Вступний фонетикоорфоепічний курс вступ
 Скачать 25.36 Mb. Скачать 25.36 Mb.
|
Particularly chemical D. Palate5. Where does food go from the oral cavity? A. Esophagus B. Stomach C. Gullet D. Pharynx E. Larynx 6. With the help of what is food segregated in the stomach? A. Stomach juice and enzymes B. Saliva and stomach juice C. Enzymes and gall D. Stomach juice and water E. Water and enzymes 7. What is there between the pharynx and stomach in the digestive tract? A. Liver B. Duodenum C. Heart D. Ribs E. Gullet 8. Where are fats split? A. In the stomach B. In the rectum C. In the anal canal D. In the gall bladder E. In the duodenum 9. What organ also takes part in digestion? A. Kidney B. Heart C. Brain D. Liver E. Lung 10. What part of the digestive tract is there between the gullet and duodenum? A. Stomach B. Large intestine C. Small intestine D. Pancreas E. Liver 11. What kind of juice takes part in digestion? A. Fruit B. Gastric C. Orange D. Apple E. Sweet 12. Through it fecal masses go out the body. A. Stomach B. Lungs C. Rectum D. Anus E. Liver 13. What does gastritis mean? A. Ulcer of the stomach B. Cancer of the stomach C. Catarrh of the stomach D. Spasm of the stomach E. Emptying of the stomach 14. Through it food gets into the stomach. A. Liver B. Esophagus C. Duodenum D. Rectum E. Pancreas 15. What does dyspepsia mean? A. Narcosis B. Fracture C. Pregnancy D. Difficulty in digestion E. Lack of vitamins 16. What substances are absorbed in the large intestine? A. Sugar and salts B. Gall and lymph C. Water and salts D. Blood and water E. Water and sugar 17. What is a part of large intestine? A. Duodenum B. Liver C. Kidney D. Colon E. Bladder 18. It doesn't belong to the digestive system. A. Heart B. Gullet C. Liver D. Pancreas E. Stomach 19. What is the synonym to the word "esophagus"? A. Bronchus B. Ventricle C. Gullet D. Gall bladder E. Bladder 20. What organ of digestion can we palpate? A. Duodenum B. Liver C. Small intestine D. Large intestine E. Pharynx 21. What does the liver secrete? A. Blood B. Hormones C. Cells D. Bile E. Urine 22. Where does food go after the duodenum? A. Into the stomach B. Into the small intestine C. Into the blood vessels D. Into the rectum E. Into the gullet 23. Where are fecal masses formed? A. In the kidneys B. In the bladder C. In the appendix D. In the rectum E. In the large intestine 24. What is the role of teeth in the oral cavity? A. To chew food B. To drink water C. To speak english D. To keep food in the mouth E. To do exercises 25. What is the function of digestion? A. Nutrition B. Exchange of substances C. Immunity D. Defense E. Supporting 26. What disease doesn't belong to gastrin diseases? A. Ulcer B. Gastritis C. Catarrh D. Gallstones E. Cancer of the stomach 27. Mouth, pharynx, gullet, , duodenum small intestine, large intestine, rectum an; anal canal form the system of digestion. a. liver b. bladder c. kidneys d. lungs e. stomach 28. What substances help to segregate food :- the stomach? A. Salts B. Acids C. Enzymes D. Urea E. Hormones 29. What doctor treats diseases of the digestive system? A. Urologist B. Neurologist C. Stomatologist D. Gastroenterologist E. Cardiologist 