И.Ю.-Марковина-З.К.-Максимова-М.Б.-Вайнштейн. Учебник для медицинских вузов и медицинских специалистов Серия xxi век Рекомендовано угчЮ по медицинскому и фармацевтическому образованию
 Скачать 1.07 Mb. Скачать 1.07 Mb.
|
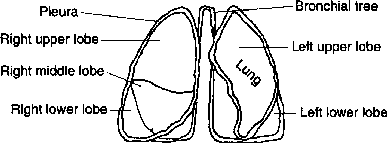 Fig. 8.Diagram of lungs. simultaneously with the increase in capacity of the thorax. The lungs expanding, the air pressure in them drops and atmospheric air rushes into the lungs through the air passages. Hence an inhalation involves a contraction of muscles, an increase in the capacity of the thorax, an expansion of the lungs, and entrance of atmospheric air into the lungs through the air passages. { < - Inhalation is followed by exhalation. The muscles participating in inhalation relax, jthe ^apKagm The ribs drop as a result of contraction of the internal intScostar^and other muscles and because of their own weight. The capacity of the thorax decreasing^he lungs become compressed', ifte pressure in {hetn rises and the air rushes out through the air passages. The respiratory movements are rhythmic. An adult at rest makes 16—20 respiratory movements per minute, children make more movements (a newborn child makes up to 60 movements a minute)/Physical exertion, particularly in untrained people, is usually accompanied by Caster respiration. Accelerated respiration is also observed in many diseases. Sleep is accompanied bwia slowing of respiration. Movements of breathing. Changes in the volume of air in the lungs are brought about by movements both of the diaphragm and ribs^ Contraction of the diaphragm increases the length of the capacity of the chest, while the upward movement of the ribs increases the cross section of the chest. Inspiration is due to contraction of the diaphragm and of the muscles attached to the ribs. These contractions are induced by nervous impulses. Expiration is a less active process than inspiration, for when the muscles relax the elasticity of the lungs themselves tends to drive out the air previously inhaled .'Any impediment to breathing due to pressure or constriction in the respiratory passage^ is especially noticeable during expiration, because it is usually of a passive character.\^Vhen the volume of breathing is increased by physical exercise many assessory muscles are involved while producing deeper inspirations. Expiration also involves a Vigorous action of the abdominal muscles. \ \ —/ * л V V ; \ V X Упражнение 9. 1) Прочтите и переведите текст А. Первый абзац перевелите письменно. 2) Найдите в тексте А ответы на следующие вопросы и считайте их. 1. How is contraction of the muscles participating in inhalation regulated? 2. Why does the size of the thoracic cavity increase? 3. When is impediment to breathing especially noticeable? 4. What processes does the inhalation (exhalation) involve? 5. What do the movements of the/ diaphragm and ribs bring about? 3) Составьте письменно план текста А. Упражнение 10. Подберитепарысинонимов. inspiration, to take place, to induce, per minute, respiration, breathing, to cause, to produce, inhalation, to occur, a minute Упражнение 11.Подберитепарыантонимов. to compress, inhalation, to contract, to increase, to drop, upward, to decrease, to rise, downward, exhalation, to expand, to relax Упражнение 12. Переведите следующие предложения, определите функции причастий. 1. For mechanical analysis the respiratory system may be divided into three parts: the gas (in the airways and air spaces), the lung structure, containing the gas, and the thorax containing the lungs. 2. Dynamic increases in airway resistance during expiration set the limit on the ventilatory capacity of the respiratory system in normal and diseased lungs. 3. While flowing through the capillaries the blood accepts the oxygen from the alveolus and deposits carbon dioxide into the alveolus. 4. Airway pressures are not everywhere equal, being most negative in the alveoli. 5. During inspiration pleural pressures become more negative, the widening tendency increasing. Упражнение 13. Переведите на английский язык. 1. Дыхание — это процесс, включающий ритмично повторяющиеся вдох и выдох. 2. На мышцы, которые участвуют в процессе дыхания, воздействуют нервные импульсы. 3. Когда диафрагма опускается, размер грудной клетки увеличивается. 