И.Ю.-Марковина-З.К.-Максимова-М.Б.-Вайнштейн. Учебник для медицинских вузов и медицинских специалистов Серия xxi век Рекомендовано угчЮ по медицинскому и фармацевтическому образованию
 Скачать 1.07 Mb. Скачать 1.07 Mb.
|
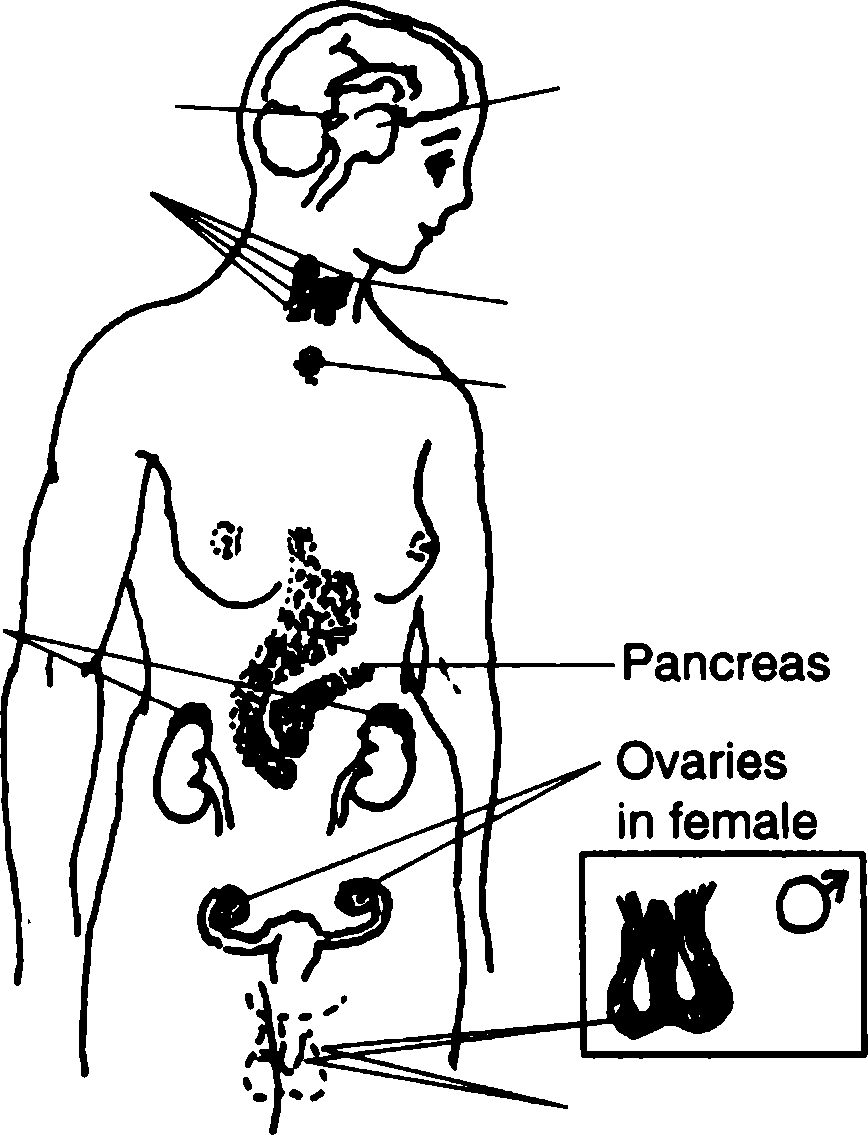 Pituitary gland Testes in male Fig. 12.The endocrine system. Pineal gland Parathyroid glands (four glands) Thyroid gland Thymus gland Adrenal glands 2. Endocrine glands or glands of internal secretion are ductless glands, that is, they empty their secretions — chemical substances called hormones (from the Greek word «hormao» — excite) — directly into the blood stream. The hormones are carried throughout the organism with the blood and are delivered to various organs whose activity they either stimulate or depress. Neither single hormone nor endocrine gland acts wholly by itself at any time. We know hormones to play a very important part in the organism. Many of them affect metabolism and the activity of the cardiovascular and other systems. A disturbance in the activity of the endocrine glands is accompanied by changes throughout the organism. These changes may be not only due to an increase in the function of a gland (hyper- function) but to a decrease (hypofunction). A hyperfunctioning gland secretes a superfluous amount of hormones and a hypofunctioning gland secretes an insufficient amount. The amount of hormones produced by the endocrine glands in 24 hours measures fractions of a milligram. The functions of all the endocrine glands are interconnected so that the glands make up a single system. Physiologists consider the hypophysis to be the chief gland of this system; they consider it to produce special substances which stimulate the activities of other endocrine glands. The activities of endocrine glancjs are regulated by the nervous i system. It is known to exercise direct control over the endocrine glands through the nerves and neurohumoral control, particularly through the hypophysis. The hormones in their turn ^ffect the functions of the different parts of the nervous system. . . ч ^ o , Упражнение 10. Прочтите и переведите текст А. Первый абзац переведите письменно. j.■ . •, , Упражнение 11. Найдите в тексте ответы на следующие вопросы и зачитайте их. 1j■ 1. The functions of various endocrine glands are different, aren't they? What are they? 2. Is the disturbance in the activity of the endocrine glands accompanied by any changes throughout the organism? 3. What is hyper- or hypofunction? 4. Why is hypophysis considered the chief gland of the endocrine system? 5. Howdotheendocrineandnervoussystemsinteract? Упражнение 12. Найдите ключевые предложения в каждой смысловой части текста А и выпишите их. Упражнение 13. Найдите в каждом ряду слово, перевод которого дан в начале ряда. 1. деятельность — activator, activities, activation, activity, activist; подобнымобразом, также — similarity, similar, simple, similarly; такимобразом, так — so, then, thus, actually; 4. влиятьна... — to effect, to defect, to affect Упражнение 14. Прочтите и переведите данные предложения. Определите, какой частью речи являются выделенные слова. 1.Thus the thyroid gland stimulates metabolism. 2. Hormones affect metabolism and the function of the cardiovascular system. 3. The functions of endocrine glands are interconnected. 4. The nervous system exercises direct control over the endocrine glands through the nerves and neurohumoral control. 5. The hormones either stimulate or depress the activity of various organs. 6. The activities of endocrine glands are regulated by the nervous system. Упражнение 15. Переведите следующие предложения. Определите функции инфинитива 1. The methods developed to establish special aspects of endocrinology have become diversified and complicated. 2. The existence of many hormones to be discussed must be regarded as probable rather than demonstrated with certainty. 3. The hypophysis is believed to be the chief endocrine gland. 4. The chief action of the thyroid hormone is to accelerate all oxidations, particularly those of fat and protein. 5. The discharge of thyroid hormone appears to be guided by a thyrotropic pituitary hormone. 6. The scientists believe insulin and anterior pituitary hormones to exert contrary actions on the blood sugar level. Упражнение 16. Переведите следующие предложения. Запомните значение парных союзовeither... or, neither... nor, so... that, notonly... but. 1. The observations of surgeons on thyroid deficiency revealed that internal secretions are not only necessary for proper growth and nutrition but for normal mental development as well. 2. An excess of the somatotropic hormone, either due to hypersecretion or injection of extracts, causes gigantism and leads to acromegaly in adults. 3. The molecular weight of insulin is so great that prospects of its synthesis seem very remote. 4. While asked the student could neither describe nor show the pineal gland in figure 12. Упражнение 17. Переведите данные предложения на английский язык письменно. 1. Нервная и эндокринная системы координируют и стимулируют деятельность организма. 2. Эндокринные железы не имеют протоков и выделяют свой секрет непосредственно в кровь, которая разносит его по организму. 3. Снижение функции или понижение активности эндокринных желез вызывает изменения в работе всего организма. 4. Деятельность всех эндокринных желез взаимосвязана и регулируется гипофизом. 5. Нервная система контролирует работу эндокринных желез. Часть II Слова к части II intermediate [,inta'mi:dj9t]апроме-dilute [daflju:t] v разбавлять, разво- жуточный, средний дить border ['bo:dd]п край; граница excessive [ik'sesiv]а избыточный, setп ряд, серия; набор чрезмерный intensify [in'tensifai] vусиливать Упражнения Упражнение 1. Прочтите и переведите следующие слова. hypothalamus, anterior, intermediate, posterior, microscope, fibre, secretion, circulation, neurons, neurohumoral, gigantism, acromegaly, oxitocin, to intensify Упражнение 2. Найдите в данном ряду слово или словосочетание, значение которого дано в начале ряда. 1. поскольку — in so far as, so far as, as far as; 2. серия, ряд — row, line, series, set; 3. тоесть — all that, so that, that is, that is why Упражнение 3. Найдите в данном ряду слово или словосочетание, синонимичное данному в начале ряда. 1. fairly - rather, too, enough, actually, completely; 2. to break up — to believe in, to end, to divide into...; 3. adults — teenagers, children, the old, grown-ups; 4. insufficient — enough, lacking, deficient, excessive Упражнение 4. Запомните значение сочетаний со словомthat. that is the point вэтомсутьдела that is to say тоесть thatiswhy вот почему nowthat теперь, когда Упражнение 5. Прочтите текст В (10 мин). 1) Разделите его на три смысловые части. 