Вступний фонетикоорфоепічний курс вступ
 Скачать 25.36 Mb. Скачать 25.36 Mb.
|
|
thyroid parathyroid (posterior) thymus j / adrenals *r Ї ,^**(suprarenalsj 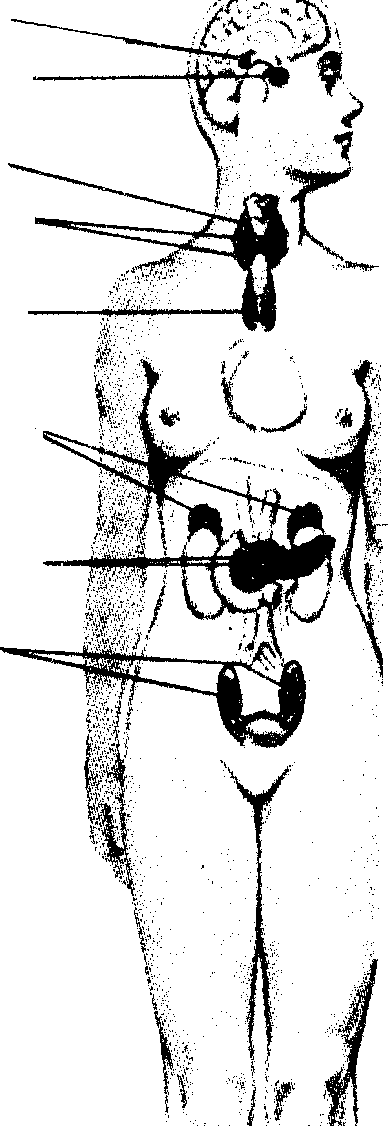 islets of Langcrhans (in pancreas) testes
Exercise 9. Read and translate the names of different diseases caused by abnormal activity of the endocrine glands. Goiter (зоб), the enlarged thyroid. Hyperthyroidism (гіпертиреоз), produces exophthalmic goiter, it leads to loss of weight, nervousness, a rapid pulse, protrusion of the eyes, sweating. Hyperthyroidism causes cretinism or myxedema because of failure of the thyroid gland. Hypoparathyroidism causes hypocalcemia. It can lead to tetany (['tetani] - правець). Addison's disease is caused by failure of the adrenal glands. It is characterized by weight loss, weakness, low blood pressure, brownish pigmentation of the skin, hypoglycemia. Diabetes insipidus (нецукровий діабет) is characterized by the heavy discharge of urine (polyuria) and intense thirst (polydipsia). Diabetes mellitus (цукровий діабет), deficiency of insulin prevents sugar from leaving the blood, so it is characterized by excess of sugar in the urine; hunger, thirst and quick loss of weight. Hyperinsulinism is the excessive secretion of insulin from the pancreas. The patients may be convulsing and fainting. Control Tests. Endocrine System. Cell. Physiological Functions of the Organism 1. What substances are produced by endocrine glands? A. Enzymes B. Hormones C. Proteins D. Vitamins E. Glucose 2. How do we call the system of glands? A. Lymphatic B. Circulatory C.Independent D. Endocrine E. Exocrine 3. What glands are not endocrine? A. Hypophisis B. Hypothalamus C. Epiphysis D. Thymus E. Sweat 4. What is the English for щитовидна залоза! A. Adrenal gland B. Pituitary gland C. Pineal gland D. Thyroid gland E. Pancreas 5. What glands are situated above the kidneys? A. Sex B. Parathyroid C. Adrenal D. Thyroid E. Thymus 6. What does the endocrine system consist of? A. Reproductive organs B. Glands of internal secretion C. Glands of external secretion D. Glands of mixed secretion E. All glands of the body 7. What gland is the regulating center of all glands? A. Hypophysis B. Hypothalamus C. Thymus D. Epiphysis E. Encephalon 8. What disease belongs to diseases of the endocrine system? A. Myocarditis B. Cholecystitis C. Bronchitis D. Diabetes E. Pneumonia 9. What medicine is used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus? A. Glucose B. Diasoline C. Insulin D. Analgin E. Dimedrol 10. What hormones are produced by the female sex glands? A. Corglycoids B. Thyroidin C. Estrogen D. Testosterone E. Adrenaline 11. What are the main functions of hormones? A. Excretion and metabolism B. Development and growth C. Growth, development and metabolism D. Excretion and growth E. Metabolism and immunity 12. Where is the thyroid gland situated? A. Under the heart B. In the front part of the neck C. In the back part of the neck D. In the left side of the chest E. In the right side of the chest 13. What is another name of the epiphysis? A. Pineal B. Pituitary C. Adrenal D. Ovary E. Testis 14. What part of the pancreas is endocrine? A. Left B. Right C. Islets D. Middle E. Central 15. What is the English for наднирникиї A. Epiphysis B. Pituitary C. Hypophysis D. Adrenals E. Parathyroids 16. stimulate the growth of the female sex organs. A. Androgens B. Testosterone C. Adrenaline D. Sex hormones E. Estrogens 17. The sex glands in males are . A. Prostate B. Ovary C. Testes D. All answers are right E. All answers are wrong 18. The sensitive part of the penis is . A. the middle part B. the glans C. the prepuce D. All the penis E. No right answer 19. Progesterone is produced in the . A. uterus B. ovary C. placenta D. corpus luteum E. follicle 20. The inlarged