Вступний фонетикоорфоепічний курс вступ
 Скачать 25.36 Mb. Скачать 25.36 Mb.
|
|
| I | Speaking | Sensory System |
| II | Grammar | Modal Verbs and Verbs of Modal Meaning |
| III | Independent Work | Drugs |
I. Speaking: Sensory System
After careful study of this unit you should be able to:
describe the function of the sensory system;
list the major senses;
describe the structure of the eye;
list several disorders of the eye; describe the structure of the ear;
list disorders of the ear;
name other special sense organs;
list general senses.
| English | Latin/Greek | Ukrainian |
| hearing | auditus/phon- | слух |
| scent | olfactus/osm- | нюх |
| thirst [0-3:st] | sitis/dips- | спрага |
| heat [hi:t] | calor/pyro-, therm- | тепло |
| cold [ksuld] | gelu/crvo- | холод |
| light [lait] | lux'phi.;- | світло |
| pupil | pupilla/coria | зіниця |
| lens | lens/phac- | кришталик |
| cornea ['кз:піз] | cornea/kcrato- | рогівка |
| iris Pairis] | iris, iridis | райдужна оболонка |
| ossicle | ossiculum | кісточка |
| cochlea ['knklio] | cochlea | завиток |
| sclera [sk'liaro] | sclera | склера (білкова оболонка) |
| glaucoma | glaucoma | глаукома |
| semicircular [,semis'3:kjul3] canal | canalis semicircularis | напівколові канали |
| vestibule | vestibulum | присінок |
| eardrum | tympanum | барабанна перетинка |
| otitis [so'taitis] media | otitis tuedia | отит, запалення середнього вуха |
Exercise 2. Read the information about the sensory system, translate it and learn by heart.
The sensory system serves fundamentally to protect the individual by detecting changes in the environment. The sensory system includes:
suspensory ligaments'
pupil ens
ciliarv muscle
Vision from receptors in the eye.
Hearing from receptors in the ear.
Taste from the tongue receptors.
Smell from receptors in the upper nasal cavities.
Pressure, heat, cold, pain, and touch from receptors in the skin.
Position and balance from the muscles, tendons, joints, and ear.
Exercise 3. Acquaint yourself with the structure of the eye using Fig. 22-1.
a) Make up your own vocabulary
using the dictionary.
Learn the words.
Describe the structure of the
eye.
Exercise 4. Read the information about eye disorders.
The conjunctiva [.krjnchjAnk'taiva] is a membrane that lines the eyelid (повіка) and cover? the anterior part of the sclera. Its inflammation is called conjunctivitis.
Eyestrain, or fatigue of the eyes, may result from overuse of the eyes: reading, watchin: TV, poor lighting, or disturbances in the focusing ability of the eyes. Hyperopia [,Ьаірз'гзирі; is farsightedness.
Myopia [таі'зиріз] is nearsightedness.
Astigmatism [Ee'stigmaetizm] is due to irregularity in the curvature of the cornea or the len> (as a result, light rays are incorrectly bent).
Strabismus [strae'bizmas] means that the muscles of the eyeballs do not coordinate, so th;: the two eyes do not work together (косоокість).
Blindness is the absence of vision. It may be caused by cataracts, glaucoma or retina detachment.
Exercise 5. Answer the following questions.
What disorders of the eyes can you name?
What is the difference between an oculist and an ophthalmologist?
What causes of eyestrain do you know?
What belongs to the sensory system?
Exercise 6. Acquaint yourself with the structure of the ear using Fig. 22-2.
a) Make up your own
vocabulary of new words.
b) Learn these words.
pinna
cochlea
eustachian (auditory) tube
c) Describe the structure of
the ear.
Exercise 7. Here is a list of ear disorders. Read it and try to memorize.
pharynx
-Otitis (inflammation of the middle ear);
-deafness (loss of hearing);
-otosclerosis (a hereditary (спадковий) disease that causes bone changes in the stapes that prevent its normal vibration);
-/jresZ>i>acM.s/s[,prezbe3'ku:sis] (a slowly progressive loss of hearing that often accompani aging).
Exercise 8. Answer the questions (use Fig. 22-3).
What are the organs of taste and smell?
What kinds of taste do you know?
Exercise 9. Read and translate the text.
Sense Organs
Sense organs are the structures in the body which are influenced by certain factors in the environment. They are also well-known as receptors. The action of the environmental factor on the body is known as a stimulus. It results in the transmission of a nerve impulse to the nerve center and from this point may influence appropriate reactions of the body or may be stored in memory.
