ГОТОВОЕ ПОСОБИЕ. Цель пособия в сжатые сроки научить студентов читать и понимать англоязычную литературу по профилю вуза
 Скачать 0.95 Mb. Скачать 0.95 Mb.
|
|
The First Calculating Devices 1. Let us take a look at the history of computers that we know today. The very first calculating device used was the ten fingers of a man's hands. This, in fact, is why today we still count in tens and multiples of tens. 2. Then the abacus was invented. People went on using some form of abacus well into the l6th century, and it is still being used in some parts of the world because it can be understood without knowing how to read. 3. During the I7th and 18th centuries many people tried to find easy ways of calculating. A mechanical way of multiplying and dividing was invented by J.Napier, a Scotsman. Now it is the modern slide rule works. Henry Briggs used Napier's ideas to produce logarithm tables which are used by all mathematicians today. 4. Calculus, another branch of mathematics, was independently invented by both Sir Isaac Newton, an Englishman, and Leibnitz, a German mathematician. The first real calculating machine appeared in 1820 as the result of several people's experiments. 5. In 1830 Charles Babbage, a gifted English mathematician, proposed to build a general-purpose problem-solving machine that was called "the analytical engine". This machine was showed at the Paris Exhibition in 1855. Babbage never finished this work, but many of his ideas were the basis for building today's computers. XVII. Answer the questions below:
XVIII. Translate passage 2 into Russian. XIX. Read the text. Define its subject. Computers Then and Now 1. The world first electronic computer was built at the University of Pennsylvania in 1946, although computer-like machine was built in the 19th century. Computers were sold commercially for the first time in the 1950s, and a lot of progress has been made since then. Computers are now much smaller and more powerful, and they can be bought much more cheaply. 2. Computers are used in many fields – in education, medicine, science, for example. They can be used to forecast the weather or to control robots which make cars. A lot of difficult calculations can be done very quickly on a computer. 3. A computer can’t think – it must be told exactly what to do. And they don’t make mistakes. Stories are heard sometimes about computers paying people much money or sending them bills for things they don’t buy. These mistakes are made by the programmers. Some years ago, a computer-controlled rocket belonging to the USA went out of control and had to be destroyed. The accident was caused by a small mistake in one line of the programme. This mistake cost the USA $ 18 million. 4. Progress is being made all the time. Today people know more about computers then they used to. And many believe we can look forward to the day when even our household jobs like cleaning will be done by computer-controlled robots. XX. Say which of the statements below are true.
XXI. Translate passage 1 into Russian. Predicates with modal verbs Сказуемое с модальными1 глаголами Значения модальных глаголов
1Модальные глаголы указывают на отношение к действию, поэтому обычно употребляются с другим глаголом, который обозначает действие и стоит в форме инфинитив. I. Compare the modal verbs below. Explain their differences. Can-may; can-could; can-might; may-might; may-could; must-may; should-can; must-should; could-should;can-must; might-could; should-may; must-might. Сказуемое с модальными глаголами  II. Define the meaning of the predicates with modal verbs. Can x; can be xed; could x; could be 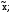 may x; may be xed; might x; might be may x; may be xed; might x; might be 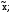 must x; must be xed; should x; can x; should be must x; must be xed; should x; can x; should be 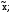 can be can be 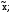 may x; could be xed; may be may x; could be xed; may be 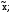 could x; must be could x; must be 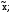 might x; should be xed; must x; can be xed; could x; may be might x; should be xed; must x; can be xed; could x; may be 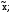 must be must be 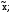 must x; might be xed; should x; may x; must be xed; can be xed; should be must x; might be xed; should x; may x; must be xed; can be xed; should be 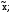 may be may be 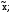 could be could be 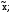 should x; might be xed; can be should x; might be xed; can be 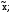 should be xed; can x; must be should be xed; can x; must be 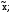 could be xed; might x; should be could be xed; might x; should be 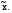 III. Define the meaning of the predicates with modal verbs. Can solve; could solve; can be solved; could be solved; may obtain; might obtain; may be obtained; might be obtained; must find; must be found; should take; should be taken; can hold; could hold; can be held; could be held; may build; may be built; must heat; must be heated; should improve; should be improved. IV. In each pair of sentences below compare the predicates by form and meaning. Define their similarities and differences.
