Англ.яз. для 1 курса. Тесты за семестр выполняются по желанию студента для самоконтроля
 Скачать 0.52 Mb. Скачать 0.52 Mb.
|
|
ЗАДАНИЯ К ТЕКСТУ: 1. Прочтите текст, пользуясь приведенным выше словарем. Изложите кратко основное содержание текста на английском языке. 2. Ответьте на вопросы: 1. What does the federal government consist of? 2. What part does the President play in the government? 3. What is the legislative power vested in? 4. How does a bill become a law? 5. What are the functions of the President? 6. What are the executive and the judicial branches represented by? 7. What are the official symbols of Russia? Education in the Russian Federation Russians have always shown a great concern for education. The right to education is stated in the Constitution of the Russian Federation. It is ensured bу compulsory secondary schools, vocational schools, and higher education establishments. It is also ensured by the development of extramural and evening courses and the system of state scholarships and grants. Education in Russia is compulsory up to the 9th form inclusive. The stages of compulsory schooling in Russia are: primary education for ages 6 – 7 to 9 – 10 inclusive; secondary education including intermediate school for ages 10 – 11 to 12 – 13 inclusive, and senior school for ages 13 – 14 to 14 – 15 inclusive. If a pupil of a secondary school wishes to go on in higher education, he or she must stay at school for two more years. Primary and secondary school together comprise 11 years of study. Every school has a “core curriculum” of academic subjects, such as Russian, Literature, Mathematics, History, a foreign language and others. Lyceums and gymnasiums offer programs giving a profound knowledge in some field of study. After finishing the 9th form one can go on to a vocational school which offers programmes of academic subjects and a program of training in a technical field, or a profession. After finishing the 11 the form of a secondary school, a lyceum or a gymnasium one can go on in higher education. All applicants must take competitive examinations. Higher education institutions, that is, institutes or universities, offer a 5-year program of academic subjects for undergraduates in a variety of fields, as well as a graduate course. If one finishes a graduate course and writes a thesis, he or she receives a candidate's degree or a doctoral degree. Higher educational establishments are headed by Rectors. Prorectors are in charge of academic and scientific work. An institute or a university has a number of faculties, each specializing in a field of study. Faculties have specialized councils which confer candidate and doctoral degrees. The system of secondary and higher education in Russia is going through a transitional period. The main objectives of the reform are: to decentralize the higher education system, to develop a new financial mechanism, to give more academic freedoms to faculties and students. All secondary schools, institutes and universities until recently have been funded by the state. Now there is quite a number of private fee-paying primary and secondary schools; some universities have fee-paying departments. Vocabulary to show a great concern for - придавать большое значение education - образование the right to education - право на образование to be stated - отмечаться, констатироваться to be ensured by smth. - обеспечиваться чем-либо compulsory - обязательный a secondary school - средняя школа a vocational school - училище a higher education establishment - высшее учебное заведение an extra-mural course - заочное обучение an evening course - вечернее обучение state scholarships and grants - государственные стипендии inclusive - включительно a stage - этап compulsory schooling - обязательное школьное обучение primary education - начальное образование Secondary education - среднее образование intermediate school - средние классы senior school - старшие классы to go on in higher education - продолжать образование в вузе a core curriculum - основная программа an academic subject - академический предмет a lyceum - лицей a gymnasium - гимназия to give a profound knowledge - давать углубленные знания an applicant - абитуриент to take competitive examinations - сдавать конкурсные экзамены a higher education institution - вуз an undergraduate - студент a graduate course - аспирантура a thesis - диссертация a candidate degree - степень кандидата наук to be headed by Rector - возглавляться ректором a specialized council - специализированный совет to confer a degree - присваивать степень to go through a transitional period - находиться в переходном периоде an objective - цель to decentralize smth. - уничтожить централизацию в чем- либо to be funded by the state - финансироваться государством a fee-paying school - платная школа ЗАДАНИЯ К ТЕКСТУ: 1. Прочтите текст, пользуясь приведенным выше словарем. Изложите кратко основное содержание текста на английском языке. 