Учебное пособие Кривцова, Кочетова. Учебное пособие для обучающихся по техническим и экономическим направлениям подготовки бакалавров
 Скачать 1.91 Mb. Скачать 1.91 Mb.
|
|
7. Look at a diagram and then present the information about the educational system of Russia in your own words. You need to write at least 100 words. 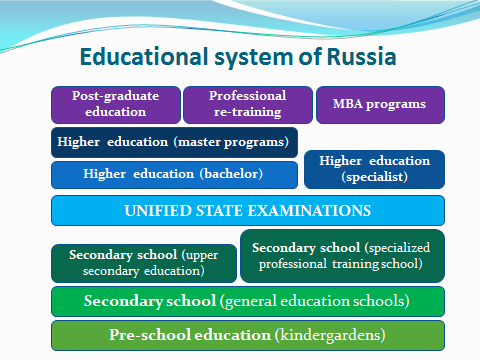
11. Translate the text into English. История создания Ростовского строительного института 14 февраля 1943 года Ростов был окончательно освобожден от фашистской оккупации. В то время население города составляло не более 170000 человек. Фашисты разрушили практически все заводы и фабрики, образовательные, культурные и общественные учреждения. В сентябре 1943 года строительные организации выступили с предложением организовать в Ростове-на-Дону Инженерно-строительный институт.16 декабря 1943 года был создан Ростовский инженерно-строительный институт (РИСИ). 7 февраля 1944 года начались первые занятия единственного тогда строительного факультета. К учебе приступило 269 студентов. К сентябрю 1945 года в институте насчитывалось уже три факультета: строительный, строительно-технологический и промышленно-транспортный. В 1944 году был произведен первый выпуск инженеров в области промышленного и гражданского строительства. Их оказалось немного – 4 человека. В следующем, 1945 году диплом получил всего один выпускник, в 1946 – 11, в 1947 – 20, в 1948 – 58, а в 1949 году уже 317 человек. К началу 70-х годов РИСИ стал одним из крупнейших инженерно-строительных вузов страны с полным набором строительных специальностей. Учебный процесс осуществлялся по 12 специальностям. Строительный факультет: промышленно-гражданское строительство; сельско-хозяйственное строительство; экономика и организация строительства. Строительно-технологический: производство строительных изделий и конструкций; экономика промышленности строительных материалов. Дорожный: автомобильные дороги; промышленный транспорт; инженерная геодезия. Архитектурный: архитектура; городское строительство. Санитарно-технический: теплогазоснабжение и вентиляция; водоснабжение и канализация. Число студентов достигало на очном отделении 4500 человек, а на заочном – более 2500.
Passive voice Страдательный залог
В форме страдательного залога могут быть только переходные глаголы, т.е. глаголы, после которых в действительном залоге стоит прямое дополнение. Образование
Употребление
В страдательном залоге часто употребляются Present, Past, Future Simple. Формы Present, Past, Future Perfect, Present, Past Progressive встречаются реже. Формы глаголов Future Progressive, а также всех времен группы Perfect Progressive в страдательном залоге не употребляются. 7. Change the sentences from Active to Passive. 1. They grow a lot of oranges in Sicily. A lot of oranges are grown in Sicily. 2. People borrow lots of books from the library every day. ________________________________________________________________ 3. They print the books in Hong Kong. ______________________________________________________________ 4. They don’t use artificial colouring in these sweets. _______________________________________________________________ 5. They make parmesan cheese near Parma. _______________________________________________________________ 6. They wrote this poem two thousand years ago. _______________________________________________________________ 7. They speak English and German here. _______________________________________________________________ 8. They will build MINI cars in oxford. _______________________________________________________________ 8. Choose the correct alternative. 1. The arrangements has been/had been made before I arrived. 2. Their wedding has been/had been announced before I knew about it. 3. The results have been/were given last night. 4. Our lunch is being /is cooked now. 5. The match wasn’t /wasn’t being played when we arrived. 6. Our house was/had been built in 2005. 9. Tick (˅) the correct sentences and correct the sentences that contain mistakes. 1. □ Glass bottles is made in that factory. __________________________ 2. □ Cocoa is produced in West Africa. __________________________ 3. □ The bread is been baked now. __________________________ 4. □ The wheel was invented a long time ago. __________________________ 5. □ New laws were being introduced when I was in Egypt.___________________ 6. □ The motor car wasn’t widely use before 1950. _______________________ 10. Translate sentences from Russian into English. 1. Университет был основан в 1944 г. 2. В настоящее время университет возглавляется профессором Вагиным. 3. Учебные аудитории оснащены современным оборудованием. 4. В университете введена многоуровневая система. 5. Выпускникам присваивается степень бакалавра наук, магистра наук. 6. Студенты зачисляются в университет согласно результатам ЕГЭ. 7. Содержание предметов определяется по государственным стандартам. 8. Все предметы группируются по областям. 9. Учебный год делится на семестры и сессии. 11. Write a new sentence with the same meaning. 1. Somebody has stolen my keys. My keys have been stolen. 2. Somebody stole my car last week. My car……………. 3. Somebody wants you on the phone. You…………….. 4. Somebody has eaten the bananas. The……………….. 5. Somebody will repair the machine. The………………. 6. Somebody is watching us. We ……………………….. 7. Somebody has to buy the food. The ………………….. 12. Complete the sentences. 1. We were invited (invite) to the party but we didn’t go. 2. The museum is very popular. Every year it ………………. (visit) by thousands of people. 3. Many buildings …………. (damage) in the storm last week. 4. A new road is going to ……………. (build) next year. 5. “Where is your jacket?” “It …………… (clean). It will be ready tomorrow.” 6. She is famous now. But in a few years her name will ………………. (forget). 7. “Shall I do the washing up?” No, it ……………….. (already /do). 8. Milk should ……………… (keep) in a fridge. 9. ……………………… you/ ever /bite by a snake. 10. My bag ……………. (steal) from my car yesterday afternoon. UNIT 3. THE SYSTEM OF HIGHER EDUCATION IN THE UNITED KINGDOM OF GREAT BRITAIN AND NORTHEN IRELAND
 1. Talk about these questions. What are these universities famous for? How old are they? Do you know any outstanding people who graduated one of these universities?