thyroid is . A. Addison's disease B. myxedema C. tetany D. goiter E. cretinism 21. What does the term polydipsia mean? A. Intense hunger B. Intense thirst C. Loss of blood D. Anemia E. Intense secretion 22. The functions of all endocrine glands are interconnected and the glands make up A. an organism B. a single system C. blood circulation D. different things E. control over the organism 23. The hormones are carried throughout the organism with . A. water B. lymph C. urine D. gall E. blood 24. The hypophysis is the chief of the endocrine system. A. gland B. brain C. cell D. organ E.receptor 25. The composition of some hormones is well known and they are made synthetically. A. simple B. various C. chemical D. mechanical E. physical 26. Without that substance our organism cannot be. A. Alcohol B. Nicotine C. Water D. Beer E. Spirit 27. What isn't harmful to your health? A. Cigarettes B. Alcohol C. Water D. Nicotine E. Spirit 28. We breath with . A. water B. nitrogen C. oxygen D. hydrogen E. air 29. Physiology studies of the body. A. the structure B. the functions C. the growth D. the weight E. the reproduction 30. The exchange of substances in the organism is called . A. heat action B. metabolism C. water balance D. immunity E. nutrition 31. What does the term myoma mean? A. Muscle tumor B. Bone tumor C. Skin tumor D. Malignant tumor E. Benign tumor 32. What does the term chondroma mean? A. Tumor of the muscle B. Tumor of the uterus C. Tumor of the heart D. Tumor of the cartilage E. Tumor of the joint 33. What doesn't describe a kind of disease? A. Chronic B. Acute C. Mortal D. Infection E. Good 34. This science studies body cells. A. Pathology B. Etiology C. Biology B. Physiology E. Cytology 35. The breakdown of nutrients or complex substances into simpler ones is called . A. Metabolism B. Botulism C. Anabolism D. Catabolism E. Organism 36. is the building of body materials. A. metabolism B. botulism C. anabolism D. catabolism E. organism 37. What is the structural unit of the living matter? A. Cell B. Tissue C. Organ D. System E. Organism 38. What is there in the center of each cell? A. Ribosome B. Lysosome C. Centriole D. Cytoplasm E. Nucleus 39. What does the term mitosis mean? A. Cell activity B. Cell division C. Cell nutrition D. Cell structure E. Cell membrane 40. What do we call the scientist who studies all about tissues? A. Histoiogist B. Epidemiologist C. Bacteriologist D. Cytologist E. Embryologist 41. The study of the cause of any disease or the theory of its origin is . A. biology B. pathology C. etiology D. microbiology E. chemistry 42. Vitamin prevents scurvy. A. A B. В c. c D. D E. E 43. Vitamin deficiency leads to infertility. 47. The excretes bile. A. A A. stomach B. В В. intestine C. C C. kidney D. D D. liver E. E E. gland 44. Vitamin A. A B. В C. C D. D E. E prevents rickets. 48. The carries oxygen round the body. A. lymph B. urine C. water D. vessel E. blood 45. What vitamin is soluble in water? A. A B. В C. K D. D E. E 49. Where do we usually take our temperature? A. In the oral cavity B. In the armpit C. In the anus D. On the neck E. In the groin 46. What is avitaminosis? A. Deficiency of any vitamin B. Increased quontity of vitamins C. Normal quontity of vitamins D. Presence of vitamins E. Absence of vitamins 50. Where do we usually take our pulse? A. On the wrist B. On the neck C. In the armpit D. In the groin E. Under the knee II. Grammar Exercises Exercise 1. Read and translate the words, pay attention to the suffixes and prefixes. Acupuncture, compatible, harmful, merely, selection, to simplify, invaluable, effectiveness, intention, possibility, scientifically, numbness, decomposition, irregularity, consciousness, regeneration, deafness, reformation. Exercise 2. What are the Ukrainian equivalents of the English proverbs?