2) Найдите предложения: а) с конструкцией «сложное юполнение»; б) с парными союзами either...or, neither...nor, so... that, notonly...but. 3) Переведите эти предложения. Text ВHypophysis (the Pituitary) We know the hypophysis to be a small oval body weighing about 0,5 g; it is located in the cranial cavity and is connected with the hypothalamus. The gland consists of an anterior lobe, an intermediate part and a posterior lobe; the borders between them can be seen only under the microscope. Experimental and clinical observations strongly suggest anterior lobe to be necessary for proper growth to adult stature, for normal development and function of the reproductive system and for control the activities of other endocrine glands. The posterior lobe remains connected to the brain by means of the pituitary stalk, through which nerve impulses travel from the hypothalamus. The anterior lobe, so far as is known, r eceives no nerve fibres of any kind, and its control must then depend on t he presence of substances in the blood. In spite of all this, there appears to be a way whereby the brain can exercise a fairly direct control over the anterior lobe. The blood vessels leading to the hypothalamus break up into capillaries; having passed through these capillaries, the blood is gathered into small veins; these veins pass downward so that they open into another set of capillaries in the anterior lobe. This is called the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system. Excision of the anterior hypophysis neither alters the lipid content of the liver nor inhibits the accumulation of large amounts of lipids in the liver. The hypothalamus has been found to secrete special substances which regulate the secretion of the hypophyseal hormones. The activities of the other endocrine glands are thus subject to neurohumoral regulation through the hypophysis. Disfunction of the anterior lobe of the hypophysis is accompanied by changes throughout the organism. For example, excessive secretion of the growth hormone in childhood results in gigantism. Such people may grow to a height of 2,5-2,6 m. Excessive secretion of this hormone in adults results not only in excessive growth of the bones of the face, fingers and toes, but in enlarged nose, tongue and certain other organs. This disease is called acromegaly. Insufficient secretion of the growth hormone in childhood is accompanied by retarded growth (dwarfism). It is a relatively rare condition iissociated with either early atrophy or absence of the anterior lobe. The posterior lobe of the hypophysis secretes oxytocin and vasopressin. Physiologists consider oxytocin to intensify the contractions of the uterine muscles and it is therefore used to boost weak labour. We know vasopressin to cause constriction of the blood vessels, especially those of the uterus. Упражнение 6. Прочтите следующие суждения. Найдите в тексте В предложения, более полно выражающие мысль данных суждений, и прочтите их. 1. The hypophysis is connected with hypothalamus. 2. There are two lobes in the gland. 3. Hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system of blood vessels supplies blood to the anterior lobe of the hypophysis. 4. Hypophysis regulates the activity of other endocrine glands. 5. Disfunction of the anterior lobe of the hypophysis is accompanied by changes of different kind throughout the organism. Часть III Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 12 Упражнение 1. Найдите и переведите предложения со сложным дополнением. 1. Thyroxine is necessary in the body to maintain a normal level of metabolism in all body cells. 2. Parathyroid hormone causes calcium to leave bone tissue and enter the blood stream. 3. Removal of the thymus gland is found to be helpful in treatment of muscular-neurological disorders. 4. Cells need oxygen to carry on metabolic processes.5. We know the pituitary gland to be also called the hypophysis. 6. Pituitary growth hormone acts on bone tissue to accelerate its growth in the body. (Ответ: 2, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите § 26 Грамматического справочника.) Упражнение 2. Укажите, в каких предложениях использованы составные союзы. 1. Insulin is necessary in the blood stream so that sugars can pass from the blood into the cells of the body. 2. In acute nephritis some glomeruli are more severely involved than others, but practically no glomerulus escapes some injury. 3. Treatment of thyrotoxicosis may include either thyroidectomy or management with antithyroid drugs. 4. The ovaries are held in place on either side of the uterus by the utero-ovarian ligaments. 5. In his last report the professor spoke neither of hyperfunction nor hvpofunction of endocrine glands'. 6. Overproduction of glucocorticoids leads not only to obesity, moonlike fullness of the face but also to elevated blood sugar, high blood pressure and weakness (fatigue). (Ответ: 1, 3, 5, 6. Если вы ошиблись, повторите § 40 Грамматического справочника.) Упражнение 3. Расшифруйте данные сокращения, i., f., oz(s), g., lb., 1., ml., cm. (Ответ:inch, foot (pi feet), ounce(s), gramme (gram), libra(nam. дляpound), litre, millilitre, centimetre.) Упражнение 4. Опишите функции эндокринных желез, используя рис. 12. LESSON THIRTEEN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Герундий (§ 23) ing-формы в различных функциях (§ 24) г -V- > Часть I л Ь \ ■ \ Слова к части I actually ['aektjuali]advдействительно, фактически touch [UtJ] vтрогать, касаться bundle[ЪлгкИ] п пучок, узел cerebrum ['seribram] п головной мозг cerebellum[ seri'belam] п мозжечок feel [fi:l] vчувствовать, ощущать feelingп чувство, ощущение treat [tri:t] vлечить; обрабатывать; обращаться treatment ['triitmsnt] п лечение, терапия; обработка; обращение Упражнения Упражнение 1. Переведите следующие предложения с герундием. 1. Stimulating the somatotropic hormone upon growth can be partly correlated with its acceleration of metabolism. 2. Certain researchers believe that the hypophysectomized animal differs essentially from the normal in that it has lost the power of converting fateto carbohydrates. 3. In acromegaly and gigantism X-ray pictures re9fr&iLfre?pening the pituitary fossa of the sphenoid bone. 4. The thyroidectomy is removing the thyroid gland. 5. Thyroxine and the somatotropic pituitary hormone are regarded as basic metabolic hormones necessary for maintaining general nutritive conditions. Упражнение 2. Найдите ing-формы в следующих предложениях. Переведитепредложения. 1. Thyrotropic hormone is of considerable importance not only in regulating the thyroid secretion but in accounting for many metabolic effects. 2. Related injections of extracts containing ketogenic hormones cause fat infiltrations of liver, reduction in fat of other tissues and keto- sis. 3. The stimulating action of the somatotropic hormone upon growth can be partly correlated with its acceleration of metabolism. 4. Injecting hormones into normal young animals results in animals of large size and precocious sexual development. 5. Acromegaly and gigantism produce overgrowing of bones and there may be an actual lengthening of the spinal column. Упражнение 3. Отработайте чтение следующих слов. nerve [na:v], touch [UtJ], actually ['aektjuali], area ['еэпэ], ether ['i:6dL anesthetics [,aenis'0etiks], novocaine ['nouvokein], yawning [p:nir)] Упражнение 4. Прочтите и переведите следующие Словосочетания. 1. to react upon each other, reaction power, the reaction of eye to the light, Wasserman reaction, reaction of sensibility; 2. to feel one's pulse, to feel like doing smth, to feel tired, to feel fine, a feeling of danger; 3. to treat with penicillin, surgical treatment, treatment by exercises, to try many treatments for pneumonia, to be under treatment Упражнение 5. Просмотрите текст А и сравните по содержанию обе части текста. Text А The Nervous System. Brain and Nerves Nerves lead from the spinal cord or from the brain to each part of the body. Then they lead from each part of the body back to the brain or spinal cord. The brain and spinal cord are the centres of this system of nerves. All parts of your body are connected by nerves. The nerve cells with their fibres make up the nervous system. When we study one nerve cell, we see that it has a long^ fibre at one end and short fibres at the other. The nerve cells send impulses to each other by means of the fibres at their ends. These fibres do not actually touch but are so close to each other that an impulse can travel from one fibre to another. Physical agents become stimuli for nerve terminals by transferring energy from the external ^orid to the nerve terminals: Thus all rierve cells connect with each other. There are millions of these connecting nerve cells. Thus a stimulus from any part of the body can reach any other part of it. In the spinal cord and brain, the nerve cells connect with each other by their connecting fibres. Outside the spinal cord and brain, certain long fibres are grouped together forming nerves. Each nerve is made up of thousands of nerve fibres together in a bundle, as a cable is made up of separate wires. The Brain Centre of the Nervous System We know the nerves to carry impulses to the brain. We know that the brain sends these impulses along so that they go to the right place. The brainjs made up of threqpartsv The cerebrum sits like a cap on the cerebellum. And the medulla is that long portion connecting the brain with the spinal cord. The cerebrum has certain parts that do certain work. Studying human beings with accidental injuries of brains helped scientists to get information about these areas. For instance they have discovered that the part for thought, memory, and feeling is found in the front of the cerebrum. The part for hearing is found at the side of the cerebrum, and the part for sight in the back of the cerebrum. 