4. Во время выдоха объем грудной клетки уменьшается, и давление в легких увеличивается. 5. Физическая нагрузка обычно сопровождается ускоренным дыханием. fv\ • Часть II ' > ; > Слова к части II excite [ik'sait] vвозбуждать cough [kof] vкашлять excitation [,eksi'teijn]nвозбуждениеcoughingnкашель cease [si:s] vпрекращать(ся) arise [a'raiz] vвозникать, появляться deep [di:p] а глубокий depth [depG] nглубина evident[ evidant] а очевидный, явный state [steit] nсостояние sneeze [sni-.z] vчихать sneezingnчихание adjust [a'djAst] vприспособлять, согласовывать alter['э:кэ] vизменять(ся) alteration [,o:lt9'reiJn] nизменение Упражнения Упражнение 1. Используя суффиксы-tion, -ate, -ly, -al, -ing,образуйте производные от следующих слов. Переведитеих. to inhibit, stimulus, automatic, reflex, spine, to relax, to excite, to cough, to sneeze, to alter Упражнение 2. Просмотрите текстВ (10 мин). 1) Выделите 4 основные фактора в процессе дыхания, описанные в тексте. 2) Найдите и переведите: а) предложения, где причастия выполняют функцию обстоятельства; б) предложения с независимым причастным оборотом; в) предложения со словамиboth, both...and. Text В Regulation of Respiration. Nervous Control of Breathing The mechanism of regulation of respiration is very complex. Schematically it is as follows. In the medulla oblongata there is the respiratory centre. In the respiratory centre both excitation and inhibition continuously alternate. When excited it transmits impulses to the spinal cord and hence along nerves to the respiratory muscles; the latter contract and an inhalation takes place. When the respiratory centre is in a state of inhibition the transmission of impulses to the respiratory muscles ceases, the muscles relax and an exhalation results. The specific stimulus of the respiratory centre is carbon dioxide. As soon as the blood accumulates a certain amount of carbon dioxide, the respiratory centre becomes excited and an inhalation takes place. During inhalation the lungs expand, which stimulates the endings of the vagus nerve embedded in the tissue of the lungs. While arising in the receptors the exeitation is transmitted along the vagus nerve to the respiratory centre and inhibits it, and an exhalation results. Thus respiration is automatically regulated; an inhalation stimulates an exhalation, and the exhalation brings about an accumulation of carbon dioxide which stimulates an inhalation. Respiration is subjected to the control of the cerebral cortex; this being demonstrated by the fact that a person can voluntarily hold his breath for a very short time or change both the rate and depth of respiration. Cortical regulation of respiration is also evident in the acceleration of respiration during emotional states. Protective acts, such as coughing and sneezing, are associated with respiration. Both of them are performed reflexly; the centres of the reflexes are situated in the medulla oblongata. Nervous control of breathing. The muscles of breathing have no independent or automatic rhythm, they contract only responding to impulses from the brain down the spinal cord. These impulses arise and are coordinated in a specialised area in the brain, the respiratory centre, which is in the medulla. The medulla is at the base of the brain and is a bulbous continuation of the spinal cord within the skull. The respiratory centre has to adjust the volume of air breathed and to maintain a uniform alkalinity of the blood; the centre effects the reciprocal alteration both of inspiration and expiration. Упражнение 4. Прочтите данные суждения. Найдите в тексте В предложения, более полно выражающие мысль суждений, и прочтите их. 1. In the respiratory centre excitation and inhibition alternate. 2. During inhalation the lungs expand. 3. Respiration is automatically regulated. 4. The cortical regulation of respiration is evident. 5. Protective acts are performed reflexly. 6. The muscles of breathing contract responding to impulses from the brain. Часть III Контрольно-обобщающие упражнения к уроку 8 Упражнение 1. Найдите и переведите предложения, где причастие I выполняет функцию обстоятельства. 1. We were talking about coming exams. 