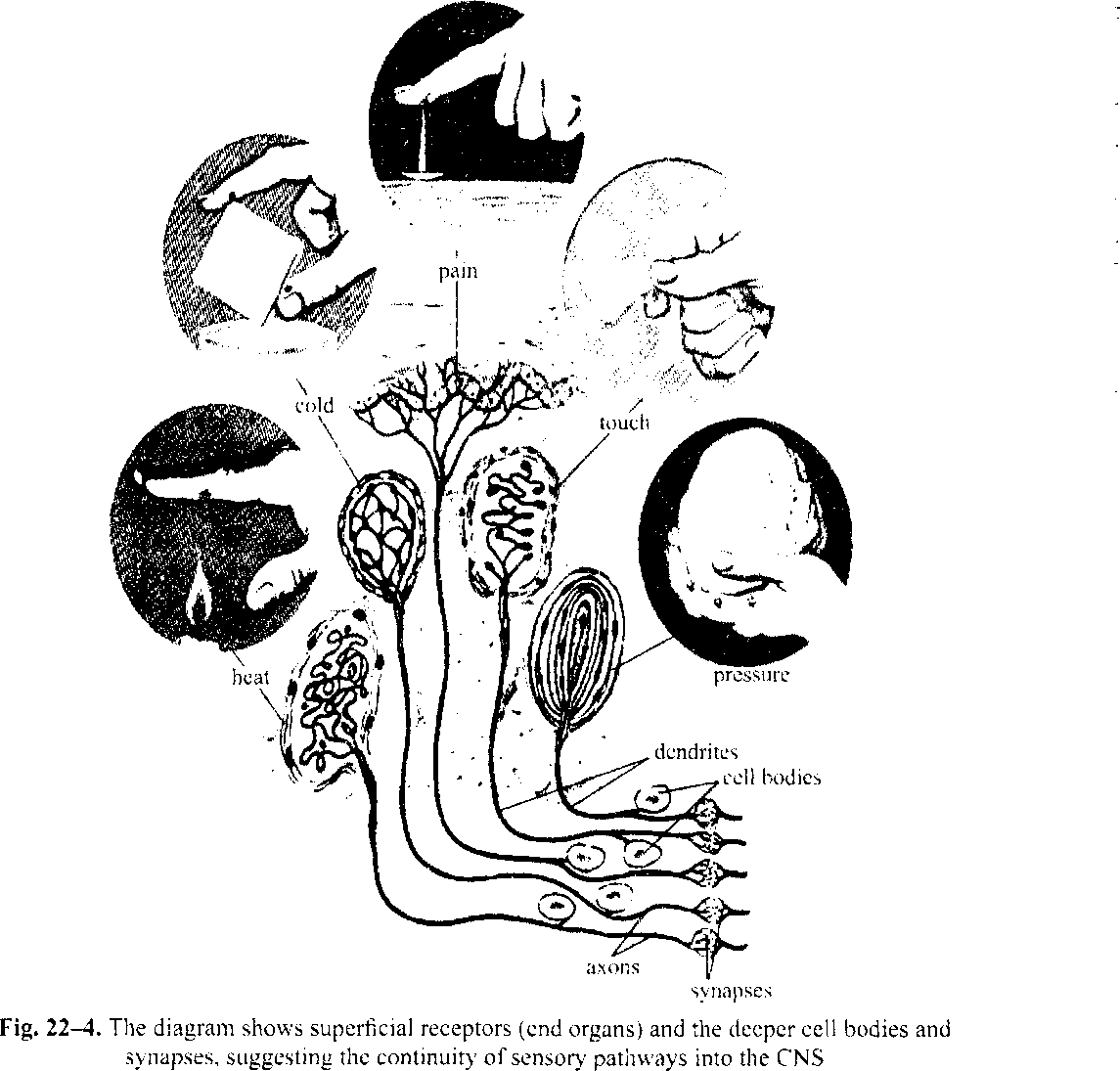
Stimuli arise from contacts with solid objects, from chemical compounds, either dissoh ec or in the gaseous state, from the incidence of light rays, from factors that damage the boc (Fig. 22-4).
Tactile corpuscles located in surface tissues may be classed as organs of touch. They are sensitive to simple pressure and give rise to images of form through the varying pressures du: to uneven and gross contours.
The varied integumentary sense organs of the human body are known to include sorr.^ sensitive only to heat, cold or pain. These organs may be free nerve endings found in the skin
Ears are the center of the auditory organs. Dissolved substances stimulate organs of taste located in the oral cavity and gases or vapors act on organs of smell. Sense organs stimulated by light are familiar to us in our own eyes. In contrast with sense organs mentioned above which are classed as exteroceptors, the body contains others called interoceptors. They are sources of sensations of hunger, thirst, nausea and external pain. Other interoceptors in the muscles, joints and tendons are associated with the maintenance of equilibrium and are classed as proprioceptors. The semicircular canals of the inner ear are also organs of equilibration.
All sense organs consist of nerve endings associated with various specialized cells or tissues. The nerves are not limited to one type of stimulation but other response may be identical under various stimuli. Thus a mechanical shock to the eye produces a sensation of light. The nerve fibers leading from the sense organs towards the central system are sensory or afferent.
Exercise 10. Find English equivalents.
Стимули виникають від контактів з твердими речовинами; вони - джерела відчуття голоду, спраги, нудоти і зовнішнього болю; всі органи відчуттів складаються з нервових закінчень.
Control Tests. Nervous System and Sense Organs
1. What system is responsible for all activities
of organs and systems of organs in the human
body?
A. Endocrine
B. Muscular
C. Nervous
D. Reproductive
E. Digestive
2. What is the role of the nervous system?
A. Regulation and control of all systems
of the body
B. Metabolism
C. Nutrition
D. Respiration
E. Production of enzymes
3. What is the structural unit of the nervous
system?
A. Enzyme
B. Hormone
C. Nephron
D. Neuron
E. Substance
4. What does the central nervous system
consist of?
A. The brain
B. The brain and spinal cord
C. The spinal cord
D. Nerves and ganglia
E. Ganglia
5. What isn't included into the neuron?
A. Axon
B. Dendrite
C. Body of neuron
D. Pigment
E. Neuron ending
6. The main property of the nerve fibre is .
