справочник по английскому. краткий справочник по грамматике АЯ с упражениями. Справочник по грамматике английского языка с тренировочными заданиями
 Скачать 0.92 Mb. Скачать 0.92 Mb.
|
Применение past perfect continuousPast perfect continuous употребляется в двух случаях: когда мы говорим о действии, которое началось в прошлом раньше другого действия (выраженного past simple) и либо ещё продолжалось, либо уже закончилось. Example: -I was very tired when I got home. I’d been working hard all day. -We’d been playing tennis for about half an hour when it started to rain heavily. Exercise 1. Use the Past Perfect Continuous Tense of the verbs in brackets. 0. It was very cold in the house and she (lie) awake for hours. /It was very cold in the house and she had been lying awake for hours. 1. All the roads were blocked: it (snow) all night long. 2. I was tired. I (work) all day long. 3. After I (walk) for an hour, I decided to have a rest. 4. She fell ill because she (work) hard. 5. Mary could see that the child (cry) for some time. 6. It became very dark and the children (speak) in low voices. 7. Jim said that he (write) all day. 8. I knew they (correspond) for years. 9. He said he (work) in a newspaper office since his return from abroad. 10. He (study) the problem for two years. Exercise 2. Put the verbs into the most suitable form: Past Indefinite, Past Continuous, Past Perfect and Past Perfect Continuous. 1. We were good friends. We (know) each other for a long time.2. It was very noisy next door. Our neighbours (have) a party. 3. John and I went for a walk. I had difficulty keeping up with him because he (walk) so fast. 4. When I arrived, everybody was sitting round the table with their mouth full. They (eat). 5. Mary was sitting on the ground. She was out of breath. She (run). 6. When I arrived, Kate (wait) for me. She was rather annoyed with me because I was late and she (wait) for a very long time. 7. I was sad when I sold my car. I (had) it for a very long time. 8. We were extremely tired at the end of the journey. We (travel) for more than 24 hours. 9. How long they (meet) before they got married? 10. How long you (take) this medicine before you got well? Exercise 3. Use the Past Perfect Continuous Tense of the verbs in brackets. 1. The actors (rehearse) the play for a month before they (stage) it. 2. He (compose) music for 2 years before he (become) famous. 3. The students (listen) to the tapes for 15 minutes before they (catch) the intonation. 4. Jim was on his hand and knees on the floor because he (look) for his pen. 5. The magnificent car (wait) at the door. It (wait) for three hours. 6. The telephone (ring) for a few minutes before somebody picked up the receiver. 7. That day the sun (shine) since morning and the sky (be) blue. 8. I (tell) him what I (do) and he (tell) me what he (do) in the last three months. 9. They (walk) along the street for half an hour before they (see) a cafe. 10. She (thank) me for what I (do). Exercise. 4. Translate from English into Russian. I took a firmer grasp of Helen’s hand which I had been holding under the table for the last hour. 2. For the last five minutes he had been shouting at me to hurry. 3. I could not believe that he had been sitting beside me all this time. 4. Silvia had been talking to him – persuading him to agree to a course of treatment, and he said he would. 5. He threw the letter he had been reading on to the table and turned to me. 6. He sat down and pulled on a pair of thick woolen overstocks Ginny had been warming by the stove. 7. He gave no sign that he noticed that a man in a blue suit had gotten up from an arm-chair where he had been sitting. 8. Gemma, who had been helping Katie to set the room tidy again, sat down at the table. 9. She looked up. No, she had not been dreaming. 10. The man, who had been staring at the blank wall, looked up at the inspector. Будущее совершенное длительное время Future Perfect Continuous Время Future Perfect Continuous указывает на действие, которое началось и продолжалось в течение некоторого времени до определенного момента в будущем. Это время используется очень редко, а в устной речи – практически никогда. Для того, чтобы поставить глагол в форму времени Future Perfect Continuous, требуется вспомогательный глагол to be во времени Future Perfect и причастие настоящего времени (форма V-ing) смыслового глагола. Next month we shall have been living together for 25 years. В следующем месяце исполнтся 25 лет, как мы живем вместе. He will have been reading a book for two hours when I come back. 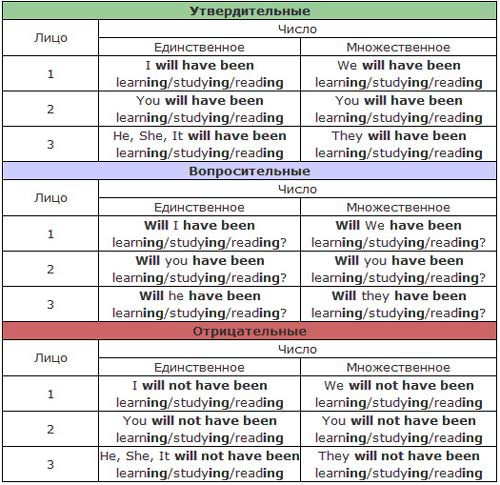 Exercise 1. Open the brackets using the verbs in the Future Perfect Continuous orFuture Simple. By the end of next week we ...............(save) money for two months I ...............(study) English for ten years by the end of next month. How long.................(work) here? They ................ (live/not) in my house for 10 years by next Monday, only nine. .....................(paint/John) my fence in two weeks? Her mother .................. .(work) at hospital for two months in March. Her mother ................. (work) at hospital next month. During the ball I ........... .(dance) only with you. We can't visit you in September,I...................(still/work). .................(you/play) in five hours? I want to use it. Exercise 2. Put the verbs into the correct form (Future II progressive). 1 .(wait / they) for 2 hours? I shall have been waiting for them for 2 hours. 2. By the end of the week I (work) here for four months. 3. By the end of this month we (live) together for six years. 