V. Give the Russian equivalents of the sentences below. 1. I want to become a materials engineer but I don’t know what I must study. 2. You may apply alloy steels for various engineering purposes. 3. The engineers can use copper for electrical conductors. 4. The fields might be very complicated ones. 5. Matter may exist in any of its states: solid, liquid, gaseous. 6. This device cannot be repaired today. 7. For a long time scientists could not discover the secret of the atom. 8. You should use these devices in your research work. 9. Chemists must create the materials which don not exist in nature. 10. This equipment can work with high accuracy. VI. Define which of the words in bold type are verbs. Give the Russian equivalents of the sentences with these verbs. (see Appendix, p. )
VII. Match each English word with the correct Russian equivalent.
VIII. In the text of task X find a word derived from the verb to connect. Give other derivatives of this verb. IX. Arrange in pairs the words with а) similar meaning, b)contrary meaning.
X. Look through the text. Define its subject. Entitle the text. 1. This is the newest of our already extensive Laser collection. The « Mars™ » Series was created purposely for the beginner. From 200mW up to 500mW, this thin 532nm Laser beam will amaze you, every time you turn it on. Its thin green beam can paint targets hundreds of feet away! 2. Made of sturdy extruded aircraft aluminium, this Laser is made tough. At a weight of only 190 grams, it is a very light Laser Wand. The more powerful is the Laser, the more visible is its beam. Being totally focusable, it can be used in expedition trip, and serve as a designator beacon in case of emergencies. At night, its beam will be visible to the search and rescue team miles and miles away. 3. It comes complete with its battery charger, a pair of red goggles and its aluminium carrying case, making an excellent gift idea! 4. However, since the UPS 747 Airplane crash on Sept. 3rd 2010, we are no longer allowed to ship batteries overseas. Therefore, Batteries are NOT included. 5. Made from Military Specification Aircraft Aluminium, this Laser Pointer is made to last years and years through heavy duty service. Its beam is able to focus from a few inches, for super hot burning applications, to infinity, for long range rescue applications. XI. Say which of the statements below are true. Correct the false ones.
XII. Translate passage 2 into Russian. XIII .Read the text. Choose the most suitable title.
1. Lasers are not a new technology. Indeed they have been with us for over 40 years and they were first theorised by Albert Einstein in 1917.Since then lasers have spread into numerous industries. Today lasers are widely used in medicine, industry, communications and scientific research in a myriad of ways. In the medical field doctors use them to perform bloodless surgery, to correct short-sight and to treat many dermatological conditions. In everyday life lasers are found at the checkout till of most supermarkets and in numerous household products including DVD players, and personal computers while via fibre optic cables lasers have become the cornerstone of modern telephone lines, cable TV and internet connections. 2. Although the medium can be a solid, liquid or gas, today most lasers use a solid medium which takes the form of a cylindrical laser crystal. This medium is then 'pumped' from an energy source to excite the atoms in the medium. Typically, this is done using very intense flashes of light or electrical charges. Atoms are the building blocks of everything around us but they are also in continuous motion – vibrating and rotating, even in solid objects like chairs or tables! They can also be in different stages of being excited. Consequently, if we apply a lot of energy to an atom we can make it more excited. For a laser to work efficiently we have to ensure that a large number of atoms reach an excited state. XIV. Answer the questions below:
XV. Translate passage 2 into Russian. Итоговый тест
World Wide Web (WWW), computer-based network of information resources that (5) ___ text and multimedia. The information on the World Wide Web can be (6) ___ and searched through the Internet, a global computer network. The World Wide Web is often (7) ___ simply as «the Web». The Web started to become a popular resource after 1993 when the first widely distributed browser (8) ___ a convenient way to access a variety of information on the Internet.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