2. When the ribs are elevated by the inspiratory muscles they are drawn toward a horizontal plane thus increasing the anteroposterior diameter of the thorax. 3. Having obtained the nesessary results the scientists used them in their future works. 4. When considering neurogenic factors that regulate local blood flow one thinks of sympathetic non-adrenergic nerves. (Ответ: 2, 3, 4. Если вы ошиблись, повторите § 20 Грамматического справочника.) Упражнение 2. Найдите и переведите предложения, где причастие II иыполняет функцию обстоятельства. 1. When excised the lungs were not allowed to collapse completely. 1. Any pressure applied to a body is opposed by an equal pressure developed by the body. 3. The stability of the lung tissues is indicated hy their behaviour when freed by surface influences.4.As mentioned ut the previous lecture next theme will be devoted to nervous control of breathing. 5. Inspiration enlargement of the anteroposterior and lateral diameters of the chest is accomplished through the contraction of muscles. (Ответ: 1, 3, 4. Если вы ошиблись, повторите § 21 Грамматического справочника.) Упражнение 3. Найдите и переведите предложения с независимым мричастным оборотом. 1. Respiration is usually either an automatic or a reflex act, each expiration sending up afferent, sensory impulses to the central nervous system. 2. It is impossible to cause death voluntarily holding the breath, 3. The air passes rhythmically into and out of the air passages, and mixes with the air already in the lungs, these two movements being known as inspiration and expiration. 4. The increase of the chest in size is due to the diaphragm, whose muscular fibres by their contraction are pushing down the abdominal organs. (Ответ: 1,3. Если вы ошиблись, повторите § 22 Грамматического справочника.) Упражнение 4, Укажите и переведите предложения, где словоbothявляется п) частью составного союза; б) местоимением. 1. Modern scientists have been successful in the use of fibrinolytic therapy in both ball and disc mitral prosthesis. 2. When the diaphragm is released both lungs collapse by their own elasticity and expel the air. УThe decrease in thoracic size during expiration is accomplished both by release of physical stresses and by active participation of contracting muscles. 4. Both these methods of examining the lungs are frequently used. 5. During forced expiration the contraction of the abdominal muscles allows both external and internal intercostals to act as expiratory muscles. (Ответ:a) 1, 3, 5; 6) 2, 4. Если вы ошиблись, повторите § 40 I рамматического справочника.) Упражнение 5. Выберите правильное значение выделенных слов. 1. A change in conditions(а) состояние, б) условие) affects the activities(а) активность, б) деятельность) of all organs. 2. Work causes (а) вызывать, б) заставлять) an increase in the metabolism. 3. A disturbance in the respiratory rhythm results from(а) являтьсярезультатом, б) приводитьк) decreased excitability of the respiratory centre. 4. This is accompanied(а) сопровождаться, б) вызываться) by various disturbances in the activities of the organism. 5. Under some conditions the gaseous interchange in the lungs decreases(а) увеличиваться, б) уменьшаться). (Ответ: la, б; 2a; За; 4a; 56.) LESSON NINE DIGESTION Инфинитив в функции подлежащего и обстоятельства (§ 25) Конструкция сравнения the ... the ... (§ 4) Функции и перевод слов due, dueto(§ 39) Часть I Слова к части I nutrient ['njuitrisnt]а питательный; п питательное вещество nutritious [nju:'tri/ds]а питательный deliver [diTivs] vдоставлять, передавать soluble ['soljubl]а растворимый insolubleа нерастворимый solution [sd'lu:Jn] п раствор connect [ks'nekt] vсоединять(ся), связываться) connection[кз'пек/п] п соединение, связь, присоединение connective [ks'nektiv]а соединительный, связующий according [a'ko:dir)] toprepсогласно, в соответствии с bacterium[Ьаек'Пзпзт](pi.bacteria[ЬаекЧюпэ]) п бактерия vomitive[ vomitiv] п рвотное (средство) vomitory[Vomitan]а рвотный nutrition [nju:'trijn] п питание, пища nutritive ['nju-.tntiv]а питательный, пищевой split [split] vрасщеплять ascend [a'send] vподниматься protein ['proutiin] nпротеин, белок remain [rfmein] vоставаться remainder [ri'meinds] nостаток undergo [,Andd'gou] vиспытывать, переносить, подвергаться чему-л. exist [igzist] vсуществовать, быть, находиться existence [igzistans] nсуществование prevent [pri'vent] vпредотвращать, предохранять, предупреждать * exception [ik'sepjn] nисключениеprevention [pri'venfn] nпредотвраще- vomit ['vomit] vстрадать рвотой, ние, предохранение, предупреж- вырвать; п рвота дение Упражнения Упражнение 1. Найдите формы инфинитива в следующих предложениях. Переведитепредложения. 