Вступний фонетикоорфоепічний курс вступ
 Скачать 25.36 Mb. Скачать 25.36 Mb.
|
|
Exercise 2. Read and translate the text. Musculoskeletal System Muscles are the active part of the motor apparatus; their contractions produce various movements. Functionally all muscles are divided into voluntary and involuntary muscles. Voluntary muscles consist of striated muscle tissue and contract by the will of man. This group includes all muscles of the head, trunk and extremities, i.e. the skeletal muscles, as well as those of some internal organs (tongue, larynx, etc.). Involuntary muscles consist of smooth muscle tissue and are found in the walls of internal organs, blood vessels and in the skin. The contractions of these muscles are not controlled by man. It should be remembered that the heart muscle, although its contractions are not controlled by the will, consists of striated muscle tissue with a special structure. The human body contains more than 650 individual muscles anchored to the skeleton, which provide pulling power so that you can move around. These muscles constitute about 40 % of our total body weight. Skeletal muscles are complex in structure. They consist of muscle fibers of different length і up to 12 cm); the fibers are usually parallel to each other and are united in bundles. Each length muscle is composed of many such bundles. There are tendons at the ends of muscle by mean? of which they are attached to bones. The muscles points of attachment to bones or other muscles are designated as origin or insertion. The point of origin is point of attachment to the bone to which the muscle is anchored The point of insertion is the point of attachment to the bone the muscle moves. Generally, the muscles are attached by tough fibrous structures called tendons. These attachments bridge one or more joints and the result of muscle contraction is movement of these joints. The body is moved primarily by muscle groups, not by individual muscles. These groups of muscles power all actions ranging from the threading of a needle to the lifting of heavy weights. Exercise 3. Look at Fig. 8-1. Explain how the muscle is attached to the bones. Exercise 4. Make a plan of the text, use sentences from it. Exercise 5. Find English equivalents of the following sentences:
5. Нерви з'єднують м'язи і центральну нервову систему. Exercise 6. Differentiate voluntary and involuntary muscles. Where are they found? Exercise 7. Describe the skeletal muscles:
radius ulna inscrtior Exercise 8. Look at Fig. 8-2, 3 and read the names of all the muscles of the human body (front and back). Exercise 9. Read the text, translate and title it. Spasm is a sudden and involuntary muscular contraction. It is always painful. The example of spasm is bellyache or colic. Atrophy may occur in a wasting or decrease in the size of a muscle. Strains and sprains are typical injures that often affect muscles. Muscular dystrophy is a hereditary disorder. Myalgia means 'muscular pain'. Myositis is a term that indicates actual inflammation of muscle tissue. Fibrositis means "inflammation of connective tissue". Tendinitis is an inflammation of muscle tendons and their attachments occurs most often in athletes. Flaffoot is a common disorder in which the arch of the foot (підйом ступні), the