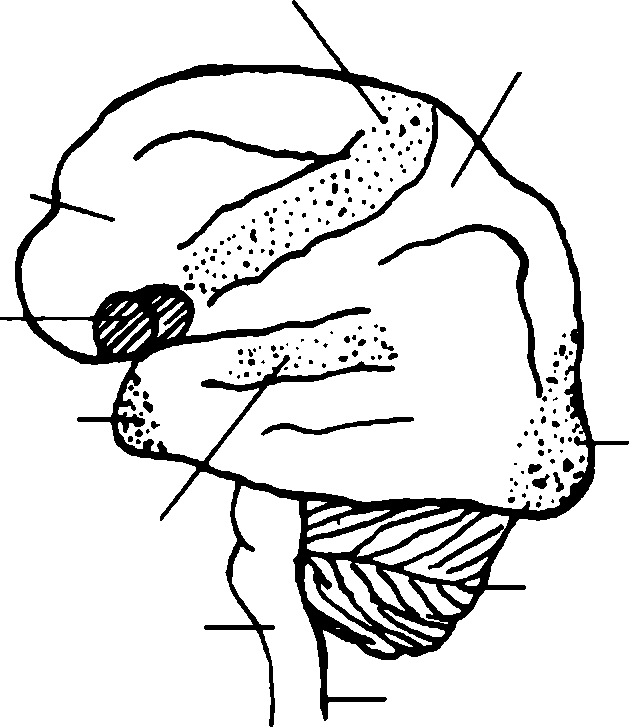 Speech area Cerebral hemispheres Fig. 13.Diagram to illustrate some of the more important centres in cerebral hemispheres. Spinal cord Cerebellum Sensory area Medulla Auditory area Smell and taste Silent area Visual area Many experiments have shown that the brain is the centre of feeling and understanding. The nerve cells in the brain can be «put to sleep» with ether or other anesthetics. Then the brain does not feel any impulses from the part being operated on. Sometimes the nerve cells near the part of our body being treated may be deadened by novocaine, as when the dentist pulls a tooth. What the novocaine does is preventing the impulses from getting to the brain from the nerve in the tooth. 6. The cerebellum is the centre for making your muscles work as a team. The medulla is the centre of certain of our most important acts: breathing and heartbeat, on which life itself depends. The medulla is also capable of controlling acts such as swallowing and yawning. Упражнение 6. Переведите письменно абзацы 5 и 6 текста A. i Упражнение 7. Найдите в тексте А ответы на следующие вопросы и зачитайте их. 1. What do we know about the structure of the nerve cell? 2. How does a nerve react to a stimulus? 3. How many parts is the brain made up of? 4. What have scientists found out about the brain? i Упражнение 8. Прочтите и переведите следующие предложения, выбрав одну из данныхing-форм, подходящую по смыслу. ^ ЧЧ. Ч b reacting, responding, combining, descending, controlling, containing, cooling,Warming У 1. A large number of narcotics or anesthetics produce depression by... directly wtith protoplasm. 2. ... decreases and ... enhances excitability. 3. The human auditory receptors are capable of U to%a range from 16 to 20 000 molecular vibrations. 4. Electromagnetic vibrations include in ... order: hertzian, infra-red, visible, ultra-violet, roentgen, gamma and cosmic rays. 5. Nerves placed in solutions ... carbohydrate and fat cause a decrease in both of these foodstuffs. 6. Cerebellum is the higher centre for ... equilibrium. л, ч , (O.'v-Л-'"Л Упражнение 9. Переведите следующие предложения сing-формами на русский язык, определите их функции. 1. The intensity of an impulse arising during the relatively refractory^ period is less and it decreases when passing through a depressed stretch of nerve. 2. Functional nerve block can be produced without cutting or injuring the fibres permanently. 3. Among the outstanding symptoms found in cerebellar disease, ataxia (i.e. the inability of maintaining equilibrium through failure of muscular coordination) received a great deal of attention. Thus, a cigarette may be raised to the eye or a spoon may reach the ear and the patient (with cerebellar disease) is quite incapable of easily touching the tip of his nose when the eyes are closed. 4. Extensive pathological changes or injury of the brain, including the frontal lobes, cause both in man and inimal disturbances and abnormalities aich as torpidity, inertia, inattention, indifference to surroundings, etc. Часть II Слова к части II {: '-'^'лН tensenчувство, ощущение; terminal[Чэ:шшэ1] nокончание cutaneoussenseкожное ощущениеscatterfskaetd] vрассеивать(ся), раз- pain [pein] nболь брасывать \ > - imell [smel] nзапах; обоняние augment ['o:gment] уувеличивать(ся), thirst [0a:st] п жажда усиливать(ся) Упражнения Упражнение 1. Прочтите и переведите следующие слова. classification, to classify, equilibrium, cutaneous, to distribute, corpuscle, reflex, stimulus Упражнение 2. Найдите в данном ряду слово, синонимичное данному в начале ряда. 1. sense - feeling, sense organs, faculty, sensation; 2. to excite — to cause, to respond, to arouse, to stimulate; 3. completely — partially, always, fully, at last, to the end; 4. to augment — to decrease, to increase, to stop, to stimulate Упражнение 3. Найдите слово, перевод которого дан в начале ряда. 1. знакомый - famous, known, near, close, familiar; 2. ощущение, иосприятие — sense, sensibility, sensation, sensationism; 3. усталость — hunger, thirst, fatigue, tired; 4. спускаться — to ascend, to come down, to go down, to descend Упражнение 4. Прочтите текст В (10 мин). 1) Скажите, какие органы чувств описаны в тексте. Опишите механизм мышечных ощущений. 2) Найдите и переведите предложения с ing-формами. щ Text В * Classification of the Senses Sense organs are specialized endings of the sensory division of the peripheral nerves. We are commonly thought to possess five senses. Actually, there are many more. We may classify them as follows: 1) the cutaneous senses — touch, heat, cold and pain; 2) the deeper senses — pressure and muscle sense; 3) the internal senses, or senses from the internal organs of the body; 4) the special senses, or those in which the receptors lie in special organs - sight, hearing, equilibrium, taste and smell; and finally 5) the general body senses — hunger, thirst, fatigue, sexual sensation, etc. The cutaneous senses. There are said to be 500,000 touch receptors in the skin. They are unevenly distributed, being most numerous in the finger tips, lips and tongue, and least numerous on the back. Their receptors are specialized structures called Meissner's corpuscles. The sense-organs for cold constitute 150,000 receptors; they are the end- organs of Krause. Warmth has about 16,000 receptors, the end-organs of Ruffini; and pain has some 3,000,000 receptors. Pain receptors, however, are not specialized; they are simply the naked ends of the pain nerves, ^soW^ftat branched at their terminals. The Pacinian corpuscles are the receptors for pressure, and the muscle spindles for muscle sense. Proprioception. Everyone knows what pain and touch are, but proprioception («muscle sense») may be less familiar. It is a very important sense since it is the sensory link of a reflex controlling muscle tone and contraction; and it also gives the brain important information about the location or position of the limbs. Muscle spindles are tiny, spindle-shaped structures scattered throughout muscles, and they are most numerous around the tendons and joints. The stimulus exciting then* is muscle contraction and joint movement. Since muscles are never completely at rest — one portion or another is contracting all the time — there is a constant flow of nerve impulses into the spinal cord over the muscle sense fibres. Any activity of muscles, such as walking, augments the flow. Let us analyze the fact of walking. One foot is lifted from the ground, moved forward, and, as it descends, the weight of the body is shifted to this foot. The other foot is then lifted, moved, etc. Once a child has learned to walk, he accomplishes this action not notising it; it is done reflexly, and this reflex is one in which the sensory information comes over the fibres of proprioception. At any instant of time, the spinal cord is receiving information as to the immediate, present location of the feet and legs, and it is sending out, over motor fibres, impulses which continue the activity. At any time, a person knows, without looking, approximately where his feet are and where his legs are, since this information is also being sent to the brain. Упражнение 6. Прочтите данные суждения. Найдите в тексте предложения, более полно выражающие мысль данных суждений. 