4. By the end of the term she (study) for nine years. 5. By midnight we (play) this computer game for 48 hours. 6. She (talk) on the phone for the last couple of hours. 7. They (look for) me all night long. 8. He (play) soccer all day long. 9. You (watch) TV all the time. 10. He (not / sleep )all morning. Exercise 3. Open the brackets and translate the sentences. 1. She (to study) in London for two years when I come here. 2. He (to teach) German for two years when I begin to teach English. 3. By next July she (to live) here for five years. 4. At six o’clock I (to work) for five hours. 5. I (to work) at the library for 8 hours when you come there.6. They will have been sitting here for 20 minutes when I come. 7. In ten minute’s time l shall have been hanging around here for exactly four hours 8. When they finish I will have been waiting for them for 30 minutes. 9. Tomorrow it will be a month as they have been working on this project. 10. He will have been working on his book for a year soon. Страдательный залог. Passive voice Когда в центре внимания говорящего находится лицо или предмет, который подвергается действию, или когда нет необходимости упоминать лицо, совершающее действие, глагол употребляется в страдательном залоге: Many students discussed this question. (Active Voice.) – This question was discussed by many students. (Passive Voice.) Страдательный залог образуется при помощи вспомогательного глагола tobe и третьей основной формы смыслового глагола (Participle II). This country is washed by many seas. В отрицательной форме частица not ставится после вспомогательного глагола: This country is not washed by many seas. В вопросительной форме страдательного залога вспомогательный глагол ставится перед подлежащим: Is this country washed by many seas? When was this monument built? Временные формы страдательного залога употребляются согласно тем же правилам, что и соответствующие им временные формы действительного залога.
Спряжение глагола totake в страдательном залоге.
Exercise 1.Make the sentences negative and interrogative. 1) The post is delivered every morning. 2) He is often sent parcels. 3) Coffee is imported from Brazil. 4) Those paintings were sold for 500 pounds each. 5) That is a good book. It was written by George Orwell. 6) The letter will be sent tomorrow. 7) The gob will be advertised in the morning paper tomorrow. 8) I was often invited to his place. 9) I was asked to do it. 10) She is often sent postcards. Exercise 2. Paraphrase the following sentences. Give two variants if possible. Model : They often show us foreign films at the University. 1) We are often shown foreign films at the University. 2) Foreign films are often shown to us at the University They publish newspapers here. 2) They deliver mail in the morning. 3) They showed the scientists a new research centre. 4) They paid him only part of the money. 5) I think you will be asked to help them. 6) The report will be typed in an hour.7) The report is prepared by the students. 8) A new skating-rink is being built in our city. 9) This house was built last year. 10) I have been invited to the party. Exercise 3. Ask general questions: 1) We are given a lot of work to do. (you) 2) Footwear is sold in this shop. (textile) 3) They are taught Spanish. (French) 4) The letter was brought in the evening. (telegram) 5) The key was lost some days ago. (book) 6) Steve will be told about it. (marry) 7) The article will be typed today. (the letters). 8) The article is prepared by the student. (it). 9) The theatre was built last year. (cinema). 10) A new shop was opened last month. (market). Exercise 4. Ask special questions. 1.They are taught two foreign languages. 2) This journal is not published in Moscow. 3) Mr.Brown was highly paid last month. 4) The library was closed yesterday. 5) The meeting will be held in room 20. 6) He will be paid a lot.7) This book will be translated by next week. 8) The letter was written last Monday. 9) The telegram was sent in the morning. 10) They are taught English. Условные предложения I и 0 типа. First Conditional, Zero Conditional В английском языке существует 2 вида условных предложений: Real conditionals для выраженя действий которые возможно или определенно будут иметь место в будущем времени и Unreal conditionals для выражения действия, которое не совершено.По степени вероятности условные предложения делятся на три типа. Условные предложения первого типа (First Conditional) выражают реальные условия в прошедшем, настоящем и будущем времени для реальных событий или фактов, о которых говорится в главном предложении: Wesignedcontactsiftheygaveusagooddiscount. Мы подписывали контракты, если нам давали выгодные скидки. We sign contracts if they give us a good discount. Мы подписываем контракты, если нам дают выгодные скидки. We shall sign contracts if they give us a good discount. Мы будем подписывать контракты, если нам будут давать выгодные скидки. Запомните: В придаточном предложении, выражающем действие в будущем и связанном с главными союзами “if”, “when” и др., употребляется форма настоящего времени. Условные предложения первого типапоказывают действия, которые могли бы произойти сегодня или завтра. Form If + Present Simple + Future Simple Positive If I find time, I’ll try to help you. Negative You won’t pass the exam, if you don’t revise. Question What will you do if you fail your exam? Zero Conditional показывают действия, выражающие реальность. Form If + Present Simple + Present Simple Пример : If you heat water, it boils. Conditional sentences Условные предложения
|