normally raised portion of the sole, breaks down so that the entire sole rests on the ground. Wearing properly fitted shoes and walking with the toes pointed straight forward may help to prevent flatfoot and other painful foot disorders. Exercise 10. Make a list of muscular disorders. Control Tests. Musculoskeletal System 1. What are the functions of the musculoskeletal system? A. Moving B. Transporting C. Building D. Moving and supporting E. Supporting 2. What is the skeleton? A. The framework of bones B. The composition of bones C. The box of bones D. The building of bones E. Lazy bones studies bones and their 3. What science diseases? A. Myology B. Osteology C. Cytology D. Histology E. Neurology 4. What science studies muscles and their diseases? A. Osteology B. Gynecology C. Therapy D. Myology E. Cardiology 5. The human skeleton consists of parts. A. 1 B. 5 C. 4 D. 2 E. 3 6. The bones of the skull are . A. built closely B. movable C. ssolated D. immovable E. simple 7. The skull has bones. A. 26 B. 20 C. 40 D. 16 E. 21 8. The skull consists of . A. facial part B. facial and cranial parts C. cranial part D. the head E. all answers are wrong 9. What is the function of cartilages? A. Connective B. Supportive C. Transporting D. Protective E. Osteopoiesis 10. What for are there joints between the bones? A. To connect bones together B. To connect bones and let them to move C. To move bones D. To protect bones from injury E. To prevent injuries 11. There are many in the spine. A. ligaments B. bones C. cartilages D. joints E. vertebrae 12. The and form the chest. A. ribs and breastbone B. trunk and limbs C. scapula and clavicula D. maxilla and mandibula E. upper and lower limbs 13. The only movable bone in the skull is the lower jaw. What for? A. To open the mouth and chew B. To smile C. To breathe D. To open bottles E. To speak english 14. Arthritis is . A. lack of calcium B. inflammation of a joint C. bone abscess D. hypovitaminosis E. dead bone tissue 15. What bone is absent in the upper limb? A. Humerus B. Femur C. Ulna D. Radilus E. Phalanges 16. Wrhat bone can't we see in the leg? A. Femur B. Tibia C. Fibula D. Knee cap E. Ulna 17. What vertebrae can't we name? A. Cervical B. Coccygeal C. Thoracic D. External E. Lumbar 18. The joints allow the bones . A. to make noise B. to move C. to work together D. to step E. to dance 19. A break of bones is . A. fracture B. rupture C. suture D. mixture E. tincture 20. The science dealing with the effect of drugs on living organisms is . A. pathology B. pharmacology C. phytotherapy D. biology E. chemistry 21. Novocaine is the medicine for relieving A. headache B. heartache C. local pain D. toothache E. earache 22. Pain in joints is . A. arthralgia B. arthroporosis C. arthropoiesis D. arthrogenesis E. arthrotomia 23. What does the term "scoliosis" mean? A. Breastbone curvature B. Spinal curvature C. Bone curvature D. Rib curvature E. Joint curvature 24. What is the structural unit of bones? A. Ganglion B. Osteon C. Nephron D. Neuron E. Acinus 25. How many bones are there in the human body? A. 216 B. 156 C. 168 D. 249 E. 170 26. How many pairs of ribs are there? A. 6 B. 7 C. 10 D. 12 E. 3 27. The largest muscle of the spine is . A. naiTow B. wide C. latissimus D. widest E. latior 28. What main groups