1. There are more senses than we are commonly thought to possess. 2. Besides touch receptors there are cold, warmth and pain receptors. i Proprioception is the sensory link of a reflex. 4. Muscle contraction ind joint movements excite muscle spindles. 5. Walking augments the How of impulses. 6. The spinal cord and the brain regulate motor activity. У пражнение 7. Передайте основное содержание текста В письменно. У пражнение 8. Назовите наиболее важные центры головного мозга. Проверьте себя по рис. 12. Часть III Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 13 Упражнение 1. Найдите герундий в данных предложениях. Переведитепредложения. 1. The brain is the primary centre for regulating and coordinating body activities. 2. Man receives his information concerning the outside world through his sense organs. 3. We know of the position of an arm or ,i leg without looking at it. 4. The nerves are trunks containing many nerve fibres which are incased in a common sheath. 5. The conditioned i сflexes discovered by I. P. Pavlov are the mechanism through which the body responds to the outside world in avoiding injury, obtaining food and performing many more complex acts. 6. The best method in this aise is removing one adrenal totally and rendering the medulla of the other non-functional by cutting the splanchnic nerves. (Ответ: 1, 3, 5, 6. Если вы ошиблись, повторите § 23 Грамматического справочника.) Упражнение 2. Найдите в следующих предложениях: а) герундий; б) причастие; в) отглагольное существительное. 1. The brain has many different parts controlling different aspects of i he body functions. 2. The cerebellum is located beneath the posterior part of the cerebrum, its function being to aid in the coordination of voluntary movements and to maintain balance and muscular tone. 3. The thalamus monitors the sensory stimuli we receive by suppressing some and magnifying others. 4. Professor told us about diagnosing the hypophi- sis disfunctions. 5. The proprioceptors in the muscles not only supply information on the condition of the muscles, but aid in controlling the energy and extent of muscular activity. 6. Paralysis often results from the plugging up of blood vessels, and consequent arrest of blood supply to an area of the brain. (Ответ: a) 3, 4, 5; 6) 1, 2; в) 6. Если вы ошиблись, повторите § 24 Грамматического справочника.) Упражнение 3. Переведите следующие пары слов. 1. a shoulder — to shoulder; 2. a load — to load; 3. a look — to look at...; 4. a sign - to sign; 5. a dream — to dream; 6. an aim — to aim (Ответ: 1. плечо—брать на себя, взваливать на плечи; 2. груз — нагружать; 3. взгляд — взглянуть на...; 4. знак — подписывать; 5. мечта (сон) - мечтать (видеть сон); 6. цель - целиться, направлять.) III. Microbiology LESSON FOURTEEN VIRUSES. BACTERIA Условные предложения (§31) Различные функции глаголов shall, will, should, would (§ 33) Часть I Слова к части I disease [di'zi:z] nзаболевание, болезнь particle ['pcctikl] nчастица expect [iks'pekt] vожидать, предполагать hereditary [hi'reditari] а наследственный facilitate [fs'siliteit] vоблегчать, способствовать core[ко:]nядро Упражнения Упражнение 1. Переведите следующие условные предложения на русский,; язык. j «> if 1. The experiment would be ready by the end of the month if they supplied us with all the necessary material on the problem. 2. If a transverse section is made through the cerebral hemispheres, the inner white matter and the embedded grey matter may be observed. 3. All sensations such as touch, pain and temperature are lost if cerebral hemispheres are destroyed. If a piece of ice were placed against the skin, it would cause a sudden change in environment of the body and the sensation of cold would result. If a man touches hot water, he quickly withdraws his hand. * пражнение 2. Напишите данные предложения так, чтобы они выражали маловероятное предположение. ()бразец: If they get all the necessary material, they will be able to go on with their experiment. If they got all the necessary material, they would be able to go on with their experiment. 1. If an object passes in front of the eyes, the changes in the intensity of the light stimulate the nerve endings in the eye. 2. If food is taken into the mouth, stimulation of the various receptors in the mucous membrane brings about reflex secretions. 3. If one can make a nerve connection between the sensitive receptor cells of the ear and the area in the brain associated with sight, it will be possible to perceive, or «see» sounds. Упражнение 3. Напишите данные предложения так, чтобы они выражали упущенную возможность совершить действие. Образец: If the doctor knows the reason of the patient's trouble, he will help him immediately. If the doctor had known the reason of the patient's trouble yesterday he would have helped him immediately. 1. If the cerebral cortex in this animal is completely removed, no connection reflexes will be formed at all. 2. If she takes part in the conference, she will make a good report. 3. If we use new apparatus, we shall save much time. 4. If the surgeon on duty does not operate patient N., serious complications may result. Упражнение 4. Переведите следующие предложения с глаголамиshall, will, should, would. 1. If you ascend in the atmosphere as in flying an airplane, climbing a high mountain, or riding a fast elevator, the atmospheric pressure, and that in the outer ear, will drop, while that in the middle ear remains the same. 2. Damage to one side of the brain will cause paralysis on the opposite side of the body. 3. He said he would prepare the report on the functions of sense organs. 4. They shall attend this lecture by all means. 5. There are certain aspects in the differential diagnosis which should be considered whenever headache is found to be a distressing complaint in a patient. 6. He would work in the Anatomical Museum if he were free. 1. to expect, expectable, expectance, expectant; 2. to facilitate, facilities, facility; 3. heredity, hereditary, hereditarily; 4. part, partial, particle Упражнение 6. Прочтите и переведите следующие словосочетания. infectious desease, diseases of childhood, to suffer from a disease, disease incidence, an expectant mother, a hereditary disease, partial pressure Упражнение 7. Просмотрите текст А и скажите, что было известно о вирусах до изобретения электронного микроскопа и что нового узнали о вирусах после его изобретения. Text А Viruses \ /jFor three-quarters of a century, scientists have known that many diseases of man, animals, plants and even of microorganisms are caused by transmissible agents which cannot be seen under the light microscope, they afe so small that they can pass through filters fine enough to hold back the most minute bacteria. These mysterious invisible agents were given the generic name;of virusesiln the 1930's, two great discoveries were made which provided concrete information concerning the nature of viruses. It was found that some of them would be crystallized almost as readily as if they were ordinary chemical substances. Chemically, the active virus particles were found to behave like giant molecules. At about the same time, the electron microscope became available and permitted pictures to be obtained of these crystals as well as of particles present