Exercise 3. Fill in the blanks with the verbs to treat, to discuss, to build in the correct form.
Exercise 4. Translate the sentences, pay attention to the sequence of tenses. 1. That patient believed that the doctor would suggest an operation. 2. The doctor said that he made the morning round every day. 3. We knew that he was ill. 4. He said that he could finish his work in time. 5. All the students knew that they had to revise for the examinations. 6. He showed me which exercises he had done. Exercise 5. Translate the sentences with modal verbs and verbs with modal meaning. 1. This doctor ought to be more attentive. 2. He needn't hurry. 3. All our students must work at the hospital. 4. They needn't do it. 5. We have to be ready to fulfill this task. 6. I think you should go out for a walk every evening. 7. What does he have to do next? 8. What has she got to do next? 9. We are to meet them there. 10. This woman has to stay at home with her sick baby. 11. He mustn't go out in the street. 12. We ought to help this nurse. Exercise 6. Change the following sentences according to the model. Model: If we changed the temperature, the reaction would change too. - If we had changed the temperature, the reaction would have changed too. 1. If this were the case, he might expect an unusual effect. 2. Unless some studies were available, the drug couldn't be applied. 3. Providing doctors prevented heart attacks, the patient would live longer. 4. If the nurses were given up-to-date apparatus, they would prevent many fatal cases. 5. If every effort of organ transplants could be made, patients might be able to survive. Exercise 7. Translate the conditional sentences. 1. If additional studies had been carried on, they might have determined the precise role of protein. 2. Overweight people are in even greater danger if they go on and off their diets, losing and gaining weight. 3. If we read much, we will know much. 4. If you read many medical books, you would know much about new techniques. 5. If I had time, I would read all the articles of this professor. Exercise 8. Translate into English. 1. Якби в мене був час, я зробив би цю роботу вчора. 2. Якби ви читали багато, то й знали б багато. 3. Якщо ми будемо багато читати, то й знатимемо багато. 4. Якби йому не допомогали друзі, він не закінчив би роботу вчасно. 5. Якби вони були тут, ми обговорили б це питання. III. Independent Work: Secretion Exercise 1. Read the text; try to understand it without using a dictionary. Secretion Secretion is a process generally brought about by an organ called a gland. A gland whether simple or highly complex in structure may be looked upon as a tube, whose walls are composed of highly specialized epithelial cells, gland cells. The tube is closed at one end. In many glands the other end of the lumen opens up, either directly or by means of a special duct, onto a free surface, such as the skin, the interior of the mouth, the lumen of the intestine, etc. The materials produced by the gland are poured onto this free surface, for which reason the secretion of this type of gland is spoken as an external secretion. The gland is surrounded by a dense network of capillaries. The distinct process may take place in a gland: the gland cell serves merely as a transfer agency, or it acts as a manufacturing plant or both. In the first instance, certain materials, water and NaCl are taken out of the blood stream by the gland cell, transferred through the cell, passed into the duct or lumen, and secreted on a free surface. All types of glands transfer water in this manner. Some glands, e.g. the sweat glands, practically limit their activity to this. Other glands take certain materials out of the blood stream and chemically transform them into new compounds which together with water and salts are then poured into the duct. The activity of a gland is normally accompanied by a great dilation of its blood vessels, without this increased flow of blood a gland cannot function for any appreciable length of time. Nevertheless in many instances its blood flow in itself is not the direct cause of secretion, for by administering certain drugs (e.g. atropine) it is possible to stop the secretion completely although the flow of blood continues. Secretion by the digestive glands is to be regarded as an active phenomenon, and not merely a passive filtration. Exercise 2. Make up a short plan of the text. Retell the text according to your plan. Exercise 3. Arrange the sentences in the right order (as in the text). 1. Some glands practically limit their activity to this. 2. The activity of a gland is normally accompanied by a great dilation of its blood vessels.
UNIT TWENTY-FIVE UNIT TWENTY-FIVE
I. Speaking: Urinary System After careful study of this unit you should be able to:
Exercise 1. Read and learn the following words and their equivalents.
