Лаба. Англ. Учебное пособие Москва Издательство мгту им. Н. Э. Баумана 2022 удк 81 378(075) ббк 81. 2 Англ С00
 Скачать 0.6 Mb. Скачать 0.6 Mb.
|
|
SPEAKING 1 16. Work in pairs. Find out as much as you can about your partner’s computer and its components by asking questions about the features listed in Table 2.2. and complete it. Whose computer is more powerful? Table 2.2. Features of Computers
READING 2 17. Read Text 2 B. Part 1 and explain the differences between hardware and software. TEXT 2 B. PART 1 Hardware and Software All computers consist of hardware. This includes the computer itself and all other physical devices. The other pieces of the computer system include software, the instructions that tell the computer what tasks to do; data, the information the computer works on; and you, the user, who tells the computer what to do, and for whom the computer does all its work. All computers use the same basic techniques for doing the tasks we give them. The computer takes in data through input devices, it manipulates the data according to its instructions, it outputs the results of its processing, and it stores data for later use. These four processes together are known as the computing cycle. What is Hardware? Your PC (Personal Computer) is a system, consisting of many components. Some of those components, like Windows XP, and all your other programs, are software. The stuff you can actually see and touch, and would likely break if you t 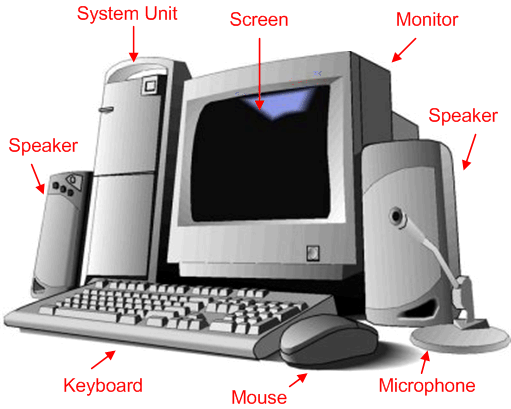 hrew it out a fifth-story window, is hardware. hrew it out a fifth-story window, is hardware. Figure 2. Computer Components: Hardware Not everybody has exactly the same hardware. But those of you who have a desktop system probably have most of the components shown in the figure (see Fig. 2). Those of you with notebook computers probably have most of the same components. Only in your case the components are all integrated into a single book-sized portable unit. The Central Processing Unit (CPU), also called a processor, is located inside the computer case on the motherboard. It is sometimes called the brain of the computer, and its job is to carry out commands. Whenever you press a key, click the mouse, or start an application, you’re sending instructions to the CPU. The CPU is generally a 2-inch ceramic square with a silicon chip located inside. The chip is usually about the size of a thumbnail. The CPU fits into the motherboard’s CPU socket, which is covered by the heat sink, an object that absorbs heat from the CPU. A processor’s speed is measured in megahertz (MHz), or millions of instructions per second, and gigahertz (GHz), or billions of instructions per second. A faster processor can execute instructions more quickly. However, the actual speed of the computer depends on the speed of many different components - not just the processor. RAM is your system’s short-term memory. Whenever your computer performs calculations, it temporarily stores the data in the RAM until it is needed. This short-term memory disappears when the computer is turned off. If you’re working on a document, spreadsheet, or other type of file, you’ll need to save it to avoid losing it. When you save a file, the data is written to the hard drive, which acts as long-term storage. RAM is measured in megabytes (MB) or gigabytes (GB). The more RAM you have, the more things your computer can do at the same time. If you don’t have enough RAM, you may notice that your computer is sluggish when you have several programs open. Because of this, many people add extra RAM to their computers to improve performance. A bit is the smallest unit of data in computer processing. A byte is a group of eight bits. A megabyte contains about one million bytes, and a gigabyte is about one billion bytes. Input is the process of entering data into the computer. The most common device used for input on microcomputers is the keyboard. Computer keyboards include many special command and function keys to do specialized input tasks. Other input devices include a mouse, which manipulates a pointer on the computer screen for giving commands and entering data; a scanner, which reads graphic images and pages of text and sends them to the computer; a modem, which receives data over phone lines; and several other devices. Once data is in a microcomputer, it is processed by the microprocessor. Microprocessors do all calculations and manipulations necessary to transform data into meaningful information. Associated with 47 the processor is the computer’s memory, which is used for storing data and programs while they’re being used by the processor. Getting processed data out of the computer is the job of output devices. The computer can display the data on a monitor screen, of which there are several types: color or monochrome, desktop or portable. You can also send data to a printer or plotter to make a paper copy, use the modem to send the data over a phone line to another computer, or use any number of specialized output devices. What do you do if you want to keep the data in a permanent form? That’s what storage devices are for. Storage devices hold data permanently, so you can save it and retrieve it later. Removable disks are used for easy, portable storage, and built-in hard disks are used for more permanent storage of larger amounts of data and programs for fast access. The most common storage devices include optical discs (such as CD-ROM) and USB flash drives (sticks). A program is a group of instructions that tells the processing devices what to do. Software can be a single program or a set of programs that work together. Two types of software are necessary to make the computer capable of performing useful work. They are the operating system and application software. The operating system contains basic instructions that tell the CPU (central processing unit) how to use other hardware devices, where to find programs, and how to load and keep track of programs in memory. Because it includes basic instructions that are important to the functioning of the computer, the operating system is the first program to be processed after the computer is turned on, and it remains in memory until the computer is turned off. For the computer to perform tasks, it needs application software in addition to the operating system. An application is a job that a computer can perform, such as creating text documents, manipulating sets of numbers, creating graphic images, and communicating with other computers. Application software is the term used to describe programs that tell the computer how to perform such jobs. The six most common types of application software are: • Word processing software, • Graphics software, • Desktop publishing software, • Spreadsheet software, • Database management software, • Communications software. Application software is what makes computer a tool for performing the tasks we most often need at school, at home, or at office. 