В. Н. Бгашев е. Ю. Долматовская английский язык для студентов машиностроительных специальностей учебник
 Скачать 1.36 Mb. Скачать 1.36 Mb.
|
|
U. Закончите предложения, выбрав соответствующий показатель времени. Electric cars will help to provide traffic safety... 2. The laboratory supplied the new calculations for designing the engine... 3. The plant produces a great number of machines... 4. She will become an engineer... 5. They finished school... 6. We worked at this plant... 7. My friend works at the research institute... 8. Several scientists work at this problem... in the past, in the near future, last year, next year, now, last month, in five years, every year Раскройте скобки, поставив глагол в нужную форму. 1. Prof. Smirnov (togive) a lecture on physics next week. He (to supply) the fundamental calculations for designing engines. 2. The Government (to establish) the Automobile Research Institute in 1920. But the scientists (to start) auto-making research in 1918. 3. We (not to take) that examination yesterday. We (to have) it in 2 weeks. 4. My father (not to work) in the field of mechanical engineering, he (to design) boats. 5. E A. Chudakov (to develop) the automobile theory? — Yes, he did. Besides, he (to provide) the basic formulas of auto-designing. 6. Nick (to know) mathematics well? — Yes, he does. He (to like) it and (to do) research in this field. 7. You (to work) in the chemistry laboratory a week ago? — No, we didn’t. We (to work) there only the day after tomorrow. 8. This programme (to include) many problems. At present we (to study) different aspects of bridge construction, testing and operation. TEXT STUDY Дополните предложения, выбрав соответствующее окончание в правом столбце. All children in Britain must receive ... a) no fees. Schools in Britain are ... b) fee-paying. State schools charge ... c) of two types. Independent schools are ... d) full-time education. Most state schools are ... e) the same school-leaving There are also ... examinations. All schools share ... f) comprehensive schools. To get into the University g) modem schools, grammar school leavers take ... schools and technical schools, A-level exams. Суммируйте информацию текста, заполнив следующую таблицу.
DISCUSSION Ответьте на вопросы по теме “Schools in Britain”. 1. Name the basic types of schools in Great Britain. 2. What is the main difference between state and independent schools? 3. What kind of education is offered by comprehensive schools? 4. What exam is shared by all secondary schools? 5. When do school leavers take the А-level exam? Сравните разные типы средних государственных и частных школ Великобритании и расскажите о том, чем они отличаются. Active Vocabulary
В Прочитайте следующие предложения и назовите значения выделенных слов. 1. Colleges are technical or professional schools which prepare students for specific job or offer a specialist qualification. 2. Technical college is a college, specializing in technical subjects. 3. College of technology also specializes in technical subjects but provides more advanced courses than a traditional technical college. 4. Polytechnics are centres for advanced courses in a wide range of subjects. 5. A course is a complete (полный, законченный) period of studies. 6. Sandwich courses are courses in which students alternate studies with practical work in industry. Прочитайте следующие слова и словосочетания. Они помогут вам полнее понять содержание текста. academic — учебный, tutorial — консультация, particular feature — отличительная черта, strong links — прочные связи, Bachelor of Arts — бакалавр искусств, Master of Arts — магистр искусств, science — наука Прочитайте текст и выполните следующие за ним упражнения. TEXT В. HIGHER EDUCATION IN GREAT BRITAIN There are some 90 universities and 70 other higher education institutions in Great Britain: polytechnics and numerous colleges for more specialized needs, such as colleges of technology, technical colleges, colleges of arts and agricultural colleges in England and Wales. They all provide a wide range of courses from lower-level technical and commercial courses through specialized courses of various kinds to advanced courses for those who want to get higher-level posts in commerce, industry and administration, or take up one of a variety of professions. Courses are a combination of lectures, seminars, tutorials and laboratory work. In a lecture the student is one of a large number of students. He listens to the lecturers, takes notes, but asks no questions. In a seminar he raises problems and discusses them with his fellow students under the direction of one of the teachers. In a tutorial he is accompanied by only a handful of students and discusses his personal academic problems with a teacher. Study in courses may be full-time and part-time. Full-time education includes sandwich courses in which periods of full-time study (for example, six months) alternate with full-time practical work and training in industry. Full-time and sandwich courses now are an important part of higher education in England and Wales. A degree is an academic qualification awarded at most universities and colleges upon completion of a higher educational course (a first degree) or a piece of research (higher degrees). If students pass their final exam at the end of a three-year course, they get their first degree. Students with a first degree become Bachelors of Arts or Science, and can put B.A. or B.Sc. after their names. If they want to go a step further and become Master of Arts or Science, they have to write an original paper, or thesis, on some subject based on a short period of research, usually soon after graduation. If students wish to become academics and perhaps teach in a university, then they will work for a higher degree, a Doctor of Philosophy — a Ph.D. For this they will have to carry out some important research work. DISCUSSION На основании полученной из текста информации дополните таблицу и логическую схему.
Логическая схема Higher Education in Great Britain  Universities 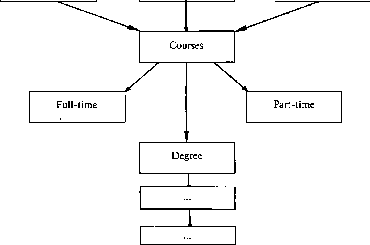 Расскажите о системе высшего образования в Великобритании, используя составленную вами схему. Step 2 A Прочитайте текст и скажите, на какие четыре группы и по какому принципу подразделяются университеты в Великобритании. TEXT A. BRITISH UNIVERSITIES There is no single, universally accepted definition of what a university should be like. British universities are different. In 1960 there were only 23 British universities. Today there are 90. They can be roughly divided into the following groups: Oxford and Cambridge: Scholars were studying in these ancient universities in the early thirteenth century. Since that time Oxford and Cambridge have continued to grow, but until the nineteenth century they were the only universities in England, and they offered no place to girls. Four universities were founded in Scotland before Scotland and England were united: St. Andrews (1411), Glasgow (1450), Aberdeen (1494) and Edinburgh (1583). The Redbrick Universities: In this group are listed all universities founded between 1850 and 1930 including London university. They were called “redbrick”, because that was the favourite building material of the time, but they are rarely referred to as “Redbrick” today. The New Universities: These were all founded after the Second World War. Some of them quickly became popular because of their modern approach to university courses. In 1992 the majority of British polytechnics, that offered a wide range of subjects and many had close links with industry and commerce in their local area, were also incorporated into universities. So at present there are four different types of universities in Great Britain. The typical academic programme for university students in Great Britain is composed of a varying number of courses or subjects within a field of specialisation. The academic activities for each subject fall into three types: lectures, at which attendance is not always compulsory, tutorials and examinations. These three categories provide the means by which students prepare themselves in specialised fields of knowledge. However, universities have never had a monopoly on higher learning. In Britain, full-time higher education also takes place outside the universities. TEXT-BASED ASSIGNMENTS |