30. If you want to eat, you are . A.hungry B. sad C. thirsty D. happy E. sick 31. What is the English for the Latin term "oesophagus"? A. Heart B. Trunk C. Chest D. Abdomen E. Gullet 32. The roof in the mouth is __, A. palace B. house C. palate D. ceiling E.tongue 33. The largest glandular organ which secretes bile. A. Tonsil B. Pancreas C. Thyroid D. Liver E. Thymus 34. Removal of the gall bladder. A. Cholecystectomy B. Gastrectomy C. Esophagotomy D. Pharyngotomy E. Enterotomy 35. Examination of the stomach and duodenum with the help of an instrument. A. Rectoromanoscopia B. Gastroenteroscopia C. Bronchoscopia D. Ophthalmoscopia E. Nephroscopia 36. What is the English for "виразка"? A. Fetus B. Ulcer C. Wound D. Abscess E. Necrosis 37. Inflammation of the large intestine. A. Cystitis B. Enteritis C. Colitis D. Proctitis E. Pharyngitis 38. Where is the stomach situated? A. In the thoracic cavity B. In the head C. On the left side D. On the right side E. In the abdominal cavity 39. What is the organ of taste? A. Mouth B. Nose C. Skin D. Tongue E. Eye 40. How many teeth does an adult person have? A. 20 B. 28 C. 32 D. 36 E. 24 41. What shape is the stomach? A. Pyriform B. Ball C. Balloon D. Tube E. Tree 42. The inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach. A. Duodenitis B. Colitis C. Enteritis D. Hepatitis E. Gastritis 43. The inflammation of the liver. A. Cholecystitis B. Hepatitis C. Duodenitis D. Pharyngitis E. Rhinitis 44. What does the act of defecation mean? A. Evacuation B. Supply C. Absorption D. Segregation E. Exhalation 45. The tiny hair in the small intestine is called a . A. bacillus B. egg C. horn D. villus E. stick 46. The process of filling cells with energy. A. Nutrition B. Micturition C. Digestion D. Production E. Excration 47. What does exchange of substances in the organism mean? A. Catabolism B. Botulism C. Metabolism D. Assimilation E. Dissimilation 48. The lack of vitamin D causes in babies. A. scurvy B. flu C. pneumonia D. rachitis E. mumps 49. The lack of vitamin C causes this disease. A. scurvy B. flu C. influenza D. pneumonia E. dysentery 50. Special food for patients. A. Vegetables B. Fruit C. Meat D. Fish E. Diet II. Grammar Exercises Exercise 1. State the part of speech of the following words and translate them.
Exercise 2. Translate the following sentences. State the form of the gerund and its function in the sentences.
Exercise 3. Compare the use of the nouns and gerunds. 1. a) The discussion of the report lasted two hours. b) They finished discussing the report at two o'clock.
Exercise 4. Complete the sentences using gerunds.
10)We made a decision after ... III. Independent Work: How to Go on a Diet? Exercise 1. Read an unfinished story and continue it (you can use the ideas given below). How to Go on a Diet? Last summer my doctor told me to go on a slimming diet, which, he said, would make me lose twenty pounds in a month. For breakfast, I was allowed to drink coffee or tea and nothing else. For lunch, grilled meat, no salt; a hundred grams of vegetables, no salt; fifty grams of cheese or yoghurt, a choice of an orange or an apple. The same for dinner. I wasn't allowed to drink