of muscles do you know? A. Flexor and extensor B. The head, trunk and extremities C. Voluntary and involuntary D. Anterior and posterior E. Front and back 29. What is diaphragm? A. The largest respiratory muscle B. The longest respiratory muscle C. The narrowest respiratory muscle D. The type of respiration E. The septum between cavities 30. What is the definition of the term "myositis"? A. Inflammation of muscles B. Rupture of muscles C. Lack of power of muscles D. The tumor of muscles E. Smooth muscle 31. What parts does the trunk consist of? A. The spine B. The vertebral column C. The chest, spine and pelvis D. The chest and pelvis E. A great number of vertebrae 32. What part contains the brain? A. Belly B. Chest C. Abdomen D. Cranium E. Trunk 33. What must we do in case of dislocation? A. Apply mustard plasters B. Apply splints C. Set a bone D. Choose a diet E. Jump upstairs 34. Inflammation of bones and joints is . A. synarthrosis B. arthritis C. osteoarthritis D. arthralgia E. osteoporosis 35. What is the medical meaning of the musculus gluteus maximus? A. To apply cups B. To apply mustard plasters C. To give medicines D. To make injections E. To sit still 36. What medicinal form is most usually used to relieve local pain in muscles? A. Dragee B. Tincture C. Tablet D. Powder E. Ointment 37. What muscles don*t belong to the head? A. Chewer muscle B. Skull muscle C. Superior oblique muscle of the head D. Musculus spinalis capitis E. Sternal muscle 38. First aid in fracture of the limb is . A. to put plaster casts B. to use splints for broken limb C. to let the person move D.to put bandage on the place of fracture E. to press on the place of pain 39. What kinds of fractures do you know? A. Open and closed B. High and low C. Oval and round D. Painful and painless E. Big and small 40. What method is used to determine fractures? A. Operation B. X-rays C. Bronchoscopy D. Narcosis E. Palpation 41. What does the term "sprain" mean? A. Перелом B. Вивих C. Забій D. Розтягнення E. Контузія 42. What is the English for the term "розрив"? A. Fracture B. Break C. Wound D. Injury E. Trauma 43. What term is used to name the endings of the tubular bone? A. Hypophysis B. Diaphysis C. Epiphysis D. Epiphysitis E. Epicrisis 44. What bone has the shape of a plate? A. Flat bone B. Knee cap C. Tarsal bone D. Heel bone E. Os breve 45. The hospital department where patients with injuries are treated is called . A. Surgical department B. Maternity department C. Traumatology department D. Neurology department E. Dermatology department 46. What must you do immediately in case of open fracture? A. Stop the bleeding B. Put a wet cloth on the wound C. Apply a splint on the broken limb D. Use X-rays to see the break E. Make the dressing secure 47. In case of injury of the spine you mustn't A. speak with the patient B. render first aid C. relive the patient's pain D. wash the patient's face E. move the patient 48. What term doesn't mean "ушкодження"? A. Sleep B. Bruise C. Wound D. Break E. Fracture 49. The longest bone of the chest is . A. Femur B. Sternum C. Tibia D. Humerus E. Ulna 50. The science which studies the structure of the human body is . A. Myology B. Osteology C. Anatomy D. Histology E. Biology II. Grammar Exercises Exercise 1. Translate the following sentences, pay attention to one-ones, that-those. 