a number of departments – много факультетов proceed to – получить ученую степень part-time – с отрывом от производства full-time – без отрыва от производства tutorial system – система обучения путем прикрепления студентов к отдельным консультантам admission – прием (в учебное заведение) submit - представлять на рассмотрение maintain – содержать application – заявление curriculum – учебный план responsible - ответственный thesis – диссертация defense – защищать national body – государственный орган
1. Write down three important facts related to the topic“The system of higher education in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland” 2. Skim the text, present its main ideas and discuss them in pairs. THE SYSTEM OF HIGHER EDUCATION IN THE UNITED KINGDOM OF GREAT BRITAINAND NORTHEN IRELAND The structure of higher education in Great Britain is very complex. The main sources of higher educational institutions are: universities, teacher-training colleges and polytechnics. There are more than 60 universities in the U.K. They greatly differ from each other in date of foundation, size, history, tradition, general organization, methods of instruction and way of student life. The 2 intellectual eyes of Britain – Oxford & Cambridge Universities – date from the 12 & 13 centuries. They are known for all over the world and are the oldest and most prestigious universities in Britain. They are often called collectively Oxbridge, but both of them are completely independent. Only education elite go to Oxford and Cambridge. In the nineteenth and the early part of the twentieth centuries the so-called Redbrick universities were founded. These include London, Manchester, Leeds, Liverpool, Sheffield, and Birmingham. During the late sixties and early seventies some 20 'new' universities were set up. Sometimes they are called 'concrete and glass' or “Whitebrick” universities. Among them are the universities of Sussex, York, East Anglia and some others. There's an interesting form of studies which is called the Open University. It's intended for people who study in their own free time and who 'attend' lectures by watching TV and listening to the radio. They keep in touch by phone and letter with their tutors and attend summer schools. The Open University students have no formal qualifications and would be unable to enter ordinary universities. Applications from candidates for admission to nearly all universities are submitted to the Universities and Colleges Admission Service (UCAS). It is the UCAS that sends the copies to different universities and each university selects its own students. Good A-level results in at least 2 subjects are necessary to get a place at a university. However, good exam passes alone are not enough. Universities choose their students after interviews. British universities are independent, self-governing institutions. Although they all receive financial support from the state (about 79 per cent) the Department of Education and Science has no control over their regulations, curriculum, examinations and the way the money is spent. Teacher education is provided mostly by teacher-training colleges which receive their grants directly from the Department of Education and Science. The great majority of colleges are maintained by the Local Education Authorities. The universities and teacher-training colleges are classed as higher educational institutions because they award degrees. The normal duration of a first degree course is three or four years. The Bachelor Degree is awarded on the results of examinations. The Master Degree is usually awarded after one or two years of studies. The highest degree is Doctor of Philosophy. It is awarded for research and defense of the thesis. Apart from the Universities and teacher-training colleges there are 30 polytechnics in England and Wales and 14 Scottish central institutions. The work of the Polytechnics is of university level. But the universities, funded directly by the state, are less controlled than the Polytechnics. Local Education Authorities are responsible for the budgets of the Polytechnics. Their work is planned and financed by the Polytechnics and Colleges Funding Council. Most degrees in Polytechnics are awarded by a national body called the Council for National Academic Awards. The Council ensures that the degrees awarded in polytechnics are equal to the degrees awarded by universities. Polytechnics award the Diploma in Technology. The usual course for the diploma is 3 years for full-time students and 4 years for “sandwich” course ones. The “sandwich” course students alternate periods of full-time education and full- time employment. These courses provide many people with the opportunity of receiving higher technical education. The academic year in Britain's universities, Polytechnics, Colleges of education is divided into 3 terms, which usually run from the beginning of October to the middle of December, the middle of January to the end of March, from the middle of April to the end of June or the beginning of July. 3. Read the text again and put the sentences and phrases below in the correct order. 1. The main sources of higher education in Great Britain. 2. Academic year in British higher educational establishments. 3. Types of British universities. 4. Admission to British universities. 5. Functions of the Department of Education and Science. 6. Scientific degrees awarded by the British higher educational establishments. 7. Polytechnics and their educational and financial authorities. 4. Match the highlighted words in the text with the definitions (1-6) below. 1. a list of subjects which are to be taught at some educational institutions 2. academic title given by a university to one who has passed an examination or defended a thesis. 3. a request, especially in written form. 4. to give as a result of an official decision, e.g. a degree, a prize, a medal. 5. money given by the state for a particular purpose, e.g. to a university or a student 6. a group of persons who do smth. together in a planned way. 5. Read the text again and decide if the sentences (1-6) below are true or false. 1. The applications for admission to British universities are sent to the Department of Education and Science. T\F 2. The Department of Education and Science does not control rules, programs and examinations in most British universities. T\F 3. Almost all teacher-training colleges receive their grants directly from the Department of Education and Science. T\F 4. The work of the Polytechnics is planned and financed by the Polytechnics and Colleges Funding Council. T\F 5. Local Educational Authorities do not bear responsibility for the budgets of the Polytechnics. T\F 6. The Council for National Academic Awards ensures that the degrees awarded by Polytechnics are equal to the degrees awarded by Universities. T\F |