2. Ответьте на вопросы: 1. What is the right to education in Russia ensured by? 2. What are the stages of compulsory schooling in Russia? 3. What programmes of study do different types of school in Russia offer? 4. What is a vocational school? 5. What is necessary for entering a higher education establishment? 6. What degrees can one get at a higher education establishment? 7. What is the structure of an institute or a university? 8. How can you prove that education in Russia is going through a transitional period? Итоговый тест за 1-й семестр 1. В каком из следующих слов звук, передаваемый “i”, отличается от остальных? 1) six, 2) five, 3) right, 4) write, 5) I'm, 6) bite, 7) mine. 2. Выберите правильный глагол: 1) Не... he wanted to post a letter. a) said b) told 2) Will you ... her to come at 6 p.m.? a) say b) tell 3) She ... to him: “Please, open the window”. a) said b) told 4) Who... you that? a) said b) told 3. Выберите правильный вспомогательный глагол: 1) We... visit our relatives on Saturday. a) shall b) should c) will d) would 2) The doctor said he... be all right soon. a) shall b) should c) will d) would 3) I'm sure you ... like her. a) shall b) should c) will d) would 4) We hoped we ... return by the end of the month. a) shall b) should c) will d) would 4. Выберите правильную форму глагола: 1) We thought you ... it. a) know b) knew 2) They said the guests .... a) arrived b) had arrived 3) The telegram said they ... on Monday. a) -will come b) would come 4) He asked what institute I... going to enter. a) am b) is c) was 5) I looked out and saw that it.... a) is raining b) was raining c) will be raining 5. Выберите правильный вариант перевода: 1) She said she lived in Pushkin street. a) Она сказала, что живет на улице Пушкина. b) Она сказала, что жила на улице Пушкина. 2) I thought it was warmer outside. a) Я думала, что на улице теплее. b) Я думала, что на улице было теплее. 3) I know you learnt French at school. a) Я знаю, что ты изучаешь французский в школе. b) Я знаю, что ты изучал французский в школе. 4) Mother said she received letters from her son every week. a) Мама сказала, что получает письма от сына каждую неделю. b) Мама сказала, что получала письма от сына каждую неделю. 6. Соотнесите две части предложения: 1) I told him... 2) We asked... 3) She wanted to know... 1) ... if they enjoyed the concert. 2) ... he would find my house easily. 3) ... who would meet her at the station. 7. Укажите, в каком предложении глагол стоит в “Future-in-the-Past”: 1) a) You should consult a doctor. b) Mother says I should ring him up. c) I knew I should finish it on time. 2) a) I would like an ice-cream. b) Who would think about it? c) She promised she would come on time. 8. Выберите правильную форму глагола: 1) We hoped that the weather... fine. a) will be b) was c) would be 2) I didn't know that it.... a) is raining b) was raining c) will be raining 3) She said her friend... English fluently. a) speaks b) spoke c) is speaking 4) They told us that they... to a new flat. a) move b) moved c) had moved 9. Завершите предложения: 1) She said she was writing the latter.... a) at that time b) by that time 2) He said he was busy.... a) now b) at the moment 3) He said he would return the book.... a) tomorrow b) the next day 4) She told me she had seen me at the theatre .... a) yesterday b) the day before 10. Выберите правильную форму глагола: 1) The teacher said our examination ... next Monday. a) would be b) had been 2) When I came home the family ... their supper. a) would have b) had had 3) They wrote they ... my letter. a) would receive b) had received 11. Выберите правильный вспомогательный глагол: 1) If I knew English well, I... take this job. a) shall b) will c) should 2) If he were rich he... buy a car. a) shall b) will c) would 3) If she asked me I... help her. a) shall b) will c) should 12. Выберите правильную форму глагола: 1) If I... her better I should turn to her for help. a) know b) knew c) will know 2) If the weather... fine you would not stay at home. a) is b) was c) were 3) If she ... him she would be happy. a) marries b) married c) will marry 13. Укажите правильный вариант перевода: 1) If I meet her today I shall give her your book. a) Если я встречу ее сегодня, я отдам ей твою книгу. b) Если бы я встретила ее сегодня, я бы отдала ей твою книгу. 