1. Spontaneous respiration was chosen to permit the development of pulmonary edema and alveolar collapse. 2. To determine progressive lung damage in this case was rather difficult. 3. To give first aid one must learn the basic first aids rules. 4. It is useful to summarize very briefly what is known about the elastic properties of elastin and collagen. 5. Experiments were made to observe the effects of temperature upon the respiratory process. Упражнение 2. Заполните пропуски подходящими по смыслу прилага- к-льнымиsooner, less, more.Переведитеданныепредложения. 1. The ... people are physically trained, the ... oxygen they have in i heir blood. 2. The ... appetizing the food is, the ... amount of secretion кcauses. 3. The ... time you spend in the sanatorium, the ... you will recover after the illness. 4. The ... capacity of the thorax decreases, the . the lungs become compressed. Упражнение 3. Переведите следующие предложения со словамиdue, dueto. 1. A diffusion block due to pulmonary edema or the opening up of iiiteriovenous anastomoses in the lungs is the usual event. 2. In one of ihese animals death was due to sudden asystole. 3. The apnea in these animals was due to inadequate blood flow and oxygen availability to vital centres in the central nervous system. 4. The lecture on physiology of respiration was delivered in due time. 5. Traumatic diseases are due i оdirect physical injury. Упражнение 4.Отработайте чтение следующих слов, переведите их. digestive [di'cfcestiv], nutrients ['njurtrisnts], lymphatic [lim'faetik], esophagus [I'sofagss], enzymes [in'zaimz], area['еэпэ], stomach ['sUm- ok], glucose [glu:kouz], carbohydrates ['ka:bou'haidrits] Упражнение 5. Запомните значение следующих суффиксов. Образуйте слова согласно данным моделям. Переведите эти слова. Прилагательное (существительное) +-ify= глагол, имеющий значение «производить действие»: classкласс —toclassifyклассы- фицироват ь. pure, intensive, solid, note, sign Прилагательное +-ty (-ity, -ety)= существительное, обозначающее состояние, положение: extremeкрайний —extremityконечность. equal, proper, human, dense, immune, certain Упражнение 6.Прочтите и переведите данные гнезда слов. 1. nutrient (п, a), nutritive, nutrition, nutritional; 2. to dissolve, solution, soluble, insoluble, solvent; 3. to vary, variant, various, variable, variability; 4. bacterium, bacterial, bacteriology, bacteriologist; 5. (to) vomit, vomiting, vomitive; 6. to digest, to ingest, digestive, digestion / | Л - •■ / / - - , сп Г ; " it.',-, ■ \ • - j Упражнение 7. Просмотрите текст А. Разделите текст на 3 части и озаглавьте их. Г ! Л . . ■ : / ^ 1 / ' \ У : TextА о ' The Digestive System and the Process of Digestion and Absorption The present text is given to explain the processes of digestion and absorption. The more we know about them, the better we shall under- Л stand how important these processes are. Every cell of the human body requires certain chemical nutrients in the fluids that^ surround it. In order to supply these nutrients, the body must breai clown complex foods into molecules small enough to pass through tissues, enter the blood stream or lymphatic systems, and be delivered in a soluble form to the various body cells. This break of insoluble forms is known as digestion; the passage of such 'substances into the blood stream or lymph is known as absorption. The human digestive tract is a long, muscular tube (up to 25 feet in length) that begins at the mouth and ends at the anus. This tube consists of the oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, small intestine, and laige intestine. Several glands, located outside the digestive tract, are also import tant in the digestive process. Our tast is to describe them in detail. These glands, known as accessory glands, are connected by ducts to the digestive tube. These accesory glands include the salivary glands,: Food qnters the |