18. Answer the following questions using information from Text 2 B. Part 1. 1. What is a computer? 2. What is hardware? 3. Give the definition of software. 4. What is a program? 5. Describe a CPU. 6. What is main memory? What sections does it have? 7. Give the definition of peripherals. 8. What is an input device? 9. What is an output device? 10. How can we use storage devices? 19. Read Text 2 B. Part 2 about some useful computer components. Fill in gaps 1-6 in the text using the sentences (A-G) below. There is one sentence that you do not need. It is nonvolatile. This component allows to get access to the Internet. The driver ensures that communication between the computer and the device is successful. Serial port is typically used to connect an external modem universal serial bus (USB) is an external connection. SCSI interfaces provide for faster data transmission rates than standard serial and parallel ports. Data are recorded magnetically on one or both surfaces. This can then be read optically by passing a light beam over the disc. TEXT 2 B. PART 2 Useful Components of Computer SCSI(pronounced «skuzzy»), acronym for small computer system interface. One type of standard interface used to connect computers to devices such as hard discs, printers, scanners, and CD-ROM drivers. 1.______ There are several peripheral devices that can be attached to a computer: VDT (visual display terminal) or monitor, the primary device for displaying information from the computer; keyboard, the primary device for entering information into the computer; mouse, the primary device for navigating and interacting with the computer; disc drive units for mass memory storage (e.g. (CDs, floppy, etc)), scanners for copying pictures and texts, printers for printed output, and modem(acronym for modulator-demodulator) for connecting to the internet. Every of mentioned above peripheral devices connected to the computer needs a driver program, a program that controls it. 2.______ For example, it is necessary for some purposes to connect different types of printers, each with its own special operating codes, to the same type of computer. This is possible because driver programs are supplied to translate the computer’s standard printing commands into the special commands needed for each printer. As it was mentioned before, immediate access memory or internal memory describes the memory locations that can be addressed directly by the central processing unit. It is either read only or read / write. Read only memory stores information that must be constantly available and is unlikely to be changed. 3.______ Read / write memory is volatile - it stores programs and data only while the computer is switched on. External memory (backing storage) is nonvolatile memory located outside the central processing unit, used to store programs and data that are not in current use. It is provided by such devices as magnetic discs floppy and hard discs or optical discs CD ROM. Floppy disc is a storage device consisting of a light flexible disc enclosed in a plastic) It is placed in a disc drive, where it rotates at high speed. 4.______ Present day average floppy discs hold not more than several megabytes, depending on the disc size, recording method,and whether one or both sides are used. CD ROM (compact disc read-only memory) is a storage device developed from the technology of the audio compact disc) It consists of a plastic coated metal disc, on which binary digital information is etched in the form of microscopic pits. 5.______ CD ROMs hold 500-700 megabytes and аre used in distributing large amounts of texts and graphics. On CD RWs (read and write discs) it’s possible to rewrite information many times. DVD can hold the amount of information up to several gigabytes. At the end it is necessary to touch the question ofdifferent kinds of connections. Slot is a rectangular opening inside a computer into which can be inserted, for example, a printed circuit board. Port (an external connection) - the socket that is used to connect the cable for a peripheral device to. The computer has different ports. Parallel port is commonly used to connect a printer. 6.______ The buses connect the computer to all peripheral devices. AGP (accelerated graphics ports) is a very high-speed connection used by the graphics card to interface with the computer. 20. Decide if the statements are true (T) or false (F) and give reasons to your opinion. 1. SCSI interfaces provide for more powerful data transmission rates than standard serial and parallel ports. 2. Every peripheral device connected to the computer needs a driver program, i.e. a program that controls it. 3. Read only memory stores information that must be constantly available and is likely to be changed and is volatile. 4. CD ROM is a storage device developed from the technology of television. 5. On CD RWs it’s possible to rewrite information many times. 6. The computer has different ports for connection. VOCABULARY DRILLING 2 21. Match each component in column A with its function in column B given in Table 2.3. Make up sentences explaining functions of computer components. Table 2.3. Functions of Computer Components
22. Match the words on the left with the words on the right. Make up your own sentences with them. A.
|
