaecology, surgery and psychiatry.
The fourth year is a mix of required and elective courses where you will gain additional experience and expertise in caring for patients.
Towards the end of medical school, you will choose a specialty in which you will spend at least three years in a residency after completing the MD programme.
During that period you may obtain a license to practice.
Variant 4. Medical Schools in the USA
1.Find the English equivalents in the text below.
образовательное учреждение
обеспечивать квалификацию и обучение
считаться лучшим
период обучения
зависеть от планов на будущее
специализироваться в какой-либо области
трудно поступить
оценивать кандидата
результаты вступительного теста
рекомендательные письма
предлагать разные курсы для получения степени
основной учебный план
2.Translate the sentences into Russian
A medical school is an educational institution that provides the required qualification and training to a doctor.
There are a number of medical schools in America and some of them are amongst the best in the world.
One such medical school is in the Harvard University, which is considered to be the best one.
The training period of a doctor depends on the future plans of the specific student.
If one wishes to do specialization in some field then the time period may extend up to eight years, otherwise a candidate must have a four year training.
It is quite difficult to get admission in one of these schools.
The faculty of any American medical school evaluates a candidate on the basis of Medical School Admission Test (MCAT) scores.
An applicant is also evaluated on the basis of personal interview and recommendation letters.
There are a number of American medical schools that offer various degree courses.
Different schools offer different curriculum but the basic curriculum involves subjects such as pathology, biochemistry, anatomy, surgery, the study of pediatrics and psychiatry including internal medicine and gynecology.
American medical schools also provide degree in nursing.
|
 Скачать 4.92 Mb.
Скачать 4.92 Mb.