in fluids and other materials having virus activity. Viruses would now be seen as concrete objects instead of being merely imagined. ^)The first unexpected fact revealed by electron microscopy was that the various viruses differ among themselves in shape and in size, as various types of bacteria. The virologist can differentiate between several types of viruses on the basis of their size and shape as revealed by electron micrographs. For example, the vaccinia virus is rather large. In contrast, the polioviruses are much smaller and yield very characteristic Crystals. As to the tobacco mosaic virus, it can be crystallized in the form of thin needles having different lengths. $The viruses that attack bacteria, which are called bacteriophages, are more complex, at least in .hape. Many of them have a thin tail and a large round or cylindrical hcad.VEach active virus particle consists of at least two very different ivpes of structural components. One structure made up of nucleic acid, carries the genetic hereditary characteristics of the virus. Another, protein in nature, is thought to protect this genetic apparatus and to facilitate its transfer from one infected cell to another. For example, electron micrographs revealed that virus of tobacco mosaic consisted of an inner constituent of nucleic acid lodged within an outer coat, cylindrical in shape and made up of protein. The central structure, the core, should be compared to the nucleus of ordinary cells in higher organisms, which also contains large amounts of nucleic acid and also carries the genetic endowment. In fact, the nucleic acid core of this virus is its most essential constituent. However, proteins and nucleic acids are not the only structural components of active viruses. Certain viral particles have recently been shown to contain lipids as part of their essential structures. High-magnification electron micrographs will reveal furthermore that some of them possess a distinct membrane. If we examined t he structure of some of bacteria under highmagnification electron mi- croscope we should see that they possess a distinct membrane. Упражнение 8. Прочтите и переведите текст А. Первый и второй абзацы переведите письменно. Упражнение 9. Найдите в тексте А ответы на следующие вопросы. 1. What have scientists known about viruses until the electrone microscope became available? 2. What two great discoveries were made in the 1930's? 3. Can the virologists differentiate between the types of viruses on the basis of their size or shape? 4. Are proteins and nucleic acids the only structural components of active viruses? Упражнение 10. Составьте письменно план текста А. Упражнение 11. Найдите в каждом абзаце текста А предложение, ныражающее основную мысль данного абзаца, и переведите его. Упражнение 12. Найдите в каждом ряду слово, синонимичное по значению первому слову ряда. 1. ordinary — everyday, common, usual, often, habitual; 2. to reveal- to detect, to open, to find, to show, to demonstrate; 3. remarkable — usual, seldom, unusual, interesting; 4. material — findings, essence,data, evidence, matter Упражнение 13. Найдите в каждом ряду слово, противоположное по значению первому слову ряда. 1. inner - outside, out, outward, outer; 2. different - some, equal, something, the same; 3. to facilitate - to prevent, to hamper, to influence, to ignore; 4. within - out, outward, outer, out of, outside Упражнение 14. Переведите следующие предложения. Определите функции глаголов:shall, should, will, would. 1. The most obvious properties of the ultramicroscopic viruses should be classified according to a) their invisibility with ordinary microscope; b) their refusal to multiply in artificial media; c) their ability to pass filters which hold back the smallest known bacteria. 2. In 1892 D. Ivanovs- ki found that the sap of leaves attacked by mosaic disease would retain its infectious qualities even after filtration. 3. Before the middle of the nineteenth century the word «virus» would be commonly applied to all toxic or poisonous substances. 4. If you examined viruses in the electron microscope, you would see that the particles of each type of virus possessed a characteristic shape and size. 5. If the strains of virus to which people are subjected are too different from thpse in the vaccine, the vaccine will become useless. 6. They shall improve their method of investigation if they want to obtain good results. Упражнение 15. Переведите на английский язык данные предложения письменно. 1. Вирусы вызывают заболевания у людей, растений и даже микроорганизмов. 2. Вирусы табачной мозаики образуют кристаллы в форме тонких иголок различной длины. 3. Некоторые вирусы, как показали последние исследования, в своей структуре помимо белка и нуклеиновой кислоты содержат липиды и оболочки. Часть II Слова к части II consequently ['konsikwsntli] advеле- moisture ['moistfa] nвлага довательно, в связи с этим pollute [pa'lu:t] vзагрязнять distinction [dis'tirjkjn] nотличие, раз- pollution [pa'lurjn] nзагрязнение граничение Управления Vnpaaoiemie1. Прочтите и переведите следующие слова. destructive, microorganisms, chlorophyll, spores, to vary, variety, ocean, especially, polluted, alkaline, reservoir, mucus, mucous Упражнение 2. Дайте исходные слова, от которых образованы следующие производные. Переведитеихнарусскийязык. 1. occurrence, occurrent; 2. moisten, moisture, moistureless; 3. distinctly, distinction, distinctive, distinctively Упражнение 3. Прочтите текст текст В (10 мин). 1) Разделите его на 2 части соответственно вопросам: What are bacteria? Where do they occur? 2) Найдите и переведите: а) условные придаточные предложения, которые выражают маловероятные предположения; б) предложения с много- жачными глаголамиshall, will, should, would. Text В What are Bacteria? Bacteria rule the world. Man is dependent upon them from the day of his birth until the hour of his death. They are man's most useful servants and his most destructive masters. One is prone to ask: What are bacteria? Where do they occur? What are their functions? Bacteria are minute single-celled living beings devoid of roots, leaves and stems. They are so small that they can be seen only with the aid of a powerful microscope; They are often spoken of as microorganisms. This term includes not only bacteria but all forms of life so small that you should require the microscope in their study. They are often referred to as germs or microbes. The early investigators considered them animals and would refer to them as «animalcules». If we examined the bacteria we should find that they have many of the characteristics of animals. Some have the power of independent motion. All are devoid of green colouring matter, chlorophyll; most of them are compelled to live upon complex foods as do the animals. Their general structure, their methods of growth, their formation of threads and spores, and their simplicity in some of the lower forms of plant life, have caused the biologist to class them as plants. However, it is impossible to make a clear-cut1 distinction between some microscopical plants and some microscopical animals.