2) If she had money she would buy this dress. a) Если у нее есть деньги, она купит это платье. b) Если бы у нее были деньги, она бы купила это платье. 3) If you knew English you would be able to help us. a) Если ты знаешь английский, ты сможешь нам помочь. b) Если бы ты знал английский, ты смог бы нам помочь. 14. Выберите правильную форму глагола: 1) If I... you I shouldn't do it. a) were b) had been 2) If they ... a taxi they wouldn't have missed the train. a) took b) had taken 3) If you ... my advice you would have bought it. a) followed b) had followed 15. Правильно соедините придаточные предложения с главными: 1. a) If the weather is fine ... b) If the weather was fine ... c) If the weather were fine ... d) If the weather had been fine ... a) ... they spent the day outside. b) ... we should go to the country. c) ... we shall have a good time. d) ... we shouldn't have stayed at home. 2. a) If you write a letter ... b) If you wrote a letter ... c) If you had written the letter ... a) ... they would have receive it by now. b) ... they would receive it soon. c) ... tell them the news. 16. Переставьте буквы в таком порядке, чтобы получились слова: 1) s o l o c h 2) r e a c h e t 17. Укажите, какое слово не имеет отношения к остальным: а) 1) happy, 2) lucky, 3) ready, 4) easy, 5) busy, 6) city, 7) pretty, 8) rainy, 9) snowy, 10) lazy. b) 1) beautiful, 2) attractive, 3) good, 4) clever, 5) nice, 6) black, 7) happy, 8) successful, 9) new, 10) interesting. 18. Укажите, к какой теме относятся все три предложения: 1) I like every piece of it. 2) It's very popular now. 3) It was written by Benjamin Britten. a) theatre b) fine art c) music 19. Поставьте предложения так, чтобы получился связный рассказ: 1) Then it is decorated and put into a cool place for some time. 2) Then they are put into a pot. 3) First different fruits are taken. 4) It is served for dessert. 5) After that the salad is mixed. 6) They are carefully washed and cut into pieces. 7) Cream may also be added. 8) This is how a fruit salad is made. 20. Прочтите интервью и ответьте на вопрос - Is Mrs. Parker young or old? Interviewer: Hello, Mrs. Parker. You look as young and beautiful as ever. May I ask you a few questions, Mrs. Parker? Mrs. Parker: Certainly. I am used to answering questions. Int.: What time do you get up? Mrs. P.: I usually get up at 6 o'clock. People of my age can't sleep long. Int.: And when do you go to bed? Mrs. P.: At 9 o'clock. Int.: What was the last film you took part in? Mrs. P.: Let me think... Well, I don't remember. Int.: What do you usually do during the day? Mrs. P.: I go out every day and walk with Philip. Int.: Is Philip your husband? Mrs. P.: No, it's my dog. We parted with my husband 5 years ago and I never married again. Int.: Thank you, Mrs. Parker. 21. Прочтите текст и ответьте на вопрос - Who did the picture belong to? One day the police found a gold ring, a picture and a coat in the car. They found out that those things belonged to a filmstar, a doctor and a businessman. The ring didn't belong to a doctor. The coat didn't belong to a businessman. The picture belonged to a woman. The filmstar didn't wear coats. II семестр КОНТРОЛЬНЫЕ ЗАДАНИЯ КОНТРОЛЬНОЕ ЗАДАНИЕ № 3
Для того чтобы правильно выполнить задание № 3, необходимо знать следующие грамматические темы: 1. Passive Voice (Страдательный залог)
Например: 1. I am asked (Меня спрашивают)/ He is asked (Его спрашивают)/ You are asked (Вас спрашивают) 2. He was asked (Его спрашивали)/ You were asked (Вас спрашивали) 3. I shall be asked (Меня спросят)/ He is asked (Его спросят)/ You will be asked (Вас спросят). 2. Функции инфинитива
3. Complex Subject (Сложное подлежащее) Структура предложения и перевод: 1 2 3 4
He is said to know everything about this matter. Говорят, что он знает все об этом деле. He is supposed to be in his office now. Предполагается, что он сейчас в офисе. 4. Complex Object (Сложное дополнение) Конструкция употребляется с ограниченным числом глаголов: to believe, to consider, to know, to report, to say, to suppose, to think и др.