Exercise 2. Learn the pronunciation of the following clinical terms. glomerulonephritis [glo,m3ruhuni'fraitis] pyelonephritis [,pai3buni'fraitis] hydronephrosis [.haidrsoni 'freusis] renal falure ['feiljs] uremia []и:з'гі:тіз] polycystic kidney [,pcli'sistik] calculi ['kaelkju: ,lai], kidney stones strictures ['striktfsz] ptosis ['tsosis] renal colic ['knlik] cystitis [sis'taitis] urethritis [ juari'Qraitis] enuresis [,enjo'ri:sis] Exercise 3. Read the texts, translate them and retell. Text A. Urinary System The urinary system is also called the excretory system, because one of its main functions is to remove waste products from the blood and eliminate them from the body. The other functions are:
But other systems also eliminate wastes. For example, the digestive system eliminates undigested food, water, salts and bile. The respiratory system eliminates carbon dioxide and water. The skin eliminates water, salts, nitrogen waste. The urinaiy system includes the kidneys, right and left; two ureters - long tubes, which lead to the lower part of the urinary bladder; the urinary bladder, which is a hollow sac for temporary collection of the urine; and the urethra - the tube, through which the urine is discharged from the bladder and passes out of the body. Text B. Kidneys The kidneys are considered to be the main organs of the urinary system. They are two in number, right and left. The kidneys are bean-shaped organs embedded in a cushion of adipose Fig. 25-1. The urinary system Fig. 25-2. The kidney tissue and located behind the abdominal cavity. They consist of outer cortex part, inner medullar part, and pelvis. The kidneys can be compared with filters, as they perform the filtration of waste products from the blood. These waste products go to the kidney through the renal arteries, rather short and thick vessels. The location of the urinary organs and their blood supply can be seen in Fig. 25-1. The kidney is an organ about 10 cm long, 5 cm wide, and 2.5 cm thick. On the inner margin there is the hilus (ворота), at which the renal artery and vein, and the ureter connect with the kidney. The renal cortex covers the kidney. The renal medulla contains the tubules that collect urine. These tubules form pyramids with the tips toward the renal pelvis. The renal pelvis is a funnel-shaped basin that forms the upper part of the ureter. Calyx ['keeliks] is a cuplike extension which surrounds the tip of pyramids and collect urine, which then passes down the ureter and bladder (Fig. 25-2). Text C. Nephrons The nephron is the smallest unit of the kidney. It is a tiny coiled tube with a bulb [ЬлІЬ] at one end. This bulb is called Bowman's capsule (капсула Боумена). which surrounds the glomerulus. Each kidney contains about 1 million nephrons. The afferent artetiole supplies the glomerulus with blood; the efferent arteriole carries blood from the glomerulus. (The detailed structure of the nephron can be seen in Fig. 25-3.) The process of filtration and formation of the urine takes place within the tiny tubules of the kidneys. Text D. Functions of Kidneys The kidneys are involved in the following processes:
- renin ['rr.nin], which is important in the regulation of blood pressure; -erythropoietin [i,ri9raupoi'i:tin], which stimulates the red bone marrow to produce red blood cells and thus prevents anemia. Text E. Urine The urine is a yellowish liquid that is about 95 per cent water and 5 per cent dissolved solids and gases. The amount of these dissolved elements is indicated by specific gravity. The urine has a specific gravity that normally varies from 1002 (very dilute urine) to 1040 (very concentrated urine). The normal substances, found during the test of the urine, are nitrogenous waste products, electrolytes, and yellow pigment. Urine examination is one of the most important parts of an evaluation of a person's physical state. Here is a list of the most significant abnormal substances found in the urine:
Exercise 4. Read the meaning of the following clinical terms and answer the question: what is each of the disorders characterized by? Glomerulonephritis - inflammation of the kidneys, primarily involving the glomerula; this disease causes destruction of the glomerular capillary walls; the complications are renal failure, retention of urea in the bloodstream (uremia). Hydronephrosis - enlargement and distention (swelling) of the kidney due to block of urine outflow, caused by renal calculi, tumors, hypertrophy of prostate or narrowing (stricture) of the ureters. Pyelitis - inflammation of a kidney pelvis. Nephrolithiasis - the formation of renal calculi (stones) in the renal pelvis, which is followed by obstruction of the kidney, ureter, or bladder. Pyelonephritis - bacterial infection of one or both kidneys usually involving both the pelvis and the functional tissue. Pyuria is found in urinalyses. Polycystic kidney — the formation of numerous fluid-filled sacs upon and within the kidney. Gout - a disease resulting from a disturbance of uric acid metabolism, characterized by an excess of uric acid in the blood and deposits of uric acid salts in various tissues, especially in the joints of the feet and hands: it causes swelling and severe pain, notably in the big toes. Exercise 5. Tell about the body systems that have excretory functions. Exercise 6. Describe the kidneys using this plan.