anything with meals. The first day was fine, though I was so hungry that I went to bed at eight. The next morning my wife said an egg with breakfast wouldn't hurt me. So I ate an egg since she is wiser than I am in these matters. At noon I lunched with a friend who said, "Meat is more fattening than potatoes. My doctor lets me eat all the potatoes 1 want to, without butter, of course". So I had potatoes with my meat. In the evening і dined with a Frenchman. He was shocked to think that I wouldn't drink wine with my dinner. So I had half a bottle of Burgundy with my dinner. I went on dieting taking my meals with different people. Each one had his own idea about dieting and I was willing to listen to everybody. Ideas Describe my meals with my lawyer, an American visitor, my colleague, my mother-in-law, my hairdresser. This is what they say: one teaspoon of cream is three times as fattening as one teaspoon of sugar; it is foolish to eat without salt; the best way to lose weight is to eat nothing but spaghetti; fish is not fattening; scrambled eggs in the morning aren't as fattening as in the evening; if you eat a lot of chocolate before dinner it will take away your appetite. Exercise 2. Answer the questions. !. Do you think 1 liked to take my meals alone or with friends? 2. Do you think 1 have put on or lost weight? 3. What do you think my doctor said? 4. Why is it not wise to listen to everybody? UNIT NINETEEN
I. Speaking: Nervous System (Part I) After careful study of this unit you should be able to: - describe the organization of the nervous system according to the structure and function;
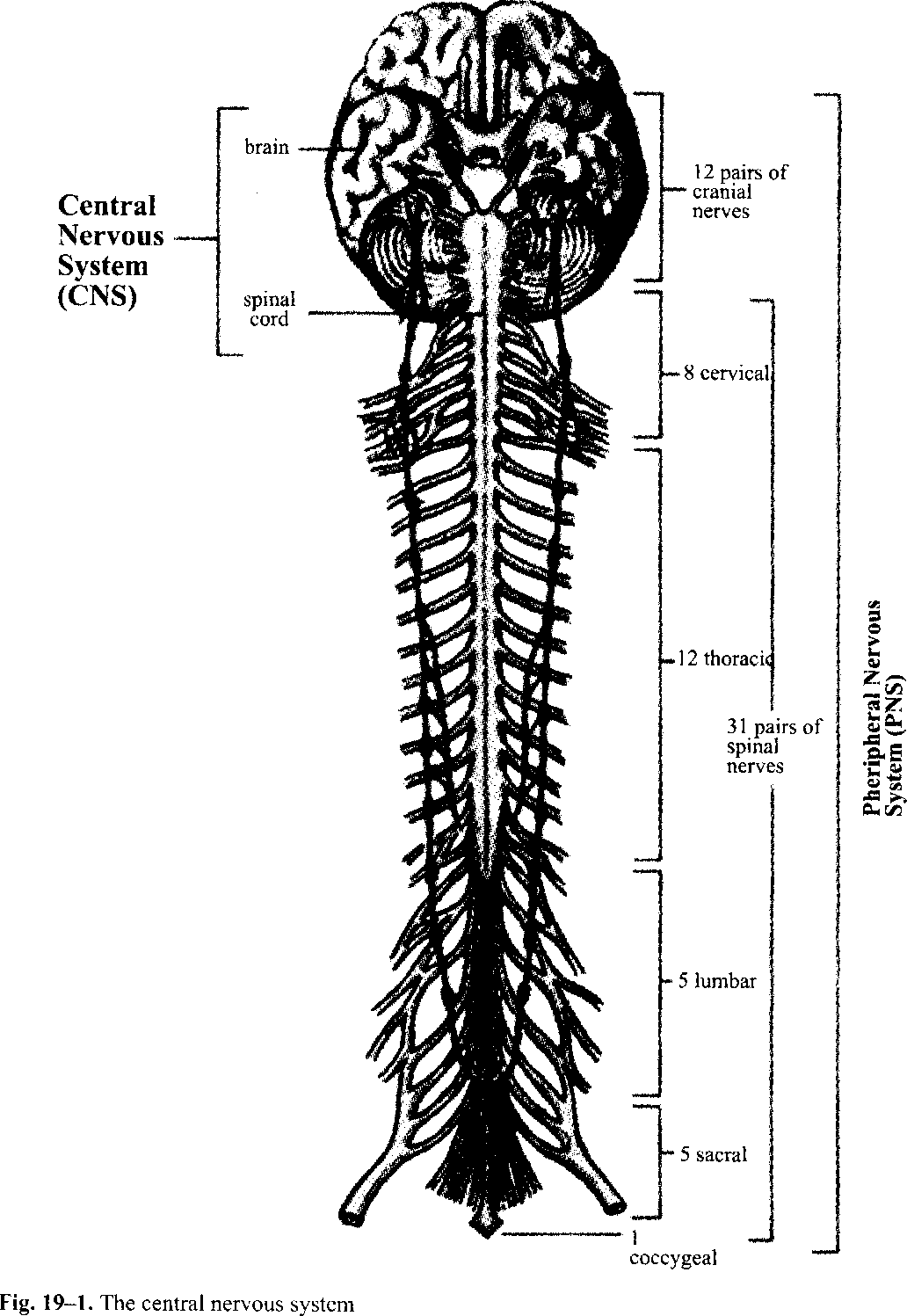
Exercise 2. Read and learn the following word combinations and their meaning, spinal cord - спинний мозок (стрижень) meninx['meninks] (pi. meninges [me'ninchjhz]) - оболонка мозку myelinsheath['JuS] мієлінова оболонка neurilemma- шваннівська оболонка (оболонка нервових волокон) synapse - синапс (спеціалізовані утвори функціонального зв'язку нейронів один з одним або і клітиною, яку вони іннервують; служать для сприйняття і передачі нервових імпульсів) stimulus['stimjuhs] подразник whitematter - біла речовина (шляхи і канатики) graymatter - сіра речовина (ядра і стовпи) sensoryneurons - сенсорні нейрони (чутливі) motorneurons - моторні нейрони (рухові) Exercise 3. Read and translate the text. Nervous System (Part I) None of the body systems is functioning alone. The body systems work together as one unit and the nervous system serves as a chief coordinating center. The nervous system has been compared to a telephone exchange, in that the brain and the spinal cord act as switching centers, and the nerve trunks act as cables for carrying messages to and from these centers. The nervous system structurally is divided into the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain, the spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which includes all of the cranial and spinal nerves (Fig. 19-1). Functional divisions of the nervous system include the somatic (voluntary) nervous system, which supplies skeletal muscles, and the visceral (involuntary) nervous system, which supplies smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, glands. The nerve cell is called a neuron (Fig. 19-2). It consists of a cell body with a nucleus and nerve fibers, which are thread-like projections of the cytoplasm. Nerve fibers are of two kinds: dendrites, which conduct impulses to the cell body, and axons, which conduct impulses away from the cell body. The job of neurons of the peripheral nervous system is to relay information to or from the central nervous system. Neurons that conduct impulses to the CNS are sensory, or afferent, neurons. Those cells that carry impulses from the CNS out to muscles and glands are motor, or efferent, neurons. The organ activated by the motor neuron is the effector. Nerve impulse is electric current that spreads along the nerve fiber. Synapse is the junction between neurons where a nerve impulse is transmitted from one neuron to the next. A nerve is a bundle of nerve fibers located outside the CNS. Bundles of nerve fibers within the CNS are tracts. The nerves are sensory (afferent), they contain only fibers that carry impulses toward the CNS (from the receptor); motor (efferent), they contain only fibers that carry impulses away from the CNS (from the receptor); mixed, they contain both motor and sensory fibers. Reflex is a simple, rapid, automatic response involving few neurons. Exercise 4, Make up a plan of the text. Exercise 5. Define the following terms. Neuron, nerves, tracts, reflex, synapse, axon, dendrite, effector. Exercise 6. Find English equivalents in the text. Подають імпульси до клітини тіла, електрохвиля, з'єднання між нейронами, як єдине ціле, центральна нервова система, головний мозок, вольова нервова система, нервові волокна і пучки, кабель для передачі повідомлень, робота нейронів, що несуть імпульси до ЦНС, від рецепторів. Exercise 7. Answer the following questions.
II. Grammar Exercises Exercise 1. Make up all possible questions to the sentence. The nervous impulse wave passes the dendrites and reaches the cell body and cell nucleus. Exercise 2. State the parts of speech of the following words. stimulate - stimulus - stimulant - stimulation neurology - neurologist - neurological compare - comparative - comparison - comparable normal - abnormal - normalize - normally structure - structural react - reaction - reactiona! - reactive Exercise 3. Translate the following sentences. Point the gerund and its function in the sentence.
10. Sterilizing the instruments, preparing the patient for the operation took me about an hour. Exercise 4. State the -ing form in the following word combinations. Gerund with noun and participle with noun express different meanings. Model: an operating room a room for operations; операційна кімната = кімната для операцій. An operating man, a reading room, a sleeping baby, a waiting hall, an examining surgeon, a reading device, a healing system. Exercise 5. Translate the sentences with gerundial complexes.
4.1 was told that he was operated on without having been anesthetized. 5. After having gathered a complete clinical history, he began to examine the patient. Exercise 6. Complete the sentences translating the phrases into English, using the gerundial complex.