^he important thing to remember is that .bacteria are the simplest forms of life, and partake of the characteristics of both plants and animals. For this reason, and for convenience, scientists agree to consider the bacteria with the plants. Where do bacteria occur? Bacteria are widely distributed, occurring nearly everywhere. They are found in all natural soils, the number varying with the kind of soil, quantity of plant and animal debris present, moisture and treatment. They decrease in number with depth. Although they occur in air, it is not their natural home as under ordinary conditions they cannot grow and multiply in it. The number and variety found in air vary. The atmosphere of some high mountains and the air over the ocean far from shore may be free from bacteria. City and country air also differ from each other in the number and kind of bacteria which they contain. There is a great variation in the air of buildings. Bacteria are especially numerous where dust is plentiful. Most natural waters contain many bacteria. In sewage and polluted waters2 they are especially numerous. If measures against pollution and contamination of water were not taken in time there would be much danger to people's health. They occur only in small numbers or not at all in deep wells3 and springs.4 A turbid stream, which contains the drainage of many cities, has a great variety and number of bacteria in opposition to the clear, rapid flowing water of uninhabited mountainous regions. 4 The intestines, owing to their alkaline reaction and the partly digested condition of their contents, are a great reservoir of bacteria. In the upper part there are few, but in the descending colon billions of bacteria are present. Sometimes they constitute one third of the total dry contents of the intestine. The health of the individual is determined by the number and kind of bacteria. The normal tissues and the blood of animals are usually free from bacteria. If ordinary saprophytic bacteria entered the animal's body they would be ingested and destroyed by leukocytes. Microorganisms are rarely found on certain healthy mucous membranes, such as those of the kidneys, bladder and lungs. Occasionally they pass through the skin or the mucous membranes of the digestive tract after which they may be found for a short time in the blood. In certain diseased conditions the blood and tissues of man and lower animals become filled with bacteria. Functions of Bacteria. The real significance of bacteria comes in the fact that we are living in a world filled with them. They cannot be kept out of the ilimentary tract. Considerable attention should be given to the favouring of i he beneficial bacteria in man. The great Russian bacteriologist Mechnikov i laimed that the rate with which man ages would be determined not by the vears he has lived, but by the bacteria, which inhabit his digestive system. Notes clear-cut четкий sewage waters сточные воды well колодец spring источник Упражнение 4. Найдите в тексте предложения, более полно выражающие мысль данных суждений. 1. Man is dependent upon bacteria. 2. Bacteria are very small. 3. Bacteria are often spoken of as microorganisms. 4. They have many characteristics of animals. 5. Some characteristics of bacteria have caused the biologist to class them as plants. 6. We are living in a world filled with bacteria. ЧастьIII . Контрольно - обобщающие упражнения к уроку 14 Упражнение 1. Найдите условные придаточные предложения, которые ныражают: а) маловероятное предположение; б) упущенную возможность совершить действие. Переведитепредложения. . ** 1. If you observe bacterial protoplasm under the optical microscope, it would appear simple in structure. 2. If the individual were in a healthy state, a large quantity of virulent microorganisms entering the body would be destroyed. 3. Certain water forms of bacteria, would die, if they were held above 30°C for more than a few minutes. 4. If bacteria had entered the body at the time of its active and unweakened condition they would have given it a very mild form of the disease. 5. It certian hygienie measures had been carried out we should have prevented the last year fatal epidemics. (Ответ:a) 1, 2, 3. 6) 4, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите § 31 Грамматического справочника.) Упражнение 2. Укажите, в каких предложениях словаshall, will, should, wouldимеют модальное значение. Переведитеэтипредложения. 1. Great care should be taken ip cultivating bacteria. 2. The water should be kept clean by filtration and safe by desinfection with chlorine to destroy pathogenic and other forms of bacteria. 3. Pasteur could not believe that two compounds which acted so differently in one respect would be absolutely identical in every other way. 4. In the investigation of yellow fever it became necessary to find human volunteers who would risk contracting yellow fever. 5. They shall correct their mistakes themselves. 6. It will be difficult to diagnose this case. (Ответ: 1, 2, 4, 5. Если вы ошиблись, повторите § 33 Грамматического справочника.) Упражнение 3. Дайте форму множественного числа от следующих слов: bacillus, bacterium, coccus, foot, virus, genus, spirillum (Ответ: bacilli, bacteria, cocci, feet, viruses, genera, spirilla.) Упражнение 4. Выберите правильное значение выделенных слов. 1. Bacteria may occur(происходить, случаться; встречаться) free or in aggregates. 2. The smallest bacteria are beyond the range(линия,ряд; предел) of our most powerful light microscopes. 3. The size of the microscopical organisms can be estimated by filtration, consequently they are referred to(направлятьк ...; упоминать; относитьк ...) as filtrable viruses. 4. Viruses attack all parts of the body excepf(исключая; помимо) the digestive system. IV. Pathology LESSON FIFTEEN OSTEOMYELITIS, FRACTURES Повторение:ВременагруппыIndefinite (Active and Passive Voice) (§§ 10, 14) Часть I Слова к части I acute [a'kju:t] а острый suppurative ['sApjus,reitiv] а гнойный suppuration [,sApjud'reiJh] nнагноение, гной distant ['distant] аотдаленныйinflammation Linfta'meijn] n воспалениеpus [pAs] nгной marrow ['maerou] nкостныймозгspread [spred] v распространять(ся) minor ['maind] анезначительныйinflame [in'fleim] v воспалятьсяoedema [I'diims] nотек «•vera [si'vis] а резкий, сильный *appropriate[э proupmt] а подходящий, it*Kionj'riicfcn] nобласть, район, зона соответствующий Упражнения Упражнение 1. Найдите и определите время и залог глаголов-сказуемых в следующих предложениях. 1. The earlier investigators of bacteria thought of them as tiny animals which were generally grouped together with the microscopic animals called protozoans. 2. Probably the bacteria are made up of various kinds of organisms, some are related to algae, others to fungi. Future research will doubtless throw more light on such relationship. 3. Before i he middle of the nineteenth century, the word «virus» was commonly applied to all toxic or poisonous substances, including snake venom. 4. Viruses are distinguished from poisons and venoms because of their infectious quality. 5. In addition to smallpox and yellow fever, viruses cause such human diseases as mumps, measles, poliomyelitis, chicken pox, Japanese Вencephalitis, infectious hepatitis, influenza and probably the common cold. Упражнение 2. Прочтите первый абзац текста А. Обратите внимание на произношение медицинских терминов. Упражнение 3. Образуйте производные слова согласно данной модели и переведите их. Существительное + -ed= прилагательное: markзнак, метка, след; черта; известность —markedотмеченный, заметный; значительный, известный. fur(мех; налет на языке); bruise(синяк); fracture(перелом); disease; dress Упражнение 4. Прочтите и переведите данные однокоренные слова. 