Exercise 7. Describe the nephron, use Fig. 25-3. Exercise 8. Answer the following questions.
10. What disorders of the urinary system do you know? II. Grammar Exercises Exercise 1. Point out the suffixes and prefixes in the words and translate them into Ukrainian. Experimental, transplantation, organic, inorganic, coagulation, miniature, metabolic, personally, mechanical, experiment, radioactivity, function, clinical, motherhood, leadership, capitalist, freedom, treatment, scientific, pressure, carelessness, infection, director, construction. Exercise 2. Translate the following clinical terms. Epidemics, asthma, sclerosis, pneumonia, bronchopneumonia, pathology, pulmonologist, urgent, allergy, infection, traumatism. Exercise 3. Remember the degrees of comparison of adjectives, translate the following sentences. 1. The earlier the diagnosis, the greater likelihood of cure. 2. The smaller the loss, the quicker the patient recovers. 3. The more primitive organism, the greater its regeneration ability. 4. The sooner the patient is operated on, the better for him. 5. The larger the heart, the lower the position which it occupies in the thorax. 6. The more fresh air, the better for patients. Exercise 4. Define participial and gerundial complexes, translate the sentences into Ukrainian. 1. Being very tired, he refused to fulfill this task. 2. By entering the brain or spinal cord, neurosurgeons are successfully doing away with disorders. 3. He proposed methods of applying local novocaine anesthesia during operations. 4. This man was discharged from the hospital completely cured, having stayed there 20 days. 5. The doctor examining the patient revealed his heart trouble. 6. They have learned the methods of examining a patient. 7. The examination of the patients having been completed, the nurses began to fulfill the doctor's prescriptions. 8. The doctor having used a new method of treatment was known to us. Exercise 5. Complete the following sentences. 1.1 should have missed the lecture if...
Exercise 6. Make up sentences using the tables. a) If I were you, But for him But for them I he you they we go for a walk, travel to the Crimea, stay in bed. consult a doctor, visit a good specialist. b) If you she we thev were you, you she we they should/would prescribe other drugs, go to the urologist, give another treatment, become a surgeon, give another diagnosis. Exercise 7. Translate into English. 1. На вашому місці я негайно звернувся б до уролога. 2. Якби в мене були гроші, я придбав би цей фонендоскоп. 3. Якби мій брат вмів плавати, ми ходили б у басейн щодня. 4. Я запізнився б на засідання, якби не взяв таксі. 5. Якби в мене був час минулого тижня, я поїхав би на екскурсію до Львова. III. Independent Work: Organism as a Whole Exercise 1. Read the text and try to understand it without using a dictionary. Organism as a Whole The organism is a single system. In a complex organism cells and intercellular substance form tissues, tissues make up organs, and organs unite in systems. All the cells, tissues, organs and systems of organs are closely interconnected and affect each other. The vital activities of the cells, tissues, organs and the whole organism are based on metabolism which consists of two interconnected processes: assimilation of nutritive substances (anabolism) and decomposition of organic substances (catabolism). The complex substances of the cells and tissues continuously split into simpler ones: at the same time they are renewed from other substances delivered to the cells and tissues from outside. The catabolism in the cells and tissues is accompanied by liberation of energy which operates all the processes in the organs and tissues (muscular contraction, heart action, cerebral activity, etc.) including anabolism. During the vital activities of the organism, which are based on metabolism, various organs and systems of organs establish close connections and interactions. This may be readily demonstrated on a skeletal muscle. Metabolism takes place in the muscle, as it does in other organs. This naturally requires a continuous supply of nutrients and oxygen which are delivered by the blood through the blood vessels. The nutrients enter the blood from the digestive system, and the oxygen from the respiratory system (through the lungs). The waste products formed in the process of metabolism pass from the muscles into the blood and are transported to the excretory organs and eliminated. The blood flows through the blood vessels because of the contractions of the heart whose work, like that of other organs, is regulated by the nervous system. The regulations between the various systems of organs can also be demonstrated by coordinated changes in their activities. Intensification of the activity of one organ or system of organs is accompanied by changes in the other system. For example, physical work causes metabolism to increase sharply in the muscles. This leads to a coordinated change in the activity of the cardiovascular, respiratory, excretory and other systems. The interdependence between the various organs and the entire organism manifests itself in a disease. Pathologic changes in one particular organ affect other systems of organs. The principle of intergrity of the organism implies that the disease of any organ must not be regarded as a purely local disturbance, but as a morbid state of the entire organism. Exercise 2. Ask 10 questions based on the text. UNIT TWENTY-SIX
|