We consider him to be our greatest poet. Мы считаем его нашим величайшим поэтом. / (или) Мы считаем, что он является нашим величайшим поэтом. Вариант 1 1. Прочтите текст и ответьте устно на следующие вопросы: 1. What researches will Helmholtz be remembered for? 2. What did Helmholtz write in his first article about? HERMAN HELMHOLTZ 1. Herman Helmholtz is famous for his contributions to physiology and theoretical physics. Although he wished to study physics, he was persuaded by his father to take up the study of medicine, entering the Medical Institute at Berlin in 1838. 2. His researches into physiological optics began about 1850 with the discovery of the ophthalmoscope (1851), followed by investigations into colour, including the problem of colour-blindness. He also made fundamental contribution to the understanding of the structure and mechanism of the human eye. 3. Helmholtz’s first, and most celebrated paper in theoretical physics was his article on the conservation of force. In this paper he proved the conservation of total energy of a system of particles which were interacting through central forces depending only on the masses and separations of the particles. Other important work in theoretical physics included the famous paper on vortex motion (1858), and the application of the principle of least action to electro dynamical problems. 4. Helmholtz was undoubtedly the most versatile of nineteenth-century scientists. From 1871 onwards he was perhaps more famous as a theoretical physicist than as a physiologist. But it seems probable that apart from his work on the conservation of energy he will ultimately be remembered more for his epoch-making researches in physiological optics and acoustics in which his talents as physiologist, physicist, mathematician and experimentalist of genius were most vividly displayed. 2. Переведите в письменной форме абзацы 3, 4. 3. Заполните пропуски соответствующей активной или пассивной формой глагола и переведите предложения на русский язык: 1. Becquerel’s discovery (followed, was followed) by an intensive research work of Marie and Pierre Curie. 2. The intensity of this process (is influenced, influenced) by many factors. 3. Mendeleyev (created, is created) the system of classifying chemical elements. 4. Переведите предложения на русский язык, обращая внимание на инфинитивные обороты: 1. Herman Helmholtz is considered to be a famous scientist. 2. Many Russian scientists are known to contribute much into the science of electricity. 3. We found out his paper to be of great interest for our research. 5. Определите функции инфинитива и переведите предложения на русский язык: 1. Herman Helmholtz made a lot of experiments to prove his theory. 2. The experiments to prove his theory were numerous. 3. To prove his theory Herman Helmholtz made a lot of experiments. Вариант 2 1. Прочтите текст и ответьте устно на следующие вопросы: 1. What laws did Newton discover? 2. Can you formulate the Law of Universal gravitation? ISAAK NEWTON 1. Isaak Newton was born in 1642 in the family of a poor farmer. The boy began his first scientific experiments at school. 2. While studying at Cambridge University, Newton formulated the binomial theorem. In 1662 Cambridge was closed because of the plague and Newton returned to his native village. For the next two years he devoted himself to scientific experimentation. 3. Newton's great discovery was the law of decomposition of light. The scientist proved that the white light of the sun is composed of rays of light of all colours of the rainbow. He also discovered the Law of Universal Gravitation which states that “every particle of matter is attracted by every other particle of matter with a force inversely proportional to the square of their distance apart”. 4. Newton applied the principle of gravitation to prove that the power which guides the moon around the earth and the planets around the sun is the force of gravity. Another application of the law of universal gravitation was Newton's exploration of the tides. 5. Newton was highly honoured by his countrymen and in 1703 he was elected President of the Royal Society. Sir Isaak Newton died in 1727 and was buried in Westminster Abbey. 2. Переведите в письменной форме абзацы 3, 4. 3. Заполните пропуски соответствующей активной или пассивной формой глагола и переведите предложения на русский язык: 1. Newton (was performed, performed) many experiments with light. 2. When Cambridge (was closed, closed) in 1662, Newton returned to his native village. 3. Mass (is measured, measured) in grams or kilograms. 