1. distant, distance, distantly; 2. evident, evidence, evidently; 3. to inflame, inflamed, inflammable, inflammation; 4. to suppurate, suppurative, suppuration;5. severe, severely, severity; 6. region, regional Упражнение 5. Прочтите и переведите следующие словосочетания. X-ray evidence, inflammation of lungs, abdominal region, regional operation, severe pain, attack of coughing, to be severely ill Упражнение 6. Просмотрите текст А и назовите основные симптомы острого остеомиелита. Text А Acute Osteomyelitis In this text we shall discuss the signs and symptoms of acute osteomyelitis, an infectious suppurative disease affecting bones. Osteomyelitis is generally caused by Staphylococcus, which reaches the bones via the blood stream from a distant focus, often a throat infection. Its rise was especially sharp during World War II, particulary in 1942-46 when the lack of due antibiotics made the disease uncured. The disease generally affects the upper end of tibia or lower end of femur. The infection is followed by intense reaction, with pus formation in the marrow spaces. From there the suppuration spreads along the marrow cavity and also through the cortex, to erupt on the surface and form a subperiosteal abscess. In some cases the marrow cavity is widely involved; in others, on the contrary, there is a large subperiosteal abscess, but little or no pus within the bone. Almost always part of bone becomes necrotic, due to the toxic effect of pus under tension and to obliteration by the subperiosteal abscess of the periosteal vessels supplying the bone cortex. The main ntitrient artery itself may be thrombosed, leading to necrosis of the major part of the bone. Acute osteomyelitis generally affects children, especially if in poor health, after an infectious fever. Sometimes there is a history of minor injury to the part a few days before the onset of acute symptoms. In a typical case the onset is sudden. Then pain and inflammation of the bone are accompanied by marked toxaemia. The temperature rises, often to 103° or 104° F, the face is flushed and the tongue is furred. The leucocyte count rises to 20.000 or more. Delirium is frequent. The pain is severe. The limb is held immobile. The skin over the inflamed region is hot and red, and dilated veins may be evident. Slight superficial edema appears early. Localising signs develop early in the case of a superficial bone such as the tibia, later if the bone is deeply placed. Acute osteomyelitis is a dangerous disease, especially when it affects a deep-seated bone, such as the upper end of the femur, pelvis or vertebrae. In those who survive the acute phase the disease often persists as chronic osteomyelitis. Eventually complete restoration of functions and general health i will be expected in most cases, when appropriate treatment is applied. Упражнение 7. Прочтите и переведите текст А Абзац 5 переведите письменно. 1. What kind of diseases is osteomyelitis. 2. When was its rise especially ■harp? Why?3.What is osteomyelitis caused by?4.Where does the infec- non localize? 5. What is the course of the disease? 6. How does the thsease begin in a typical case? 7. Does the disease persist as a chronic one or is complete restoration of functions and general health possible? Упражнение 9. Переведите данные предложения. Определите, какой частью речи являются выделенные слова. 1. The disease generally affects the upper end of tibia or lower end of lemur. 2. The infection is followed by intense reaction, with pus formation in the marrow spaces. 3. Almost always part of the bone becomes necrotic, due to the toxic effect of pus under the tension. 4. The main nutrient artery itself may be thrombosed. 5. In those who survive the acute phase the disease often persists as chronic osteomyelitis. > Упражнение 10. Найдите в каждом абзаце предложения, выражающие основную мысль данного абзаца. Выпишите их. Упражнение 11. Найдите в каждом ряду слово, синонимичное по значению первому слову ряда. 1. distant - obvious, remote, far-away, distinct, close; 2. to involve - to invent, to include, to invite, to affect; 3. to spread — to go over, to divide, to distribute, to cover, to scatter; 4. onset - attack, beginning, process, turning-point; 5. severe — low, short-turn, acute, chronic; 6. region — locality, district, area, part, partition Упражнение 12. Найдите в каждом ряду слово, противоположное по шачению первому слову ряда. 1. acute — dye, due, dull, dry; 2. minor — main, general, major, important; 3. evident — unclear, obscure; 4. appropriate - unsuitable, unfitting, common; 5. deeply — above, outside, superficially Упражнение 13. Поставьте глаголы-сказуемые в форму действительного залога. 1. Acute osteomyelitis is generally caused by Staphylococcus aureus. 2. The infection was followed by intense reaction with pus formation in the marrow spaces. 3. After hospitalization he was prescribed appropriate treatment at home by his family doctor. 4. The wound will be dressed by her every second day. Упражнение 14. Переведите следующие предожения на английский язык письменно. 1. Ее отправили в больницу два дня назад. 2. Доктор сказал, что нужна срочная операция. 3. При остеомиелите поражаются кости. 4. Гипсовую повязку снимут через три дня. 5. Рана зажила и больному разрешили двигаться, 6. При остеомиелите в костном мозге образуется гной. Часть II Слова к части II fracture ['fraektfa] п перелом siteп место (расположение) damage ['daemidft] vповреждать; п повреждение tear [tea] vрвать, разрывать prompt [promt]а быстрый heal [hi:l] vизлечивать; заживлять healing ['hi:lir)] nизлечивание; заживление relationship [ri'leijnfip] nвзаимоотношения accomplish [d'komplij] vвыполнять, завершать, достигать degree [di'gri:] nстепень tender ['tenda] а болезненный tendernessnболезненность bruise [bru:z] nсиняк, кровоподтек bruisingnпосинение swellingnопухание, опухоль bleed [bli:d] vкровоточить bleedingnкровотечение dress [dres] vбинтовать dressingnповязка Упражнения Упражнение 1. Прочтите и переведите следующие слова. communication, position, to restore, correct, to protect, irregularly, especially, to fix Упражнение 2. Найдите в данном ряду слово, значение которого дано в начале ряда. 1. повреждать (наноситьущерб) — to wound, to hurt, to damage, to harm; 2. заживлять - to cure, to restore, to heal, to treat; 3. выполнять (завершать) — to fulfil, to complete, to finish; 4. рвать, ранить — to separate, to lacerate, to tear Упражнение 3. Назовите корневые слова, от которых образованы данные производные, и переведите их на русский язык. 1. relation, relationship, relative, relatively; 2. tenderly, tenderness, tender-hearted; 3. swelling, swelled; 4. dressed, dressing >пражнение 4. Прочтите текст В'(Ю мин). 1) Скажите, какие типы пере- шмов описаны в тексте. 2) Найдите в тексте предложения с глаголом- казуемым в действительном и страдательном залоге. Укажитевремяска- |усмого. 3) Переведитепредложения. Text ВFractures A fracture is a broken bone. There may be different types of fractures. A closed or simple fracture results from an injury which breaks a bone without causing any external wound at the site of the break. In case of ,m open or compound fracture there is a wound of the skin at the site of i he fracture, and this will allow communication between the outside air .md the broken bone, therefore it is «open». When the sharp ends of a broken bone damage an internal organ such as the brain or lungs, this is known as «complicated fracture». In compound fractures early and prompt healing with good function will be obtained only by early repositions in correct position. This is necessary not only to restore the bone structures, but to place the soft parts in relationship for correct function as well. All compound fracture patients must be protected against movement, muscle spasm, and loss of position. This is accomplished by fixation of fracture fragments in plaster of Paris casts1 or in any other way. Frequent dressing of wounds in compound fractures is unnecessary. What are the symptoms and signs of a fracture? Shock is always present in some degree with any fracture. Sometimes it may be severe. Pain and lendemess at the site of fracture is quickly followed by bruising and swelling. Bleeding is frequent in case of an open fracture. Irregularity on the surface of the bone may also be seen, e.g. on the collar-bone or the bone of an arm. In an open fracture the ends of the broken bone may be sticking out of the wound. A person's leg which was broken may be turned underneath him with the foot turned round the wrong way. The bones of the leg may be bent in a place where there is a joint, e.g. between the knee and the foot if both bones of the leg are broken. First-aid treatment of fracture. Lay the patient down. This will lessen shock. If there is a fracture of the skull raise the patient's head and shoulders a little and support them. Stop bleeding if the fracture is open, and apply a dressing. In all open fractures there is some bleeding, but it can generally be stopped by putting on a dressing. If bleeding continues, it is necessary to use indirect pressure, especially if the bleeding is from an artery. Fix the damaged part so that any movement by the patient cannot cause the broken bone to move, as this will increase the deformity, cause great pain and make shock worse. Notes 1. plaster of Paris cast гипсоваяповязка Упражнение 6. Найдите в тексте предложения, более полно выражающие мысль данных суждений, и прочтите их. 1. There may be different types of fractures: closed, open, complete. 