1. I don't like this book, give me another one. 2. The bones of the extremities are longer than those of the spine. 3. The bones of the skull are those which compose the head and face. 4. This lecture is more interesting than the one I attended last week. 5. The weight of the lung is less than that of the heart. Exercise 2. Put the verbs in the correct form. 1. "What (to be) you doing now"? "I (to be) preparing for my physics test". 2. Yesterday from 2 till 6 o'clock we (to be) working in our scientific laboratory. 3. When I was at my sister's at 4 p.m. yesterday she (to be) learning Latin. 4. Tomorrow at 5 p.m. I (to be) preparing a lecture. Exercise 3. Make up disjunctive questions based on the following sentences. 1. All patients are usually excited before the operation. 2. The tablets which you took weren't sweet. 3. He has a very high blood pressure. 4. These patients will be well again soon. 5. There are many slips on the registering clerk's table. 6. There wasn't any serious complication after measles. 7. There were some out-patients in the room. 8. Your respiration doesn't accelerate after physical work. 9. The doctor noted some changes in the lung. 10. The course of physiotherapy will arrest the process of inflammation. 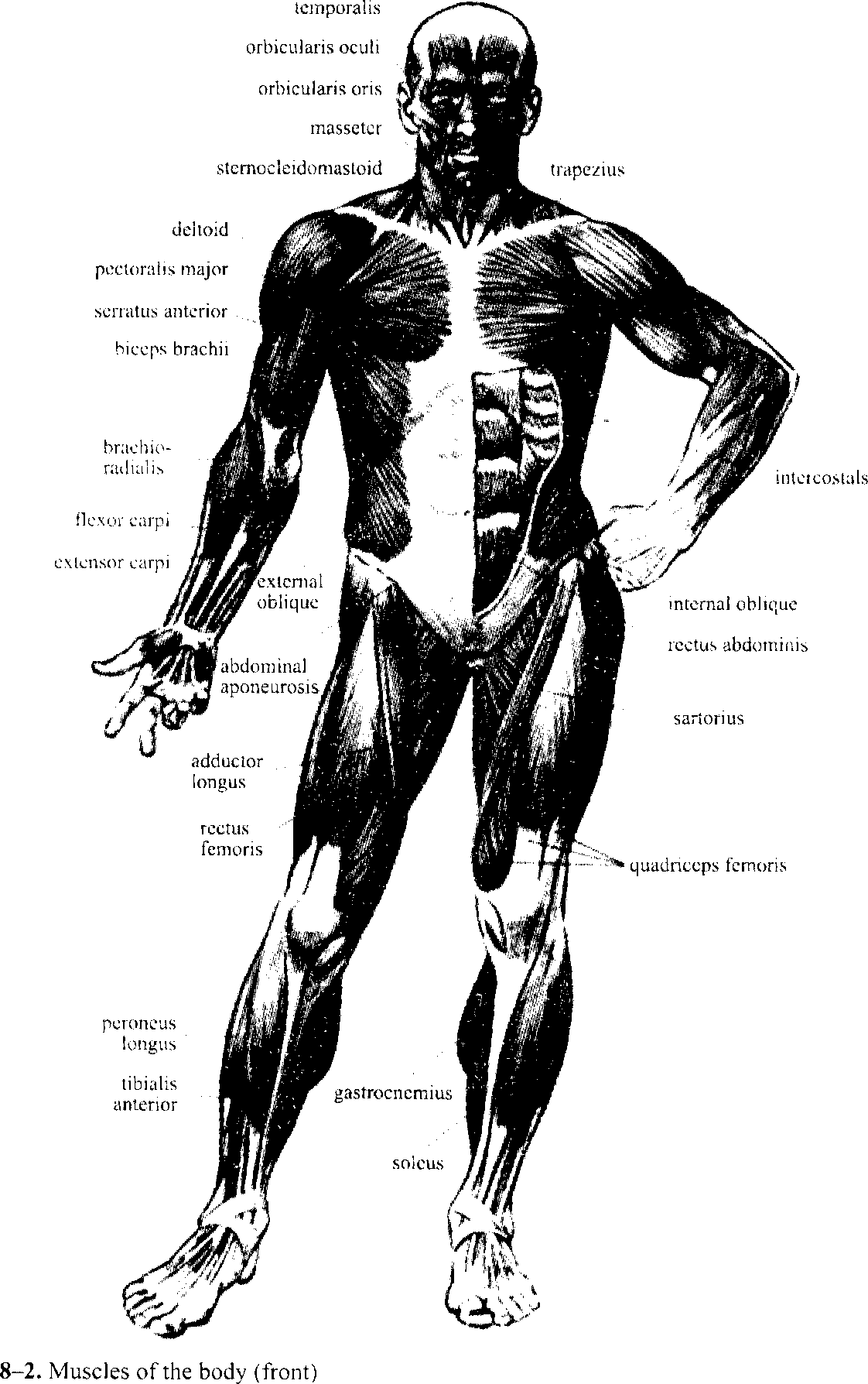 Exercise 4. Translate the sentences, name the function of the infinitive in the sentences. 1. To save this patient's life doctors decided to perform the operation. 2. To save patient's life is necessary. 3. This man to be rendered first aid suffers from heart disease. 4. They want to render him first aid. 5. It is necessary to examine this man, to render him first aid. 6. The patient to be operated on was brought to the operating room. 7. To prevent the danger of infection the surgeons use sterile instruments. 8. To prevent the danger of infection is very important. 9. Measures to be taken to protect the health of people are various. 10. They want to prevent the danger of infection. 11. The patients to be admitted to this department suffer from pneumonia. 12. To transfuse blood from one person to another the medical staff must have some technical skills. Exercise 5. Substitute complex sentences with the Subjective Infinitive Complex, use the model. Model: It is said that the experiments are very interesting. The experiments are said to be very interesting. 1. It is known that streptomycin is the substance of the highest antibacterial activity. 2. It was said that constriction of the stomach muscles was the most probable diagnosis. 3. It is believed that he is an excellent surgeon. 4. It appeared that he had been wounded. 5. It seems that the disorder is curable. Exercise 6. Translate the sentences, underline the Subjective Infinitive Complex, use the model. Model: She is known to be an expert nurse. Відомо, що вона досвідчена медсестра.
III. Independent Work: Muscle Tissues Exercise 1. Read the text. Muscle Tissues Muscle is composed of elongated cells which have the power of contracting or reducing their length. This property of contraction is ultimately a molecular phenomenon and is due to the presence of protein molecules which can stretch out or shorten. The following three types of muscle occur in the body. |