4. Переведите предложения на русский язык, обращая внимание на инфинитивные обороты: 1. My parents want me to become a chemist. 2. He is believed to be a very talented person. 3. Newton is considered to be one of the greatest English scientists. 5. Определите функции инфинитива и переведите предложения на русский язык: 1. То carry out this experiment will take you a lot of time. 2. The experiment to be carried out in our laboratory is very important. 3. He forgot to register the results of the experiment. Вариант 3 1. Прочтите текст и ответьте устно на следующие вопросы: 1. What was the boy interested in? 2. Which of Faraday's discoveries do you know? MICHAEL FARADAY 1. Michael Faraday, English experimental physicist, was born in 1791 in a poor family. The boy began to work as an apprentice at a bookbinder's shop at an early age. One day a man entered the shop and found the boy studying an article on electricity. The man was surprised to see a boy so interested in such a difficult subject and gave him four tickets for the lectures at the Royal Institutions. 2. The boy went to the lectures and made notes of what he heard. At the end of the lecture he came to Sir Humphry Davy, the great English scientist, and showed him his notes. Davy was surprised. Later he made Faraday his assistant and helped him in his education. 3. Faraday had many important discoveries. Among his works are the concept of the magnetic field and the magnetic “lines of force”, production of new kinds of optical glass, and research on electrolysis. 4. Faraday produced the first mechanical motion by means of a permanent magnet and an electric current. This is the principle upon which the modern electric motor is based. 5. Faraday was very modest and he loved his work more than honours. He refused to become President of the Royal Society and also refused to be knighted. 2. Переведите в письменной форме абзацы 1, 2, 3. 3. Заполните пропуски соответствующей активной или пассивной формой глагола и переведите предложения на русский язык: 1. The unit of electricity “farad” (was named, named) after M. Faraday. 2. The first lightning rod (was invented, invented) by B. Franklin, the outstanding American scientist. 3. At Cambridge, Newton (was read, read) with great interest the writings of Galileo. 4. Переведите предложения на русский язык, обращая внимание на инфинитивные обороты: 1. Faraday is believed to be a great English physicist. 2. We consider Tsiolkovsky to be the father of astronautics. 3. Popov is known to be the inventor of radio in Russia. 5. Определите функции инфинитива и переведите предложения на русский язык: 1. In 1810 Faraday began to attend lectures on natural philosophy. 2. To study the nature of light and colour Newton carried out many experiments with a prism. 3. The lecture to be delivered by a well-known scientist is devoted to the problems of ecology. Вариант 4 1. Прочтите текст и ответьте устно на следующие вопросы: 1. How old was Lomonosov when he left his native village? 2. When was the first Russian University founded? M. V. LOMONOSOV 1. M. V. Lomonosov was born in 1711 in the village of Denisovka near Arkhangelsk in the family of a fisherman. At the age of 17 he left his native village and made his way to Moscow. In Moscow he entered the Slavonic-Greek-Latin Academy. Lomonosov didn't finish his last grade, as he was sent with eleven other pupils to St. Petersburg to study at the Academy of Sciences. 2. Less than a year after he came to Petersburg Lomonosov was sent abroad to study metallurgy and mining. In 1741 Lomonosov returned to Russia and began to teach chemistry and physics at the Academy. 3. Lomonosov established the fundamental law of chemical change of substance which is called the Law of Conservation of Mass. 4. Lomonosov founded a new science that we call today physical chemistry. He also studied electrical phenomena in atmosphere of the Earth, the nature of light, and designed an improved telescope. Lomonosov considered nature to be in a state of constant change and development. Coal, oil, etc. were all formed as a result of evolution. 5. Lomonosov was a great scientist. His works in poetry had a great influence on Russian literature. Owing to his efforts, the first Russian University was founded in Moscow in 1755. This university bearing his name became the centre of knowledge and science in Russia. 2. Переведите в письменной форме абзацы 1, 2, 4. 3. Заполните пропуски соответствующей активной или пассивной формой глагола и переведите предложения на русский язык: 1. In 1745 Lomonosov (was appointed, appointed) a professor at the Academy of Sciences. 