2. In compound fractures early healing may be obtained. 3. Compound fracture patients must be protected against movement. 4. Bleeding should be stopped. 5. Fix the damaged part. Упражнение 7.ПередайтеосновноесодержаниетекстаВ. Часть III Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 15 Упражнение 1. Укажите, в каких предложениях глагол стоит в страдательном залоге. 1. The bones of the leg were bent between the knee and the foot. 2. In all open fractures there is some bleeding. 3. Roentgenograms revealed new bone formation. 4. The fractures are caused by direct violence and indirect violence. 5. Pain and tenderness in the bone were followed by bruising. 6. Thepatient'slegwasheldimmobill. (Ответ: 1, 4, 5, 6. Если вы ошиблись, повторите § 4 Грамматического справочника.) ) I Упражнение 2. Определите, в каких предложениях глаголtobeявляется: а) частью страдательного залога; б) глагрлом-связкой. 1. If the limb is distorted consult a traumatologist. 2. In patients with broken bones in an arm or hand the affected limb is secured to the body with bandages. 3. One of the patients was a boy of ten with complaints of pain in both arms. 4. It was necessary to apply plaster of Paris cast at once. 5. The bleeding was stopped by putting on a dressing. 6. The diagnosis of a complicated fracture was made and the girl was directed to the traumatological department. 7. Doctor N. was particularly attentive to the man with a comlicated fracture. (Ответ: a) 1,2, 5, 6; б) 3, 4, 7. Если вы ошиблись, повторите § 15 Грамматического справочника.) Упражнение 3. Выберите правильные значения выделенных слов. 1. They dreamed of(мечтали, виделивосне) becoming surgeons after they graduated from the Institute. 2. They learned(учить, изучать, узнавать) that their group would begin their practical studies on Friday. 3. Their practical studies in surgery will begin at the surgical department (кафедра, факультет, отдел, отделение). LESSON SIXTEEN CORONARY HEART DISEASES Повторение:ВременагруппыPerfect (Active and Passive Voice) (§§ 12, 14) Часть I Слова к части I die [dai] v умирать death [deO] n смерть obstruction [ab strAkJn] n препятствие recover [ri'kAva] v выздоравливать recovery nвыздоровление notice ['noutisj v замечать; отмечатьexperience [iks'piarians] n опыт; случай; переживание; v испытыватьestimate ['estimeit] v считать; оценивать estimation[ esti'meijn] n оценкаailment ['eilmgnt] n заболеваниеchief [tfi:f] аглавныйillness nзаболевание, болезнь Упражнения Упражнение 1. Найдите глаголы-сказуемые в следующих предложениях. Определитеихвремяизалог. 1. The marked increase in patients entering emergency rooms in hospitals has resulted in a need for increasing facilities in almost every hospital. 2. The patient was examined for an injury to his leg which had been broken in an automobile accident. 3. Four weeks later the deep abrasions of the thigh were skin grafted. 4. If a bone in the forearm is broken the splint must reach above the elbow and extend below the wrist. 5. For thousands of years mankind had accumulated knowledge in surgery, but real development in this field of medicine started only in the 19th century. 6. By the end of the week we shall have explored surgically the posterior tibial artery. Упражнение 2. Образуйте 2 пары предложений от данных ниже: а) с глаголом-сказуемым в PresentPerfect (Active, Passive); б) с глаголом- сказуемым в PastPerfect (Active, Passive) согласно образцу. Образец: The nurse (to dress) the patient's wound. The nurse has dressed the patient's wound. The patient's wound has been dressed by the nurse. The nurse had dressed the patient's wound. The patient's wound had been dressed by the nurse. 1. The teacher (to demonstrate) open fracture of the thorax. 2. The physician (to examine) the boy with osteomyelitis. 3. He (to apply) plaster of Paris cast. 4. The students (to see) patients with a complicated fracture. Упражнение 3. Прочтите и переведите следующие слова и словосочетания. heart, coronary, contraction, approximately, surface, diabetic, per cent, angina pectoris, obesity, fortunately, degenerative, severity Упражнение 4. Запомните значение суффикса -ness. Образуйте существительные от следующих прилагательных согласно модели и переведите их. Прилагательное + -ness= существительное со значением качества или состояния: acuteострый —acutenessострота. ill, sick, excessive, distinctive, calm ■» Упражнение 5. Прочтите и переведите следующие гнезда слов. 1. to expert — experience, experienced; 2. to die — death, deadly, dying; 3. to cease — cessation, ceaseless; 4. to obstruct — obstructive, obstruction; 5. to recover - recovery, recoverable Упражнение 6. Прочтите и переведите следующие словосочетания. to recover sight (hearing, voice, one's breath, consciousness); dead- born; to experience pain; an obstruction in the throat ^ пражнение 7. Просмотрите текст А и изложите основные факты текста. Text A Coronary Heart Disease 1. The coronary blood vessels surrounding the heart have derived their n.ime from the fact that they encircle the heart like a crown, or corona. I hese vessels transport almost a half pint of blood every minute over the nrface of the heart. Any sudden blockage of one of the coronary arteries deprives that section of the heart of its blood supply. Cardiac cells die, heart contractions may cease, and circulation may come to a standstill. If i coronary artery is completely plugged, the condition is. called a coronary occlusion'or heart at- Ql. tack. The vascular pathologic disorder itself has been very variable. If the obstruction is only partial or in one of the smaller coronary tributaries, prompt treatment often leads to the individual's recovery. An occlusion in main coronary arteries is very serious and may cause Fig. 14.Coronary arteries supplying the heart.sudden death 0ther causes of the coronary disease in- lude heavy physical exercise, aging, diatetic habits, obesity, smoking, or hypertension. Pain which had been developed in the heart may be due to a blood - ilow deficiency in the coronary vessels. This is referred to (actually felt in) i he left arm and shoulder. Such pain from the heart has been called mgina pectoris. Angina pectoris may not actually be noticed until the \sork load is too great in relation to the flow in the coronary vessels. Teople who had experienced it repeatedly often do not feel pain unless i hey experience strong emotion. Others experience it much of the time. Fortunately, the great majority of coronary disease patients will have recovered and have been able to lead active, useful lives, when i hey receive proper treatment under good medical supervision. There ire many preparations which have been effective and are under clinical investigation at the present time. ь Heart and Artery Diseases Superi< vena с |