III. Independent Work: Role of Nervous System Exercise 1. Read and translate the text. Role of Nervous System The nervous system regulates the activities of different organs and of the entire organism. Muscular contractions, glandular secretion, heat action, metabolism and many other processes continuously operating in the organism are controlled by the nervous system. The nervous system links the various organs and systems, coordinates all their activities and ensures the integrity of the organism. The work of each organ or system of organs may be affected by various conditions. A change in function of one organ or system of organs leads to changes in the function of other organs and systems. For example, during physical work involving intensive muscular contraction the metabolism in muscles increases, which consequently increases the requirement in nutrients and oxygen. A reflex response causes the heart and lungs to work more intensively, with the result that the flow of the blood to the muscles increases. At the same time heat production and heat loss increase, the excretory organs work harder. The unity of the organism and its external environment is affected through the nervous system. All the outside stimuli are perceived by the nervous system through the sense organs. In response to the stimuli the functions of the various organs change and the organism adapts itself to its surroundings or, as I. Pavlov put it1, the organism is equilibrated with the external environment. This equilibrium forms the basis of the organism's vital activities. Thus in response to ingestion of food the activity of the digestive glands increases and is adapted to the character of the ingested food. A rise in temperature of the surrounding air causes an increased flow of blood to the skin and greater perspiration, which prevents overheating of the organism. It should be remembered that unlike animals, man can himself considerably change his external environment. Man's brain is the material basis of thinking and speech. I. Pavlov demonstrated that man's so-called psychic activity is based on physiological processes operating in the cerebral cortex. Note: 1as I. Pavlov put it - як сформулював І. Павлов Exercise 2. Make up a plan of the text. Exercise 3. Find sentences about the nervous system. Exercise 4. Tell about the unity of the human body and the external environment. Exercise 5. Speak about the role of the nervous system. UNIT TWENTY
I. Speaking: Nervous System (Part II) After careful study of this unit you should be able to:
Exercise 1. Read and learn the following English words and their equivalents.
Exercise 2. Read and translate the texts, get ready to answer the questions about:
the branches of the spinal nerves; the disorders of the spinal nerves; the parts of the autonomic nervous system; the functions of the autonomic nervous system. reflex activities; conduction of sensory impulses (to the brain); conduction of motor impulses (from the brain). dorsal root /. gangliorTy^ ventral - horn cell-body spinal nerve the motor nerve cells in the spinal cord; the preventive medicine is the oral Sabin vaccine), paraplegia (the loss of sensation and motion in the lower part of the body), tumors that grow from within the cord or that compress the cord from outside. Text 2. Spinal Nerves Look at Fig. 19-1. There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, each pair is numbered according to the level of the spinal cord from which it arises. Each spinal nerve has small posterior divisions and rather large anterior divisions. The larger anterior branches form networks called plexuses, which innervate (іннервують) different parts of the body. The three main plexuses are described as follows:
The disorders of the spinal nerves are: - neuritis (inflammation of a nerve);
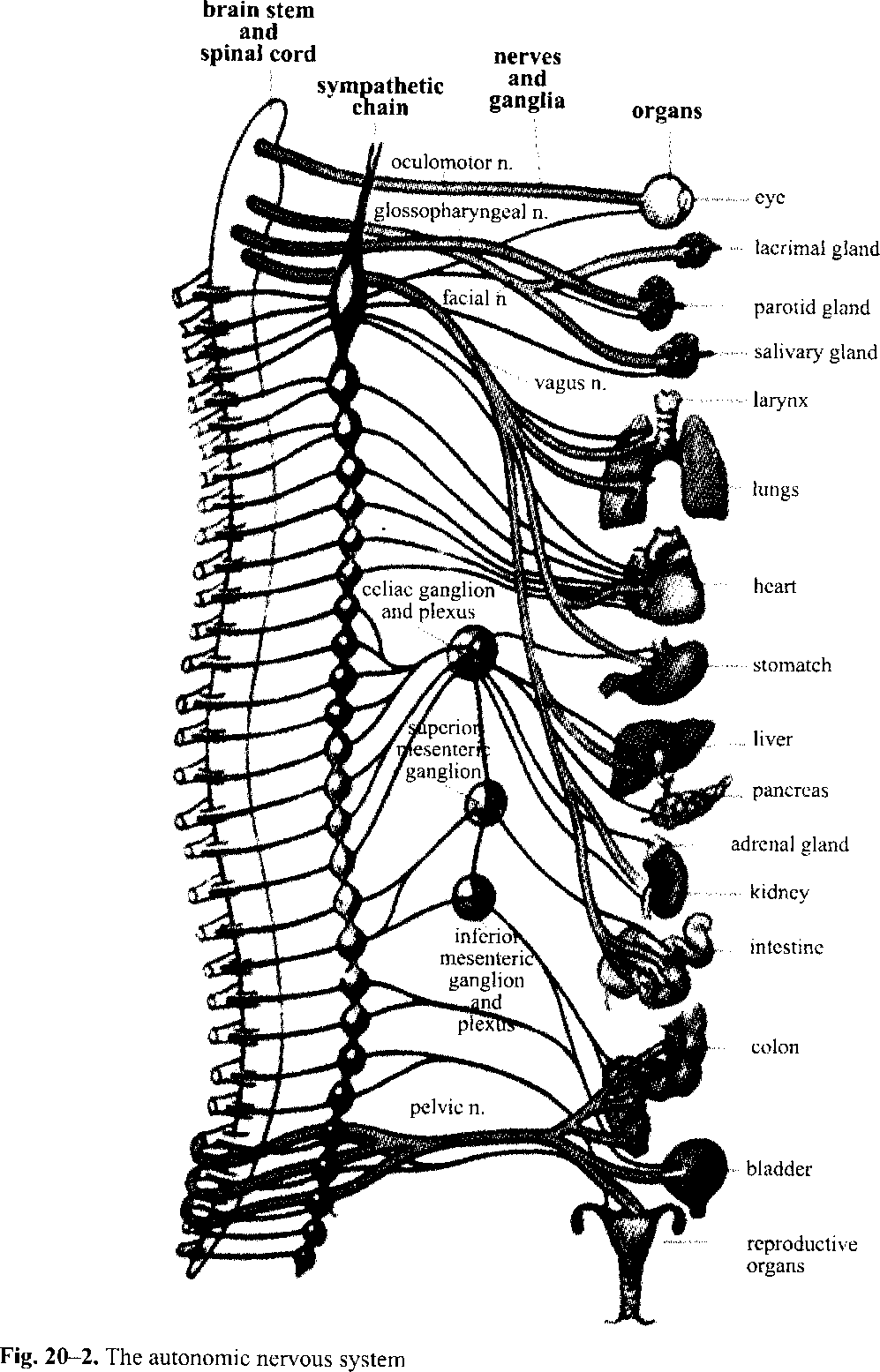
Text 3. Autonomic Nervous System Look at Fig. 20-2. The autonomic nervous system is the motor (efferent) division of the visceral (involuntary) nervous system. It has many ganglia that serve as relay stations. In these ganglia each message is transferred at a synapse from the first neuron to the second one from there to the muscle or gland cell. This differs from the voluntary (somatic) nervous system, in which each motor nerve fiber extends all the way from the spinal cord to the skeletal muscle with no intervening synapse. The autonomic nervous system has sympathetic pathways and parasympathetic pathways. The sympathetic pathways begin in the spinal cord with cell bodies in the thoracolumbar area and then their nerve fibers extend to ganglia where they form a synapse with a second set of neurons, whose fibers extend to the glands and involuntary muscle tissues. These second neurons act on the effectors by releasing the neurotransmitter epinephrine (adrenaline), so the sympathetic system can also be called adrenergic [aedri пз:дзік]. The parasympathetic pathways begin in the craniosacral areas, with fibers arising from cell bodies of midbrain, medulla, and sacral part of the spinal cord, and stimulate the visceral tissues. The neurons of this part of the nervous system release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, so it is called cholinergic [кт)1і'пз:дзік]. The autonomic nervous system regulates the action of the glands, the smooth muscles of hollow organs, and the heart. The sympathetic part tends to act as an accelerator for the organs needed to meet a stressful situation. The parasympathetic part normally acts as a balance for the sympathetic system once a crisis has passed. The autonomic nervous system, together with the endocrine system, regulates our responses to stress. Exercise 3. Write out all terms of Greek origin form Texts 1, 2, 3. Exercise 4. Define the following terms. Plexus, ganglia, autonomic nervous system, somatic nervous system, neuritis, neuron, herpes zoster, synapse, nervous system. Exercise 5. Differentiate between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. II. Grammar Exercises Exercise 1. Translate the following sentences. Pay attention to the translation of the indefinite gerund active as a: a) noun:
b) infinitive:
c) |