2. The first electric lamp (was invented, invented) in 1873 by A. N. Lodygin. 3. In 1911 Marie Curie (was received, received) the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. 4. Переведите предложения на русский язык, обращая внимание на инфинитивные обороты: 1. Lomonosov considered chemistry to be his "main profession". 2. The air is known to be a mixture of gases. 3. Lomonosov is considered to be a great Russian scientist. 5. Определите функции инфинитива и переведите предложения на русский язык: 1. Lomonosov began to work at an early age. 2. Edison founded an electric company to supply electricity to New York and other places. 3. The experiment to be made by this scientist will give us important information. Вариант 5 1. Прочтите текст и ответьте устно на следующие вопросы: 1. What did Mendeleev discover? 2. What fields of science do his works embrace? DMITRY MENDELEEV 1. D. I. Mendeleev was born in 1834 at Tobolsk in the family of the director of the town gymnasium. He received his secondary education at Tobolsk and then entered the Petersburg Pedagogical Institute. After graduation he worked as a teacher for two years. 2. In 1859 he presented his thesis, received his master's degree and went abroad on a two-year scientific commission. Upon his return to Russia he was elected professor of the Petersburg University, where he carried on his scientific and pedagogical activity for 23 years. 3. In 1906 he issued a book under the title Contribution to the Knowledge of Russia which contained thoughts of the further development of Russian industry and economy. The greatest result of Mendeleev's creative effort was the discovery of the Periodic Table of Elements. 4. One of Mendeleev's prominent works is his book Principles of Chemistry in which inorganic chemistry was for the first time explained from the standpoint of the Periodic Law. 5. A great scientist, Mendeleev devoted his life and energies to the progress of his country. His works embrace various fields of science – chemistry, physics, physical chemistry, geophysics. 2. Переведите в письменной форме абзацы 1, 2, 4. 3. Заполните пропуски соответствующей активной или пассивной формой глагола и переведите предложения на русский язык: 1. At first, the Periodic Law (was received, received) very coldly by other scientists. 2. In 1893 Mendeleyev (was appointed, appointed) Director of the Bureau of Weights and Measures. 3. В. Franklin (was founded, founded) the first public library and the University of Pennsylvania. 4. Переведите предложения на русский язык, обращая внимание на инфинитивные обороты: 1. The year 1895 is considered to be the date of the invention of the radio. 2. We consider Mendeleyev to be a great Russian scientist. 3. Manchester is known to be the centre of cotton industry. КОНТРОЛЬНОЕ ЗАДАНИЕ № 4
1. Conditional Sentences (Условные предложения)
2. Sequence of Tenses (Согласование времен) 1. Если глагол-сказуемое главного предложения стоит в настоящем времени, то глагол-сказуемое придаточного предложения может стоять в любом, требуемом по смыслу времени: 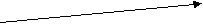 he studies English. he studies English.H  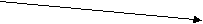 e says that he studied English last year. e says that he studied English last year. he will study English next year. 2. Если же сказуемое главного предложения стоит в Past Indefinite, то сказуемое дополнительного придаточного предложения должно стоять в одном из прошедших времен:  he studied English. he studied English. (действие, одновременное с действием главного предложении) H   e said that he had studied English. e said that he had studied English.(действие предшествует действию главного предложения) he would study English. (действие совершается после действия главного предложения) В русском языке согласования времен нет. Сравните перевод предложений в (1) и (2): 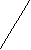 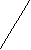 (1) он изучает (2) он изучает... (1) он изучает (2) он изучает... английский. английский.   он изучал… он изучал… он изучал… он изучал… О   н говорит, что Он сказал, что н говорит, что Он сказал, что он будет изучать… он будет изучать.. 3. Gerund (Герундий) Образование: основа глагола + -ing – reading Например: ask + ing = asking teach + ing = teaching
Вариант 1 1. Прочтите текст и ответьте устно на следующие вопросы: 1. What is unusual for a foreigner in Australia? 2. What kind of country is Australia? |

 . совпадает с Past Indefinite
. совпадает с Past Indefinite